Apr 28, 2025
Ariffud M.
6min Read
In the internet landscape, the role of web servers has become crucial. NGINX, an open-source web server software, stands out for its versatility and advanced capabilities. Besides serving web pages, NGINX is a multifaceted tool to optimize website performance and security.
Therefore, understanding NGINX is essential for anyone involved in web technology, whether for personal projects or large-scale enterprise applications.
This article will explain what NGINX is, explore its functions, and guide you on how to get started with the web server software. Let’s begin.
Download glossary for web beginners
NGINX is an open-source web server software known for its high performance and low resource usage. It excels in serving static content and is widely used as a load balancer and as a reverse proxy. NGINX is compatible with various operating systems and transcends the traditional role of a mere web server.
There are two versions of NGINX: NGINX Open Source and NGINX Plus.
The open-source version adeptly manages network traffic, ensuring efficient resource utilization and making it a top choice for modern web applications. NGINX Plus, the commercial version, offers additional features such as advanced load balancing, content cache, and health checks.
Having both an open-source and a premium solution underscores NGINX’s commitment to adaptability and innovation in server technology.
NGINX server operates on a scalable and asynchronous event-driven architecture.
At its core, NGINX employs a master process and multiple worker processes. The master process reads and evaluates configuration files and manages worker processes. Meanwhile, the worker processes handle the actual processing of requests.
Unlike servers that create a new process for each request, NGINX’s worker processes can take thousands of concurrent requests. This reduces overhead and increases NGINX’s capacity to manage heavy network traffic.
NGINX can also manage incoming and outgoing traffic as a reverse proxy server and API gateway, acting as an intermediary for client requests seeking resources from other servers. In this role, NGINX can perform functions like load balancing, SSL/TLS termination, and caching.
NGINX also functions as a proxy server, directing client requests to the appropriate back-end server while managing responses. This includes modifying the HTTP header of requests and responses to enhance security or performance.
Users can also add additional modules to the NGINX architecture to expand its capabilities. Its modularity and efficient handling of instances make NGINX a powerful tool for various web applications, from simple websites to complex microservices architectures.
Let’s explore how NGINX can be applied across various web environments and scenarios.
Optimized handling of static files helps provide a satisfactory user experience. One of NGINX’s primary strengths is efficient static content delivery, which includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript files, and images.
The NGINX server achieves this efficiency through effective request routing. When a user requests a web page, NGINX quickly locates and serves the necessary static content. It can also handle multiple requests concurrently, ensuring maximum performance even under heavy load.
Additionally, features like auto indexing contribute significantly to this efficiency. Auto indexing in NGINX allows for faster retrieval and display of static content, accelerating the response time. This capability is especially useful for websites with large static files.
NGINX stands out as an efficient load balancer, adept at distributing incoming web traffic across multiple servers. By evenly distributing requests, NGINX load balancing ensures no single server becomes a bottleneck, particularly during peak times or high-demand situations.
The benefits of using NGINX as a load balancer are substantial.
Firstly, it improves website availability. By sharing the load among multiple servers, NGINX minimizes the risk of downtime caused by overloading a single server. If one server experiences issues, the others can continue to operate, thereby maintaining the website’s uptime.
Secondly, NGINX’s load-balancing capabilities reduce each server’s load. This enhances the performance of the web servers and extends their lifespan by preventing overuse. Therefore, NGINX helps maintain a balanced and healthy server environment, which is crucial for operating large-scale web apps.
A reverse proxy service is critical in modern web architectures, especially when employing NGINX for microservices. The NGINX reverse proxy acts as a mediator that handles client requests before they reach the back-end servers.
Implementing NGINX as a reverse proxy protects back-end servers from direct exposure to the internet. It can intercept and inspect incoming traffic, reducing the attack surface and mitigating potential vulnerabilities. Therefore, only the necessary traffic reaches each service.
This NGINX security arrangement mainly benefits microservices architectures where multiple services operate simultaneously.
NGINX is often compared with Apache, another widely used web server software. Understanding their fundamental differences is essential to make an informed choice for your needs.
Apache, known for its flexibility and power, has been a popular web server software for many years. It operates on a process-based model, creating a new process for each request. This traditional method can be resource-intensive, especially under heavy loads.
In contrast, NGINX uses a more resource-efficient method to maintain high performance. It employs an event-driven model to handle multiple requests within a single thread. This minimizes resource usage, making NGINX particularly efficient under high-traffic conditions.
When deciding between NGINX and Apache, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements of your web applications.
Apache is well-suited for complex configurations and dynamic content processing, making it a robust choice for various applications.
Meanwhile, NGINX excels in serving static content, load balancing, and handling high concurrent requests. This makes NGINX ideal for high-traffic websites and applications prioritizing performance and efficiency.
To effectively use NGINX, you must first learn how to set up and configure it. Although compatible with various operating systems, NGINX is prevalent on Linux due to its performance and security features.
Hostinger’s VPS plans provide an optimized Linux environment, perfect for running NGINX. These plans ensure your NGINX setup runs smoothly and efficiently, offering the necessary resources and support.
As one of the best VPS hosting providers in the market, Hostinger gives you the flexibility to customize your server. This allows you to configure NGINX, install necessary modules, and adjust settings to meet your requirements.
