Dec 22, 2025
Leonardus N.
21min Read

WordPress is the most popular content management system (CMS), with 43.2% of all websites running on its software. Unfortunately, its popularity attracts all sorts of cybercriminals who exploit the platform’s security vulnerabilities.
This doesn’t mean that WordPress has a terrible security system, as security breaches can also happen due to the users’ lack of security awareness. Therefore, it’s best to apply precautionary security measures before your website becomes a hacker target.
We will discuss 22 methods to improve WordPress security and protect your site from various cyberattacks. The article will include best practices and tips, with or without WordPress plugins. Some methods are also applicable to other platforms than WordPress.
Download WordPress security checklist
No time to read? Find out more about WordPress security measures in our tutorial instead.

Implementing one or two WordPress security measures won’t be enough to make your WordPress website completely safe.
Download our WordPress Security Checklist to help track your progress in applying important security measures to your website. We also share some WordPress security tips to help you protect your site further.
1. Keep your site up to date.
2. Use secure wp-admin login credentials.
3. Setup safelist and blocklist for the admin page.
4. Use a trusted WordPress theme.
5. Install an SSL certificate for a secure data transfer.
6. Remove unused WordPress themes and plugins.
7. Enable two-factor authentication.
8. Create backups regularly.
9. Limit the number of failed login attempts.
10. Change your WordPress login page URL.
11. Automatically log out idle users.
12. Monitor user activity.
13. Regularly scan your site for malware.
14. Disable the PHP error reporting feature.
15. Migrate to a more secure web host.
16. Disable file editing.
17. Use .htaccess to disable PHP file execution and protect the wp-config.php file.
18. Change the default WordPress database prefix.
19. Disable the XML-RPC feature.
20. Hide your WordPress version.
21. Block hotlinking from other websites.
22. Manage file and folder permissions.
In this section, we will go over six general WordPress security tips that don’t require advanced technical knowledge and high-risk investments. Even a beginner will be able to do these simple tasks, like updating WordPress software and removing unused themes.
WordPress releases regular software updates to improve performance and security, protecting your site from cyber threats.
Updating your WordPress version is one of the simplest ways to improve WordPress security. However, 35.3% of WordPress sites are running on an older WordPress version, making them more vulnerable.
To check whether you have the latest WordPress version, log in to your WordPress admin area and navigate to Dashboard → Updates on the left menu panel. If it shows that your version is outdated, we recommend updating it as soon as possible.
We also recommend updating the themes and plugins installed on your WordPress site. Outdated themes and plugins may conflict with the newly updated WordPress core software, causing errors and making your site prone to security threats.
Automate updates to prevent running your website on outdated software. With WordPress auto-updates, Hostinger users can easily do so from the hPanel dashboard.
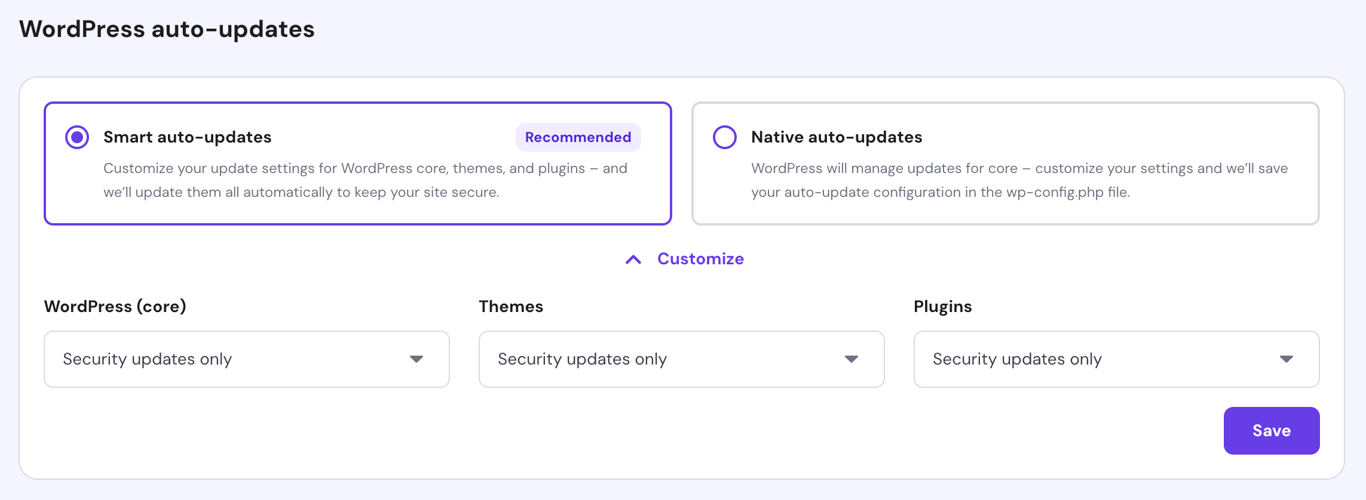
Enabling automatic updates eases up your workload, but it can crash your website due to incompatibility with older plugins or themes. If you enable this option, make sure that your website is backed up regularly so that you can revert to the previous version in case of an error.
One of the most common mistakes users make is using easy-to-guess usernames, such as “admin”, “administrator”, or “test”. This puts your site at a higher risk of brute force attacks. Moreover, attackers also use this type of attack to target WordPress sites that don’t have strong passwords.
Therefore, we recommend making your username and password unique and more complex.
