Sep 03, 2025
Hasna A. & Matleena S.
6min Read
The “401 Unauthorized” error is an HTTP status code that occurs when a web server denies access to a specific web page or resource you are trying to reach. This happens because the request lacks valid authentication credentials, such as a username and password, or the provided credentials are incorrect.
This error doesn’t affect your ability to access other parts of the website that don’t require authentication. Essentially, the server recognizes your request but will not fulfill it until you can prove you have permission to access the content.
There are seven quick methods to fix the “401 Unauthorized” error:
Keep reading for a walkthrough of all the methods to solve the 401 error, learn the causes, and recognize error variations.
The 401 page may appear when you’re trying to gain access to restricted resources, such as a password-protected page, with invalid authentication credentials. As a result, you’re unable to open the page.
First thing to do is double-check whether you’re logged in with a valid user ID and password. If you’re sure that you have entered valid authentication credentials, try changing the password.
If you’re having trouble accessing a password-protected WordPress site, make sure you know how to change your WordPress admin password.
In case you’re accessing a resource via an application programming interface (API), ensure that your API keys or tokens are correct and have the necessary permissions. Incorrect or missing API credentials can also trigger a 401 error.
A wrong URL is a common cause of 401 HTTP status codes. So, make sure that the web address is typed correctly in your browser’s address bar, especially if it includes special characters or numbers.
Typos in hyperlinks from other sites can also lead to this error. If unsure, navigate from the website’s homepage or use a search engine to find the correct web pages.
A corrupted or outdated browser cache and cookies may lead to a server authentication failure. It’s also possible that the current cache and cookies are outdated and in need of manual refreshing.
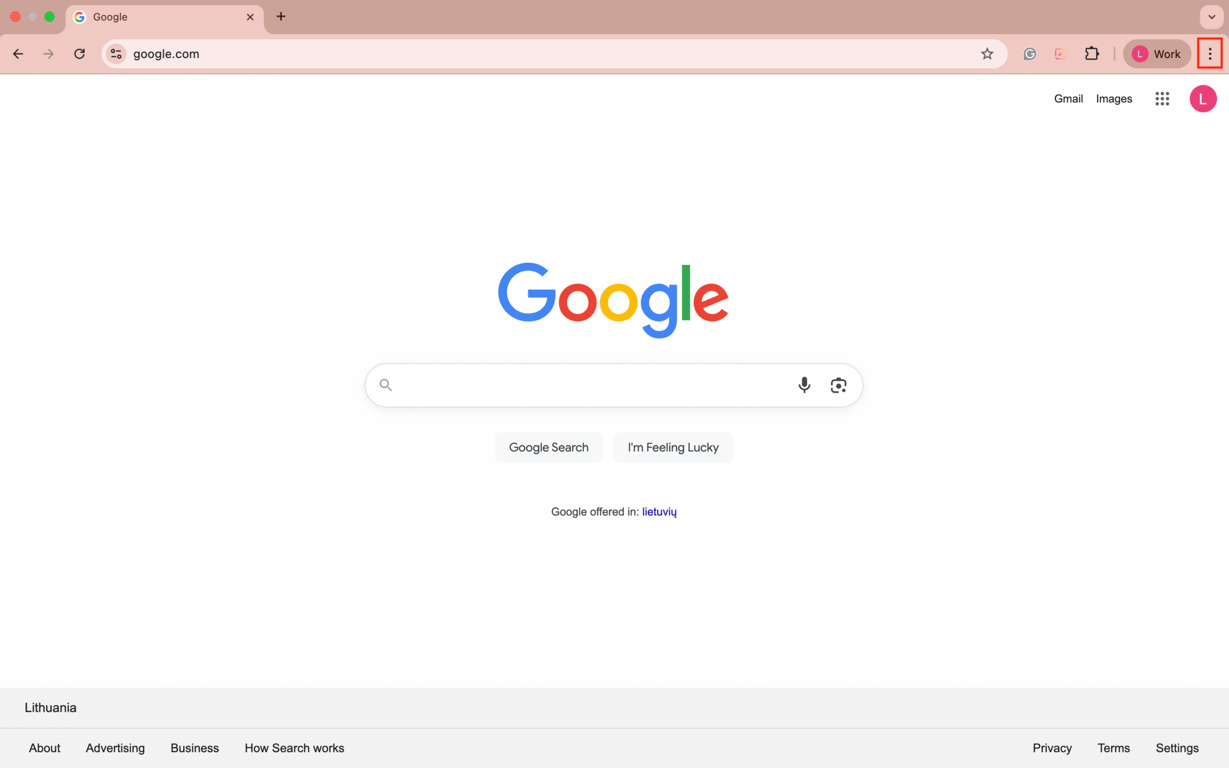
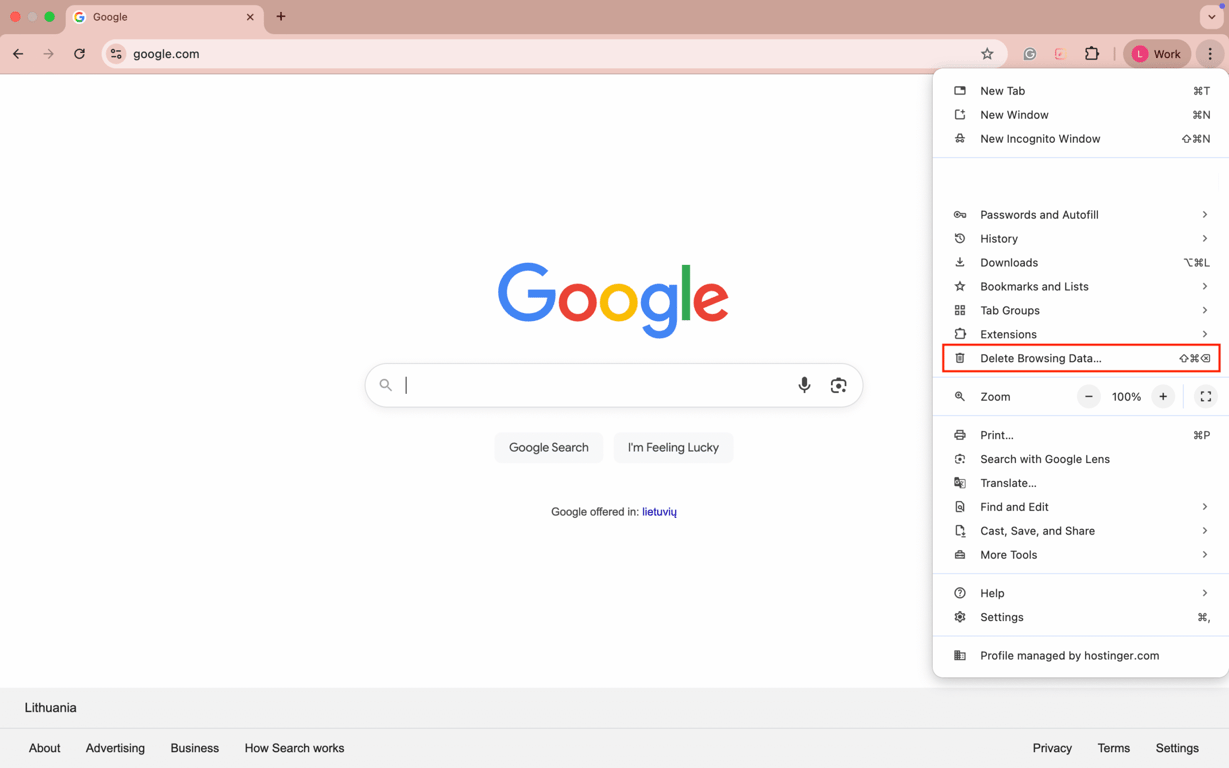
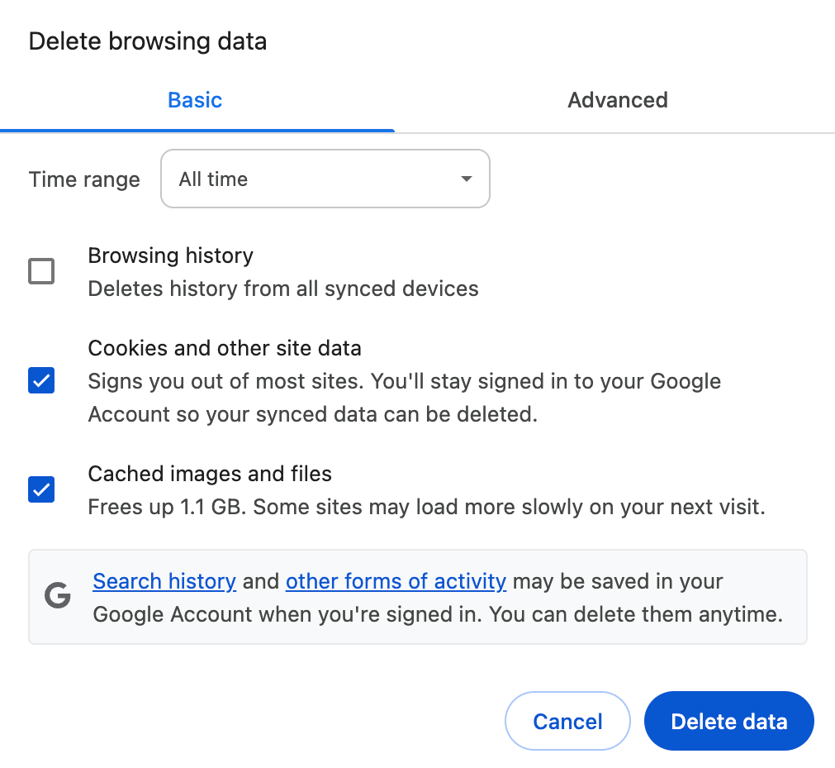
To delete the cached data and browser cookies, go to your browser’s settings and find the option to clear them. If you use Google Chrome, follow these steps:
For a detailed guide on how to do this on other browsers, check out our tutorial on how to clear browser cache.
