Sep 10, 2025
Jordana A.
7min Read
Ecommerce is the process of buying and selling goods or services over the internet. Instead of a physical store, businesses and individuals reach customers through websites, apps, or online marketplaces. It’s a straightforward process: a customer visits a site, finds something they like, adds it to their cart, and checks out using a secure payment system.
There are various ways to sell online, such as creating your own store with tools like WooCommerce or Magento or joining established marketplaces like Amazon or Mercado Libre. These platforms help you list products, track inventory, accept payments, and manage orders easily.
One of the biggest advantages of ecommerce is flexibility. You can run your store 24/7, reach customers around the world, and avoid many costs that come with physical shops. Plus, thanks to user-friendly website builders, even beginners with no coding experience can launch a professional-looking online store.
To start an online store, a few key pieces need to work together: an online storefront, secure payment processing, and a reliable order fulfillment system. These parts create a smooth experience for both customers and businesses, from discovering a product to its delivery.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how an ecommerce transaction usually works:
Ecommerce businesses can take many forms depending on who’s buying and who’s selling. Consequently, there are different types of ecommerce business models, each with its own unique characteristics.
Here are the most common types, starting with the one you’re likely most familiar with:
Dropshipping, wholesaling, and white labeling are types of ecommerce by revenue model. The difference is in how products are sourced and delivered.
Ecommerce platforms let you list products, accept payments, and manage your day-to-day operations. The choice of platform impacts your site’s appearance, functionality, and ease of maintenance, so it’s worth comparing your options before making a decision.
Let’s explore the three most popular ecommerce platforms:
A website can be a powerful ecommerce platform with the right tools to sell products or services online. At a minimum, it should let you display products with descriptions and prices, add items to a shopping cart, and process payments securely.
There should also be an order management system to track sales, handle shipping, and manage returns. A secure payment gateway protects customer data during transactions, while customer accounts make shopping easier by saving details and order history for future visits.
Different ecommerce platforms offer these features and more to better suit specific niches or audiences.
Hostinger’s AI website builder, for example, is perfect for beginners and professionals who want to launch an online store quickly. The Business plan includes built-in AI tools, support for 100+ payment methods, and five email addresses per site for just $2.99/month.
Manic Cherry uses this ecommerce platform to sell premium skateboard art. With Hostinger Website Builder, they’ve set up an efficient online store and now take orders worldwide.
Key benefits of using a website for ecommerce:
Hostinger AI Website Builder includes a 14-day free trial and a 30-day money-back guarantee.
An online marketplace hosts products from multiple third-party sellers in one place. Unlike a single-brand website that only sells its own products, this ecommerce platform brings together a variety of goods and services from different vendors. It serves as a digital intermediary, connecting buyers and sellers while processing transactions for a fee or commission.
Amazon and Mercado Libre are two of the most popular online marketplaces, offering a mix of products from various sellers as well as their own. These platforms handle the user interface, payment processing, and customer experience, while sellers manage their own inventory and shipping.

The benefits of using an online marketplace as an ecommerce platform include:
Social media platforms have evolved from simple communication tools into powerful ecommerce platforms.
Rising social commerce trends allow businesses to sell products directly within the social media environment. Instead of marketing products and linking to other sites, social commerce lets customers browse and buy directly within the app.
