Dec 26, 2025
Noviantika G. & Aris S.
8min Read

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution based on Debian designed to be user-friendly, secure, and versatile for different use cases. It was introduced in 2004 by the British company Canonical with the purpose of creating an easy-to-use alternative to other Linux distributions, which at the time required more technical expertise to use.
Here’s what you need to know about Ubuntu:
The Ubuntu operating system is a free, open-source Linux distribution that serves as a powerful platform for various use cases, including desktop computing, cloud environments, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It’s developed from Debian with the goal of making Linux accessible to average users.
Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu, plays a central role in its development by releasing new versions every six months and providing commercial support. However, the OS also relies heavily on the global open-source community, which contributes code, tests for bugs, and provides free technical support.
While it started as a desktop OS, Ubuntu is now widely used on other platforms like web servers and cloud infrastructure. Many users choose it for its advantages over other OSes, which we will explore next.
Ubuntu is popular because it offers various benefits across security, performance, and usability, making it the preferred choice for both technical and non-technical users.
Ubuntu is free and open-source, meaning its source code is available for anyone to inspect, modify, and enhance.
Users can create multiple copies, customize the operating system code, and distribute their Ubuntu versions without paying license fees. This makes Ubuntu stand out from other non-Linux operating systems, like Windows or macOS, which require purchasing licenses.
The desktop version of Ubuntu is renowned for its graphical user interface, called GNOME. This desktop environment features a clean layout, with minimal icons and easy-to-find menu bars.
The applications are located in a dedicated section similar to macOS’s dock or Windows’s Start Menu, allowing new users coming from these operating systems to adapt easily.
Users can also modify various aspects of the GNOME desktop environment to better fit their preferences, including changing the system font and adding widgets.
Ubuntu offers a secure architecture out of the box by offering various security features, including:
Additionally, because Ubuntu is open-source, its code undergoes constant review by a global community. Thanks to this, security vulnerabilities are identified and patched much faster than in closed-source operating systems.
The combination of these aspects makes Ubuntu suitable for sensitive environments where data integrity is crucial.
Users running Ubuntu benefit from this distro’s vast software ecosystem and extensive compatibility with popular applications. In addition to the graphical Ubuntu Software Center, it offers the Advanced Package Tool (APT) command-line utility, which enables you to easily manage software packages via terminal.

For example, you can check, download, install, update, and remove software packages by running a single line of command.
Additionally, the Snapcraft feature enables users to install snaps, which are universal packages that work across various Linux distributions.
As one of the most popular distributions, Ubuntu is compatible with widely-used productivity and development tools, including Firefox, LibreOffice, VS Code, and Slack.
While not a minimal distribution, many users prefer Ubuntu for its lightweight nature and excellent performance compared to other well-known operating systems, such as Windows and macOS. That’s because this distro runs with fewer background services by default and manages hardware more efficiently.
The user interface of the Ubuntu desktop requires 4 GB of RAM for physical installations (2 GB for virtualized installations) provided there are no additional customizations or add-ons.
Meanwhile, modern versions of Windows and macOS officially require 4 GB and 8 GB respectively as minimums, though 16 GB is increasingly recommended for optimal performance.
For older hardware, Ubuntu offers even lighter variants like Lubuntu and Xubuntu, which consume significantly fewer system resources.
Since Ubuntu is free for both personal and commercial use, organizations can deploy it across several machines while maintaining cost efficiency. This reduces the overall IT budget, enabling businesses to allocate more resources to hardware or other critical infrastructure.
Ubuntu’s Long Term Support (LTS) provides five years of standard security updates at no cost, with optional extended support available through Ubuntu Pro (10 years total, free for personal use) and Legacy add-on (up to 15 years for enterprise customers)
Canonical’s approach to data privacy differs from many proprietary operating systems. Ubuntu doesn’t collect user data except when necessary for legal reasons or service provision.
