What is VPS (virtual private server) hosting?

VPS (virtual private server) hosting is a service that provides users with virtual machines running on a physical server, each with dedicated virtual resources, its own operating system, and independent configuration. It uses a virtualization layer to partition the physical server’s resources, enabling each virtual instance to run independently and fully isolated from other environments.
Compared to shared hosting or similar solutions, VPS offers improved performance, a higher level of privacy, complete control over the hosting environment, and seamless scalability. However, it requires technical expertise to manage, especially if the hosting provider doesn’t offer tools that help streamline the task.
Given its flexibility, VPS is suitable for various use cases. For example, you can run an automation platform 24/7, deploy scalable applications using containers, create a cloud-based data sharing solution, and host a multiplayer game server.
Explore VPS hosting in more depth, including how it works and how it stacks up against other popular hosting types. Also, learn more about its benefits and common use cases so you can make an informed decision whether it is the right solution for your needs.
What is VPS hosting?
VPS hosting is a service that uses virtualization technology to provide users with a virtual server with dedicated resources and an independent operating system.
It essentially lets users rent a virtual server to store files and data of a website or web application, making them accessible online. Whenever an online visitor wants to access your website, their browser sends a request to your server, which transfers the necessary files through the internet.
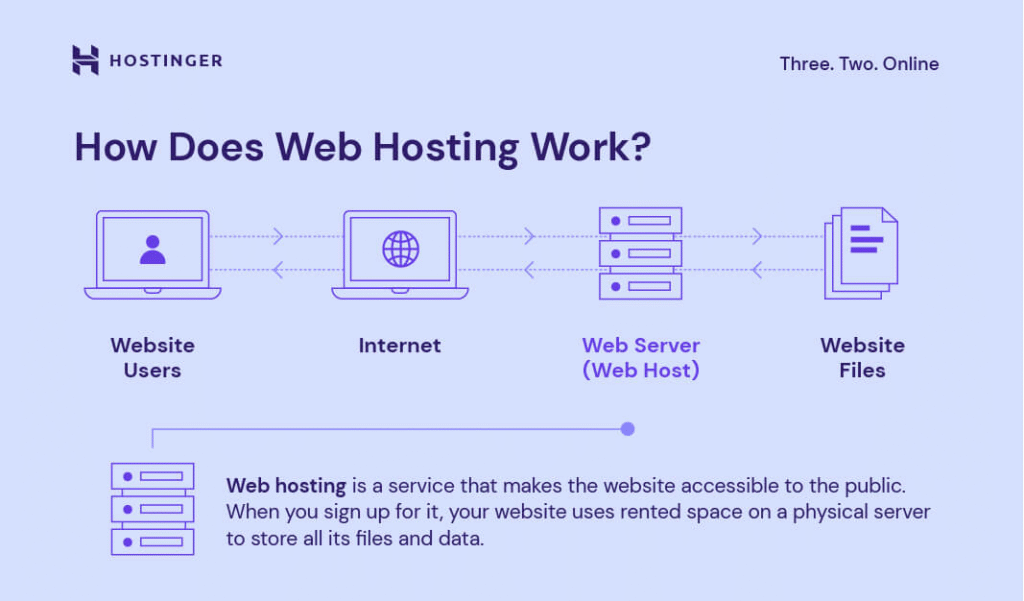
A VPS solution is different from the typical shared hosting in several important aspects:
- Dedicated resources. Each user has their own server resource (vCPU, RAM, storage, operating system, and bandwidth) allocation.
- Isolated environment. Virtual environments in a VPS run independently and fully isolated from each other, eliminating resource contention.
- Complete control. Users have full root access over their VPS, allowing them to freely use and customize their hosting environment as superuser.
- Self-managed. Since the user has the flexibility to install any software and configure their virtual environment, they also have to manage the server themselves.
How does VPS hosting work?
VPS hosting works by splitting a physical server into multiple virtual environments for several clients. Here’s a breakdown of its working principle:
- Hypervisor installation. Your hosting provider uses virtualization technology (hypervisor) to create a virtual layer on top of the physical server’s hardware.
