Sep 18, 2025
Brian & Jordana A.
28min Read

WordPress SEO is the process of optimizing a WordPress website to rank higher in search engines like Google. It makes your site easier to discover, helping you attract more visitors, readers, or customers.
For WordPress site owners, SEO is a top priority because it boosts visibility, brings in free organic traffic, and builds trust with the audience. A website that appears on the first page of search results has a much higher chance of growing into a successful project, blog, or business.
WordPress SEO has four key components:
WordPress SEO refers to applying search engine optimization practices to websites built with WordPress. While SEO in general is about boosting a website’s visibility in search engines, WordPress SEO focuses on using the platform’s features, themes, and plugins to improve optimization.
In many ways, SEO for WordPress websites is much like SEO for any other site. You still need to do keyword research, create valuable content, optimize titles and images, and build quality backlinks. The core principles of search engine optimization stay the same regardless of the platform.
The main difference is that WordPress offers tools that simplify the process. For example, you can install SEO plugins to manage meta descriptions and sitemaps and use speed-optimized, mobile-friendly themes. This makes SEO more accessible, even if you don’t have advanced technical skills.
Here’s why SEO is crucial for WordPress websites:
WordPress is one of the most SEO-friendly platforms, giving your content strong visibility in search engines from the start. With features like customizable permalinks, schema markup support, and mobile-responsive themes, the CMS provides a solid foundation for search engine optimization without requiring advanced technical knowledge.
What’s more, WordPress makes it easy to apply essential SEO practices. You can optimize titles, headings, and meta descriptions using built-in tools or plugins. Many themes are designed to load quickly and work well on mobile devices, while plugins handle XML sitemaps and improve site speed. With the right plugins and hosting provider, maintaining SEO performance becomes much simpler.
That said, WordPress alone won’t guarantee top rankings. To get the best results, you’ll still need to follow proven search engine optimization tips ‒ picking the right keywords, creating quality content, and using SEO plugins effectively. These steps will help you make the most of WordPress and increase your search rankings.
In WordPress SEO, “basics” refers to the foundation of your site: web hosting and essential configurations. Reliable hosting, HTTPS, and clean permalinks are small but critical steps that shape how search engines view your website. Setting these up correctly allows you to apply other WordPress SEO best practices more effectively.
Your hosting provider is the base of your WordPress website. It determines how quickly your site loads, how much traffic it can handle, and whether it stays online. Since speed and uptime influence rankings, poor hosting directly hurts your SEO efforts.
When you choose a web hosting service, prioritize speed, security, and reliability. Look for providers that offer built-in caching and servers optimized for WordPress. A provider with global data centers and a content delivery network (CDN) like Hostinger also reduces loading times for visitors worldwide.
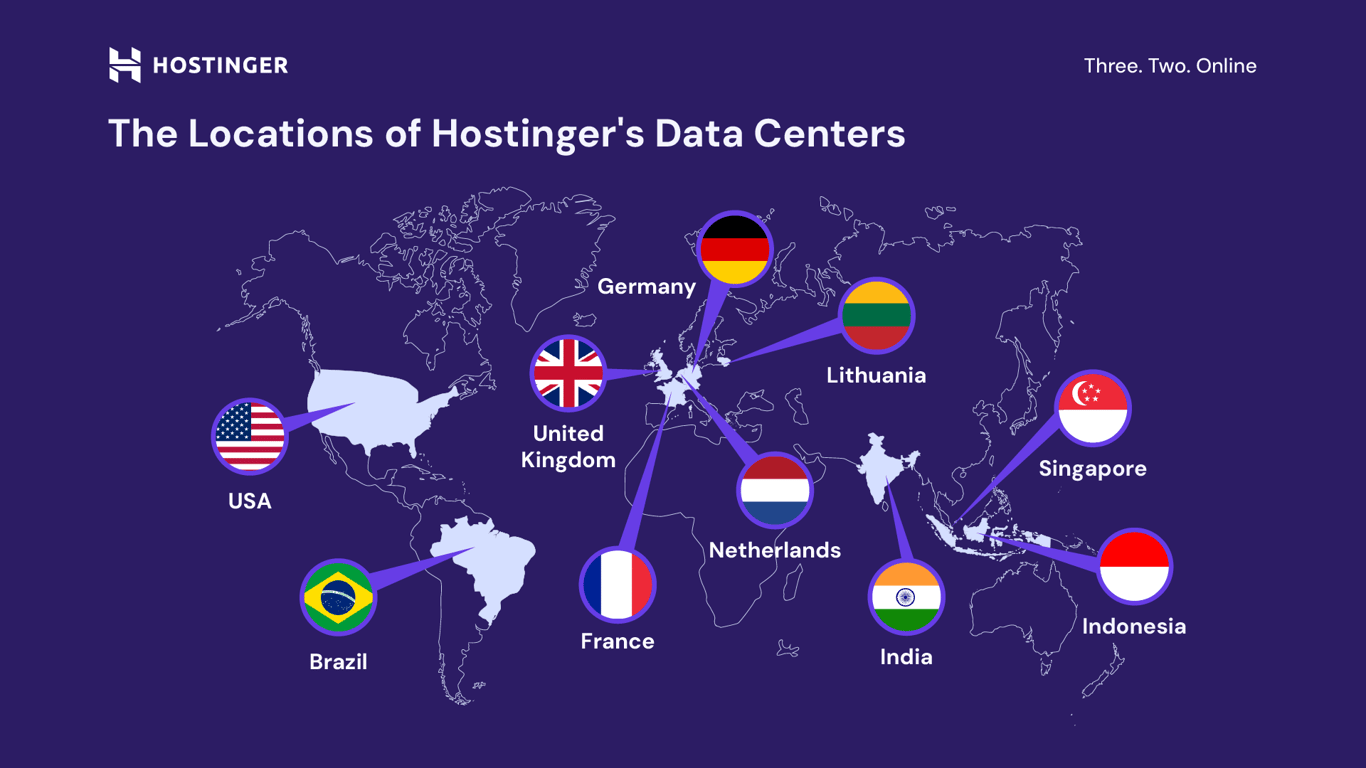
It’s also important to consider support and scalability. A good hosting provider will offer 24/7 support, automatic updates, and the flexibility to upgrade as your site grows. By starting with fast and reliable WordPress hosting, you’ll create a strong base for all your future SEO efforts.
One of the main ways to improve SEO is to invest in fast, reliable hosting with good uptime and quick support.
Our WordPress site has been hosted with Hostinger for more than two years now. When we first migrated from Bluehost, we were shocked at how much better the Lighthouse scores were and how much better our site performed on Google search results.

An SSL certificate encrypts the connection between your website and its visitors, protecting sensitive information like logins and payments. Once installed, your site’s URL changes to HTTPS and shows a padlock icon in browsers, signaling security to users.
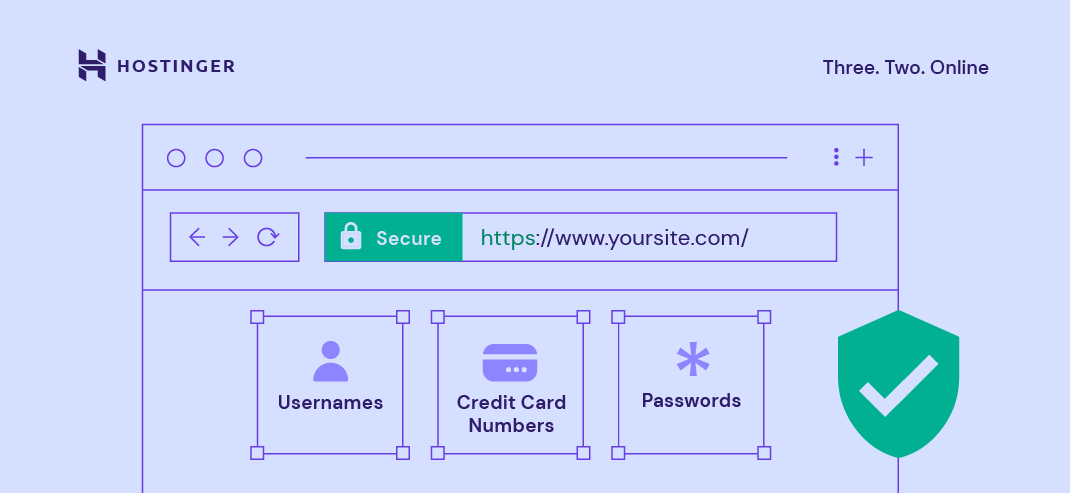
Google uses HTTPS as a ranking factor, and browsers often warn users if a site is not secure. That’s why an SSL certificate is essential to avoid losing traffic and hurting your website’s conversions.
At Hostinger, all WordPress hosting plans include unlimited free SSL certificates that are automatically installed for new websites.
If, for some reason, an SSL certificate isn’t enabled by default, you can manually install and activate it via the hPanel dashboard:
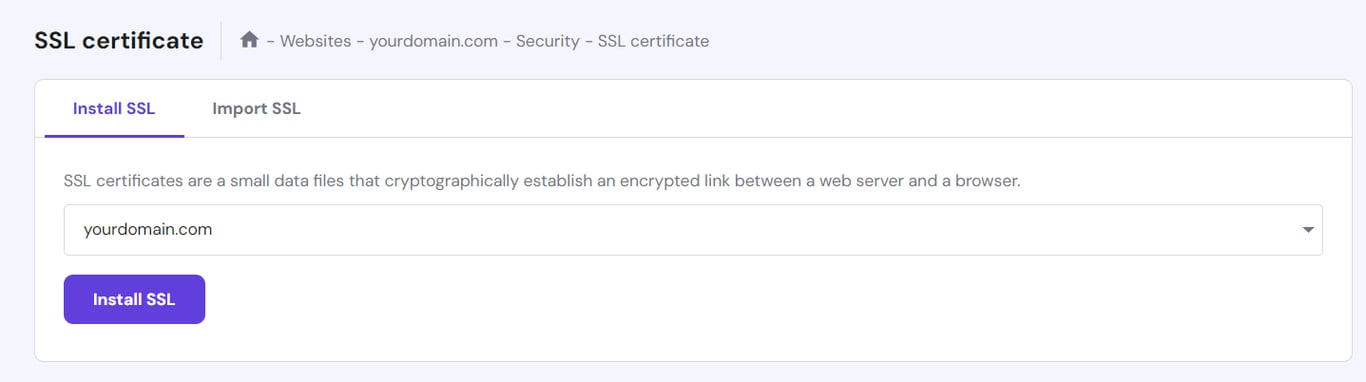
Keep in mind that the installation process can take up to an hour. Once it’s complete, your domain will automatically switch to HTTPS.
WordPress includes an option to discourage search engines from indexing a particular website. This can be useful for sites under development, private blogs, or content the owner wants to prevent from appearing in search engine results.
When this option is enabled, your web pages may not appear in search results, meaning they won’t generate traffic. So, unless your website is under maintenance, make sure this visibility setting is turned off.
To double-check, log in to your WordPress Dashboard and head to Settings → Reading. Find the Search engine visibility checkbox and ensure it’s unchecked.
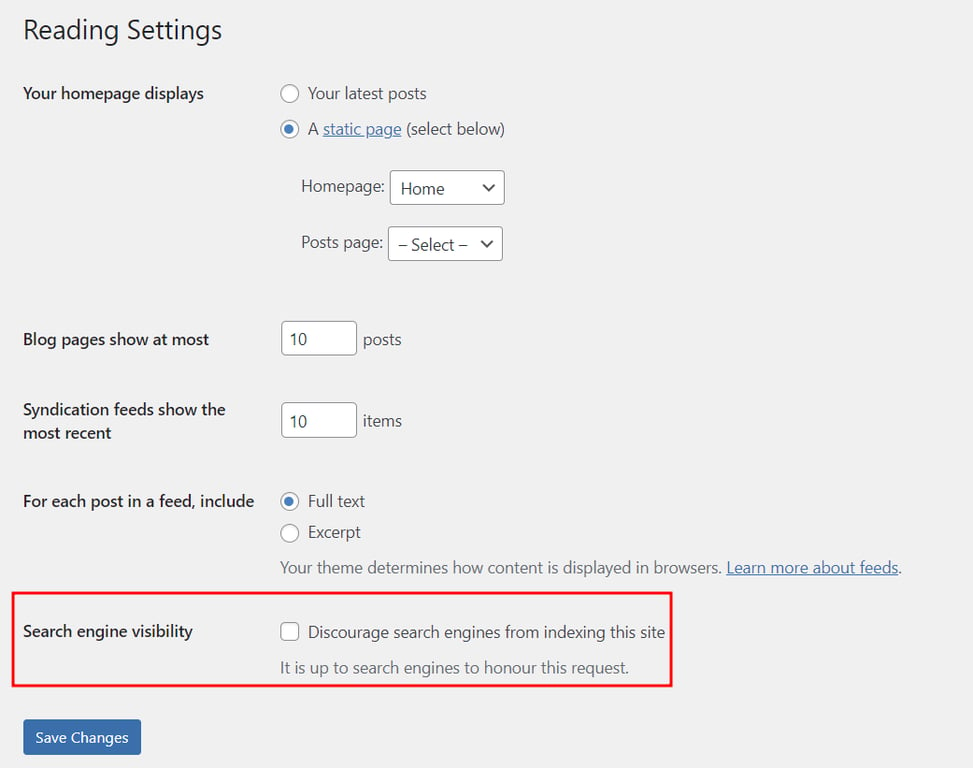
Important! Don’t check this box if it’s already unchecked. Enabling it, even temporarily, can result in the website losing all its search engine rankings, which could significantly impact its visibility and traffic.
