Sep 11, 2025
Jordana A. & Ariffud M.
7min Read
JavaScript (JS) is a lightweight, interpreted scripting language that creates dynamic and interactive content on websites.
It handles everything from simple animations and interactive maps to complex web applications. While HTML provides the structure and CSS adjusts the styling, JavaScript makes websites responsive to user actions.
Understanding JavaScript requires familiarity with its core elements:
If you prefer a visual guide to learn what JavaScript is, watch the video below from Hostinger Academy:

Download glossary for web beginners
The main features of JavaScript are its versatility and efficiency in creating dynamic web content. These characteristics make it a cornerstone of modern web development.
JavaScript’s syntax is the set of rules that define how to write JavaScript code. Understanding these basics is the first step to writing functional code.
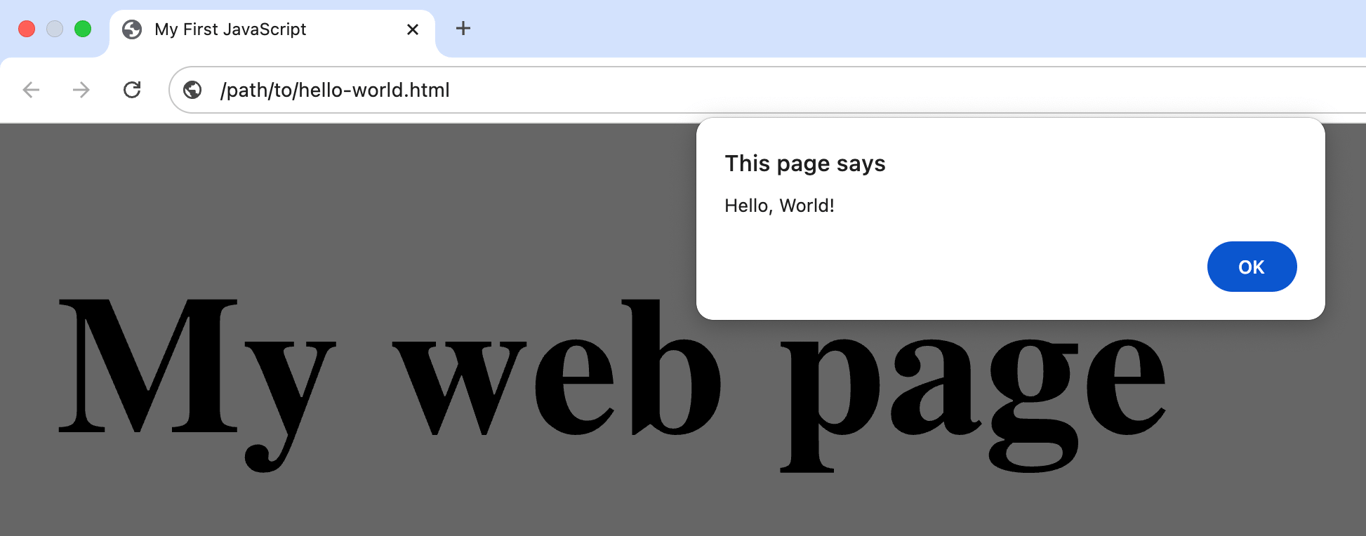
Here is a simple “Hello, World!” example in JavaScript. This code creates a function that shows an alert pop-up in the browser:
// This function displays a pop-up box
function greet() {
alert("Hello, World!");
}
// This line calls the function to make it run
greet();To see this code in action, copy and paste it into an HTML file, save it, and open it with any web browser. Here’s a complete template you can use:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First JavaScript</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My web page</h1>
<script>
// This function displays a pop-up box
function greet() {
alert("Hello, World!");
}
// This line calls the function to make it run
greet();
</script>
</body>
</html>When you open this HTML file in your browser, the JavaScript inside the <script> tags runs automatically, and you will see the “Hello, World!” pop-up appear.
The primary advantage of JavaScript is its ability to create rich, interactive user interfaces that run directly in the browser. This client-side execution leads to several key benefits.
The main disadvantage of JavaScript is that its client-side execution can introduce security vulnerabilities and browser inconsistencies.
JavaScript is a versatile language with applications in nearly every area of software development, from the web browser to the server and beyond.
Web and mobile app development
Developers use JavaScript to build the front end of both websites and mobile applications. Modern frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js let them create complex, single-page applications (SPAs).
An SPA is a website that interacts with the user by dynamically rewriting the current page instead of loading entirely new pages from a server. This approach creates a faster, smoother user experience.
