How to start an online business in 2025 + profitable ideas to consider
With global online retail sales projected to surpass $7 trillion by 2025, the market offers a promising opportunity for aspiring entrepreneurs. Luckily, website-building solutions have become so accessible that anyone of all technical skill levels can start an online business at home.
If you don’t know where to start, this article will be your guide. From choosing a niche to setting up your own website, we’ll cover everything you need to launch a successful online business in 2025.
We will also explore good online business ideas to give you some inspiration and look at why starting an online business is an opportunity you shouldn’t miss.
Download checklist: How to start an online business
Why Start an Online Business
When it comes to numbers, the eCommerce industry’s long-term growth is steady. eCommerce statistics indicate that online sales could make up 20.8% of global retail sales by 2025, thanks to the increasing popularity of online shopping.
One contributing factor is the low barriers to entry for aspiring sellers today. Various website-building options empower small business owners to expand their online reach without needing advanced technical knowledge.
Consequently, more brands are joining online marketplaces to meet the growing demand, boosting global sales.
Online business models offer several advantages over traditional ones. They’re more adaptable to market trends and typically have lower startup costs. Moreover, automated sales and marketing processes make these models scalable.
Here are more reasons to start your own online business:
- Round-the-clock accessibility ‒ offer a seamless 24/7 customer experience, expanding your audience without extra staff or geographical constraints.
- Flexibility in lifestyles and goals ‒ make money online, whether as a side hustle or a full-time job, from anywhere with internet access. You can set your own hours for better work-life balance.
- Data-driven decision-making ‒ use tools and software to compile and analyze accurate data for informed decisions on product development, marketing strategies, and improving the customer experience.
- Eco-friendly ‒ many online businesses have a smaller ecological footprint than traditional models, as they require less physical space and resources.
- Niche market opportunities ‒ the internet’s wide reach helps eCommerce brands target niche markets that traditional businesses may overlook.
- Innovative revenue streams ‒ explore different revenue models like subscriptions, digital products, affiliate marketing, and online advertising to diversify income sources and increase profitability.
How to Start an Online Business
Now that you know the benefits of selling online, let’s go through the essential steps to get your eCommerce business up and running.
1. Choose Your Online Business Niche
Choosing the right niche is crucial for a successful online business. It determines your target audience, influences marketing strategies, and impacts the overall business sustainability.
Find your niche by brainstorming ideas based on your interests, the market demand, and potential profitability. Align your passion and expertise with customer needs to ensure your business offers tangible value, easing your effort in building industry credibility. Doing what you love also keeps you motivated and encourages innovation.
For instance, those experienced or passionate about health can provide online coaching and wellness programs. Built By Nando is one of many successful online businesses in this niche, providing online fitness programs and supplements for health enthusiasts.
2. Conduct Market Research
Once you’ve chosen your niche, gather data on customers and competitors to assess market demand and identify key industry trends. Online market research helps tailor your products or services to meet your target audience’s needs and stand out from the competition.
Here are common market research methods and the specific insights they produce:
- Surveys and questionnaires ‒ great for discovering potential customers’ preferences, pain points, and factors influencing their buying decisions.
- Competitor analysis ‒ reveals other businesses’ strengths, weaknesses, pricing strategies, and product offerings to identify market gaps.
- Social listening ‒ gain real-time insights into trends, customer sentiments, and emerging needs in your niche from social networks and forums.
Next, define your target market using analytics tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Insights, and keyword research platforms. These insights can help you understand your audience’s online shopping behavior, search queries, demographics, and interests.
3. Create a Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
A unique value proposition (UVP) is a statement that describes the benefit of your offer, how you solve customers’ needs, and what sets you apart from the competition. It helps potential customers understand why they should choose your brand over others.
For example, Dropbox’s UVP, “Your stuff, anywhere,” highlights its file accessibility feature across devices. Meanwhile, Coursera’s UVP, “Learn without limits,” establishes itself as a platform where anyone can upgrade their skill set.
A compelling UVP should consist of at least one of these elements :
- Customer needs ‒ your products or services can solve the target market’s pain points.