A permalink is the URL of a specific page or post. Clean, readable permalinks look trustworthy, appear better in search results, and help users understand what a page is about. In contrast, messy or random URLs can look suspicious and discourage clicks.
In WordPress, you can set up a permalink structure that creates simple, SEO-friendly URLs, making your site clearer for both visitors and search engines.
To do so, head to Settings → Permalinks from your WordPress admin dashboard. Then, select the Custom Structure option and include the necessary tags.
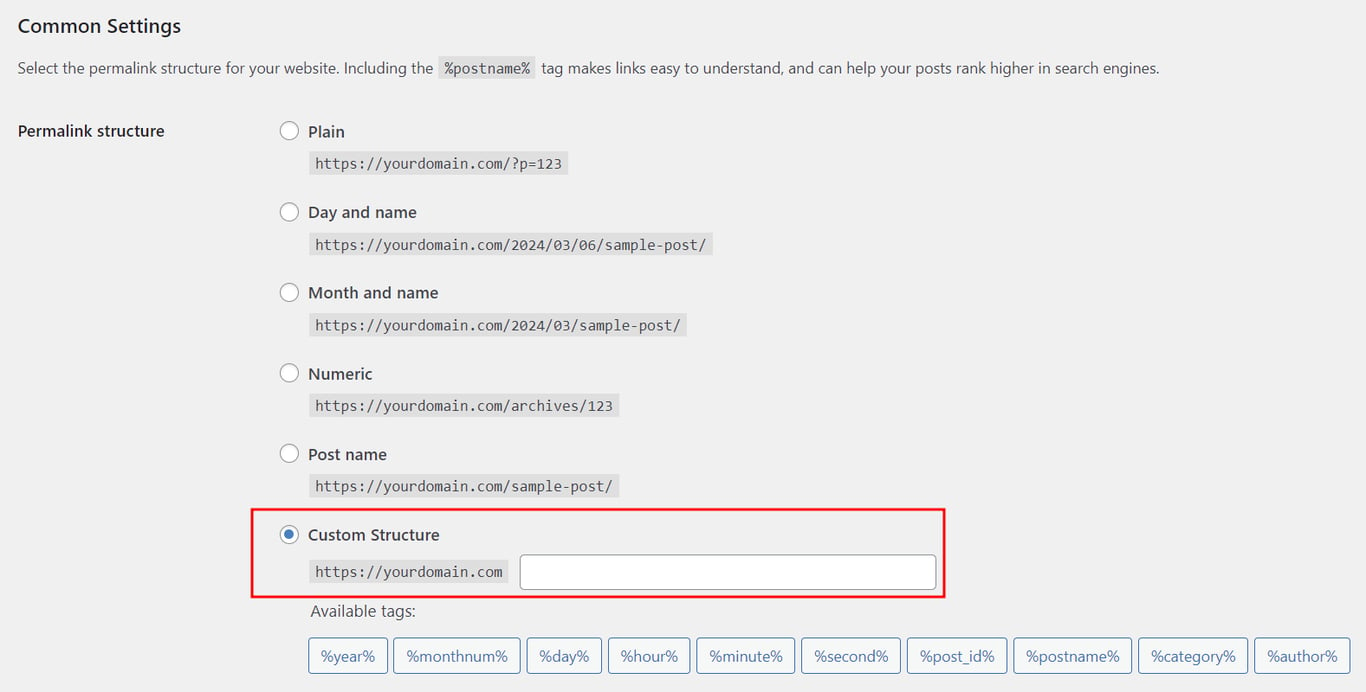
Choose tags based on your website’s type. For example, news sites often include the date and title in their URLs. Meanwhile, online store permalinks usually include the category and post title.
If your website is already online, remember to redirect your old URLs to the new ones after changing the permalink structure to prevent 404 errors. More details on the steps later.
A WordPress SEO plugin adds SEO tools to your dashboard, helping you optimize meta titles, descriptions, sitemaps, and readability without coding. It offers on-page recommendations like keyword use and internal links while automating tasks like sitemaps and schema markup for better search engine visibility.
Popular WordPress SEO plugins like Yoast SEO, All in One SEO (AIOSEO), and Rank Math SEO are among the best SEO tools for WordPress users looking to improve their site’s optimization. Yoast SEO is known for its beginner-friendly interface and content analysis tool. AIOSEO offers real-time optimization recommendations and WooCommerce integration for online stores. Meanwhile, Rank Math SEO provides advanced SEO analysis and reports to score your site’s performance.
To install a WordPress SEO plugin, go to your dashboard and head to Plugins → Add New. Search for the plugin you want, click Install Now, and activate it.
On-page search engine optimization (SEO) focuses on optimizing content and elements within your site to make it easier for both users and search engines to understand. This crucial component affects everything visitors engage with, from titles and headings to images and links, improving the overall user experience and search engine visibility.
In WordPress, this includes doing keyword research, building topical authority with in-depth content and strategic internal linking, publishing original, high-quality posts, and applying a local SEO strategy for region-specific audiences. These steps make your website more relevant and competitive in search results.
Keyword research involves identifying the words and phrases people use in search engines to find relevant information. It’s essential for SEO because it provides insights into your audience’s interests and search behavior. By strategically incorporating these keywords into your WordPress content, titles, and meta descriptions, you can improve your chances of ranking higher and attracting targeted traffic.
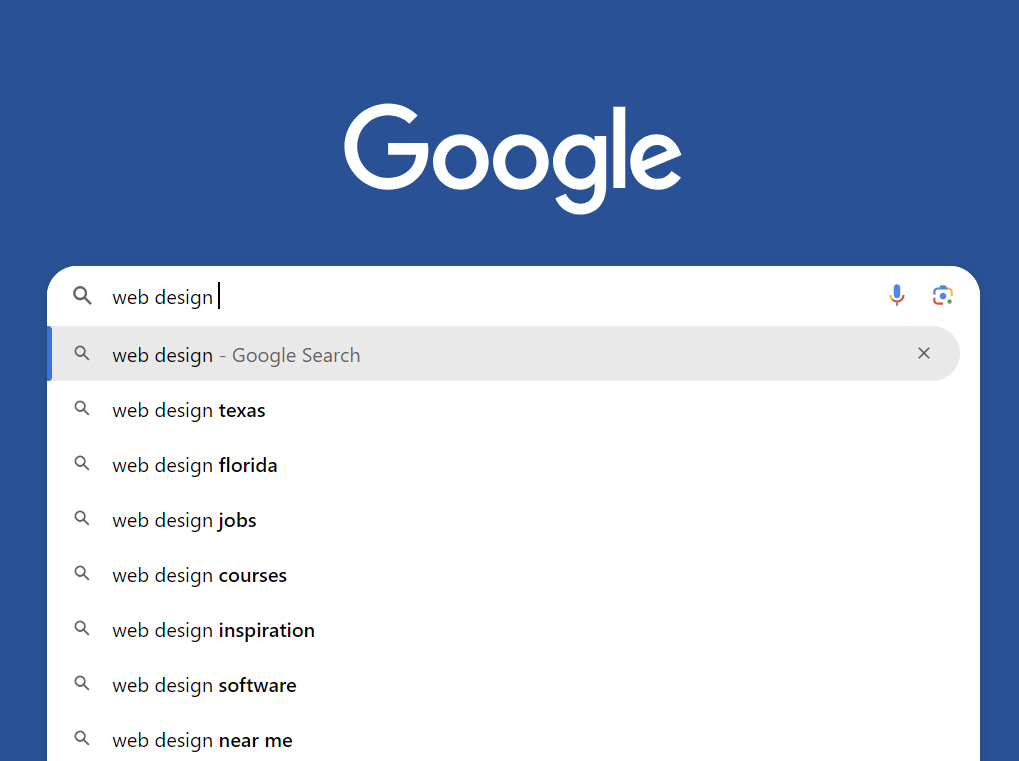
You can leverage Google’s autocomplete predictions to discover what users are searching for. These predictions are based on real queries people type into Google’s search box, giving you valuable insight into popular and trending topics.
For example, if you type “web design” as a keyword, automatic suggestions like “web design courses” and “web design software” will also pop up.
Type your keyword in Google’s search box and add a letter (a, b, c, d, and so on) after it to reveal additional keyword suggestions. After gathering several topic ideas, use free tools like Moz Keyword Explorer and Google Keyword Planner to check their monthly search volumes.
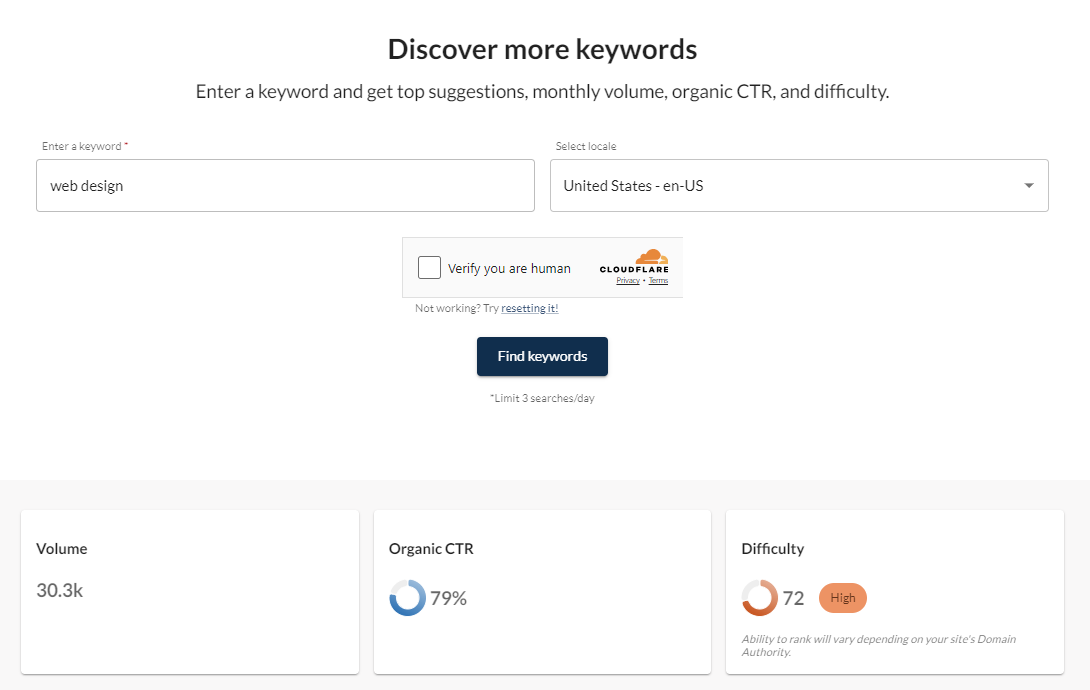
Keep in mind that free keyword research tools have limitations. For example, Moz lets you run only three keyword searches per day, while Google Keyword Planner shows search volume ranges instead of exact numbers.
If you want to conduct more in-depth research, we recommend investing in a paid tool like Ahrefs. Open the Keyword Explorer page, enter your website niche (in our example, “web design”), select your target location, and click Search to view detailed keyword data.