Alternatively, follow these steps to create a new WordPress administrator account with a new username:
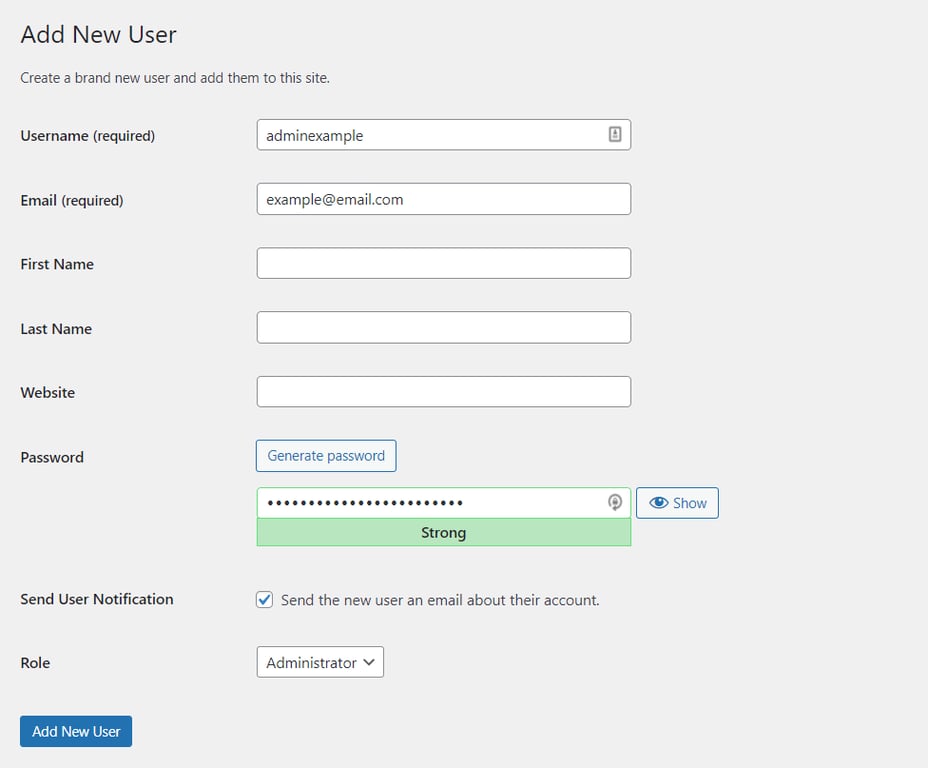
Incorporate numbers, symbols, and uppercase and lowercase letters into your password. We also recommend using more than 12 characters as longer passwords are way harder to crack.
The longer password – the safer. However, strong passwords don’t have to be long and complex – use special symbols and numbers instead of well-known letters. For example, 41@bAm@! instead of Alabama! is easy to recall and harder to crack. Alternatively, use a pattern on the keyboard instead of actual words, like qpzmwoxn. Additionally, mix these two to create a stronger password.
If you need help generating a strong password, use online tools like 1Password. You can also use their password management services to store strong passwords safely. That way, you don’t have to memorize them.
After creating a new WordPress admin username, you’ll need to delete your old admin username. Here are the steps to do so:
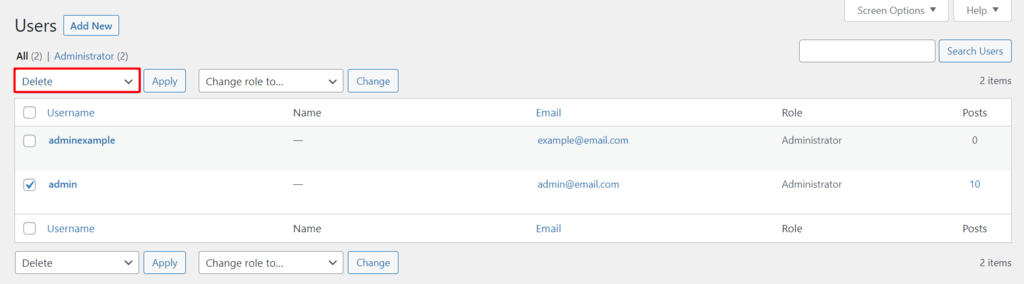
To keep your site safe, it’s also important to check the network before logging in. If you’re unknowingly connected to a Hotspot Honeypot, a network operated by hackers, you risk leaking login credentials to the operators.
Even public networks such as a school library’s WiFi may not be as secure as it appears. Hackers can intercept your connection and steal unencrypted data, including login credentials.
For that reason, we recommend using a VPN when you connect to a public network. It provides a layer of encryption to the connection, making it harder to intercept data and protecting your online activities.
Enabling URL lockdown protects your login page from unauthorized IP addresses and brute force attacks. To do that, you need a web application firewall (WAF) service for WordPress, such as Cloudflare or Sucuri.
Using Cloudflare, it’s possible to configure a zone lockdown rule. It specifies the URLs you want to lockdown and the IP range allowed to access these URLs. Anyone outside the specified IP range won’t be able to access them.
Looking for how to set up other rules on your CDN? Check out our guide to configuring Cloudflare page rules.
Sucuri has a similar feature called URL path blacklist. First, you add the login page URL to the blocklist so that no one can access it. Then, you safelist authorized IP addresses to access the login page.
Alternatively, restrict access to your login page by configuring your site’s .htaccess file. Navigate to your root directory to access the file.
Before making any changes, we strongly advise you to back up the old .htaccess file. If anything goes wrong, you’ll be able to restore your site easily.
Adding this rule to your .htaccess will limit access to your wp-login.php to only one IP. Thus, attackers won’t be able to get in your login page from other locations.
# Block IPs for login Apache 2.2 <files /wp-login.php> order deny,allow allow from MYIP allow from MYIP2 deny from all </files> # Block IPS for login Apache 2.4 <Files "wp-login.php"> Require all denied </Files>
This rule should be placed after the # BEGIN WordPress and # END WordPress statements, as shown below.
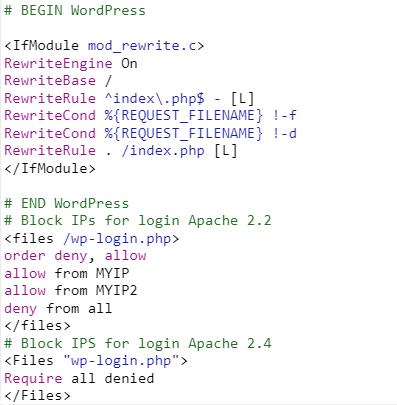
This rule applies even if you don’t have a static IP, since you can restrict logins to your ISP common range.
You can also use this rule to restrict other authenticated URLs, such as /wp-admin.
Note that blocklisting is effective only against known threats. Hackers can design malware specifically to evade detection by tools that use a blocklist system. While safelisting offers more robust security, it can also be more complex to implement, especially if you want a third party to do it – they will need information on all the applications you use.
Nulled WordPress themes are unauthorized copies of premium themes. They might seem cheap, but they have many security problems.
Most nulled themes are hacked versions of original themes. Hackers add harmful code, like malware and spam links. These themes can also create backdoors for more attacks on your WordPress site.
Since nulled themes are illegal, you won’t get any support from the developers. If something goes wrong, you’ll need to fix it yourself.
To stay safe, use themes from the official WordPress repository or trusted developers. You can also find many premium themes in reputable theme marketplaces like ThemeForest and Envato.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encrypts data exchanged between websites and visitors, enhancing security against data theft by attackers. Websites with an SSL certificate use HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP, making them easy to identify.