- Unique benefits ‒ determine what makes your products or services unique and their advantages over competitors.
- Credibility and trustworthiness ‒ include endorsements, certifications, or a strong track record that builds trust.
- Emotional connection ‒ highlight the personal benefits and experiences your product or service offers, tapping into what motivates your customers’ decisions.
Ensure your UVP is memorable and easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or complex language that makes your UVP difficult to remember.
4. Consider Legal Aspects of Starting an Online Business
Just like a brick-and-mortar business, an online company must follow the laws that apply to its country and business type.
Basic legal requirements generally include:
- Business registration ‒ you might need to register your online business with the relevant authorities, depending on your location and business structure.
- Business license ‒ your company may need licenses and permits to sell online if it operates in a regulated industry or as a sole proprietorship or a limited liability company (LLC).
- Tax registration ‒ meet tax requirements by getting a sales tax license or value-added tax (VAT) number, as needed.
If your new business will collect personal information for advertising or other purposes, you must follow data protection and privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Data Protection Act (DPA). Explain on your privacy policy page how you collect, use, keep, and protect customer data.
You should also have terms of service or conditions for your online business. This legal agreement protects your rights, limits liability, and explains service terms to users.
Consult legal experts before deciding on a business structure to ensure compliance with online business laws. Their advice can also help protect your business interests and intellectual property, including branding and copyrights, in the long run.
Did You Know?
Hostinger Website Builder provides templates to help you create legal pages for privacy policies and terms and conditions in minutes. Simply review and adapt the guidelines to ensure compliance with actual laws that apply to your business.
5. Build Your Online Business Website
After learning the steps to develop a good online business idea and comply with regulations, it is time to set up an online business website. If you want to do it yourself, use a CMS or a website builder to simplify the process.
A content management system (CMS) is a software application that enables users to design their website and add functionality using themes and plugins. It’s highly customizable and scalable, but this is a self-hosted solution meaning you will need to purchase a hosting plan from a third-party provider. It requires a domain name too.
In contrast, a website builder usually includes all the necessary services in its subscription plans to launch a website. The built-in tools and features are easy to use, even for those who don’t know how to make a website. You can scale your plan by upgrading or downgrading as needed.
Check out our article to learn the differences between a CMS and a website builder.
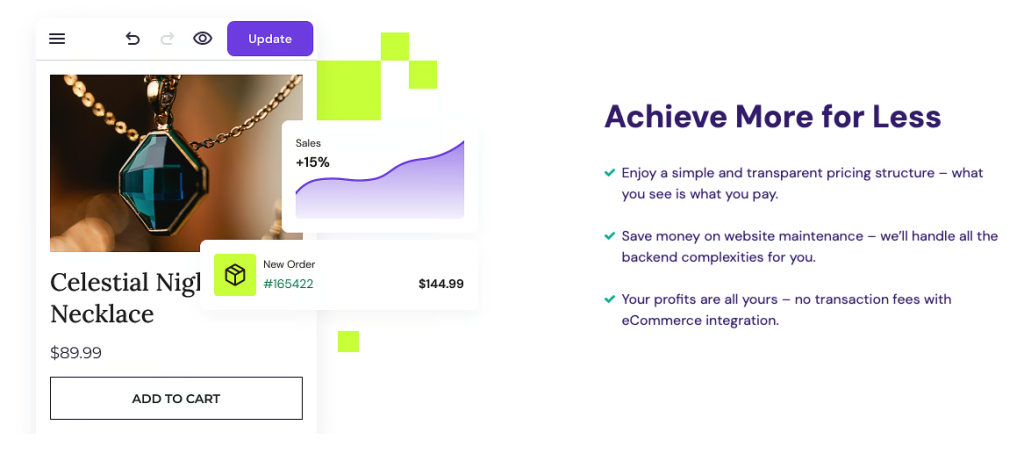
Our fully-hosted business website maker streamlines web development with artificial intelligence (AI). Design your website using a pre-built template or let AI generate a custom design that fits your branding needs.