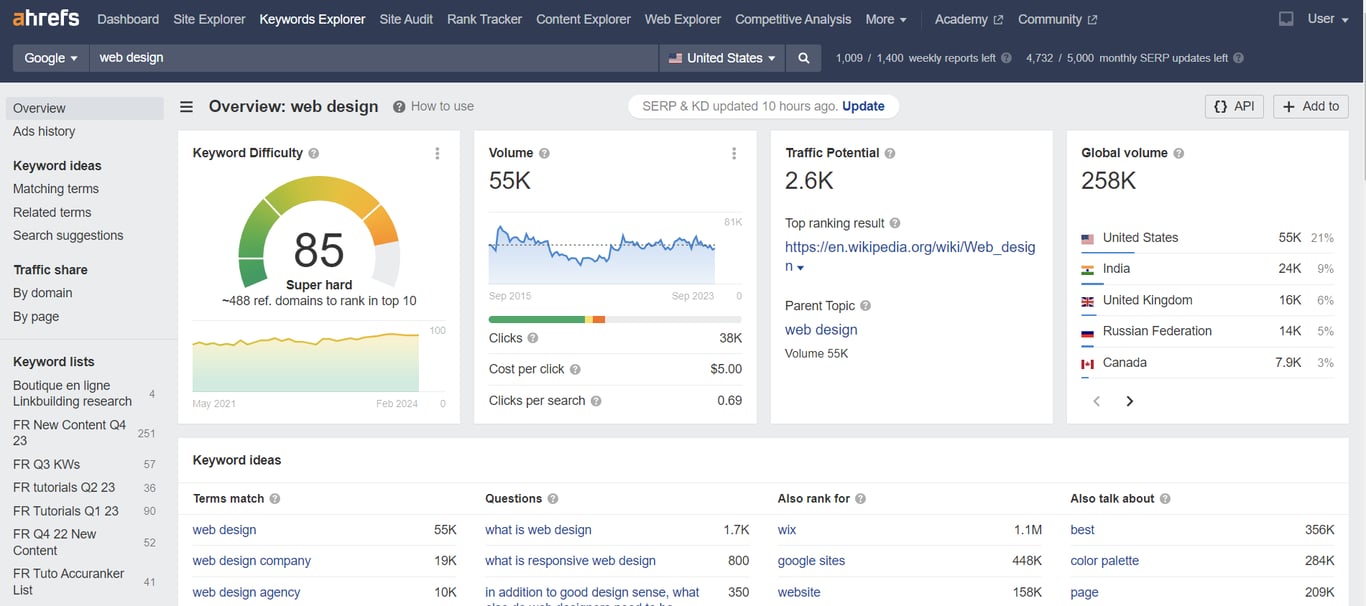
As shown in the screenshot above, this term has a stable volume of around 55,000 monthly searches, but it’s also highly competitive.
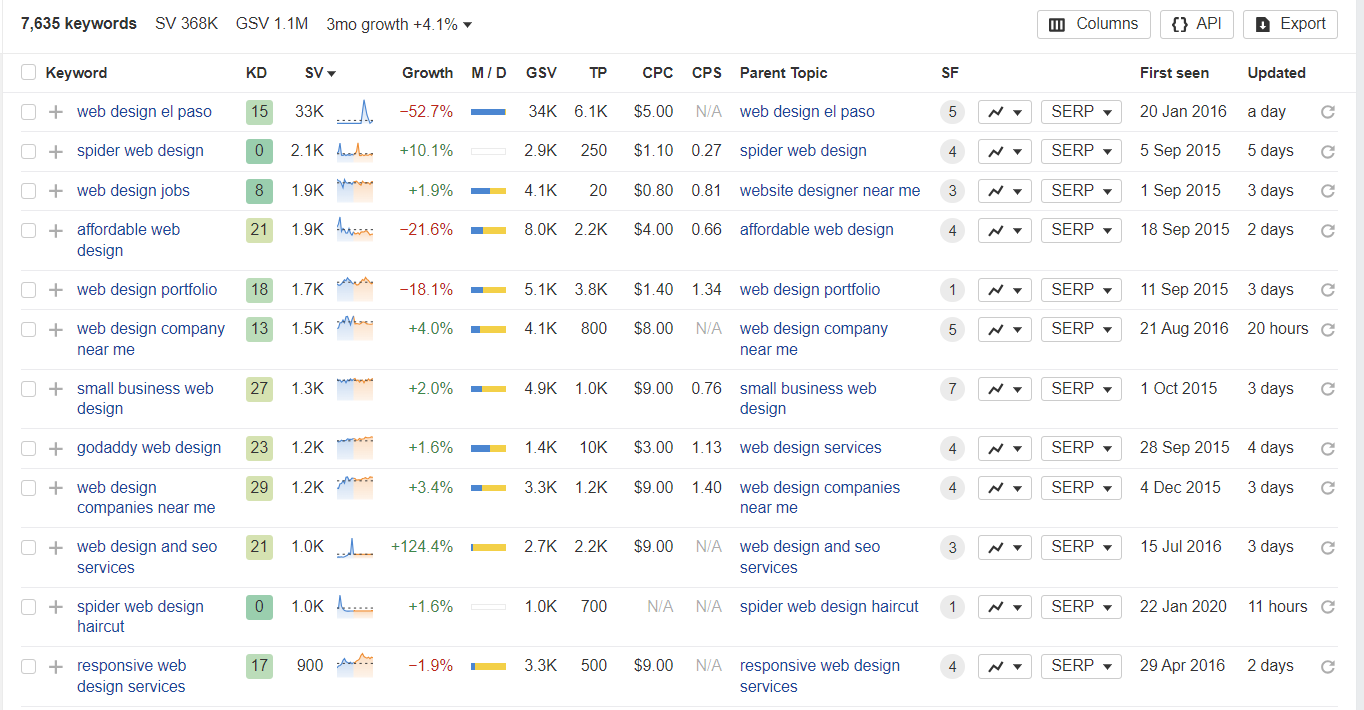
At this stage, it’s better to focus on long-tail keywords ‒ longer and more specific phrases. They’re typically easier to rank for compared to broad keywords, which are often dominated by major brands.
You can find such queries in Ahrefs by navigating to Keyword Ideas → Matching terms on the left sidebar. Then set the keyword difficulty (KD) to 30. The tool will show you potential topic ideas with lower competition.
With AI-powered search on the rise, keyword research now focuses more on context and intent rather than exact matches. This makes it essential to target phrases and topics that reflect how users naturally ask questions.
Here are some tips to guide your keyword research in the AI search era:
Topical authority is the credibility your website earns by covering a subject thoroughly. Rather than publishing just one or two articles, you create multiple pieces that explore different aspects of the same topic. This signals to search engines that your site is a reliable source, improving your chances of ranking higher for related keywords.
Here’s what John Pennypacker, the VP of Sales and Marketing at Deep Cognition, has to say:
“Instead of just targeting broad keywords, we built interconnected content hubs. For example, we created a main page on ‘Machine Learning in Business’ with links to more specific pages like ‘Neural Networks for Predictive Analytics’ and ‘Random Forests in Customer Segmentation.’
This approach helped us rank for long-tail keywords and showed search engines we had deep expertise in our niche. Our organic traffic jumped by 40% within three months of implementing this strategy.”
To establish your site’s topical authority, you need a well-planned content cluster:
Here’s an example of a content cluster:
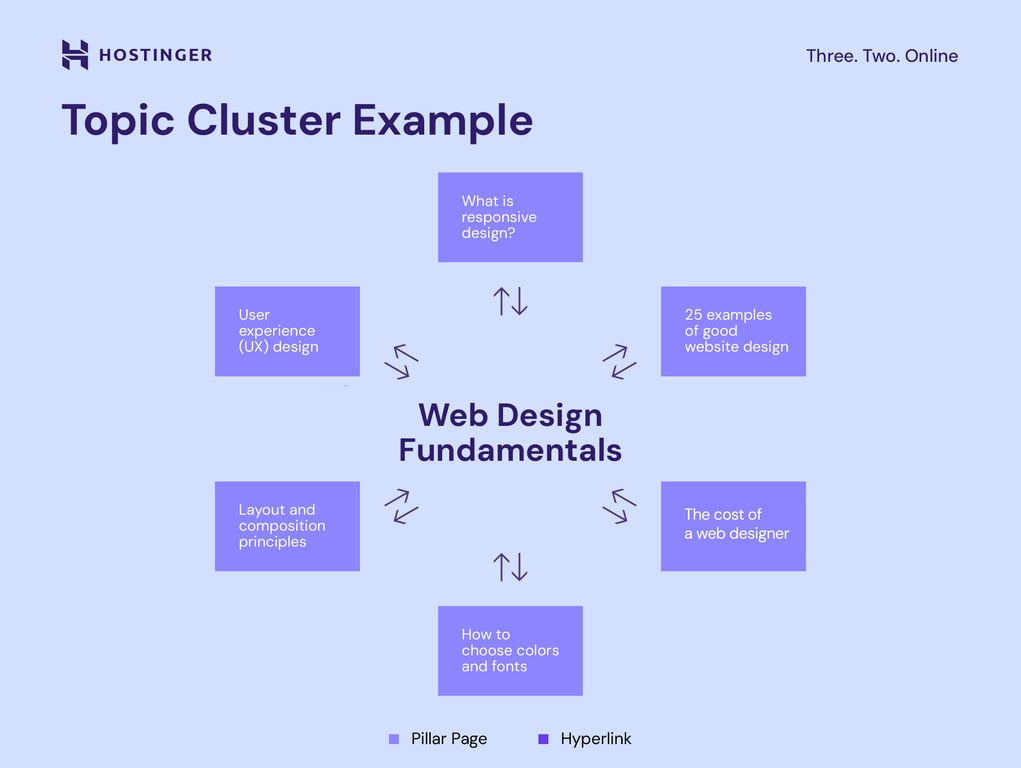
Organizing content around core topics with interlinked subtopics creates a natural flow for both visitors and search engines. This structure not only enhances user experience but also strengthens your website’s authority within its niche.
Topical authority has worked wonders for Sean Begg Flint, the Founder and Director of Position Digital. The SEO agency increased a client’s site traffic to over 10,000 visitors in less than six months.
We use Table of Contents Plus to create comprehensive pillar pages with clear, navigable structures. For a financial services client, this strategy helped us go from zero to over 10,000 monthly visitors in less than six months. The pillar content provided a strong foundation that improved the site’s overall authority, while the cluster content captured specific, high-intent searches.
Search engines prioritize original, high-quality content because it offers the most value to users. Well-written articles that are accurate, comprehensive, and easy to read signal relevance and authority, which helps improve your rankings.
This strategy is even more important in the era of AI search and large language models (LLMs). AI systems pull information from multiple sources to generate answers, and they favor clear, well-structured, and trustworthy content. When you publish great content on WordPress, you’re more likely to get picked up by AI and cited in its results, extending your visibility beyond traditional search engines.
Follow these best practices to improve the quality of your content.
People use search engines like Google for different purposes – some are looking for information, while others are ready to make a purchase.
By understanding what users are searching for, you can tailor your content to meet their specific needs and expectations.
Here are common types of search intent:
Sometimes, figuring out what users really want can be tricky. In these cases, look at the top-ranking pages for your keyword to understand what kind of content Google believes is most useful.
Readers often skim content, so use clear headings to divide it into sections. Follow a logical hierarchy, placing H2 tags after H1, H3 after H2, and so on, to help both readers and search engines understand the flow.
Keep headings concise, ideally between 50-70 characters, and consider phrasing some as questions to increase your chances of appearing in Google’s featured snippets or People Also Ask sections.
Remember to include your primary and secondary keywords in headings to highlight key terms and boost your page’s relevance in search results.
Here’s an example of a well-structured content layout:
H1: What is UX design? H2: The difference between UX and UI design H2: Types of projects a UX designer does H3: Website design H3: Software design H3: Augmented reality H2: How to become a UX designer H2: Conclusion
Google uses the E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) to evaluate content quality. To stand out, include insights and perspectives that only you or subject-matter experts can offer.
You can gather unique insights by connecting with experts on platforms like Connectively or Help a B2B Writer, interviewing them, and weaving their advice into your articles. Be sure to include a detailed author bio with their name, photo, role, and links to professional profiles like LinkedIn. This helps both readers and Google recognize that your content comes from a real expert.
During E-E-A-T testing at Hostinger, we noticed that even though overall organic traffic declined, the articles in the test group actually received more clicks and impressions than before. This indicates that the improvement wasn’t part of a broader site trend but likely resulted from adding co-authors.
The most significant growth occurred on high-traffic pages (100+ clicks), with most experiencing increased impressions and clicks. Although a few pages saw a drop, the overall result was positive. This suggests that showcasing clear author expertise helped strengthen E-E-A-T signals, making the pages more resilient during a general traffic decline.
Incorporate relevant keywords naturally throughout your content, including in meta titles, meta descriptions, headings, image alt tags, and the main text.
Avoid overusing exact keywords, as this is considered keyword stuffing. Google’s algorithms are becoming better at understanding context, related topics, and user intent.
For example, Google understands that terms like “software,” “mobile apps,” and “computer programming” are closely related, even if they aren’t explicitly used together.
If you need help creating high-quality, SEO-friendly content, check out our top AI content generators for the best options.
Meta titles and meta descriptions are short pieces of text that appear in search engine results. The title tells users and search engines what the page is about, while the description summarizes it.