Most hosting companies include SSL with their plans. Hostinger, for example, provides free lifetime Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates on all its WordPress hosting plans. Our users can check their SSL status via Websites → Security → SSL from the hPanel dashboard.
For non-Hostinger users, plugins like Really Simple SSL or SSL Insecure Content Fixer can handle the technical aspects and SSL activation in a few clicks. The former’s premium version lets you activate HTTP Strict Transport Security headers to enforce HTTPS usage on the site.
Once done, change your site’s URL from HTTP to HTTPS. To do so, navigate to Settings → General and update the URLs in the WordPress Address and Site Address fields.
Keeping unused plugins and themes on the site can be harmful, especially if the plugins and themes haven’t been updated. Outdated plugins and themes increase the risk of cyberattacks as hackers can use them to gain access to your site.
Follow these steps to delete an unused WordPress plugin:
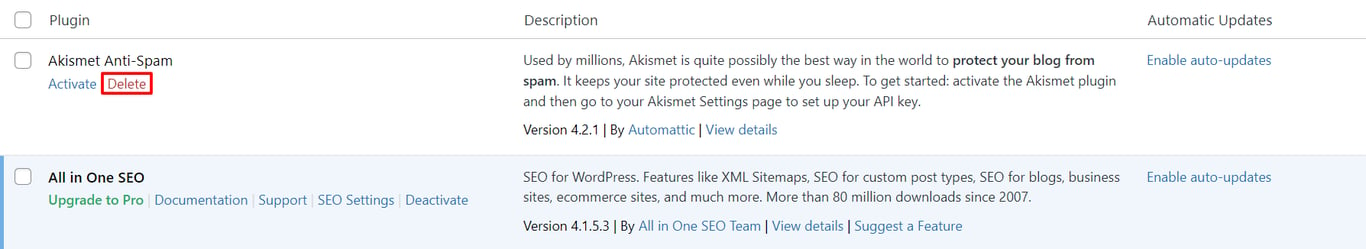
Note that the delete button will only be available after deactivating the plugin.
Meanwhile, here are the steps to delete an unused theme:
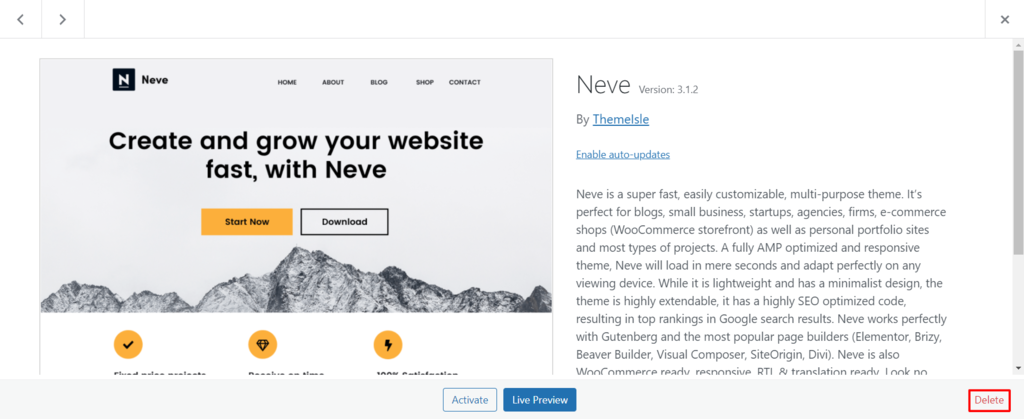
Hostinger users can manage installed plugins and themes from the hPanel dashboard. Go to Websites → WordPress → Security and scroll down to the Installed themes and Installed plugins. Click on the trash can icon to remove inactive add-ons.
When deleting a popular WordPress plugin or theme from your WordPress dashboard, you might not have the option to use a custom uninstaller, where you can choose to completely remove all of the data regarding that plugin or theme. In this case, you’ll need to do it via an FTP client by accessing your database and removing the plugin or theme entries manually.
The next method to improve WordPress security is by using WordPress plugins.
It’s a convenient way to protect your website, but remember not to install all of these plugins at once without further consideration since too many plugins can slow down your site.
First, identify your needs to choose the most effective plugins for your website.
Activate two-factor authentication (2FA) to reinforce the login process on your WordPress website. This authentication method adds a second layer of WordPress security to the login page, as it requires you to input a unique code to complete the login process.
The code is available only to you via a text message or a third-party authentication app.
To apply 2FA on your WordPress site, install a login security plugin like Wordfence Login Security. Additionally, you’ll need to install a third-party authentication app such as Google Authenticator on your mobile phone.
If you’re not sure which two-factor authentication plugin to use, choose the most frequently updated and reviewed one.
Once you have installed the plugin and the authentication app, follow these steps to enable two-factor authentication:
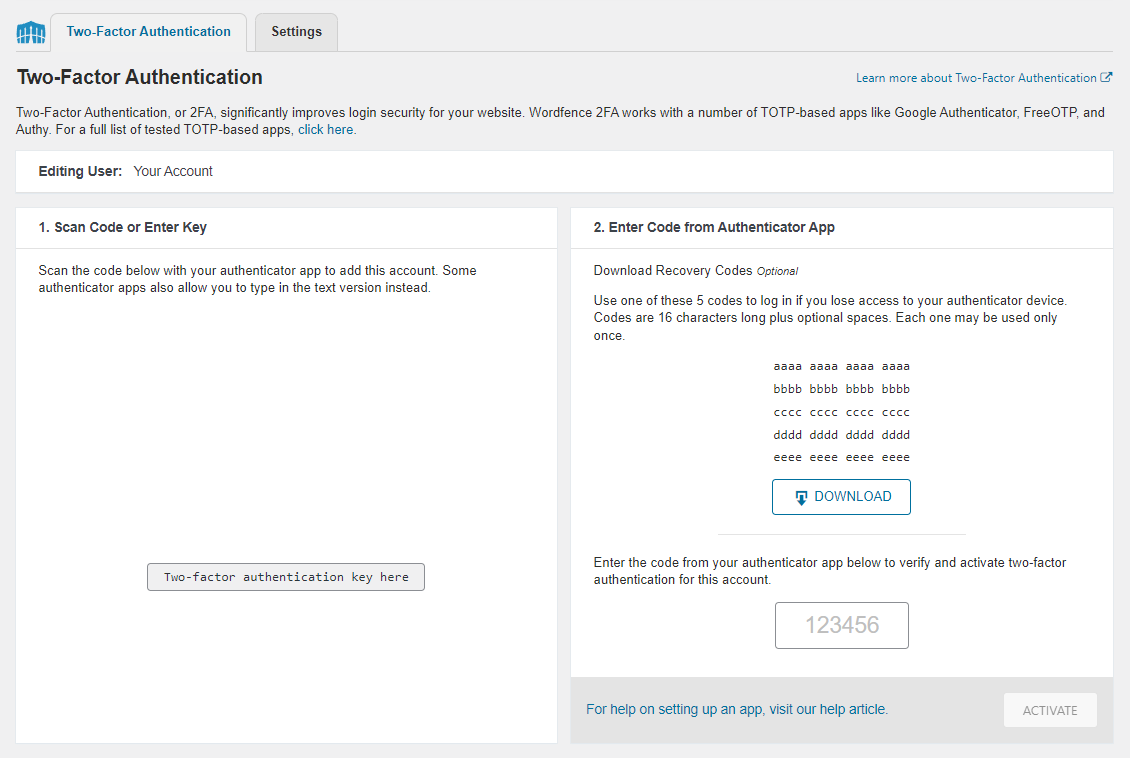
Also, download the provided recovery codes in case you lose access to the device that contains the authentication app.