Hostinger Website Builder offers the following features:
- eCommerce functionality ‒ integrated tools like product listings, shopping carts, and secure payment gateways for seamless online transactions.
- Website template library ‒ designer-made eCommerce templates for building mobile-friendly websites.
- Drag-and-drop editor ‒ rearrange and customize web elements effortlessly, no coding required.
- AI tools ‒ design your brand logo, predict user behavior with heatmaps, and craft unique product descriptions and blog posts in one platform.
- Search engine optimization (SEO) ‒ improve your site’s visibility on search engines to attract more customers and boost sales.
- Social media integration ‒ strengthen your social media marketing by adding social icons, feeds, and share buttons to your store.
- Analytics and reporting ‒ leverage our built-in analytics tool or integrate your website with Google Analytics to track web traffic and monitor user behavior.
- Customer support ‒ Hostinger’s Customer Success team provides 24/7 support in over 10 languages via live chat and email.
See our tips on picking the right domain name, such as using your business name to enhance brand recognition.
6. Set Up Operational Framework
A successful business requires a solid operational framework. It can involve establishing processes for online payments, inventory management, and scheduling, depending on your business model.
Start by picking reliable payment gateways that integrate seamlessly with your website. Secure and easy-to-use gateways make the checkout process smooth with different payment options, easing conversions for customers.
With Hostinger Website Builder, you can accept online payments through PayPal and Stripe. Keep in mind that availability depends on the region where your store and customers are.
Prioritize implementing security measures like SSL/TLS encryption to safeguard data and ensure secure transactions. For instance, Hostinger automatically installs free SSL certificates for users on Premium, Cloud, and WordPress hosting plans. This practice helps build customer trust, as it protects personal and financial information against cyber threats.
For product-based online businesses, managing inventory is crucial. Hostinger Website Builder includes a built-in inventory management feature, so you can easily restock and organize items.
If you’re starting a service-based business, consider investing in an online scheduling tool to streamline appointment booking. The appointment feature in our builder provides easy booking options, so there’s no need to integrate a third-party tool.
7. Prepare Digital Marketing Strategies
There are numerous online marketing strategies to promote your online business. Identify the most effective digital marketing campaign by conducting A/B testing. You can also perform market research to gain insights into your competitors’ strategies to see what works.
Outperform your competition in search engines by implementing eCommerce SEO best practices, such as:
- Keyword research ‒ identify your target audience’s search queries, then write your product descriptions, alt text, and meta tags with relevant target keywords for better rankings.
- Website speed optimization ‒ reduce load times to improve the user experience and lower bounce rates.
- Market monitoring ‒ keep up with the latest eCommerce trends to anticipate changes in customer behavior and market demand.
- Local SEO ‒ set up and optimize your Google My Business profile for better visibility in local search results.
Boost your SEO efforts by also focusing on social media marketing. Build a strong social media presence with eye-catching content that reflects your brand’s personality. Most importantly, interact with your audience on the social media platforms they use most to maximize engagement and awareness.
According to digital marketing statistics, increased exposure is the primary benefit of using social media for marketing, with 86% of marketers acknowledging its crucial role in boosting brand visibility and driving traffic.
Additionally, consider exploring other digital marketing strategies like email marketing and content marketing.
Email marketing is great for lead generation and maintaining customer relationships, while content marketing involves creating valuable and informative content for your audience. Both can drive traffic to your site and improve conversion rates.
For inspiration, check out how Red Zebra Coaching successfully uses Hostinger Website Builder for its newsletter campaigns and blog as part of its marketing strategy.
Once you’ve identified the best channels, summarize your business goals and marketing strategies in a business plan. A well-planned business strategy facilitates effective business growth and helps convince potential investors to support your venture.
Suggested Reading for Effective Digital Marketing Strategies
How to Create an SEO-Friendly Website
Email Marketing for Beginners
Digital Marketing Pricing
8. Launch Your Online Business
After finalizing your business strategy and setting up your eCommerce platform, it’s time to launch your new business. To ensure its success, you need a launch strategy that will attract potential customers and create buzz around your brand.