- Resource partitioning. The hypervisor divides the server’s CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth into isolated virtual environments called VPSes.
- Independent allocation. Each virtual environment receives dedicated resources and can run its own operating system and software configurations without interference from other instances.
- Administrative control. Users get root-level access to their virtual server, enabling complete customization and management of their hosting environment.
VPS technology is similar to creating multi-boot partitions on your own computer when you want to run more than one OS (e.g., Windows and Linux) on the same storage. With VPS hosting, you have the same root-level access as if you had a dedicated server, but at a much lower cost.

VPS hosting pros and cons
Before choosing VPS hosting, consider these key benefits and limitations:
Pros
The most important upsides to using VPS hosting are:
- Higher performance. VPS provides more dedicated resources than most other types of hosting, which translates to improved performance. VPSes are also more reliable than shared servers because these virtual environments aren’t affected by traffic surges and issues on other instances.
- Complete control. Since each VPS is fully independent, users have complete control of their hosting environment. This enables them to log in as a root user and customize any configuration as needed.
- Improved privacy. The high level of isolation between environments in VPS hosting means other users on the same server can’t access your data. This translates to higher privacy, which is especially crucial if you collect sensitive files or information.
- Easily scalable. Resources in a VPS can be adjusted through the virtualization layer, and providers typically maintain resource pools to accommodate scaling needs. VPS hosting also supports horizontal scaling by provisioning additional instances and distributing the load between them.
- Cost effectiveness. Since multiple users share the same underlying infrastructure, the VPS hosting cost is lower than dedicated hosting. You only pay for fractions of the hardware, which reduces the price significantly.
Cons
The downsides of using a VPS hosting solution include:
- Technical requirements. Since you have full control over the hosting environment, setting up your VPS can be more complicated. That said, several VPS providers offer built-in tools that make the configuration and management process more beginner-friendly.
- Security responsibility. Since VPS hosting services are commonly self-managed, users are responsible for tasks like firewall management, software updates, and security patching. While providers include basic security features, proper self-management is mandatory to avoid vulnerabilities.
- Inconsistency across hosts. Depending on the provider, VPS offerings may use different CPU architectures, virtualization technologies, or operating system options. These variations can affect performance and software compatibility.
What is the difference between VPS and other types of hosting?
There are different types of web hosting with varied pricing, performance, and reliability that are suitable for specific use cases. Below, you can read about how VPS hosting compares to other hosting solutions.
VPS vs shared hosting
Small businesses and bloggers commonly use shared hosting as a starting point for their low-traffic websites. In this type of hosting, you share the same physical server with several other hosting company clients. You don’t get dedicated resources, as your site runs on the same operating system as everyone else’s.
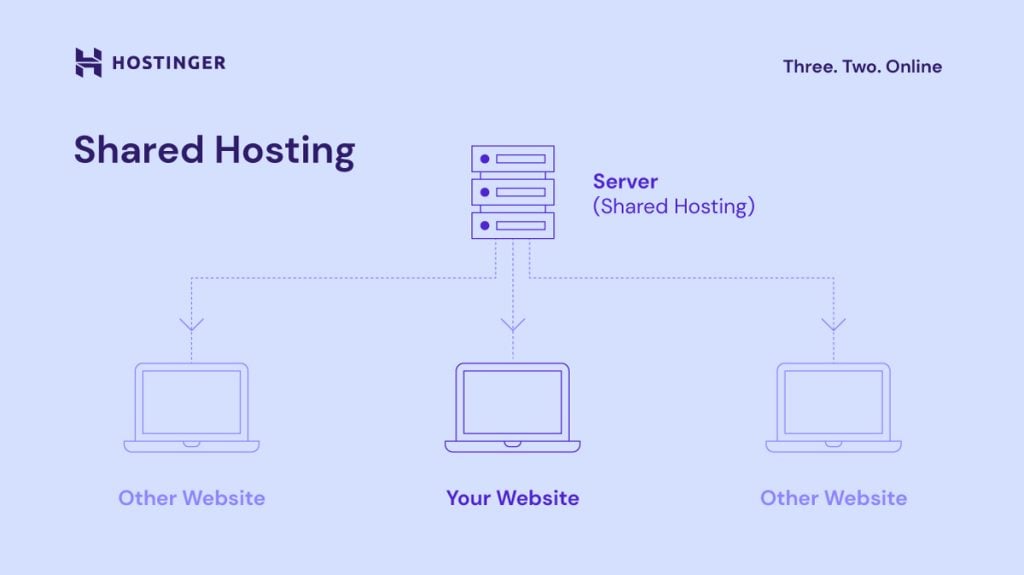
The needs of other users will affect the memory and computing power your site can use. For instance, if there’s a sudden traffic spike on a website hosted on the same server, your page load time may increase. You can’t choose your operating system and other server software either, as all users use the same configuration.
