Feb 02, 2026
Ariffud M.
11min Read

Large language models, or LLMs, are AI systems that understand and generate human-like text. They power platforms like chatbots, virtual assistants, and content generators.
The LLM market is growing rapidly as businesses integrate these tools into their everyday operations.
This article compiles essential statistics and insights from reputable sources to help you understand the current state and future direction of LLMs. It covers everything from market size and industry adoption to real-world usage and emerging challenges.
Scroll down to see how LLMs are shaping work and business. This data-packed overview will get you up to speed.
The demand for large language models continues to rise globally. This section presents growth projections on market value and regional expansion in the coming years.
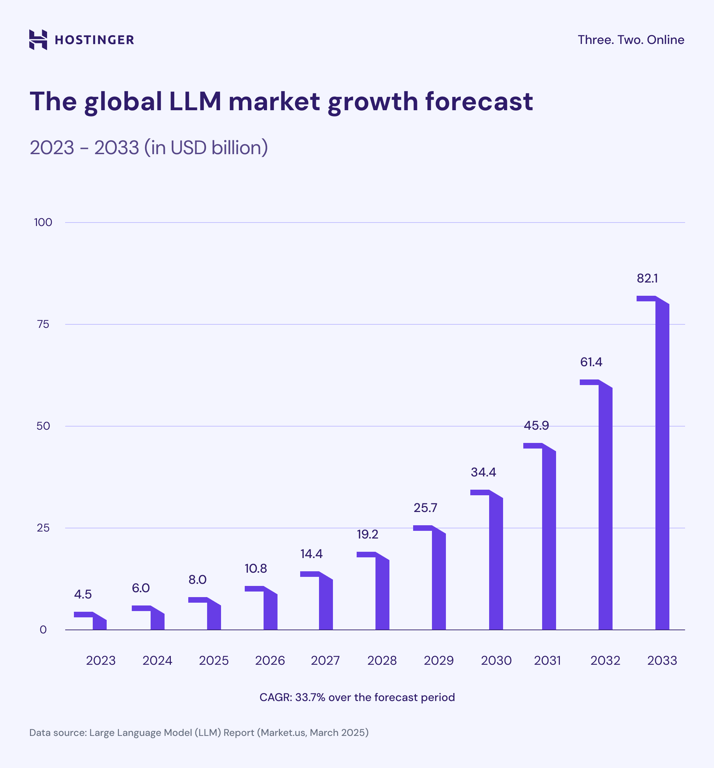
The global LLM market was valued at $4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $82.1 billion by 2033. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.7% over the forecast period.
The rising demand for advanced AI-powered tools across industries – particularly for improved data handling and more sophisticated customer interaction solutions – contributes to this growth.
Valued at $2.08 billion in 2024, the market for LLM-powered tools is predicted to reach $15.64 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 49.6%.
This surge reflects the growing interest in technologies like multimodal AI, real-time content moderation, and LLM-driven forecasting, especially in the finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity sectors.
The North American LLM market is projected to grow from $848.65 million in 2023 to $105.5 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 72.17%.
As the largest regional market, this increase is driven by substantial AI investments, established tech infrastructure, and active research.
The Asia-Pacific LLM market is on track for rapid expansion, with a projected CAGR of 89.21% – the highest among all regions. It’s expected to scale from $416.56 million in 2023 to $94 billion by 2030.
China, Japan, and South Korea drive this growth through significant AI investments and the widespread adoption of language technologies.
Europe’s LLM market is expected to rise significantly, reaching $50.1 billion by 2030 – up from $270.61 million in 2023.
This reflects a CAGR of 83.3%, supported by the region’s strong focus on ethical AI development and strict data protection regulations across key sectors like healthcare and finance.
Different industries are adopting LLMs in unique ways. Find out how retail, healthcare, and tech sectors use AI-powered solutions, and who key providers are, below.
According to Iopex, around 201 million – or 67% – of organizations globally now use generative AI, which refers to systems powered by LLMs that create content such as text, code, or responses based on user input.
With over 300 million companies worldwide, this reflects broad adoption across industries.
In the financial sector, for example, 60% of Bank of America’s clients use LLM-based solutions for tasks like investment and retirement planning.
As of 2024, the retail and ecommerce sector holds the largest share of the global LLM market, accounting for over 27.5%.
LLMs analyze customer data, generate tailored recommendations, and improve service through real-time support.
They also assist with demand forecasting and inventory management, helping businesses optimize supply chains and reduce operational costs.