Consider the following factors when planning your small business launch:
- Clear goals ‒ set realistic goals for brand awareness, customer engagement, and sales. Pick relevant metrics to measure your performance.
- Timeline ‒ align it with your launch goals to ensure each phase strategically contributes to your business objectives.
- Operational readiness ‒ test your online business setup to ensure all features and operations are fully functional.
- Marketing plan ‒ decide which channels to use for creating anticipation and excitement. For instance, share product teasers on social media ahead of the launch day and host a virtual launch event with Q&A sessions and live demonstrations of your product.
- Contingency plan ‒ have backup plans for potential challenges like website downtime and payment gateway issues.
9. Grow and Scale the Online Business
Taking your business online is just the beginning. The next big task is to grow and scale your small business to its full potential.
Focus on expanding your marketing efforts, exploring new markets, and refining your sales strategies to get more clients. Implement automation into your business operations to enhance your productivity and expand your offerings. Most importantly, maintain good client communication to understand their needs and build lasting relationships.
Scaling a business is a gradual process, so don’t get discouraged if growth doesn’t happen as quickly as you’d like. Etsy, for example, took about a decade to become a global leader in artisanal goods. Consistently track your progress, analyze data, and make informed decisions to pave your path to success.
That said, it’s also important to stay adaptable. That means being prepared to pivot or diversify based on market trends, customer feedback, and business performance.
Pivoting may be necessary if your business plan isn’t meeting targets or if consumer behavior shifts. On the other hand, diversification can be an excellent growth strategy to explore new products or markets and attract a broader customer base.
Profitable Online Business Ideas
The key to launching a profitable business is finding a venture that suits your skills, passions, and target market.
If you’re looking for inspiration, here are some popular online business ideas to start in 2025.
Self-Publish an eBook
Leverage your passion for writing to make 35-75% royalties from the eBook’s sale, depending on the platform. This online business idea requires low startup costs and has long-term earnings potential. Moreover, it positions you as an expert in your niche, opening doors for public engagements and consulting opportunities.
Lara West taps into this online business idea and uses her eCommerce platform to market her eBook and audiobooks.
Start an Online Store
Starting an online store typically requires a sizeable initial investment for the stock, storage, and store setup. However, the estimated income ranges between $1,000-10,000/month based on the target market’s size, making it a potentially lucrative venture.
To start your business online, research trending products to sell online and plan the packaging and pricing accordingly. Set up customer support with care to ensure excellent service delivery.
Take a look at how Step One Sportswear sells premium gym clothes, handles shipping, and tackles returns and exchanges.
Start a Dropshipping Business
This idea involves setting up an online business with a third-party vendor who manages production, storage, and shipping for you. For this reason, it requires lower startup costs than a traditional online store, making it suitable for beginners.
The estimated income is $200-3,000/month, depending on the online store and market size. Check out our guide on starting a dropshipping business to learn more about this venture.
Create an Online Course
Start your own online business by sharing your expertise and knowledge with others. This business idea can help you earn between $1,000-50,000/month, depending on the production expenses and the number of students.
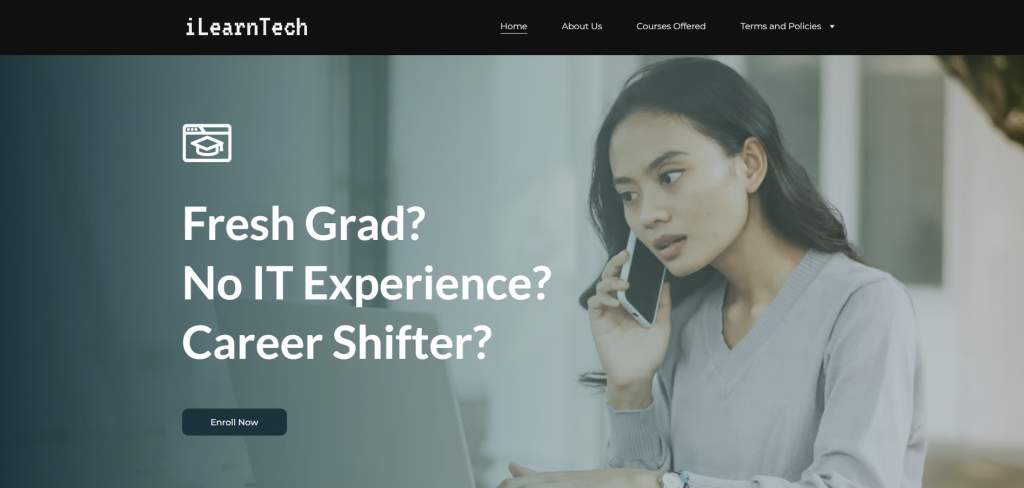
For example, iLearnTech sells learning programs on C# and DevOps. The pre-recorded course materials and downloadable resources make for an excellent passive income stream. See our tutorial for the steps to sell courses online.