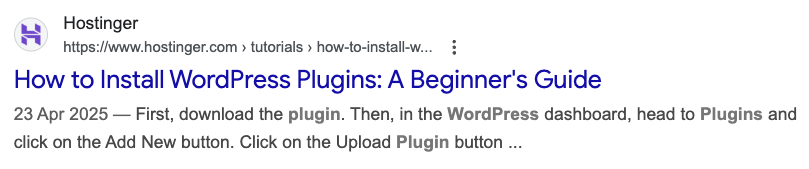
Both are often the first thing people see when searching, so writing good meta titles and meta descriptions is key to attracting clicks and increasing visibility.
The easiest way to add meta titles and descriptions in WordPress is by using an SEO plugin like AIOSEO or Yoast SEO. These tools let you edit and preview your titles and descriptions directly in the post editor instead of editing your theme’s header.php file.
If you use Yoast SEO, scroll down to the bottom half of the block editor to see how your metadata will look in search engine results.
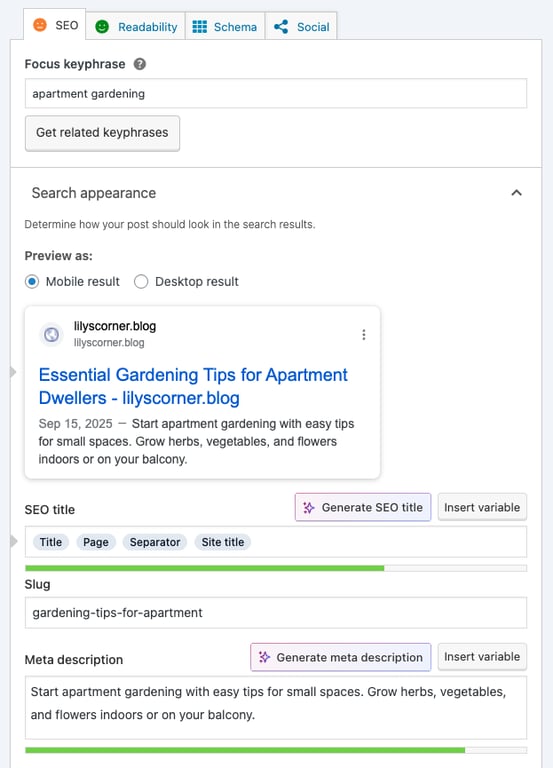
Here are some tips to improve your meta titles and meta descriptions:
Alt text, also known as alt tags, helps search engines understand the subject matter of your images. helps search engines understand the subject of your images. For visually impaired users, screen readers depend on alt text to describe the content and meaning of images.
WordPress lets you add alt text to images through the Media Library and the block editor. We recommend using the Media Library, as it allows you to easily attach alt text to images whenever you reuse them.
To do this, head to Media → Library, select your image, and fill in the Alternative Text box.
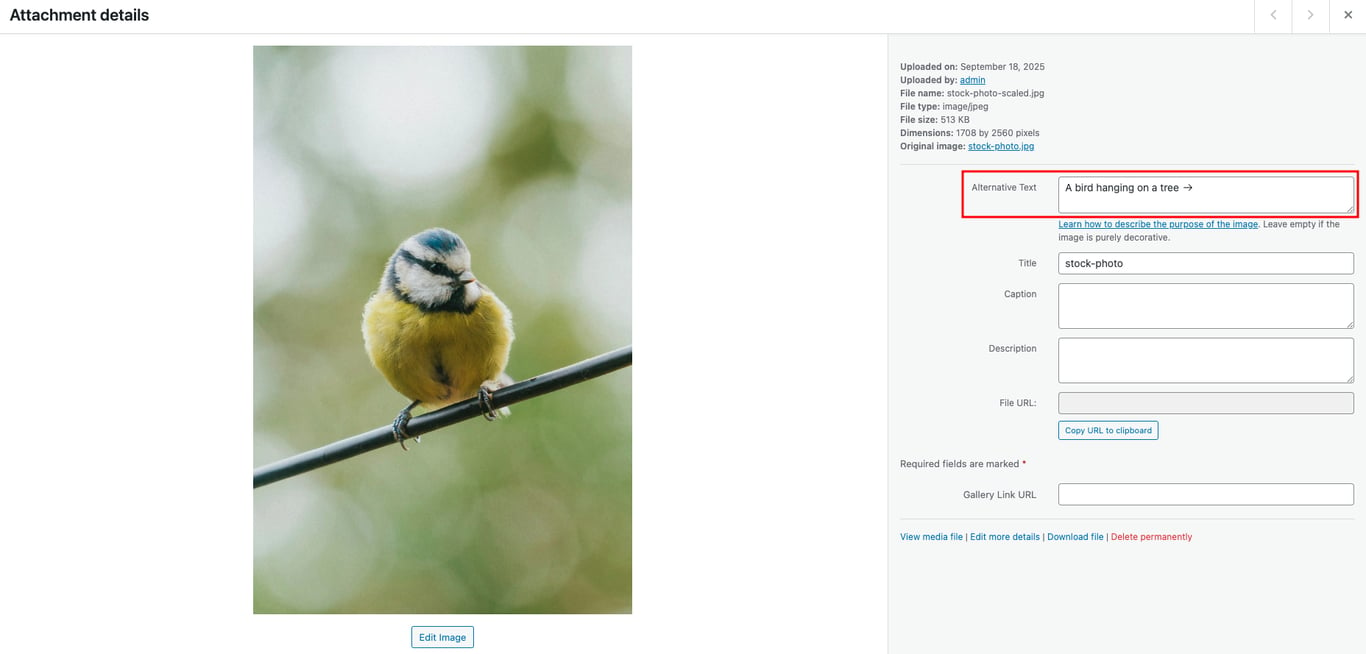
When writing alt text, follow these best practices:
A solid internal linking strategy is key to building topical authority. More importantly, it helps users easily find the content they’re looking for.
There are two main types of internal links: navigational and contextual.
Navigational internal links, typically located on the navigation bar, sidebar, or footer, contain the website’s main menu or structure and help users find the page they need.
Meanwhile, contextual internal links are embedded in your content pieces. For example, in a tutorial titled “What is a UX audit,” you can include an internal link to explain more about web design best practices and what makes a good website.

Internal links are crucial for SEO and offer several key benefits:
Here are some SEO tips for a strong internal linking strategy.
Instead of waiting until your site has a lot of content, establish a strong internal linking structure from your first posts.
Every time you write a new article, make sure it links to relevant content pieces that already exist on your site.
We ensure every new piece of content is linked to at least three other relevant pages on the site. This practice helps distribute link equity and keeps visitors engaged longer.
We rely on the Link Whisper plugin to automate and suggest internal links based on relevance. Implementing a robust internal linking strategy for a niche industry client led to a 20% decrease in bounce rate and a notable increase in session duration, contributing to overall traffic growth.
Naturally, you’ll want to link to all relevant content pieces. However, excessive links can make your blog post look spammy, negatively affecting your SEO rankings. Be selective about which pages you link to, ensuring each link adds value for your readers.
Focus on linking to pages that have the greatest impact on your business, such as your homepage, pillar pages, landing pages, and product or service pages. These pages are crucial for building brand awareness and driving sales.
Opt for keywords related to the content you’re linking to rather than generic phrases like “click here.” This not only helps users understand what to expect but also provides search engines with crucial context about your pages, further improving your SEO.
Keep in mind that your keywords don’t have to be an exact match. For instance, if your post discusses “How to create a WordPress site,” using “make a WordPress site” as the anchor text for your link should do the trick.
You can create an internal link with custom anchor text via the WordPress block editor. Highlight the anchor text and click on the link icon in your editor’s toolbar. Paste your page’s URL and hit Enter to save.
External links to other websites help readers explore topics you haven’t covered and signal to Google that your site values user experience, which is a key ranking factor.
Always link to reliable sources to boost your content’s credibility. Linking to high-quality websites also strengthens your site’s topical authority, showing search engines that your content is well-researched and connected to trusted information.
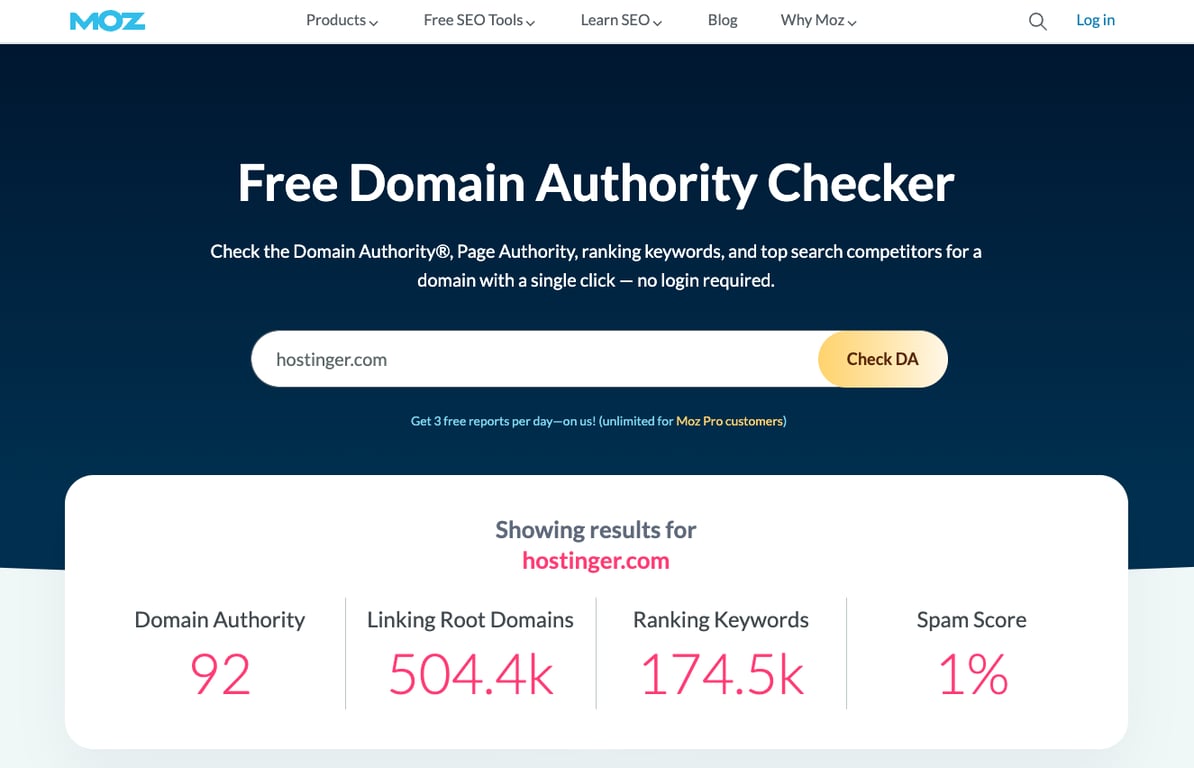
Tools like Moz, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can help you check a website’s domain authority (DA), which measures its quality and reliability. Higher DA scores (70-100) typically represent more reputable sources.
In addition to domain authority, here are some important WordPress SEO tips when including external links:
If you use an external link to a website you don’t want to be associated with, include the nofollow rel attribute. It stops search engines from crawling the link, preserving its “link juice” as a ranking factor.
You can easily add nofollow external links using the WordPress code editor:
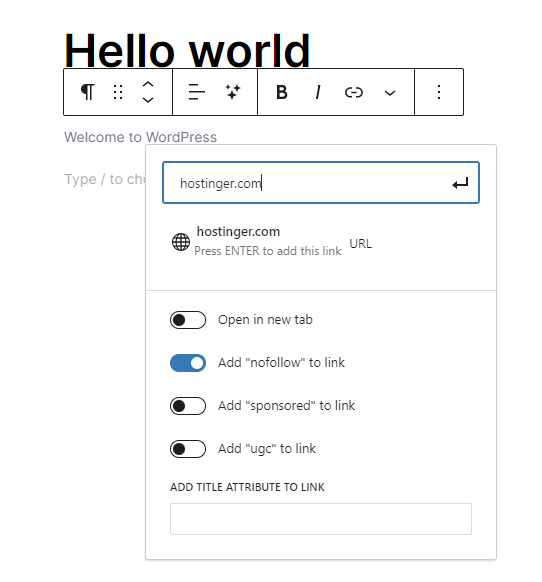
If you use affiliate links, add the rel=”sponsored” attribute. For links in user-generated content like comments or forums, use rel=”ugc” to tell search engines where they come from.