For mobile development, frameworks like React Native and NativeScript let developers write code once and deploy it as a native app on both iOS and Android, which saves significant development time.
Web servers and back-end applications
With the introduction of Node.js, developers often choose JavaScript to build fast and scalable back-end applications.
Node.js runs JavaScript on a server, handling tasks such as processing data, managing user authentication, and managing database communication.
Its non-blocking architecture makes it highly efficient. Node.js handles many user requests simultaneously without slowing down, making it ideal for real-time applications like chat apps and live data streams.
Website interactive behaviors
One of JavaScript’s original and most important uses is adding interactive behaviors to websites. Examples include clickable dropdown menus, animated sliders, and interactive forms that validate input instantly.
JavaScript also lets parts of a web page update without a full reload.
Using a method called AJAX, it fetches data from the server in the background, creating the seamless experiences you see on platforms like Google Maps or when social media feeds update automatically.
Game development
JavaScript also powers browser-based games. Combined with HTML5’s <canvas> element and graphics-rendering technologies like WebGL, developers can build complex 2D and 3D games that run directly in the browser without plugins.
Many popular web games, including the viral puzzle game 2048, use these technologies.
JavaScript’s ecosystem includes thousands of frameworks and libraries that provide pre-written code to help developers build applications more quickly and efficiently.
React
Developed and maintained by Meta, React is a front-end library for building user interfaces. Its main innovation is a component-based architecture, which lets you build complex UIs by combining small, isolated pieces of code called components.
Think of it like building with Lego bricks – each brick is simple on its own, but you can combine them to create anything. This approach makes code highly reusable and easier to manage, which is why React is extremely popular for developing SPAs.
Angular
Angular is a comprehensive front-end framework developed and maintained by Google. Unlike React, which is just a library for the UI, Angular is a full-featured platform.
It provides a structured set of rules and tools for building large, enterprise-scale applications. Angular uses TypeScript, which adds type checking to JavaScript to help catch errors during development.
Vue.js
Vue.js stands out for its simplicity and approachability. Many developers consider it the easiest of the “big three” (React, Angular, Vue) for beginners to learn.
Vue is a progressive framework, meaning you can use it to enhance a small part of an existing website or scale it up to build a complex SPA from scratch. Its flexibility and excellent documentation have made it a favorite among many developers.
Node.js
Unlike the others, Node.js is not a front-end framework. It is a back-end runtime environment that runs JavaScript on a server. Before Node.js, developers could only use JavaScript in the browser.
Now, developers use Node.js to build entire web servers, create APIs, and connect to databases, all with the same language they use for the front end. This ability to use one language for both client and server is a major advantage.
jQuery
Popular with the motto ‘write less, do more,’ jQuery was incredibly influential for many years. It simplified tasks like handling events, animating elements, and making API requests.
While modern frameworks like React and Vue have replaced jQuery in most new projects, millions of existing websites and content management systems (like WordPress) still rely on it.
It’s less common in new development but remains an important part of JavaScript’s history.
Additionally, if you want to improve application performance, consider exploring JavaScript compilers. Tools like Babel and ReScript can optimize code, reduce file sizes, and improve execution speed.
A key difference is that JavaScript functions primarily as an interpreted scripting language for browsers, while many other popular languages compile code and run mainly on servers.
The table below compares JavaScript with other common languages, including Java, PHP, Python, and C#:
| Feature | JavaScript | Java | PHP | Python | C# |
| Execution | Runs in browsers or on servers (with Node.js) | Runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) | Runs on servers | Runs on servers | Runs on the .NET Framework |
| Typing | Dynamically typed | Statically typed | Dynamically typed | Dynamically typed | Statically typed |
| Compilation | Interpreted (just-in-time compilation in modern browsers) | Compiled to bytecode | Interpreted | Interpreted | Compiled |
| Primary use | Interactive front end, back-end servers, mobile apps | Enterprise-level apps, Android apps | Web development, content management systems | Web development, data science, AI, automation | Windows apps, game development, web services |
Now that you understand what JavaScript is, the next logical step is to put that knowledge into practice. The way you add JavaScript to a website depends on the platform you’re using. We have two guides to help you get started:
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
March 24 2020
This site is amazing doesnt reuire any further modifications
April 18 2021
Hello there, I would like to know how to connect to MySQL table in Java script so that I may manipulate values from the table using events. Kind regards L. Matlanyane
May 19 2021
Hi Lekhetho, Check out these MySQL tutorials :)
September 29 2021
nice