In the United States, 21% of healthcare organizations use LLMs to answer patient questions, while 20% operate medical chatbots. Additionally, 18% apply LLMs for biomedical research.
Other common uses include information extraction (19%), clinical coding (17%), and medical text summarization (16%).
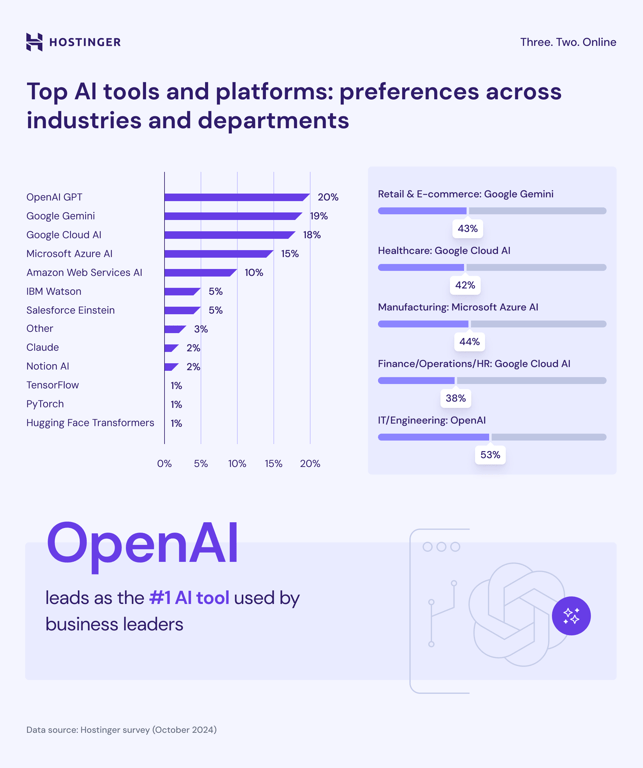
Different industries show distinct preferences for AI tools. A recent AI in business survey reveals that OpenAI is the most widely used overall, especially among IT and engineering teams, where 53% report using its products.
Interestingly, Google Cloud AI tops more sectors, including healthcare (42%) and finance, operations, and HR (38%).
Other AI platforms also dominate specific industries – Google’s Gemini holds 43% of the retail and ecommerce market, while Microsoft Azure AI leads manufacturing with 44%.
LLMs are changing how professionals work, with more people using AI daily. In this section, we uncover usage patterns, gender differences, and the dominance of key tools in the AI ecosystem.
A study by Amperly in April 2024 found that 52% of US professionals earning over $125,000 use LLMs daily at work. In contrast, only 20.8% of professionals aged 18 to 24 reported daily AI usage.
This suggests that higher income and experience levels correlate with more frequent adoption of AI tools in professional settings.
The same Amperly report shows that 37.3% of professionals engage with AI chatbots daily, while 46% do so several times a week.
Just 16.7% interact with AI less than once weekly. This pattern highlights AI’s growing role in everyday work across various professional roles.
Speaking of gender, 44.1% of men use AI daily for work, compared to 29.5% of women.
This gap coincides with differences in self-assessed AI skills: nearly half of women (48.2%) consider themselves beginners, while only 20.5% of men do.
Additionally, about 48.3% of all respondents rate their AI expertise as intermediate, with 18.3% identifying as experts.
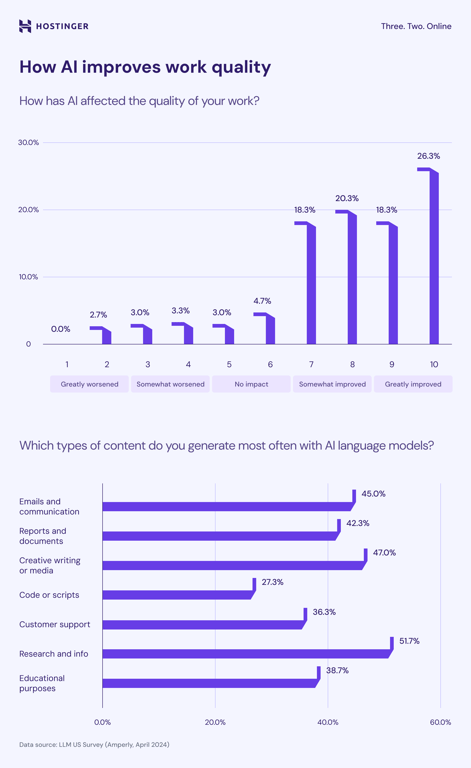
On a scale of 1 to 10, 87.9% of professionals rate the impact of AI on their work quality as 6 or higher, with 26.3% giving it a perfect 10.