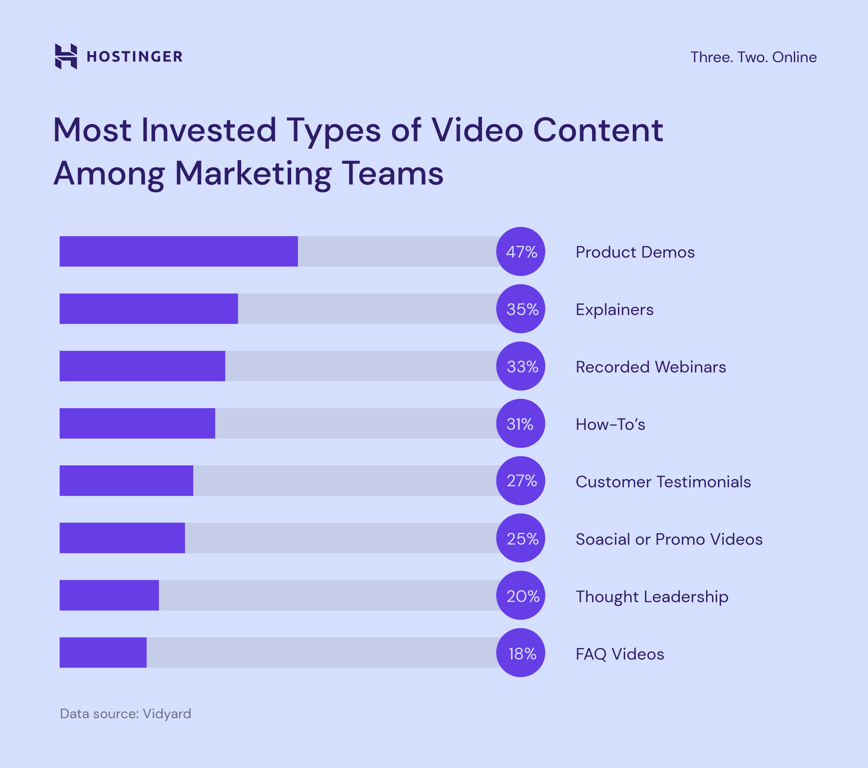
Video is a powerful way to engage your audience. People retain 95% of information from watching a video compared to only 10% from reading text. According to the latest digital marketing statistics, product demos, explainers, and webinars are the most effective formats.
Instead of uploading videos directly to WordPress, which can slow down your site, embed them from platforms like YouTube or Vimeo. In the block editor, click the + icon, choose the YouTube or Vimeo block, paste the video URL, and click Embed.
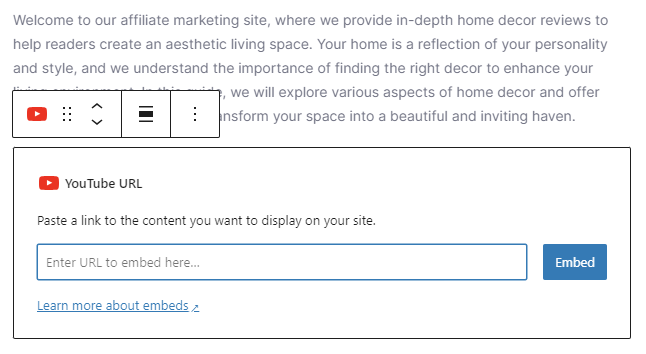
Here are four tips for creating successful video content:
For one of our educational clients, embedding explainer videos and interactive diagrams within their blog posts not only enriched the user experience but also improved dwell time and social shares.
We use Embed Plus for YouTube to easily embed videos and Interactive Content by H5P to add interactive diagrams and quizzes. This multimedia approach led to a 35% increase in traffic over four months.
The “last updated” date shows when an article was most recently refreshed. It’s typically displayed at the top of the page or just below the title, often alongside the original publish date.
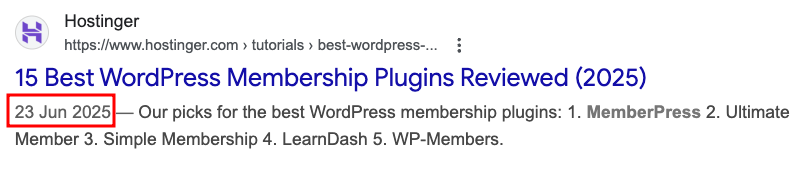
Adding the “last updated” date is beneficial because it signals to both readers and search engines that your content is current. Google favors fresh content, and visitors are more likely to trust information that’s clearly maintained.
It can also improve your chances of appearing in Google Discover, which highlights timely content on mobile devices. Since Discover prefers recent updates, displaying the last updated date increases the likelihood of your articles being featured and reaching new readers.
You can make the “last updated” date visible using a plugin. Here’s how to do it with WP Last Modified Info:
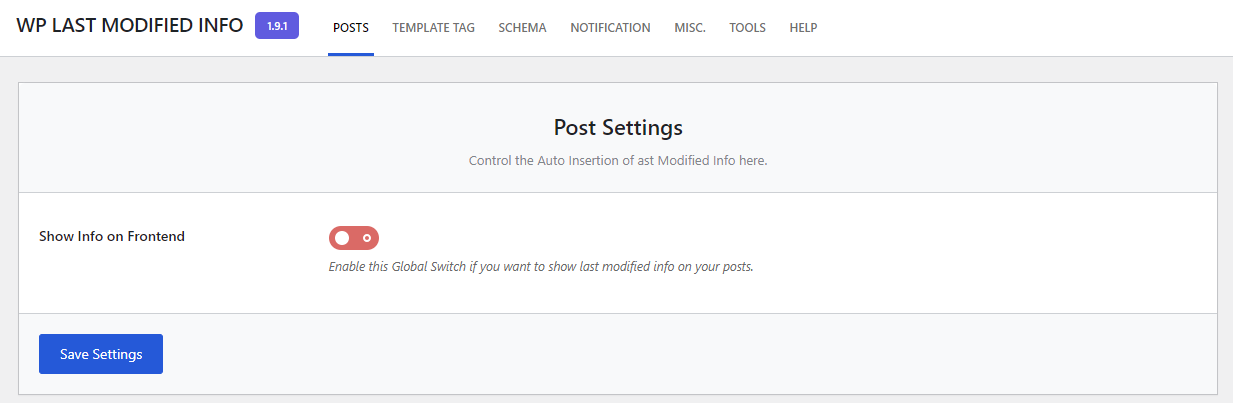
Next, head to your posts and pages and check if your WordPress site shows the “last updated” date. To display the element in the block editor, click the + icon and search for Modified Date.
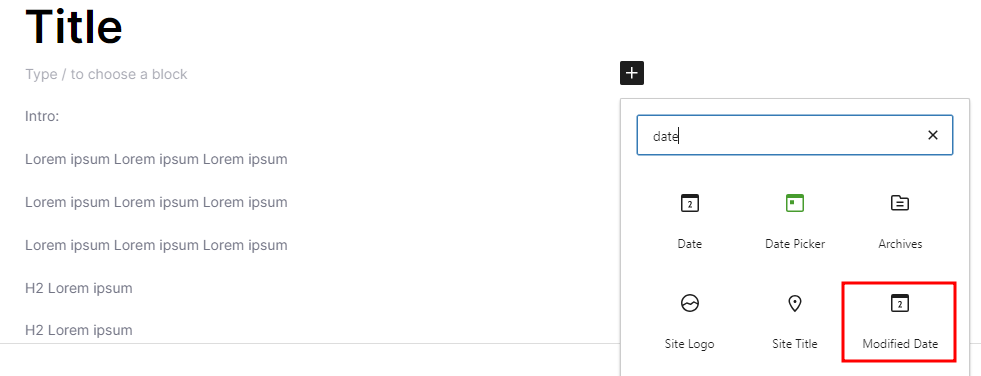
On the right sidebar, toggle on the Display last modified date option. This will automatically update the date whenever you make changes to the content.
If your business has a physical location, local SEO helps attract nearby customers by improving visibility in location-based searches. Creating a Google Business Profile is the first step. Add your company name, address, phone number, and other details so Google can display your business in local results.
Local SEO matters because Google measures distance and relevance when showing results. For example, if you run a barber shop in New York, your business can appear when someone nearby searches for “best barber near me.”
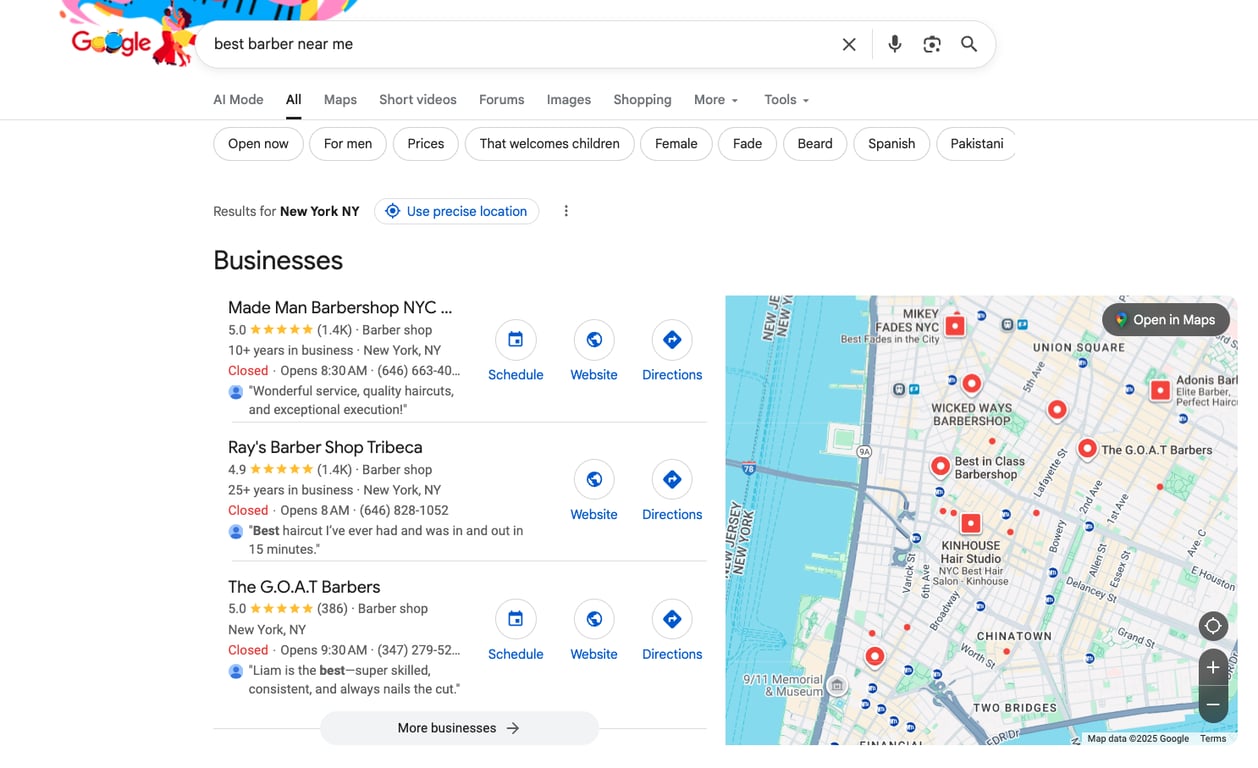
Keep these tips in mind to make the most of your local SEO efforts:
Technical SEO is the process of improving the behind-the-scenes elements of your website so search engines can crawl, index, and display your content more effectively. While on-page SEO focuses on what visitors see, technical SEO ensures your site is fast, secure, and properly structured for a great user experience.
Common methods of enhancing technical SEO in WordPress include optimizing website performance, submitting a sitemap to search engines, organizing your content with tags and categories, and adding an llm.txt file to guide AI crawlers. These are just a few of the techniques we’ll cover to help you strengthen your website’s technical foundation.
Search engines use website performance as a ranking factor because fast sites provide a better user experience. According to website load time statistics, nearly 50% of users expect a website to load in two seconds or less, meaning slow pages can quickly drive visitors away.
Google measures performance using Core Web Vitals, which focus on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. You can check your site’s performance with tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix, which highlight issues and suggest specific improvements.