Regularly creating a WordPress site backup is an important mitigation task because it will help you recover your site after incidents, such as cyberattacks or physical damage to the data center.
The backup file should include your entire WordPress installation files, like your database and the WordPress core files.
With WordPress, backing up a site can be done using a plugin like All-in-One WP Migration. Follow these steps to create a backup file with this plugin:
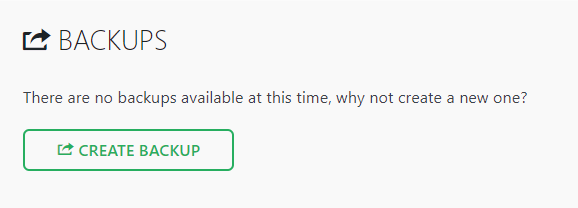
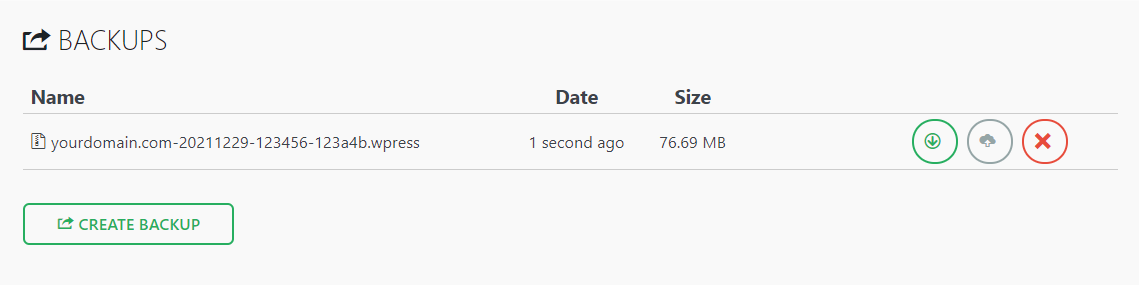
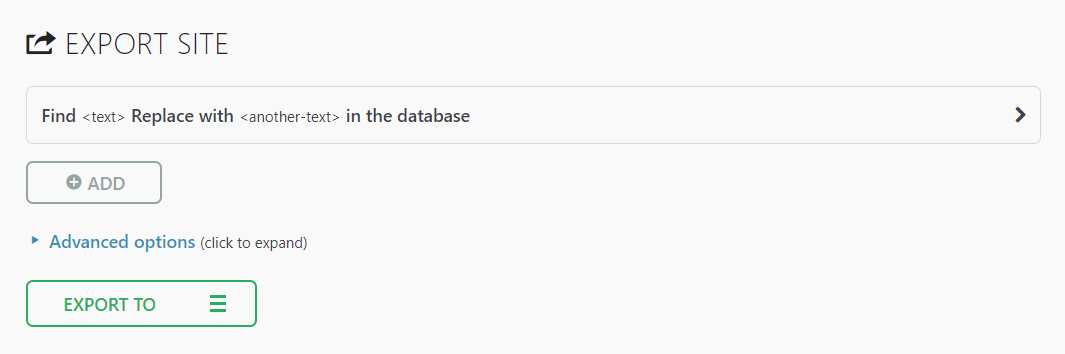
In case of an incident, you can restore your WordPress site using All-in-One WP Migration’s importing tool.
Hostinger includes a user-friendly backup feature on the hPanel dashboard with all hosting plans. Navigate to Websites → Files → Backups to manage your backups, including generating a new one and restoring an old version.
Users on the WordPress Business hosting plan and higher can also benefit from built-in daily backups.
I wouldn’t recommend storing website backups on a personal computer. Instead, use storage applications like Google Drive. But if you decide to do so, the best way would be to store it in at least three locations, such as your computer, a USB flash drive, and an external storage like Dropbox.
WordPress allows its users to make an unlimited number of login attempts on the site. Unfortunately, hackers can brute force their way to your WordPress admin area by using various password combinations until they find the right one.
Thus, you should limit login attempts to prevent such attacks on the website. Limiting failed attempts also helps monitor any suspicious activities on your site.
Most users only need a single try or a few failed attempts, so you should be suspicious of any questionable IP addresses that reach the attempt limit.
One way to limit the login attempts in order to increase WordPress security is by using a plugin. There are many great options available, such as:
One of the risks of implementing this WordPress security measure is getting a legitimate user locked out of WordPress admin. However, you shouldn’t be worried about that, as there are many ways to recover locked-out WordPress accounts.
To take a step further to protect your website from brute force attacks, consider changing the login page’s URL.
All WordPress websites have the same default login URL – yourdomain.com/wp-admin. Using the default login URL makes it easy for hackers to target your login page.
Plugins like WPS Hide Login and Change wp-admin Login enable custom login URL settings.
If you use the WPS Hide Login plugin, here are the steps to change your WordPress login page URL:
Many users forget to log out of the website and leave their sessions running. Hence, letting someone else who will use the same device access their user accounts and potentially exploit confidential data. This especially applies to users who use public computers in internet cafes or public libraries.
Therefore, it’s crucial to configure your WordPress website to log inactive users out automatically. Most banking sites use this technique to prevent unauthorized visitors from accessing their sites, ensuring that their client’s data is safe.
Using a WordPress security plugin like Inactive Logout is one of the easiest ways to log out idle user accounts automatically. Aside from terminating idle users, this plugin can also send a custom message to alert idle users that their website session will end soon.