Start a Podcast
Do a solo or group podcast discussion on your preferred topics and earn $500-10,000/month through monetization. Invest in quality recording equipment to improve your podcast’s quality. Once you build a solid audience base, you can start attracting sponsors and generate revenue.
Check out our guide to start a podcast and monetize it.
Conclusion
More sellers are becoming online business owners due to the eCommerce industry’s growing profitability. This business model offers endless opportunities for individuals to start selling without the high startup costs of a traditional brick-and-mortar business.
Let’s recap the steps to start an online business:
- Choose your online business niche.
- Conduct market research.
- Create a unique value proposition (UVP).
- Fulfill the legal requirements.
- Create your own online store website.
- Set up an operational framework.
- Plan digital marketing strategies.
- Launch your eCommerce store.
- Grow and scale your small business.
In this article, we also went through some of the best online business ideas for inspiration to get you started. We hope these tips help you build an online business that suits your skills, passion, and goals. Good luck!
How to Start an Online Business FAQ
This section answers the most common questions about starting a business online.
How Much Capital Do I Need to Start an Online Business?
The initial investment needed to start a small business online varies. If you handle the setup yourself, you can keep costs low just by purchasing hosting and a domain. However, expenses will increase if you hire professional web developers and designers or if you opt for premium tools.
Read our article on website costs for small businesses to see a detailed price breakdown.
Can I Start an Online Business With No Money?
Starting your own business on a free online platform is possible, but these platforms often come with limited features and weaker security. This can restrict business growth and potentially harm your brand in the long run. We recommend starting with standard hosting and tools and then upgrading as your business grows.
What Type of Online Business Is the Most Profitable?
The most profitable online business type depends on the market demand, your skills, and effort. Selling digital products like eBooks, online courses, and apps is lucrative due to low startup costs and high-profit margins. Meanwhile, services like marketing, consulting, and writing can become increasingly profitable as you establish yourself as an authority in your field. That’s why it’s crucial to align your online business with your passions and expertise.
How Do I Select the Right Business Model for My Online Business?
Choosing the right business model for your online store involves assessing your target audience and product or service type. For example, B2B is ideal for companies targeting other businesses, while B2C is great for selling fast-moving products like food and apparel. Align the model with your target market, products, and capacity for managing customer demand and fulfilling sales processes.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.




Comments
September 19 2021
I agree Putri! There’s so much to do when starting a new business ? Lisnic.com actually has some really great resources that might help you! I read their blog daily!
January 15 2022
Great post on how to start online business
January 31 2024
I'm interested
February 07 2024
Hi there! Great to hear that. Starting an online business can be an exciting journey filled with opportunities. We hope our article proves helpful to you as you embark on your online business journey ?
February 07 2024
Hi...Dear, I am confident in my abilities to be successful in this opportunity because it is my dream of experience to do a online business ever since I was a child.
February 20 2024
Hi Rema! That's wonderful. Wishing you the best as you embark on this exciting journey ?
March 22 2024
Great to acknowledge that online business is search a big opportunity for livelihood .It has been my dream to be a part taker of this kind of business and because of that, I suggest to begin soon.
March 26 2024
Absolutely! Wishing you the best of luck ?