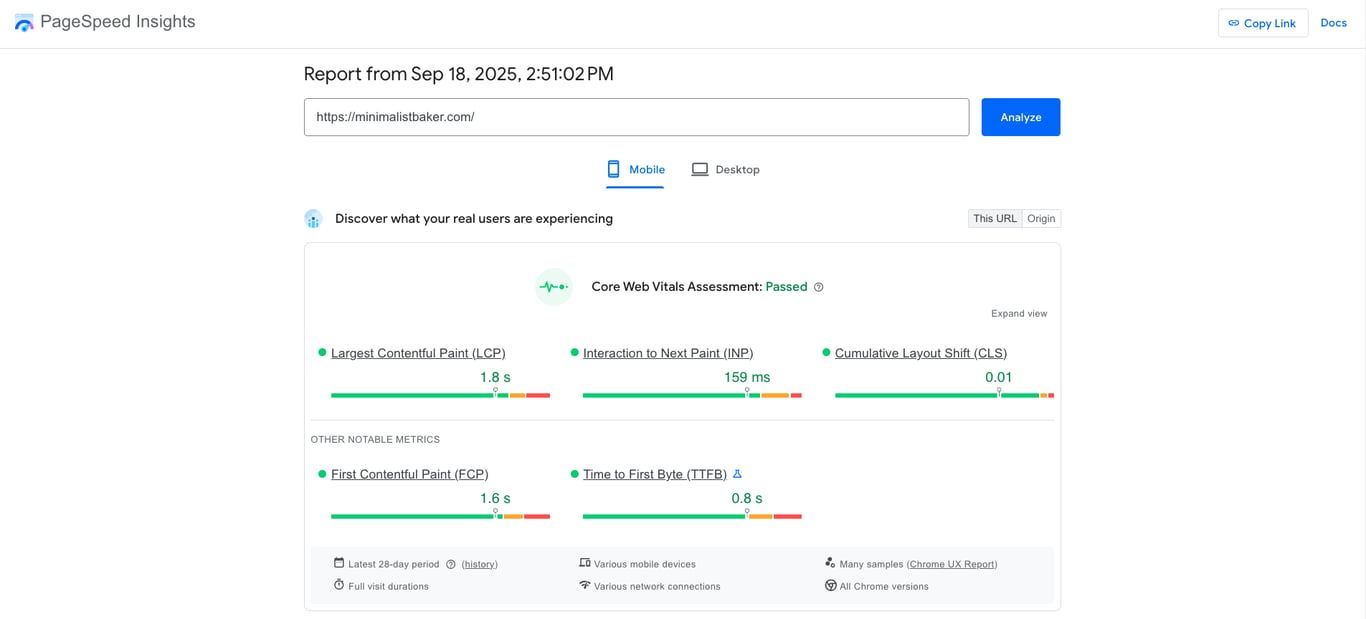
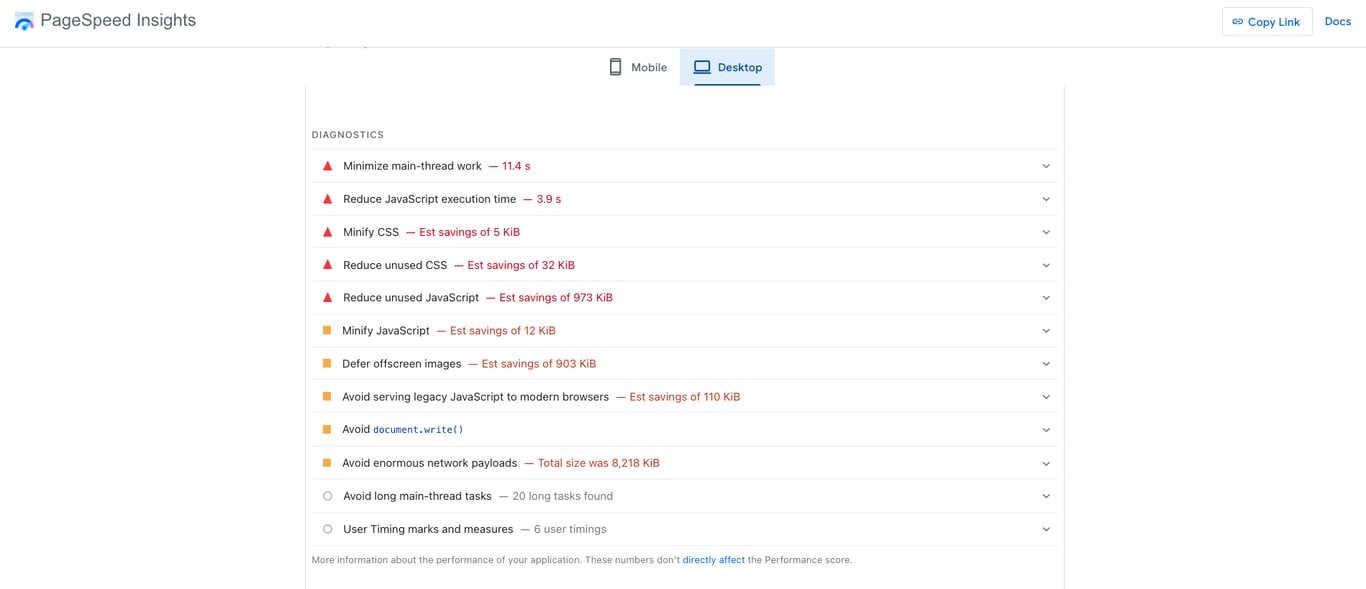
Some of the steps to optimize WordPress speed overlap with the basics, such as choosing the right web hosting or using a CDN. Beyond that, you can install a caching plugin to reduce load times, uninstall inactive plugins, and pick a lightweight, optimized theme. Keeping your WordPress core, themes, and plugins updated also helps maintain smooth performance.
It’s also important to optimize images in WordPress, as large image files are one of the main causes of slow pages. Use optimization plugins or convert images to modern formats like WebP to reduce file sizes without losing quality. Deleting unused files in your media library also helps free up server space and keep your site running efficiently.
We saw a significant improvement in traffic after reducing our load time to under two seconds. This was achieved by implementing advanced image optimization techniques such as lazy loading and deferring offscreen images. We also use a content delivery network (CDN), fine-tune our caching strategy, and minimize JavaScript. WP Rocket is our go-to plugin for caching, while Smush helps with image compression. Lazy Load by WP Rocket ensures offscreen images are loaded only when needed.
A sitemap is a file that lists your website’s important pages so search engines can find and index them more efficiently. Submitting a sitemap helps search engines understand your site’s structure, which is especially useful if you run a large website or add new content regularly.
There are two main types of WordPress sitemaps: HTML and XML. An HTML sitemap gives users an overview of your site’s content, while an XML sitemap lists all your site’s URLs in a structured format for search engines. You can easily create and set up both using an SEO plugin like AIOSEO or WP Sitemap Page.
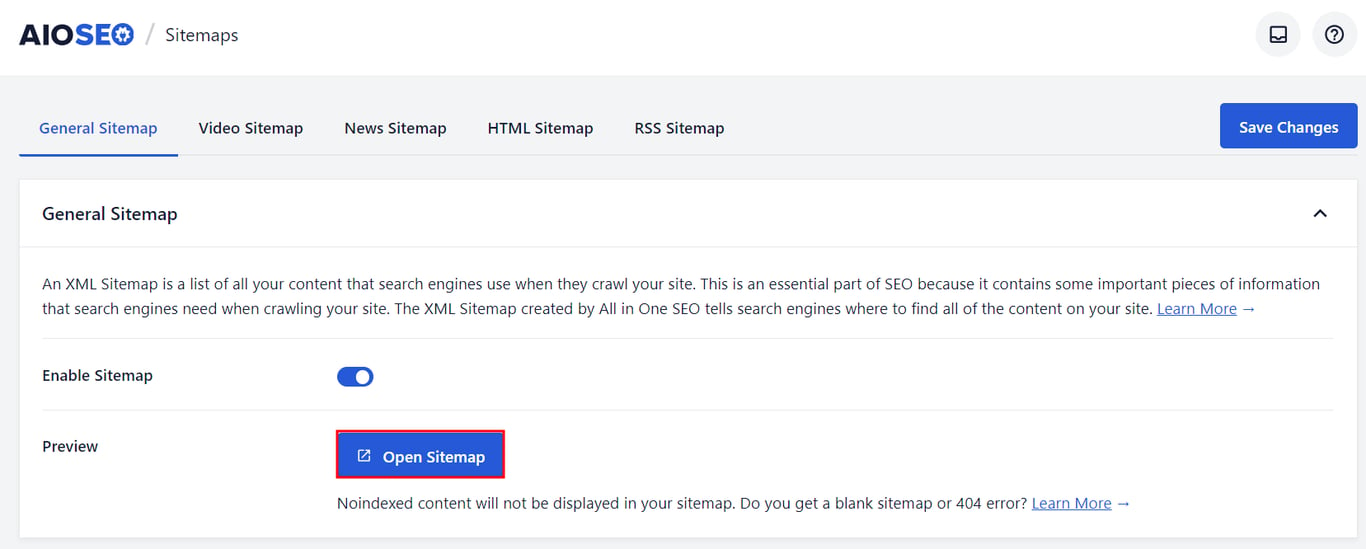
To submit the sitemap to search engines, use Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools. Log in, navigate to the sitemap section, and enter your XML sitemap URL ‒ usually yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml. Once you submit your sitemap, search engines will crawl it regularly to keep your content indexed.
When you create sitemaps using a plugin, be aware that WordPress themes may generate a lot of different content types and taxonomies, many of which you don’t want or need in organic search results.
That’s why it’s important to review the generated sitemaps and exclude any posts and pages you don’t want to be indexed. If you use parallax effects, your site will often have several versions of the homepage or other content, so make sure to noindex these posts and pages to remove them from the sitemap.
As you publish more content, organize it with categories and tags to make navigation easier.
Categories are broad groupings for your posts, while WordPress tags are more specific labels that include details of the content. These two elements work together as part of the WordPress taxonomy, which helps structure your site for both users and search engines.
For example, on a cooking blog, you might create categories like Breakfast, Lunch, and Dinner. Within a Breakfast post about pancakes, you could add tags like easy recipes, pancakes, or maple syrup.
Categories give readers a high-level overview of your content, while tags highlight individual topics and make it easier for search engines to understand relationships between posts. Using categories and tags correctly helps visitors find related content and strengthens your SEO by showing clear topic connections.
Assign the correct categories and tags from the editor’s sidebar. Navigate to Post from the admin dashboard to create a new category or tag.
Breadcrumbs are small navigation links that show users where they are on your site and are usually displayed at the top of a page. They improve the user experience and help search engines understand your site structure, contributing to your SEO efforts.
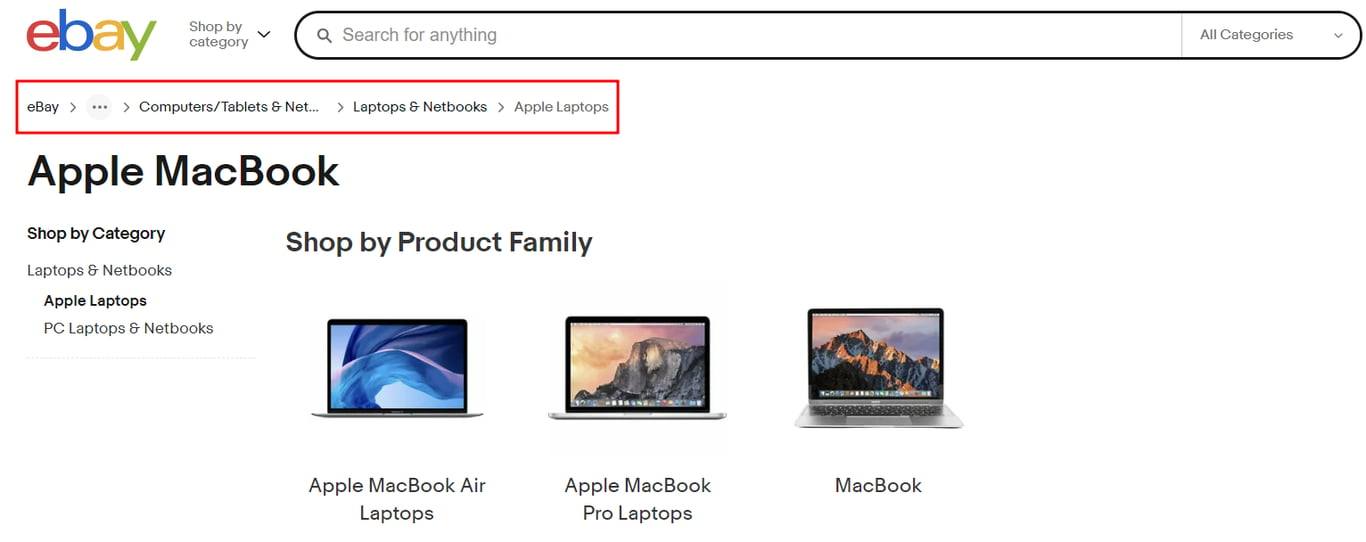
Adding breadcrumbs navigation in WordPress can be done in multiple ways. Many WordPress SEO themes include breadcrumbs by default, so you only need to enable them. Alternatively, you can add them with an SEO plugin.
The robots.txt file, a small text file in your website’s root directory, tells search engine crawlers which parts of your site to access. This is vital for SEO, as it prevents unimportant or duplicate pages from being indexed and guides crawlers to show users more relevant content.
By default, WordPress generates a basic robots.txt, but customizing it gives you more control. Like other SEO elements, you can create or edit the file manually or have your SEO plugin set it up. Once configured, submit it to Google Search Console to help the search engine find any crawling issues affecting site visibility.