Given the limitations, the price of this web hosting type is commonly the cheapest compared to other services. It’s also beginner-friendly since your hosting provider handles every aspect of your shared hosting environment.
When comparing shared hosting and VPS, a virtual private server is like renting your own apartment in a building: you have your private space, dedicated utilities, and complete control over how you set it up. Shared hosting, by comparison, is like sharing a single apartment with multiple roommates, where you’re limited by shared resources and house rules.
VPS vs cloud hosting
The concept of cloud hosting is similar to that of traditional web hosting. Cloud hosting distributes your website across multiple interconnected servers rather than relying on a single physical machine. This distributed approach provides automatic scaling, improved uptime, and better resource allocation compared to traditional single-server hosting.
With cloud hosting services, enjoy managed convenience similar to shared hosting, as providers handle server maintenance and scaling automatically. However, cloud hosting offers better performance consistency and can handle traffic spikes more effectively than shared hosting.
Given the benefits, cloud hosting is perfect for entrepreneurs and businesses with resource-intensive websites. However, VPS remains a more suitable solution for users looking for a higher level of customization and control over their hosting infrastructure.
VPS vs WordPress hosting
The WordPress hosting solution is specifically designed for deploying websites built on the WordPress content management system (CMS). It’s similar to shared and cloud hosting, but offers built-in features that streamline WordPress site management, such as one-click installation, pre-installed plugins, or a WP command-line interface.
Although it’s also possible to set up a WordPress site on a VPS, you can’t enjoy the custom-built servers and additional features of this type of hosting. You will also miss the managed service and the simplicity of maintaining your hosting environment.
However, if you still choose a VPS for your WordPress site, you have the freedom to set up and configure your hosting environment according to your business needs.
VPS vs dedicated hosting
With dedicated hosting, you rent an entire physical server for your business. Its excellent performance, flexibility, and customizability make this hosting solution suitable for enterprises looking to deploy large-scale projects.
While VPS hosting allows you to configure any operating system and software package, dedicated hosting goes one step further. It also lets you customize the hardware, as the entire server is reserved for a client. In some cases, a dedicated server can also run on-site (for instance, in your office), but without the support of the provider.
The main downside of dedicated hosting is its hefty price tag, which is unsuitable for personal use or deploying smaller projects. It’s also more difficult to scale than a VPS because the providers have to physically change the hardware to upgrade the resources or assemble a new machine to provision a new system.
VPS hosting use cases
Given its flexibility, VPS hosting is suitable for various tasks or projects. Here are some of the most common use cases for VPS for both businesses and individuals.
Automations
VPS is often widely used to automate specific tasks, leveraging its ability to reliably run any script, bot, or platform 24/7. For example, developers can deploy CI/CD tools for deployment or execute a custom script for data scraping.
VPS is also popular for self-hosting n8n, a platform that lets you create a workflow to automate various tasks. Compared to cloud subscription plans, using a VPS is more cost-efficient since there’s no usage limit, offers a higher level of customizability, and complete data control without any vendor lock-in policy.
Control panels
VPS is ideal if you want to install various control panels for different tasks, whether it’s managing the server itself, creating websites, or managing custom email accounts. Popular control panels for VPS include Coolify, cPanel, Plesk, and CyberPanel.