While the overwhelming majority see benefits, a small portion (9%) reported declining quality after using AI.
Regarding usage, 51.7% of respondents use LLMs for research and information gathering, 47% for creative writing tasks, and 45% for emails and other communications.
Notably, 27.3% use AI for coding and scripting – significantly more than those whose primary job involves coding – suggesting AI helps many adopt new technical skills.
In 2024, chatbots and virtual assistants captured the largest global LLM market share at over 27.1%.
Their widespread use meets the demand for 24/7 customer support, efficient query handling, and consistent user experiences.
AI advancements have enabled these tools to handle complex tasks like personalized assistance and technical support, driving continued growth in this segment.
By 2025, the number of apps utilizing LLMs will surge to 750 million globally. As mentioned earlier, chatbots and virtual assistants make up a large portion of this total.
However, as people increasingly use AI for writing and coding, content generation tools and web app development platforms are also expected to see significant adoption.
In the US, 69% of respondents use OpenAI’s ChatGPT, making it the most widely used LLM. Google Gemini follows with 40% usage, including 11.3% who depend on Gemini exclusively.
Although ChatGPT remains dominant, its market share has started to decline as competitors like Google gain traction.
The data also shows that 61.3% of users rely on just one AI platform, with ChatGPT once again being the top choice for single-platform users (38%).
This highlights ChatGPT’s early adoption advantage before others became widely available.
As of May 2025, ChatGPT’s ecosystem – including standalone web and app versions plus Microsoft Copilot – has about 501 million monthly users globally. It holds 74.2% of the LLM market, slightly down from 74.3% in April.
Standalone ChatGPT accounts for 462 million users (59.9% market share).
ChatGPT remains the dominant player by a wide margin, with a more than three times larger user base than its closest competitors combined – Gemini, Perplexity, and Claude – who hold about 23% of the market.
Rising LLM usage is strongly linked to increasing investment and innovation. We explore spending forecasts, business investment plans, and the key factors driving LLM adoption.
Worldwide spending on generative AI is forecast to reach $644 billion in 2025, marking a 76.4% jump from 2024, according to Gartner.
This rapid growth spans all core markets. Services saw an astonishing 162.6% surge, reaching $28 billion.
Both devices and software nearly doubled their previous year’s figures, with $398 billion and $37 billion, respectively.
The servers segment, already heavily invested in, stands at $181 billion – second only to devices – with about a one-third increase from 2024.
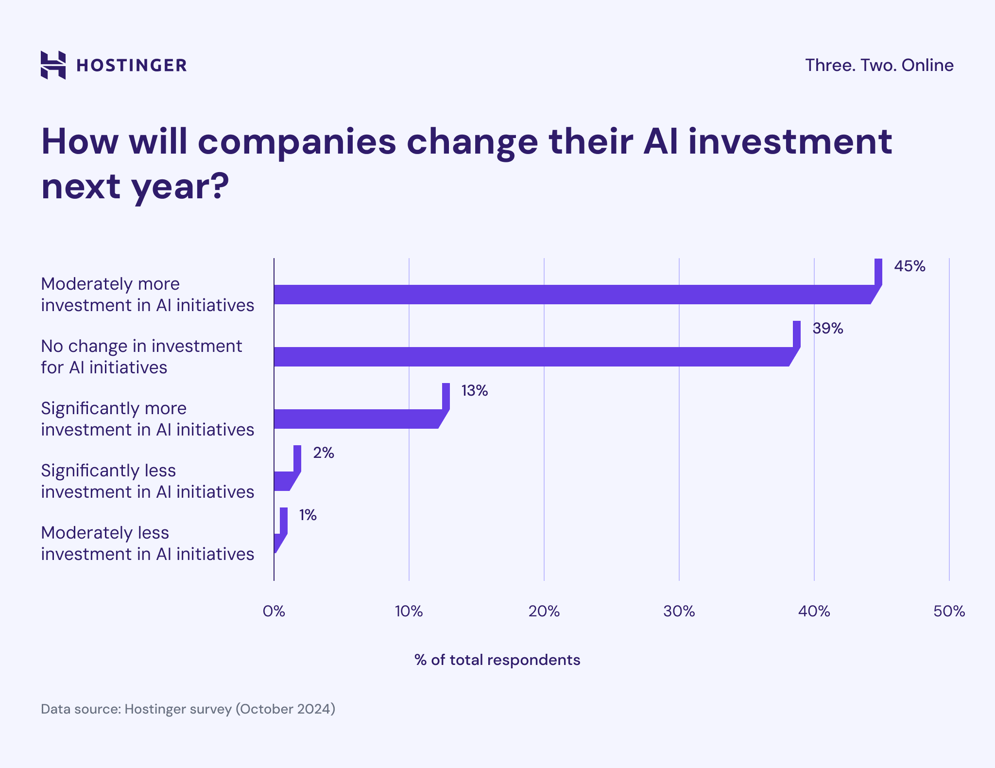
AI statistics from October 2024 discover that more than half (58%) of companies plan to increase their AI investments over the next year. Of these, 45% intend to increase spending moderately, while 13% expect significant growth.