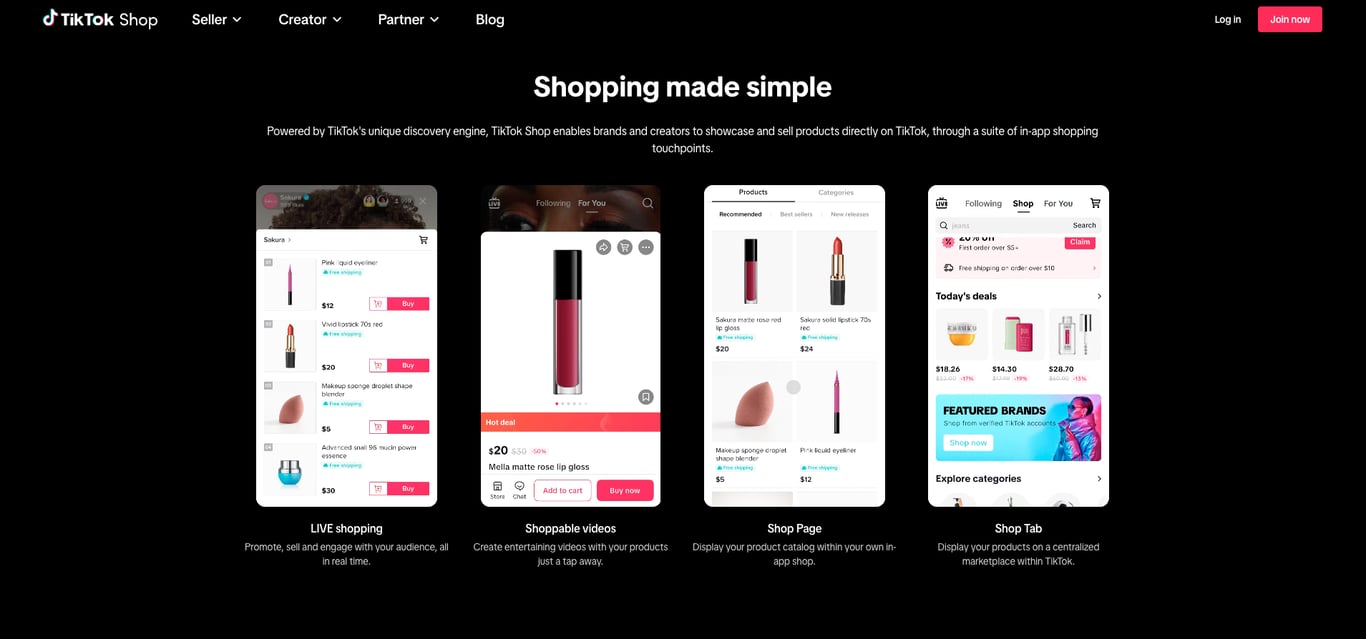
A great example of this is TikTok Shop, which allows businesses to sell products directly through in-feed videos, live streams, and product showcases. For instance, during a live stream, a seller can feature a product, and viewers can tap a pinned link to buy it instantly. This feature turns casual browsing into an engaging shopping experience.
Here’s why social media works as an ecommerce platform:
Ecommerce offers many benefits, including lower costs, wider reach, 24/7 sales, scalability, and data-driven marketing. However, it also comes with some challenges, from intense competition and higher return rates to vulnerability to technical issues and security risks.
Advantages of ecommerce
Disadvantages of ecommerce
Still not sure if ecommerce is right for you? Our guide on ecommerce advantages and disadvantages offers more insights to help you decide.
To start an ecommerce website, first define your niche by deciding what products to sell and who your target audience is. This helps you focus and stand out in a competitive market.
Next, choose the right platform for your business. It will impact your store’s design, functionality, and ease of management, so make sure it has the features you need, is easy to use, and can grow with your business.
Once you have your platform, set up your online store. Apply web design best practices, add your products, and configure payment and shipping options. Check out our ecommerce website examples for inspiration.
As you scale your business, implement effective selling and conversion rate optimization (CRO) strategies. Focus on driving traffic to your store through marketing, SEO, and social media. Additionally, A/B testing different elements like product page layouts and call-to-action (CTA) buttons to see what resonates with your audience and drives sales.

According to ecommerce statistics, it’s estimated that by 2025, 2.77 billion people ‒ nearly one-third of the global population ‒ will be shopping online. Online sales are predicted to account for nearly a quarter of all global retail sales by 2027, with global ecommerce revenue exceeding $6.4 trillion by 2029.
Ecommerce has become crucial for financial success, driven by how people shop. Most customers buy online at least once a month. During the holidays, online shopping spikes even more, accounting for about 24% of the year’s total sales. This shows just how much potential there is for businesses to capture a large share of sales.
The rise of mobile users also contributes to ecommerce growth. Almost half of all shopping journeys start and end on a retailer’s website or app. Consumers are also placing a higher value on convenience and efficiency, making it essential for businesses to optimize their websites for mobile and offer features like guest checkout.
All these trends show that for businesses to remain competitive, embracing ecommerce is no longer optional.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
October 05 2020
HI, I want to make an ecommerce website in wordpress with woodmart theme.Please tell me which hosting service will be best for this type of e-commerce store. Will your hosting service support wood Mart theme in wordpress woocommerce? Thanks
November 18 2020
Hey there Amir. Yes we would support the theme. For the plan recommendation, I'd recommend you to message support@hostinger.com with some more info about your project, such as expected visitors, etc.
January 12 2021
thanks for sharing this precious information with us, this is really helpful for me