Be careful not to block important areas, as it can hurt rankings. For example, if you accidentally block the wp-content folder, search engines won’t be able to crawl your images, CSS, or JavaScript files.
The llms.txt file is a new standard designed for AI crawlers, similar to how robots.txt works for traditional search engines. It gives LLMs clear instructions on how they can access and use your website’s content.
Implementing it increases the chances of your content appearing in AI-powered search results while protecting it from unwanted scraping.
You can generate an llms.txt file quickly using an online llms.txt generator like Wordlift. If you’re a Hostinger user, you can also set it up directly with the built-in Hostinger plugin. Head to Hostinger → Tools from your WordPress admin dashboard and toggle on the LLM Optimization option.
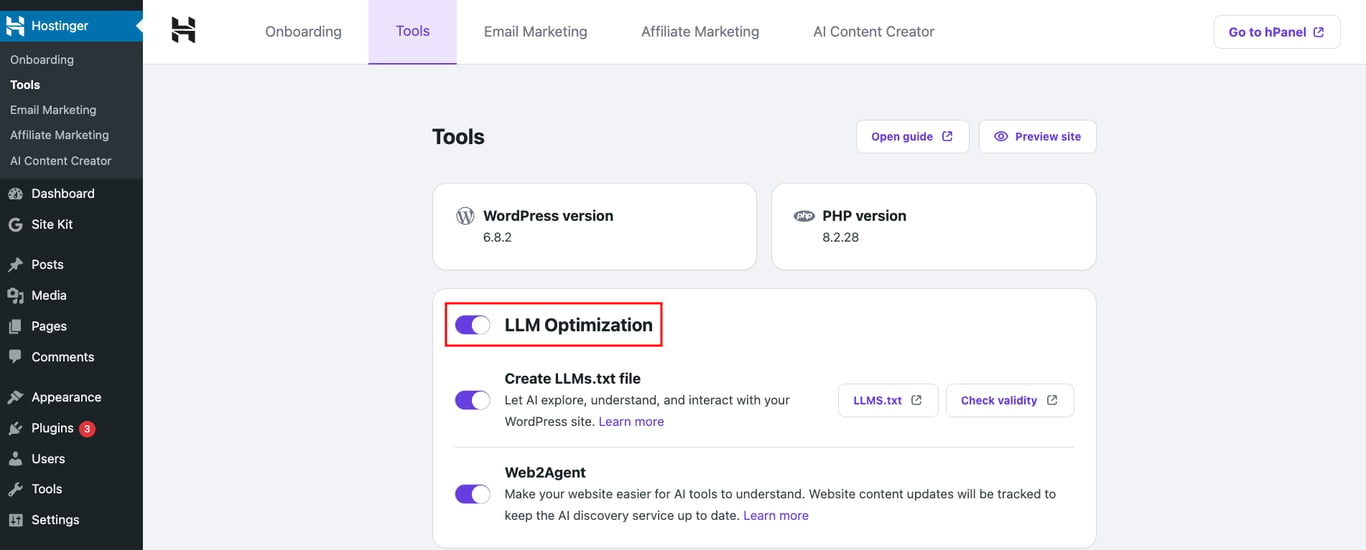
Schema markup, also called structured data, is code you add to a web page to help search engines better understand its content. With this extra context, they can generate rich snippets that appear above regular results.
Rich snippets can include star ratings, product details, carousels, images, or even step-by-step tutorials, boosting visibility and driving organic traffic.
The simplest way to add schema markup to your WordPress site is with a plugin like Schema, though you can also add it manually for custom use cases on individual posts or pages. Keep in mind that manual implementation is more technical and time-consuming.
After adding the schema, test it with Google’s Schema Markup Testing Tool. The Rich Results Test will confirm whether your markup is valid and show which elements search engines can recognize, helping you fix issues early.
To increase the chances of your pages appearing as rich results, make sure you follow Google’s structured data guidelines. This includes using the correct schema type for your content, keeping the markup error-free, and matching the data with what’s actually visible on the page.
However, note that rich snippets are not guaranteed even with valid schema.
With search engines constantly updating their algorithms and competitors regularly publishing new content, SEO is an ongoing process. Results don’t happen overnight, and it typically takes a few months to see significant improvements, depending on your niche and competition.
That’s why maintaining your WordPress SEO performance requires consistent effort to keep your site optimized, visible, and competitive.
You can achieve this by regularly tracking SEO metrics like traffic and rankings, and auditing your content to update outdated information. Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your site target the same keyword, causing them to compete against each other in search rankings. Avoid this by combining similar content, and use the noindex tag for low-value or duplicate pages to prevent them from appearing in search results.
Fixing broken links and setting up proper redirects to avoid 404 errors also improves user experience and visitor retention.
Tracking SEO metrics lets you see if your efforts are paying off. Here are the key metrics to keep an eye on:
Free tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console help you monitor these metrics and identify areas for improvement without spending money. The most common way to add Google Analytics to WordPress is by pasting the tracking code into your theme’s header.php file.
However, if you’re not comfortable with coding, a Google Analytics WordPress plugin lets you integrate it code-free.
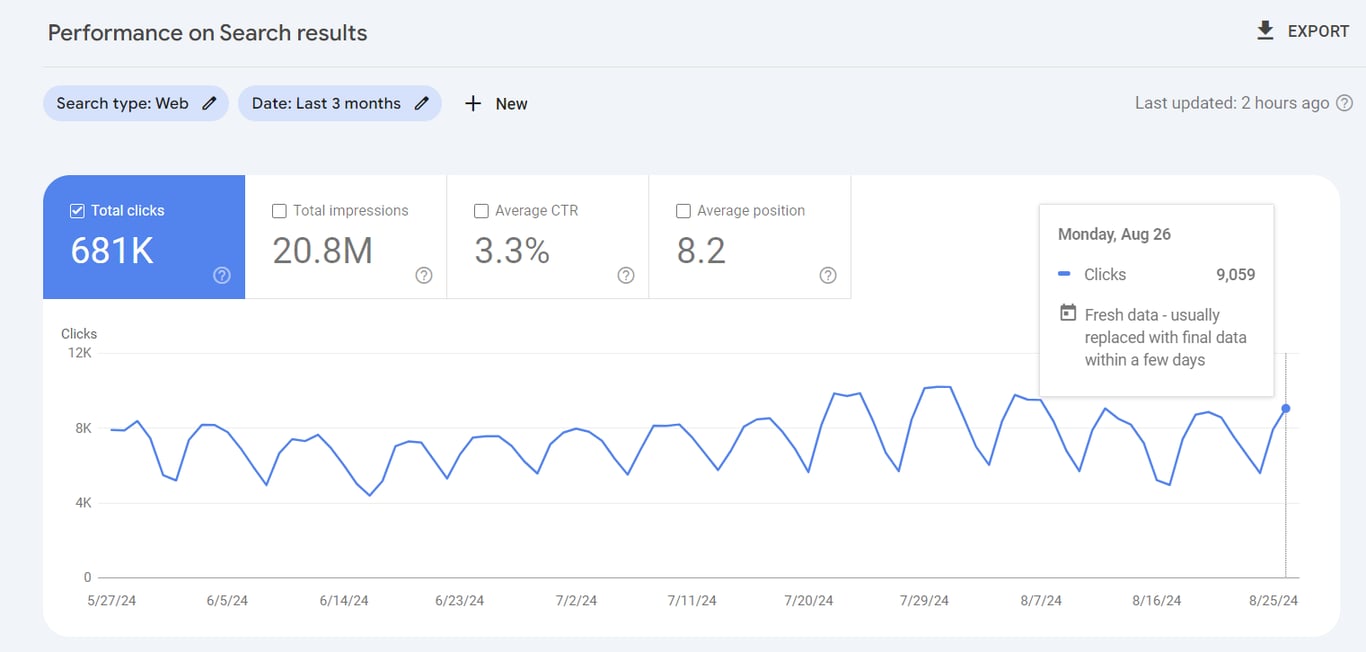
A content audit matters for SEO because fresh, high-quality pages signal to search engines that your site is relevant. As your content library grows, reviewing it periodically helps you see what’s working, what needs improvement, and what you should remove.
Start by gathering all your pages and posts manually or using a website crawler like Screaming Frog. Then, review SEO metrics to identify which content is driving results. For content that’s underperforming, you can either restructure it or prune it altogether.
Here’s how to get the most from your audit:
If you’re publishing new posts every week or working in a fast-changing niche like tech or marketing, I recommend auditing every 3-6 months. For slower-paced sites, once every 6-12 months should be enough. A page usually isn’t worth updating if it hasn’t brought in any traffic for months, covers a topic that’s no longer relevant, or is too thin to expand into something valuable. In those cases, it’s better to prune the page so it won’t send negative signals to search engines and negatively impact your site’s SEO.
Keyword cannibalization happens when two or more pages rank for the same keyword. It can damage your overall SEO effort since the traffic will be split across multiple pages. Even worse, the page with better conversion chances might rank lower, hurting your conversion rate in the process.
To fix overlapping content, adjust your SEO strategy so each page targets a unique angle or keyword. Start by clarifying the intent behind each page, then assign a new focus keyword to the one you want to repurpose ‒ ideally, a long-tail variation that highlights a different aspect of the topic. Update the content, headings, and metadata so the new keyword is naturally integrated.
Next, strengthen the page with internal links from related posts using anchor text that includes the new keyword. After publishing, track both the updated and original page in Google Search Console to monitor rankings, clicks, and impressions.
Before creating new content, check whether you already rank for the target keyword. A quick way to do this is to Google the keyword and see if any of your pages show up. If you’re already in the top 100 and the existing article has the same angle you’re planning, it’s better to update that piece instead of writing a new one.
Low-value content consists of pages and posts that search engines and visitors don’t consider valuable.
Examples of low-value content in WordPress include:
It’s best to discourage search engines from indexing this type of content to maintain your site’s authority.
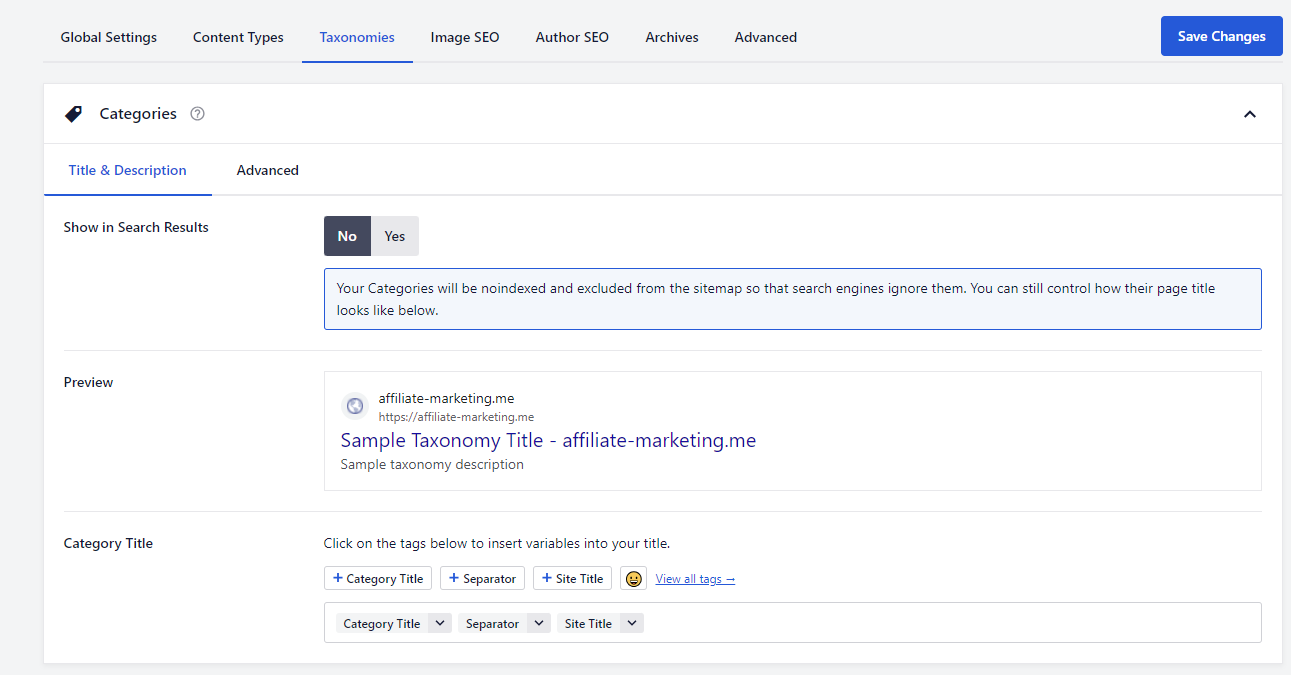
You can perform an SEO audit process using tools like Ahrefs to find low-value content on your site. Once you’ve found pages targeting low-priority keywords with poor rankings and traffic, add the noindex tag.