The data in the domain name system (DNS) cache lets your device match URLs to their IP addresses faster for shorter loading times. However, unlike the browser’s cache and cookies, the DNS cache operates on the system level.
Although rare, a DNS error may result in the 401 HTTP status code. The cache may be outdated and contain incorrect URL and IP address details.
Flushing your DNS will clear the existing DNS records of your device. Thsi will force it to make a completely new request and re-authenticate the URLs.
Follow our guide on how to flush the DNS cache if you’re not sure how to do it.
If you’re a website owner trying to solve the 401 error, it’s worth temporarily disabling password protection for the problematic section of your website.
If you have enabled password protection using .htaccess and .htpasswd files, follow these steps to disable it:
Find the .htaccess file that you created when you first enabled password protection. Its content should look similar to this:
AuthType Basic AuthName "Your authorization required message." AuthUserFile /path/to/.htpasswd require valid-user
For more information, follow this guide to learn how to locate and create a WordPress .htaccess file.
If you host a website on Hostinger, you can manage password-protected website directories on hPanel.
If you get the “401 Unauthorized” error as a website’s administrator, you can try to identify its cause by disabling the plugins, modules, and themes you have installed on your website.
For example, if you have a WordPress site and can access its admin dashboard, consider changing your theme to the default and disabling all your plugins.
To change back to the default theme, go to Appearance → Themes and Activate the default theme.
To disable all WordPress plugins at the same time, go to Plugins → Installed Plugins. Bulk-select all the plugins, choose Deactivate from the drop-down menu, and click Apply.
The process to change your design template and disable the modules should be similar to any other CMS dashboard.
If you don’t have access to your WordPress admin dashboard, you can disable your WordPress plugins by opening the File Manager on your hosting account and renaming the Plugins folder. Hostinger users can manage their plugins straight from hPanel.
Similarly, you can change your WordPress theme without opening the admin dashboard by making changes to files through File Manager and phpMyAdmin.
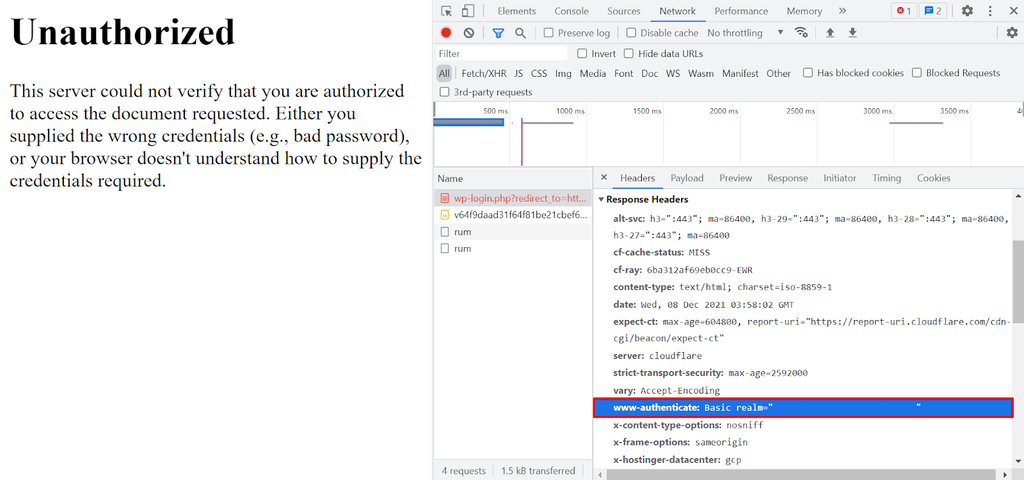
A server generating a “401 Unauthorized” response has to send a WWW-Authenticate header field containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource, according to the IETF.
This response header determines the authentication method the web browser should follow to access a specific page. Knowing what response the header sends and which authentication method is used will help determine the problem.
To check a WWW-Authenticate header for the cause of the 401 error, follow these steps:
A 401 error occurs when a page requires valid authentication credentials but they’re missing, invalid, or expired. Some common triggers include:
When encountering a 401 response, instead of reaching the intended web page, your browser will display an error message. These messages serve as indicators of the specific type of 401 error you’re experiencing.
Commonly seen messages include:
Each variation of the 401 error provides insights into why the authentication process failed, helping you diagnose and resolve access issues.
Below is a detailed list of various 401 error codes, along with their specific meanings:
The 401 error is just one example of the many errors in the 400 range you might encounter. Another common one that often causes confusion is the 403 Forbidden error.
While a 401 error means unauthorized access due to invalid or missing credentials, a 403 error indicates you’re forbidden from accessing the page, even with valid credentials, often due to permissions set by the website administrator. The difference lies in the root cause:
401 and 403 are just two of the many errors you might encounter online. If you’d like to learn what different codes stand for and the steps to fix them, read our complete guide to HTTP status codes.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.