Meanwhile, 39% of businesses plan to maintain their current investment levels, and only 3% anticipate cutting back AI spending.
In 2023, the world’s top five LLM manufacturers accounted for approximately 88.22% of the worldwide market revenue.
Although the exact lineup of leading vendors isn’t disclosed, key giants in the industry include OpenAI (ChatGPT), Google (PaLM), Meta (LLaMA), AI21 Labs (Jurassic), Cohere, Anthropic (Claude), Microsoft (Turing-NLG, Orca), Huawei (Pangu), Naver (HyperCLOVA), and Tencent (Hunyuan).
57% of US professionals cite enhancing productivity as their main reason for using LLMs at work. Close behind, 56.7% report exploring innovative approaches with AI, while 54.3% use LLMs to improve their work quality.
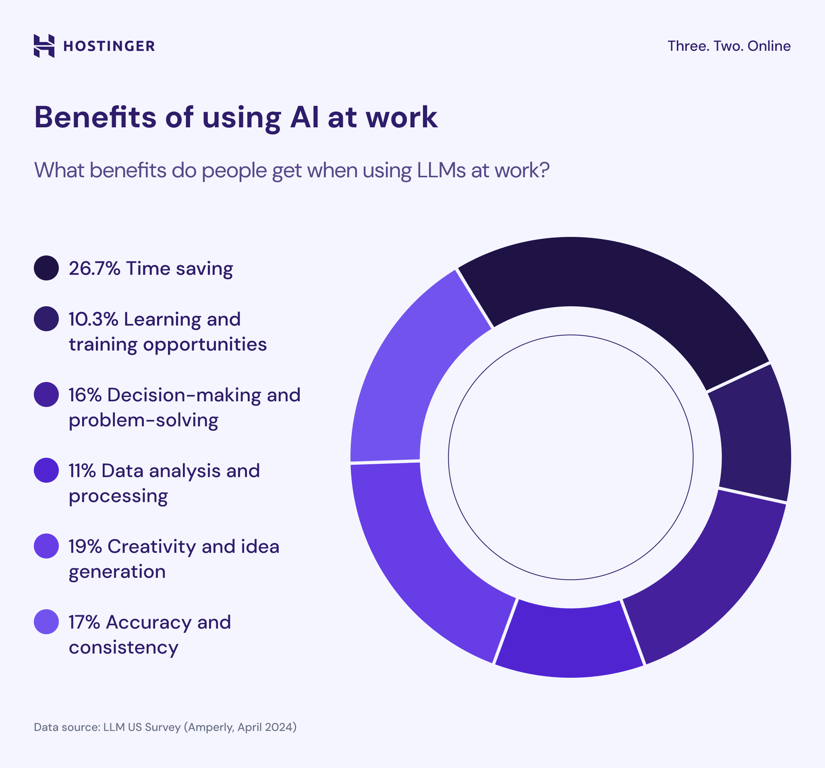
LLMs impact both efficiency and creativity in the workplace. A survey shows that 26.7% of professionals identify time savings as the leading benefit of using LLMs at work.
Creativity and idea generation follow at 19%, with a notable gender difference: nearly a quarter of women (22.3%) report this benefit compared to just 16.2% of men.
Rounding out the top five are accuracy and consistency (17%), decision-making and problem-solving (16%), and data analysis and processing (11%).
As more people use LLMs, concerns are growing around their reliability, fairness, and environmental impact.
Keep reading as we highlight the key challenges users and businesses face when working with these powerful AI models.