Identify any unwanted or malicious actions that put your website in danger by tracking activities in your admin area.
We recommend this method for those who have multiple users or authors accessing their WordPress website. That’s because users may change settings that they should not, like altering themes or configuring plugins.
By monitoring their activities, you will know who is responsible for those unwanted changes and if an unauthorized person has breached your WordPress website.
The easiest way to track user activity is by using a WordPress plugin, such as:
The AV-TEST Institute registers over 450,000 new malware and potentially unwanted applications (PUA) every day. Some malware even have a polymorphic nature, meaning they can modify themselves to avoid security detection.
Thus, it’s crucial to regularly scan your WordPress site for malware since attackers always develop new types of threats.
Fortunately, many great WordPress malware scanner plugins can check for malicious software and improve WordPress security.
Our experts recommend these security plugins to install on your site:
If your WordPress website is infected with malware, follow these key points:
1. Be sure to always have your wp-admin area accessible, perform a scan, and get rid of the malware.
2. Make sure that your plugins, themes, and WordPress core software are up to date.
3. Check for vulnerabilities in your database to see if your plugins or themes are listed there as a risk.
It’s also possible to enhance your website security without using plugins. Most of these tasks will involve tweaking your site’s code, but no need to worry – we’ll show you how to do it step by step.
The PHP error reporting displays the full information about your website’s paths and file structure, making it a great feature for monitoring your site’s PHP scripts.
However, showing your website’s vulnerabilities on the backend is a serious WordPress security flaw.
For example, if it displays a specific plugin on which the error message has appeared, cybercriminals could use that plugin’s vulnerabilities.
There are two ways to disable PHP error reporting – via the PHP file or your hosting account’s control panel.
Modifying the PHP File
Follow these steps to modify your PHP file:
error_reporting(0); @ini_set(‘display_errors’, 0);
Changing PHP settings using the control panel
If you don’t want to code, disable the PHP error reporting via your hosting provider’s control panel. Here’s how to do so via hPanel:
Multiple WordPress security measures won’t matter much if the hosting environment is prone to cyberattacks. Your hosting provider should guarantee a safe space for all your website data and files on their server, so it’s critical to choose the one that has an excellent security level.
If you think your current web hosting company is not secure enough, it’s time to migrate your WordPress website to a new hosting platform. Here’s what you need to consider when searching for a secure web host:
Hostinger’s WordPress hosting offers the essential resources and features needed to protect your WordPress website, such as a web application firewall and a malware scanner like Monarx. We also provide virtual private servers and cloud hosting service if you prefer to keep resources isolated.
WordPress has a built-in file editor that makes editing WordPress PHP files easy. However, this feature can become a problem if hackers gain control of it.