Plugins like AIOSEO make it easy to noindex category and tag pages in bulk. Head to All in One SEO → Search Appearance from the WordPress dashboard. Within the Taxonomies tab, select No next to Show in Search Results. Don’t forget to save your changes.
A broken link is any link on your site that no longer works, usually returning a 404 error. This can happen if the destination page was deleted, the URL was mistyped, or the linked site went offline. Broken links hurt SEO because they disrupt the user experience, waste crawler resources, and can signal to search engines that your site isn’t being maintained.
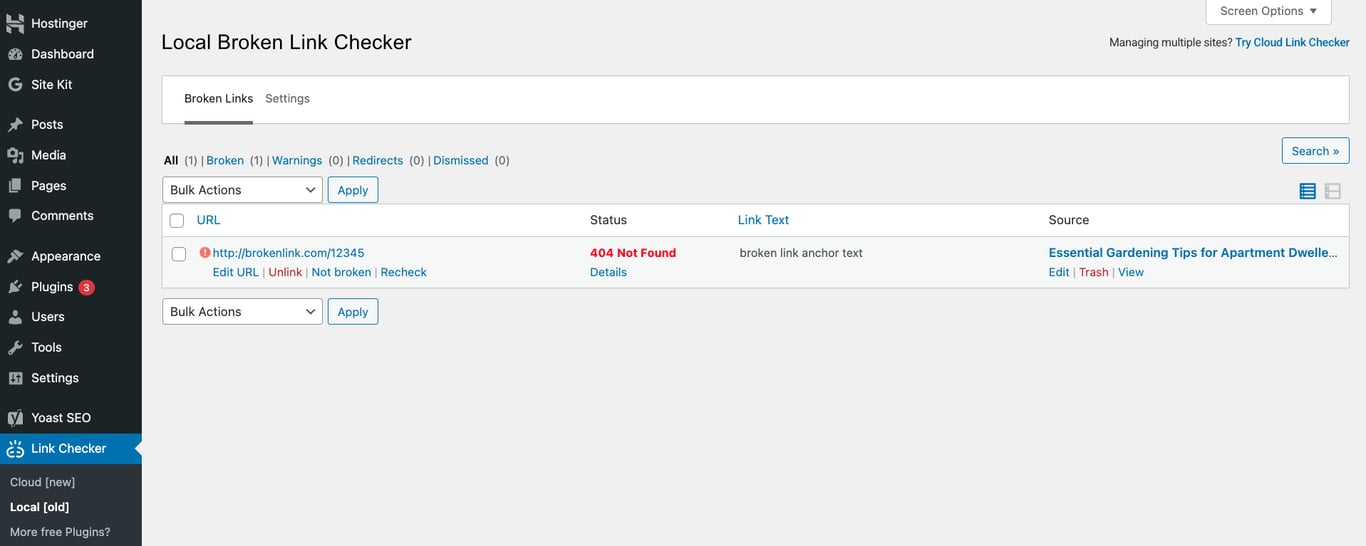
The easiest way to fix broken links is to use a free broken link checker plugin like Broken Link Checker. SEO tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Google Search Console also include broken link reports as part of their analysis. Alternatively, you can run a full site crawl with Screaming Frog to detect and export broken URLs.
With Broken Link Checker, go to Link Checker → Old from your WordPress dashboard to view all identified broken links and missing images. Hover over a broken link, then select Edit URL to replace it or Unlink to remove it. If you receive a false-positive, you can dismiss, recheck, or mark the link as not broken.
When a broken link points to a page that has a relevant replacement, one of the best fixes is to set up a redirection.
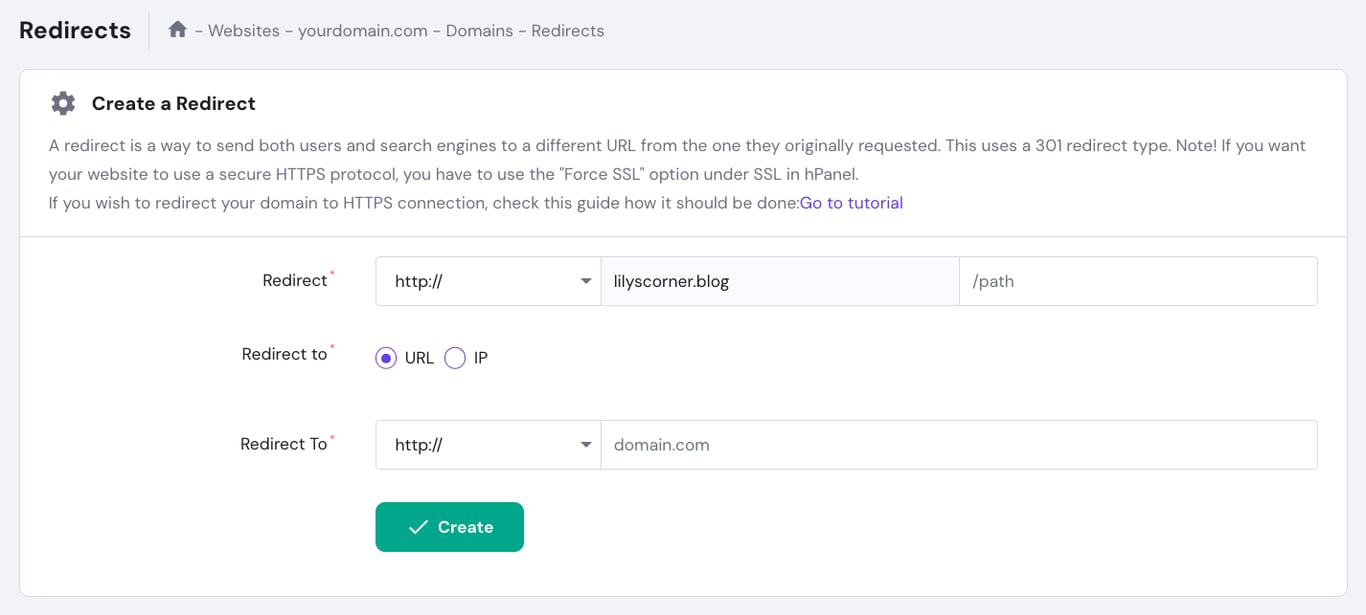
A 301 redirect sends users and search engines from an old or deleted URL to new content, preventing 404 errors. Beyond improving the user experience, this practice also helps preserve the link equity and ranking power of your old URLs.
You can create 301 redirects using a plugin like 301 Redirects. If you’re a Hostinger user, do this via Domains → Redirects in your hPanel dashboard. You’ll see all existing redirects listed at the bottom of the page.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) focuses on optimizing content for AI-driven search tools like chatbots and generative search engines. As more users turn to AI platforms for quick answers, summaries, and recommendations, GEO is becoming increasingly important.
Website owners are now exploring ways to make their content stand out not only on Google but also in AI-generated search results. However, this doesn’t mean GEO will replace SEO – both work together to enhance visibility across different platforms.
SEO remains the foundation, as many practices like keyword research, structured data, and quality content are essential for GEO strategies. Traditional search engines are still the go-to for tasks like fact-checking or staying updated, both of which are vital for driving organic traffic.
By combining SEO and GEO, you can maximize your reach. Strong WordPress SEO practices, such as structured content, schema markup, and fast-loading pages, also benefit GEO by making your site easier for AI systems to read and use.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this topic, our GEO tutorial is a great starting point.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
July 08 2018
I am a new blogger and running a blog on Health niche. I read so many articles on internet about how to rank a blog, how to increase search engine ranking, and many more but today I read your article. It is totally different and informative as compared to other blog articles. I am highly impressed by the way you describe each and every SEO tip in a descriptive manner. I liked your writing style too. According to me, you read so many articles before writing this and there is no doubt that you are an experienced blogger. These days, no one wants to share their knowledge with everyone but you are a different guy. You are truly an inspiration for other bloggers. I will surely apply all the SEO tips you shared in this article and will hope for the best. Thanks for sharing these SEO tips with us.
July 15 2018
Thank you for the feedback! I hope our WordPress SEO tips will increase your traffic 100x ;)
July 14 2018
I read the whole article and learned a lot of things. I didn't know about the 'Fetch as Google' thing. Thanks anyway!
July 15 2018
Awesome, I'm glad to hear you found the guide useful!
August 06 2018
Thanks for this amazing write-up! Your article alone gave me a lot of insights and information. Keep on sharing amazing stuffs like this one! Great post!
October 25 2019
I am a new blogger and running a blog on Government Jobs niche. I read so many articles on internet about how to rank a blog, how to increase search engine ranking, and many more but today I read your article. It is totally different and informative as compared to other blog articles. I am highly impressed by the way you describe each and every SEO tip in a descriptive manner. I liked your writing style tomuch
October 25 2019
This article is an excellent example of a SEO post itself. Despite that all of the techniques are well know to the average blogger, all of those are true. Even though this article is almost perfect, it don't appear on the first page of "Seo tips" and holds a seventh place on longer keyword - "wordpress seo tips". This pattern shows that even with the perfect article you can not always be first in the Google results. But don't be discouraged by that - maintain best practices for SEO, put in the work, exploit long tail keywords and results will come to.
February 27 2020
Thanks for sharing with us, really a very help full post for us.
April 10 2020
This is very best seo tips used this seo tips and got best results.
September 07 2020
Very nice blog for beginners it is to know about that its really very usefull to make this content of post i really thank you for sharing this post.
November 11 2020
You are very very welcome, Jeffery.
October 20 2020
Your blog is very nice… I got more information From your blog page… Thanks for sharing is this great information. Also, please help me with some SEO suggestions for my website: https://www.tech-act.com/
February 02 2021
Hi, Sampada! Feel free to check out out piece on best WordPress SEO plugins ;)
December 23 2020
Most informative content I have ever read on Internet. Thank you so much for spending my time pretty efficiency :)
February 09 2021
Happy you liked it!
December 24 2020
I really like your writing style, great information, thank you for posting. I completely admitted myself with this post. Once again I just would like to say that keep it up like this.
April 27 2021
Google’s AdWords Keyword Planner is helpful for prioritizing keywords and discovering new queries. The Keyword Planner provides monthly search volume trends and competition scores for paid advertisers.
June 06 2021
I'm new blogger i have seen a lot of videos on YouTube and read a lot of articles but the knowledge i get from this article is incredible. You're such a amazing guy Bro.
July 20 2021
Very nice tutorial. That's why I bought Hostingers hosting, as the support system is awesome.
July 26 2021
Heya Deepak! Happy to hear that the customer support is awesome :)
September 06 2021
Very useful information!! You have provided really valuable and in-depth knowledge, which has proven to be quite beneficial to me. Thank you for giving such useful information.
September 20 2021
Happy to hear you found it useful!
September 24 2021
Only this post proved that any body is not equal you and your level
December 20 2021
aweosme
December 28 2021
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing this info.
January 17 2022
Thanks
April 15 2022
I wanted to post you a tiny note so as to thank you so much the moment again just for the gorgeous ideas you've shown at this time. It is quite remarkably generous of you to supply unreservedly exactly what many people would've distributed for an e-book in making some dough for their own end, most importantly given that you might well have done it if you wanted. The tips in addition served to become a great way to realize that the rest have a similar dreams much like my very own to know the truth a great deal more in respect of this matter. I'm sure there are many more enjoyable moments up front for individuals who look over your blog.
April 19 2022
Happy to hear you're enjoying our tutorials; the team always appreciates any feedback ;)
April 15 2022
you are truly a excellent webmaster. The website loading velocity is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. Moreover, The contents are masterwork. you've done a great process in this subject!
April 22 2022
With havin so much content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright violation? My site has a lot of completely unique content I've either written myself or outsourced but it looks like a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my authorization. Do you know any solutions to help prevent content from being stolen? I'd definitely appreciate it.
April 25 2022
Hi Darren! As long as your content is unique, you can always file a complaint with DMCA. Once DMCA approves your complaint, they will contact the host of the website and demand to remove the copied content in question. Good luck!
March 25 2024
Thank you for highlighting the significance of Search Engine Optimization in such a clear and informative way! Your post not only tackles its importance but also offers actionable tips. Looking forward to implementing these strategies!
March 26 2024
You're welcome! Wishing you success in implementing these strategies ?
November 19 2024
Before I decide for a managed wordpress hosting (for one year), may I ask, have I to do all these steps and following by myself or Hostinger does everything, and not to send me written steps?????
November 20 2024
Hey there! When it comes to SEO optimization, it's mainly up to you to implement the steps, but we make it easier with tools like AI content generation, WordPress acceleration with LiteSpeed, and advanced WooCommerce optimization. So, you won’t be left doing everything from scratch—these features will help you boost your site’s SEO :)