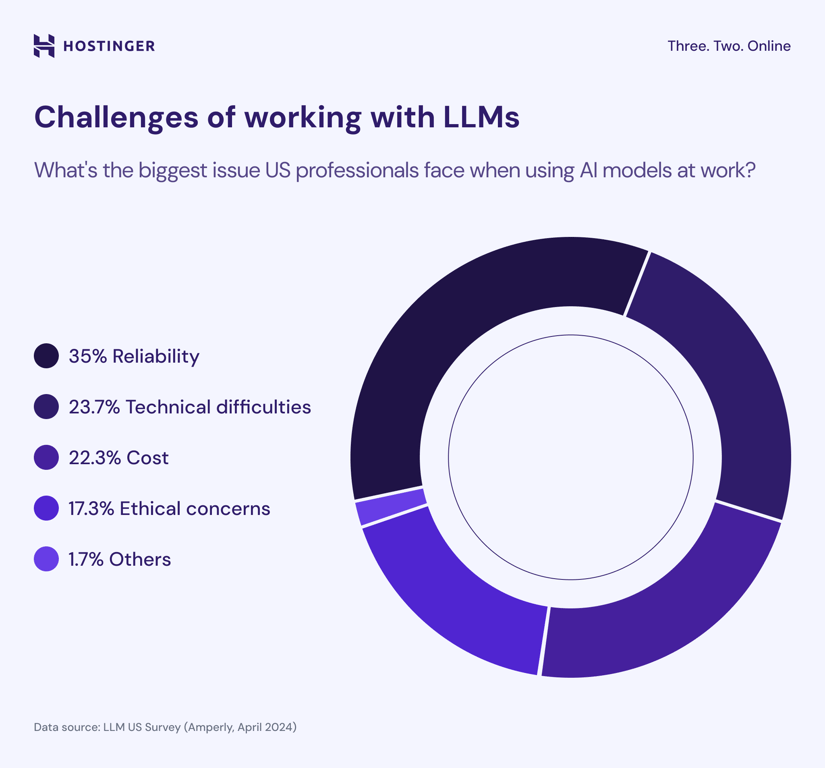
What challenges do users face when working with LLMs?
A recent US study found that reliability was the most common issue, with 35% of respondents identifying it as their biggest concern. Many noted that AI tools often produce inconsistent or inaccurate results.
Technical difficulties ranked second, affecting about one-quarter (23.7%) of users.
Cost was the third major hurdle, mentioned by 22.3%. Ironically, this concern was notably higher among those earning over $100,000, possibly because they are responsible for purchasing AI tools for their teams.
Nature’s 2024 LLM bias study reports that all major LLMs exhibit gender bias, with GPT-2 having the highest levels – reducing female-specific word usage by over 43% compared to human writing.
Even ChatGPT, the least biased, uses 24.5% fewer female-related terms.
Racial bias also appears frequently. In hiring tests, all models favor white-sounding names 85% of the time, while they rarely select Black male names.
These patterns of underrepresenting women’s and minorities’ perspectives reflect biases in both training data and AI design. They raise critical fairness concerns as LLMs see increasing use in sensitive decision-making contexts.
Training LLMs requires significant energy. For example, GPT-3’s training consumed roughly 1,064 MWh of electricity – equivalent to 405 years of continuous use of Nvidia V100 GPUs.
This intensive energy use produced about 460 metric tons of CO2 emissions.
To put this in perspective, these emissions equal driving nearly 1.18 million miles in an average gasoline-powered car or powering 58 homes for a year.
On a daily basis, GPT-3 consumes around 2,916 kWh of energy, generating about 1.3 tons of CO2 – comparable to burning 1,413 pounds of coal or charging over 153,000 smartphones.
New privacy challenges are emerging for organizations with the rise of generative AI.
Cisco’s survey of 2,600 security and privacy professionals reveals that 92% view this technology as fundamentally novel, requiring new risk management approaches.
Breaking down their concerns, most respondents (69%) acknowledge that using generative AI could potentially harm legal and intellectual property rights.
Worries about data being shared publicly or with competitors and the risk of AI returning inaccurate information follow closely (both at 68%).
Enterprises and professionals are preparing for a new era of AI-driven workflows and career opportunities. Let’s examine the future outlook for LLMs, focusing on automation, bias reduction, and low-code innovation.
Recent automation trends show that by 2026, 30% of enterprises plan to automate more than half of their network activities, up from less than 10% in mid-2023.
Nearly 90% of large enterprises now consider hyperautomation a strategic priority.