For this reason, some WordPress users prefer to deactivate this feature. Add the following line of code to the wp-config.php file to disable file editing:
define( 'DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true );
If you want to re-enable this feature on your WordPress site, simply remove the previous code from wp-config.php using an FTP client or your hosting provider’s File Manager.
The .htaccess file ensures that WordPress links work properly. Without this file declaring the correct rules, you will get many 404 Not Found errors on your site.
Furthermore, .htaccess can block access from specific IPs, restrict access to only one IP, and disable PHP execution on particular folders. Below we’ll show you how to use .htaccess to harden your WordPress security.
Important! Always back up your existing .htaccess file before making any changes to it. This can help you to restore your site easily if anything goes wrong.
Disabling PHP Execution in Specific Folders
Hackers often upload backdoor scripts to the Uploads folder. By default, this folder only hosts uploaded media files, so it shouldn’t contain any PHP files.
To secure your WordPress site, disable the PHP execution in the folder by creating a new .htaccess file in /wp-content/uploads/ with these rules:
<Files *.php> deny from all </Files>
Protecting the wp-config.php File
The wp-config.php file in the root directory contains WordPress core settings and MySQL database details. Thus, the file is usually a hacker’s primary target.
Protect this file and keep WordPress secure by implementing these .htaccess rules:
<files wp-config.php> order allow,deny deny from all </files>
WordPress database holds and stores all crucial information required for your site to function. Therefore, hackers often target the database with SQL injection attacks. This technique injects harmful code into the database and can bypass WordPress security measures and retrieve the database content.
Over 50% of cyberattacks consist of SQL injection, making it one of the biggest threats. Hackers execute this attack because many users forget to change the default database prefix wp_.
Let’s take a look at two methods that you can implement to protect your WordPress database from SQL injection attacks.
Important! Before proceeding, make sure to back up your MySQL database.
Changing table prefix

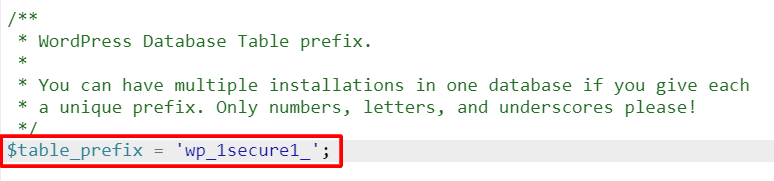
// ** MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host ** // /** The name of the database for WordPress */ define( 'DB_NAME', 'MySQL Database' );
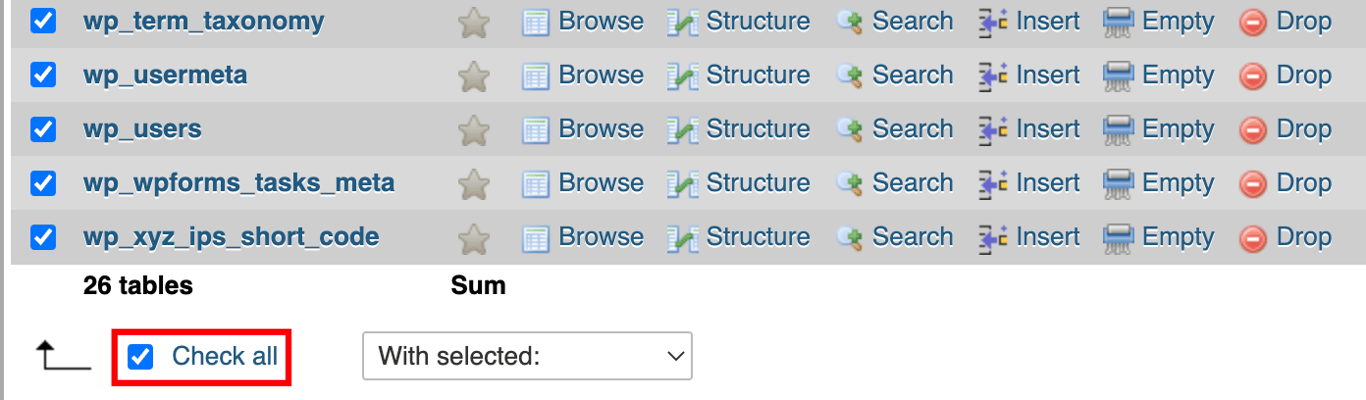
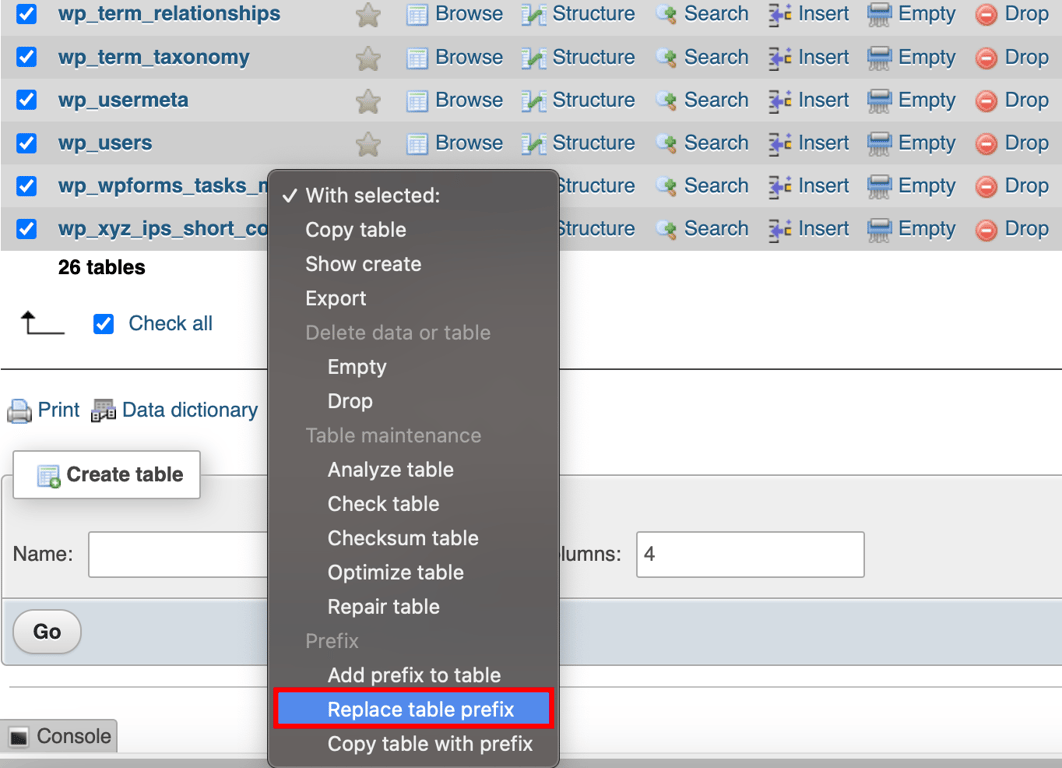
Updating prefix values in the tables
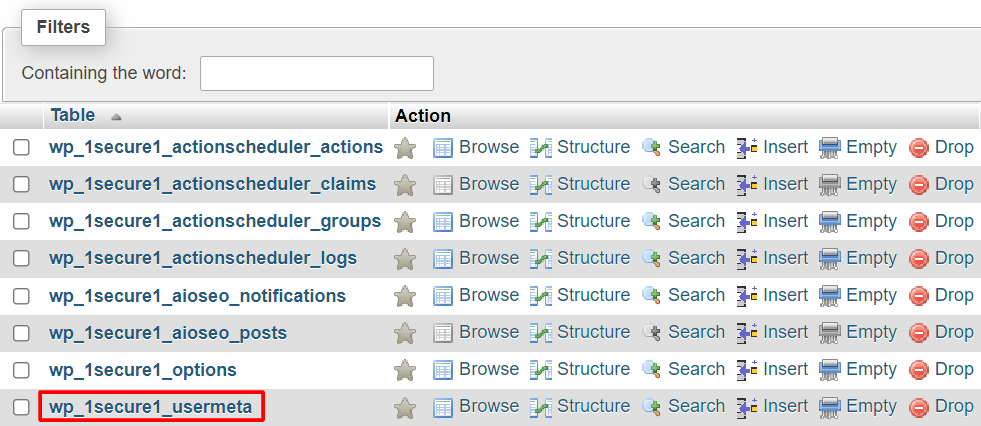
Depending on the number of WordPress plugins installed on your site, you may need to update some values in the database manually. Do this by running separate SQL queries on tables that are likely to have values with the wp_ prefix – these include the options and usermeta tables.
Use the code below to filter all values that contain the following prefix:
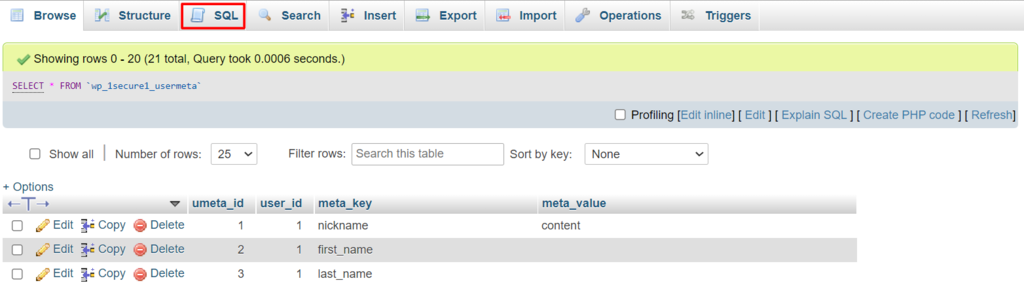
SELECT * FROM `wp_1secure1_tablename` WHERE `field_name` LIKE '%wp_%'
wp_1secure1_tablename contains the table name in which you want to perform the query. Meanwhile, field_name represents the name of the field/column where values with wp_ prefix most likely appear.