Depending on your VPS hosting provider, some control panels might already be pre-installed. Otherwise, you can set them up manually using commands or using a one-click installer, like Hostinger’s OS template.
Game servers
For general users, VPS is popularly used to set up a dedicated game server for multiplayer titles like Minecraft and Counter-Strike 2. A VPS is an excellent choice because it offers higher stability and scalability compared to a personal machine.
Moreover, you can deploy a VPS in different locations, allowing you to set up a multiplayer host close to your player base for minimal gameplay latency. Check out our dedicated game server guide to learn more about the benefits of deploying a game server on a VPS and tips for choosing the right host.
Containerization
A VPS is a great environment for containerization because it offers full control and consistent uptime for running Docker. This lets you run multiple isolated applications on a single virtual instance without dependency conflicts, making the most of your resources.
By installing Docker on a VPS, you combine virtualization-level isolation with container-level isolation, creating a highly scalable and secure hosting infrastructure. As demand grows, you can scale vertically by deploying more containers on the same VPS, or scale horizontally by spinning up additional VPS instances.
Frameworks
VPS is commonly used to deploy websites or applications built with custom frameworks, something that you can’t do with shared hosting given the limited customizability. For example, you can install Django on your virtual server to deploy a custom Python project.
In addition to allowing you to set up various frameworks, VPS hosting’s high level of customization also enables you to tweak the hosting environment to optimize its performance. For instance, you can configure Unicorn and Redis after installing Ruby on Rails to make your application more responsive.
File sharing
VPS hosting is often used as a centralized file storage or cloud-based sharing platform. For example, you can deploy Nextcloud on your VPS to create a centralized online collaboration platform that streamlines teamwork.
This use case mainly benefits from the virtual server’s high level of isolation, control, and privacy, which ensures optimal data security. Moreover, VPS hosting’s excellent performance contributes to a responsive data stream, which is crucial for real-time sharing and collaboration.
What are the next steps after buying a VPS?
If you feel that VPS hosting is the right solution for your needs, your next step would be to purchase a plan from a reputable host. With so many options available, we recommend checking our selection of top VPS hosting providers to learn more about the options and factors to consider when shopping for a VPS.
If you are switching from shared hosting to a VPS, Hostinger is an excellent place to start. We offer various built-in features that help beginners use VPS easily, even with minimal technical knowledge. For example, you can ask our AI assistant, Kodee, to manage several aspects of your server by simply chatting with it.
Since VPS is often self-managed, there are several crucial practices to follow after purchasing a plan to ensure optimal security and usability. For example, you must point a domain name so you can install an SSL/TLS certificate and setup additional security tools, like fail2ban. To help you get started, read our guide on what to do after purchasing a VPS.
Note that VPS requires ongoing management to maintain its performance and security. If you wish to learn more about this type of hosting, we offer a comprehensive catalog of VPS tutorials to help you get started.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
October 02 2020
Would your VPS work in India?
November 18 2020
Hey Loren. Yes it would.
December 28 2021
Excellent post. I want to thank you for this informative, I really appreciate sharing this great post. Thanks for sharing this…
December 28 2021
So which should we choose? VPS or cloud? When moving up from shared hosting with Hosting? Tx
December 30 2021
Hi! It would depend largely on your technical knowledge - if you don't want a lot of hastle, Cloud would be the easiest option with a simple, one-click upgrade. While moving to VPS will require a lot more technical knowledge setting it up, you would have a lot more control over the server. I would suggest checking out our How to Choose a Plan guide to help you out :)
January 18 2022
what system use is vps nesesartly required, Android or computer?
January 18 2022
Hi! If you purchase VPS hosting, the OS of your device will not matter, as it will be a separate server. That being said, in order to manage your VPS, you'll likely need to connect to SSH, so in order to manage do so, you will need a computer. If you mean to ask about the OS, available with Hostinger, you can check out the full list of pre-installed OS here.
May 29 2022
how do i connect cpanel to my VPS server pls? i bought VPS and i really need help linking the cpanel.
May 31 2022
Hi Rosaline, please check out this guide on how to use cPanel with your VPS ?