After preparing your virtual private server, install the NGINX web server. The installation process might vary slightly based on your Linux distribution, but it generally involves downloading the NGINX package and executing a few simple Linux commands.
Once the NGINX installation is done, the next step is configuring NGINX to suit your needs. This might include setting up NGINX for web hosting, configuring it to handle PHP applications, or implementing NGINX SSL/TLS for secure HTTPS connections.
NGINX configuration can be complex due to many options to optimize performance and security. Kodee, Hostinger’s VPS AI assistant, is an invaluable tool in simplifying this process.

Available for all our VPS plans, this AI-powered tool provides precise guidance to configure and manage your web apps with NGINX. For example, you can ask, “How can I increase NGINX performance?”
Kodee will respond with comprehensive answers, including step-by-step guides, commands, or scripts. You can ask further questions to clarify details or explore additional configuration options. With this tool, you can tailor your setup to perfectly meet your needs.
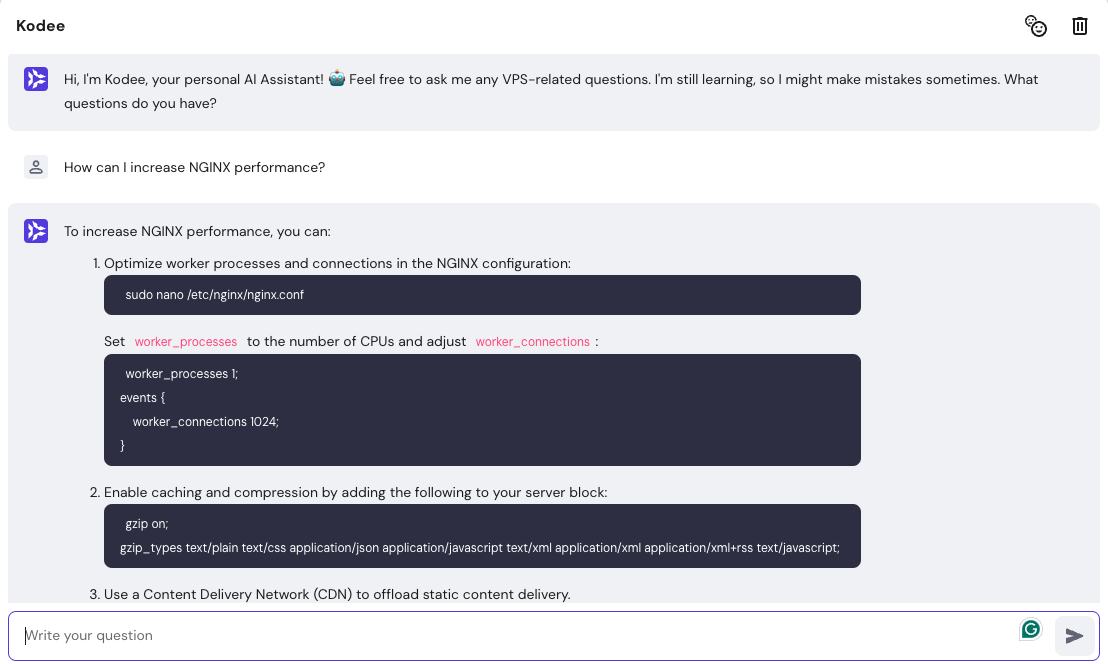
Learn more about Kodee and how it can assist with server management by reading best AI prompts for efficient VPS management.
NGINX is an open-source web server software that has gained widespread popularity for its versatility and performance. Throughout this article, we have explored what NGINX is and how it works.
We’ve also highlighted the numerous NGINX benefits for web infrastructure. From efficiently serving static content to acting as a potent load balancer and a secure reverse proxy for microservices, NGINX offers a blend of speed, security, and scalability. This makes it an invaluable tool for both developers and system administrators.
NGINX stands out as a reliable and robust solution suitable for various applications, from small personal blogs to complex enterprise-level systems. This web server software transforms how you manage web applications and services, offering maximum performance and flexibility.
How to Create a Redirect Using NGINX
How to Install WordPress Using NGINX on Ubuntu
This section will answer the most common questions on what is NGINX.
NGINX is renowned as a web server software and a reverse proxy for web application servers. NGINX features include efficient handling of static and index files, load balancing, SSL/TLS offloading, caching, and compression. These features and its scalability make NGINX ideal for modern web infrastructures.
NGINX is well-suited for beginners thanks to its simple setup and extensive documentation. Additionally, the NGINX community support offers valuable resources, forums, and tutorials, making the learning curve manageable for users new to web server management.
NGINX’s popularity stems from its proficient error and data handling, as well as robust security features. NGINX CMS integration and adaptability to Kubernetes and other deployment tools contribute to seamless web application deployment and management. Furthermore, the NGINX caching mechanism enhances website speed and reliability.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
November 19 2023
I keep getting a pop up when I try to open texts that say 404 Bad Request Nginx Why?
November 24 2023
Hello, there! The 404 error typically indicates that the server couldn’t find the requested resource, like a missing web page or a broken link. So, I recommend checking out the insightful and comprehensive tutorial about how to fix error 404. Hope it helps ?