Here’s how to manually change the prefix value:
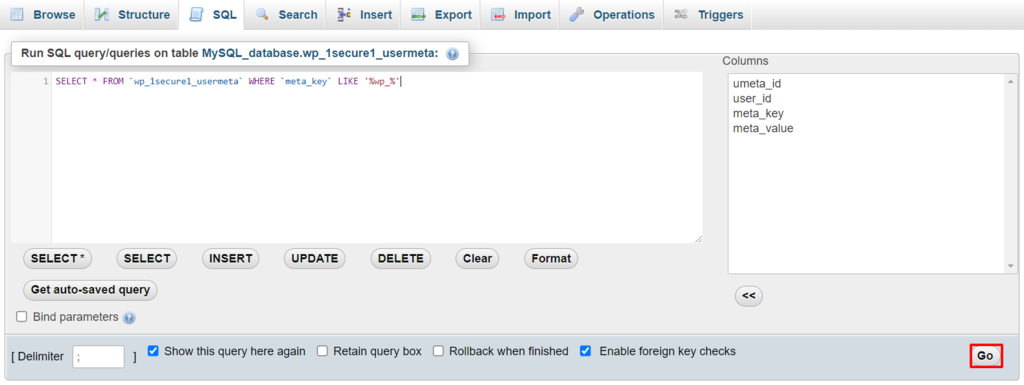
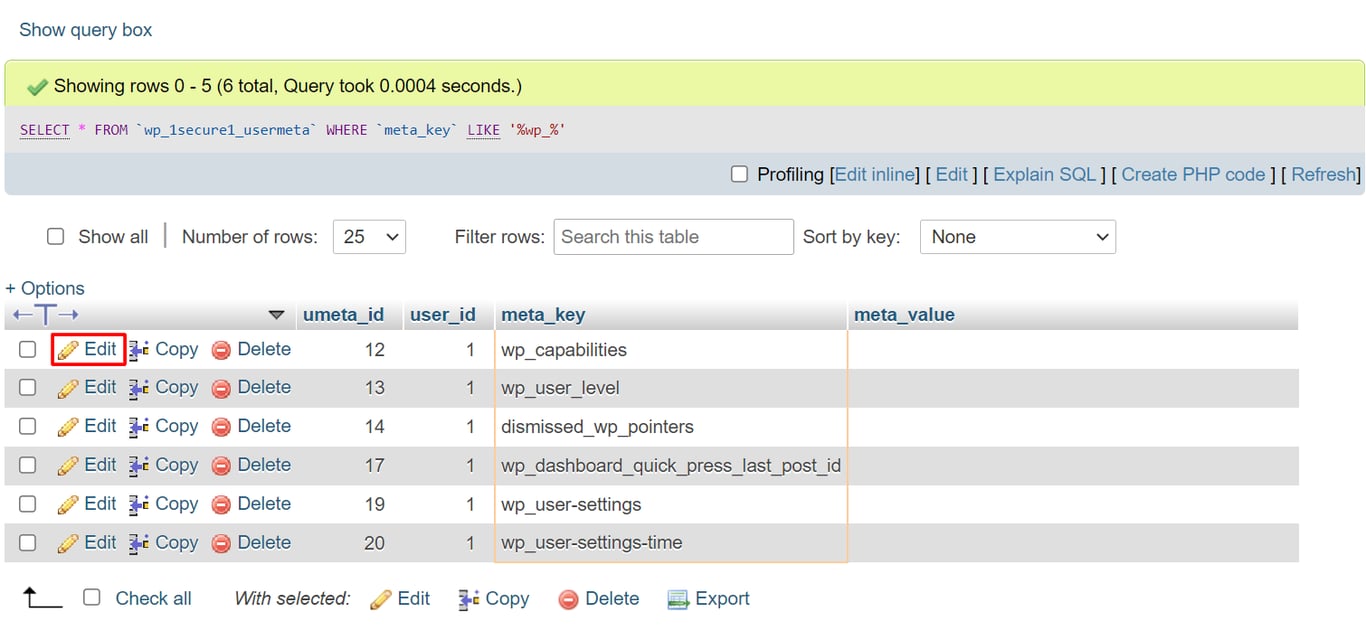
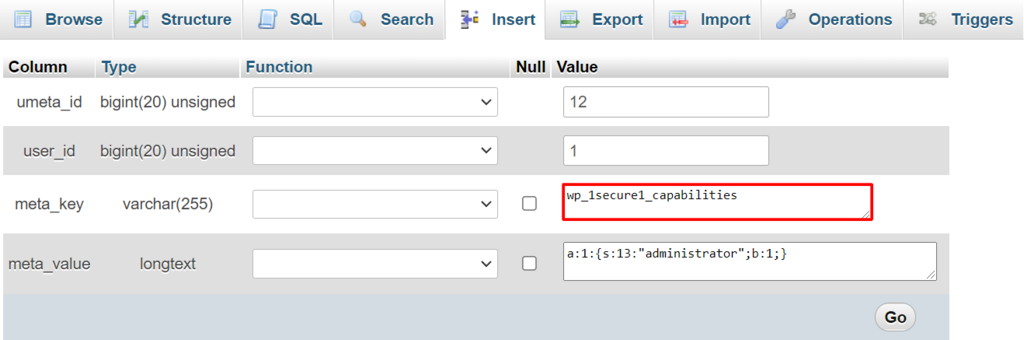
XML-RPC is a WordPress feature for accessing and publishing content via mobile devices, enabling trackbacks and pingbacks, and using the Jetpack plugin on your WordPress website.
However, XML-RPC has some weaknesses that hackers can exploit. The feature lets them make multiple login attempts without being detected by the security software, making your site prone to brute force attacks.
Hackers can also take advantage of the XML-RPC pingback function to perform DDoS attacks. It allows attackers to send pingbacks to thousands of websites at once, which can crash the targeted sites.
To determine whether XML-RPC is enabled, run your site through an XML-RPC validation service and see whether you receive a success message. This means that the XML-RPC function is running.
You can disable the XML-RPC function either by using a plugin or manually.
Disabling XML-RPC using a plugin
Using a plugin is the faster and simpler way to block the XML-RPC feature on your website. We recommend using the Hostinger Tools plugin. It can automatically turn off some of the XML-RPC functionalities, preventing hackers from performing attacks using this WordPress security flaw.
Disabling XML-RPC manually
Another way to stop all incoming XML-RPC requests is by doing it manually. Locate the .htaccess file in your root directory and paste the following code snippet:
# Block WordPress xmlrpc.php requests <Files xmlrpc.php> order deny,allow deny from all allow from 000.00.000.000 </Files>
To allow XML-RPC to access a particular IP, replace the 000.00.000.000 with the IP address or delete the code line altogether.
Hackers can break into your site easier if they know which version of WordPress you’re running. They can use that version’s vulnerabilities to attack your site, especially if it’s an older WordPress version.