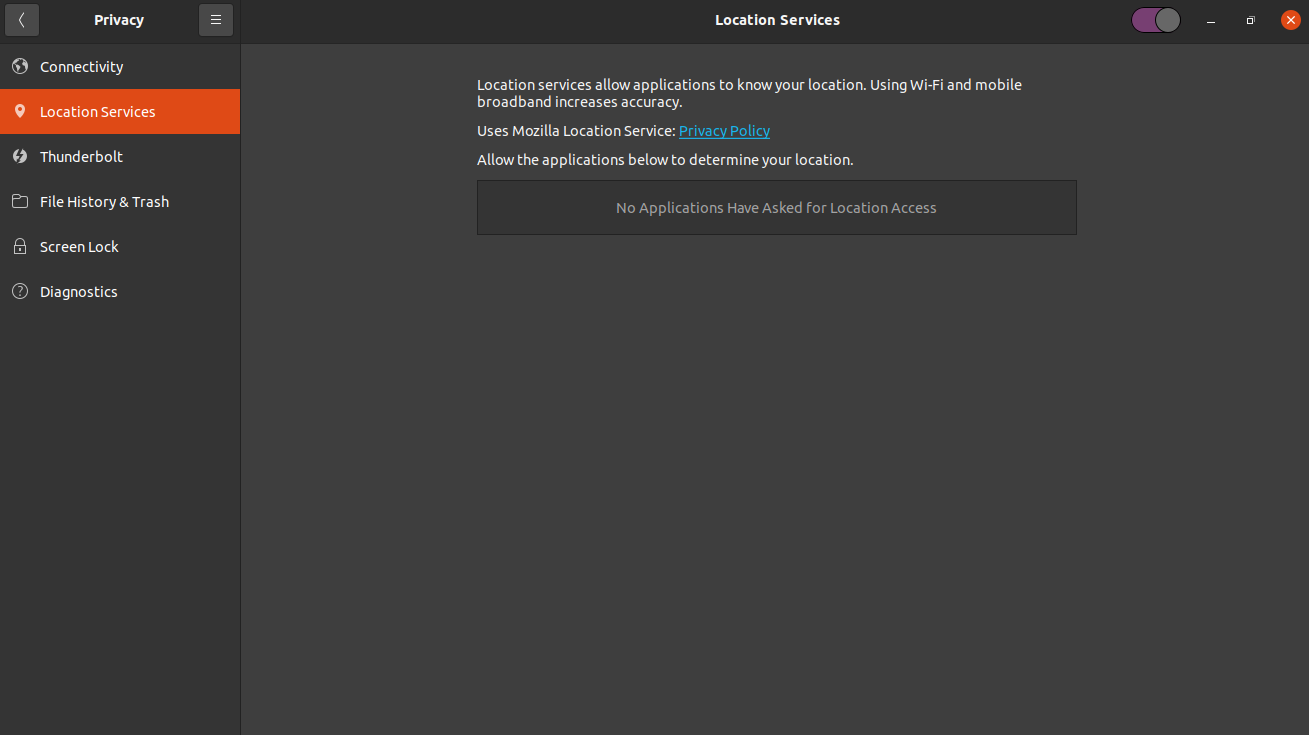
Moreover, users have granular control over their privacy. For instance, you can easily disable location services or opt out of usage data collection by navigating to the Privacy menu and blocking Ubuntu from collecting crash data from the Problem Reporting page in Settings.
Ubuntu is popular among a wide range of users, from software engineers building complex applications to students learning their first programming language.
Ubuntu is popular among developers for its native support of command-line tools and programming languages. It enables them to set up virtually any web stacks to deploy their project, including LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) and MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js).
Essential tools like Git, Docker, and VS Code also run natively on Ubuntu. Since developers can mirror their production server on the development environment, it helps eliminate incompatibility issues during deployment.
For enterprises, Ubuntu serves as the operating system for production servers, private clouds, and large-scale infrastructure. Its reliability and long-term support make it a trusted choice for companies running workloads where integrity is critical.
Since provisioning Ubuntu is easy, many enterprises use it on systems like public clouds and virtual private servers (VPSs) that are often scaled up and down.
This distro’s performance and extensive compatibility also make it a popular OS for deploying CI/CD pipelines and secure container deployments with tools like Kubernetes.

Many users choose Ubuntu for their personal machines to browse the internet, use email and various other applications, and work on documents. It is an excellent choice for users who want a secure, fast, and affordable operating system.
The pre-installed software suite covers most daily needs, including a web browser, media player, and office suite, making Ubuntu a ready-to-use solution out of the box.
Moreover, its intuitive user interface allows non-tech-savvy users to adapt easily, unlike several other Linux distributions, such as Arch.
Many schools and universities utilize Ubuntu to offer students a free and open learning environment. It’s widely used in the computer science field to teach operating system concepts, programming, and command-line basics.
Since it runs well on low-cost hardware like the Raspberry Pi, Ubuntu is also a staple in robotics and electronics labs.
Due to its lightweight nature, Ubuntu is a popular option for IoT and embedded devices that typically use less powerful hardware. While vanilla Ubuntu can be used for such systems, this distro has a variant specifically designed for this purpose.
Called Ubuntu Core, this stripped-down version of the OS is highly confined and secure, making it ideal for smart appliances, digital signage, industrial robots, and home automation gateways.
The focus of Ubuntu Core is on reliability and security updates, which are critical for devices that are often deployed in the field and difficult to access physically.
Given its extensive ecosystem and software library, Ubuntu has found a niche in the creative industries. Artists and creators use it to run powerful open-source tools like Blender for 3D modeling, Kdenlive for video editing, and GIMP for graphic design.