Luckily, it’s possible to hide the information from your site using the WordPress Theme Editor. Follow the steps to do so:
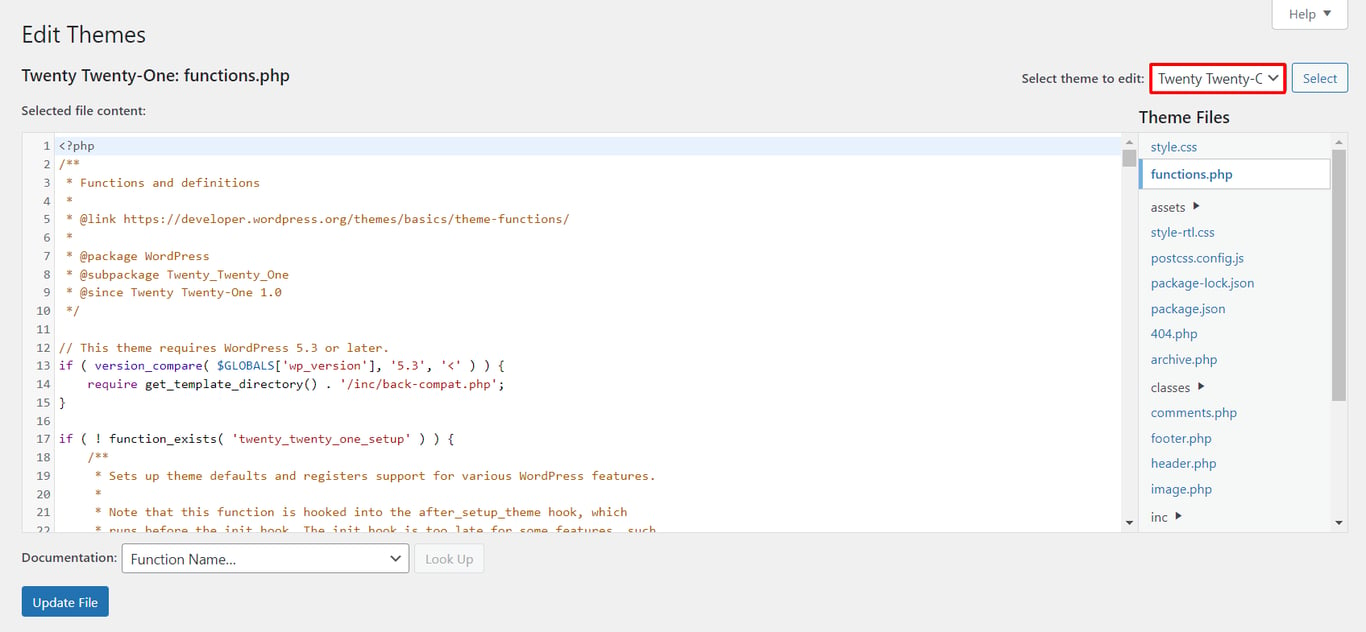
function dartcreations_remove_version() {
return '';
} add_filter('the_generator', 'dartcreations_remove_version');remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');Hotlinking is the term used when someone displays your website’s asset, usually a picture, on their website. Every time people visit a website with hotlinks to your content, it uses up your web server resources, slowing down your site.
To see if your content was hotlinked, type the following query in Google Images, replacing yourwebsite.com with your domain name:
inurl:yourwebsite.com -site:yourwebsite.com
To prevent hotlinking, use an FTP client, a WordPress security plugin, a CDN, or edit the control panel’s settings.
Prevent hackers from gaining access to your admin account by determining which users can read, write, or execute your WordPress files or folders.
You can use your web host’s File Manager, FTP client, or via command line to manage file and folder permissions.
Generally, permissions are set by default, which may vary depending on different files or folders. Specifically for the wp-admin folder and wp-config file, make sure only to allow the Owner to write it.
If your WordPress site gets hacked, you risk losing important data, assets, and credibility. Furthermore, these security issues can jeopardize your customers’ personal data and billing information.
The cost of cybercrime damages can reach up to $10.5 trillion per year by 2025. Surely you don’t want to become a hacker target and contribute to that.
Based on WPScan Vulnerability Database, these are some of the most common types of WordPress security vulnerabilities:
We recommend reading our other article to learn more about identifying and fixing a hacked WordPress site to help minimize data and financial loss.
Check out our guide about web application security and protect your site from cyber attacks.
Cyberattacks may come in different forms, from malware injection to DDoS attacks. WordPress websites, in particular, are common targets for hackers due to the CMS’s popularity. Therefore, WordPress website owners must know how to secure their sites.
However, securing a WordPress site is not a one-time task. You need to continuously reassess it since cyberattacks are ever-evolving. The risk will always be there, but you can apply WordPress security measures to reduce those risks.
We hope this article has helped you understand the importance of WordPress security measures and how to implement them.
Feel free to leave a comment if you have any questions or more WordPress security tips.
Setting up a website firewall is necessary as it helps guard your WordPress site against hacking attempts or other forms of cyberattacks by blocking unwanted traffic. Since WordPress doesn’t have a built-in website firewall, you can set it up by downloading a plugin like Sucuri.
As a platform, WordPress is a secure and safe to use. WordPress security is not only about the technology but also about the human factors. No matter how safe the platform is, your site can easily be hacked if you don’t take other security measures (use strong passwords etc).
If your browser shows that your WordPress site is not secure, that means your site doesn’t have an SSL certificate or the SSL isn’t configured correctly. Consider installing one or switching to HTTPS to fix the issue.
Yes, installing a hack scanner security plugin such as Jetpack and Sucuri can help protect your site for the long term. Remember to only install the necessary ones as having too many plugins can break your site.
Start by making sure that you use a secure WordPress hosting. Then, configure your site for better WordPress security: manage file permissions, disable PHP error reporting and XML-RPC, restrict access to wp-config.php, and block hotlinking from other websites.
Many WordPress sites get hacked because the site owner doesn’t use enough security measures. This leaves sites with various vulnerabilities that open the way for potential attackers. Attackers also regularly target WordPress-powered websites because it’s used by almost half of the existing websites.
Your WordPress site might have security vulnerabilities like outdated plugins, weak passwords, and unprotected access to the wp-admin directory. Apply regular website maintenance and use our WordPress Security Checklist to ensure you’ve applied sufficient security measures to your site.
We recommend Wordfence or Sucuri as the best WordPress security plugins. Both are similar, offering malware a WordPress scanner, web application firewall, and traffic monitoring. Sucuri is great if you have an online store, but if you’re looking for a free plugin, then Wordfence is a great option.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.