Since Ubuntu is lightweight, it allows independent creators and studios to build cost-effective workstations. Moreover, creators can avoid paying for a software license because most design and creative tools in Linux are open-source.
As a flexible and customizable operating system, Ubuntu is suitable for a wide range of tasks, from basic desktop usage to advanced artificial intelligence models.
Compared to other Linux distributions, Ubuntu is the most widely used desktop operating system for general productivity. This distribution offers one of the most beginner-friendly experiences, while other distros typically require more technical expertise.
Ubuntu’s graphical user interface (GUI) feels intuitive, allowing users to easily perform day-to-day tasks like web browsing, streaming media, photo editing, and document creation.
Moreover, its performance and extensive open-source software library make it an excellent choice for general users, regardless of their tasks.
Ubuntu’s compatibility with a wide range of development tools and web stacks makes it the standard for coding environments. Developers use it to write code in various languages, simulate runtime using different web stacks, and debug applications using tools like GNU Debugger (GDB).
Moreover, developers enjoy Ubuntu’s robust package management tool, apt. It allows developers to install libraries and dependencies with simple commands, streamlining the setup of complex development workflows.
Ubuntu is suitable for hosting environments, including cloud infrastructures and VPS. Since this operating system is resource-efficient, it minimizes performance overhead, ensuring the deployed application runs optimally.
Moreover, Ubuntu’s flexibility enables system administrators to fine-tune their hosting environment to their needs, such as adjusting the firewall rules and configuring system services.
As mentioned earlier, provisioning this distribution is easy and cost-efficient, making it an excellent choice for scalable hosting.
Ubuntu has become an increasingly popular option for AI and machine learning workflows. It serves as the reference platform for both emerging and established AI frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Research labs and AI startups prefer Ubuntu because it offers easy access to the latest GPU drivers and libraries required for training deep learning models, while remaining resource-efficient.
Ubuntu is an excellent alternative to Windows for gamers, due to significant advancements in Linux gaming compatibility. Platforms like Steam have integrated Proton, a compatibility layer that allows thousands of Windows-exclusive games to run smoothly on Ubuntu.
With easy access to NVIDIA and AMD graphics card drivers, Ubuntu offers a viable and high-performance gaming experience. For several non-Linux-native games, you can still use the Wine compatibility layer to run them on Ubuntu.
Ubuntu is a variant of Linux, but it is important to distinguish between the two. Linux is the kernel, the core component that facilitates the communication between the computer’s hardware and software.
Ubuntu is a distribution built on top of the Linux kernel. It adds the graphical interface, package management tools, and specific software configurations that make the computer usable for humans.
Here’s a comparison of Ubuntu vs Linux in several aspects:
| Aspect | Ubuntu | Linux |
| Interface | The server version has a command-line interface, while the desktop counterpart uses GNOME. | Doesn’t have a user-facing interface. |
| Release cycle | Maintained by Canonical, new releases are rolled out every six months (non-LTS) and two years (LTS). | Maintained by the Linux community, with new releases every few weeks, typically every 2-3 months. |
| Support | Community and official from Canonical. | Community only. |
| Package management | Uses the APT package manager. | Doesn’t have a package manager, as it depends on the distro developer. |
| Target audience | End-users, such as general developers or students. | Distro developers or companies. |
After understanding Ubuntu, the next step is to try it on your machine. Depending on your needs, choose between the desktop version with a graphical user interface or the command-line-based server variant.
After deciding, download the Ubuntu operating system image from its official website. Then, boot the ISO file into your computer or virtual machine, and complete the installation process. Check our guide on how to install Ubuntu to learn more about the steps in more detail.
If you already use Hostinger VPS hosting, you don’t need to download the Ubuntu image and manually install it. Instead, simply head to hPanel and select the corresponding VPS template, which will automatically set up the distro on your server.
For our Ubuntu VPS hosting users, simply complete the onboarding process, and our system will automatically set up the operating system.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
November 23 2023
Thinking of switching to Linux
November 24 2023
Hi there! It's always a good idea to keep your options open and explore different possibilities. Linux is a great alternative, and it's becoming increasingly popular. It's a very versatile and powerful operating system, and it can be customized to fit your specific needs ?
August 03 2025
What is the Ubuntu
August 14 2025
Ubuntu is a free, open-source Linux OS for computers and virtual private servers :)
December 04 2025
Much has been said about Ubuntu but nothing was mentioned as to how to make money with Ubuntu.
December 10 2025
Ubuntu itself doesn’t make money, but you can use it as a tool to earn. For instance, you could set up web servers, provide consulting services, or build and sell software. There’s plenty of room to turn your skills into opportunities ;)