Hyperautomation combines AI, robotic process automation (RPA), IoT, and process mining to automate complex business processes end-to-end, reducing manual work and errors while boosting productivity.
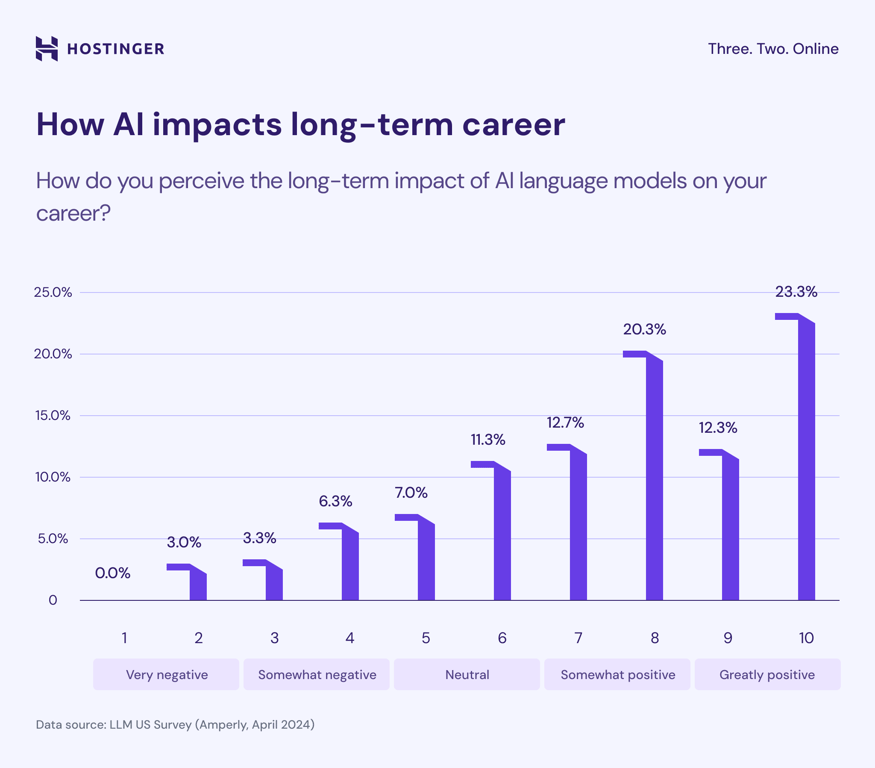
Seventy-one percent of professionals worry that LLMs will replace some or all human labor or tasks.
At the same time, a strong majority (80%) believe AI will positively impact their careers. Nearly a quarter (23.3%) rate AI’s impact on their career as a perfect 10.
Even those who expect AI to fully automate tasks in their field remain optimistic about future opportunities.
These views correlate with education level. The most pessimistic come from those with middle school, vocational, or technical education – 26.1% expect a negative career impact. In contrast, only 5.2% of university-educated respondents share this concern.
By 2026, over 70% of LLM apps will include bias mitigation and transparency features to ensure responsible AI use.
This is especially crucial in sectors like healthcare, where LLMs have achieved 83.3% diagnostic accuracy, highlighting the need to protect patient data and guarantee fair treatment outcomes.
Low-code platforms are expected to power 75% of new apps. Recent low-code trends show this growth results from rising demand for automation and a persistent shortage of skilled developers.
Despite projected growth in the IT workforce, many companies still struggle to fill open positions.
AI-based low-code tools offer visual interfaces and pre-built components that let non-technical employees build apps, helping organizations meet demand and accelerate digital transformation.
Large language models are reshaping the way people work and how businesses innovate.
The impact is clear: 88% of professionals credit LLMs with improving the quality of their output at work, and the number of LLM-powered apps is expected to reach 750 million globally by 2025.
Despite challenges like inconsistent output, training data biases, and potential job displacement, organizations continue adopting LLMs to unlock new ways of working and solving problems.
Looking ahead, integrating LLMs with automation and low-code platforms will help businesses boost productivity, foster creativity, and accelerate digital transformation.
There’s no exact count, but hundreds of LLMs exist globally. About 70 open-source models are available in Ollama’s library. Companies also create new models – either from open-source bases or from scratch – and since models constantly emerge, evolve, or retire, accurate tracking is difficult.
ChatGPT is popular, but whether an LLM is “better” will depend on what you want to use it for. Specific models may variably excel at tasks like coding, text or image generation, or translation. You’ll need to do some research to find out which LLM best matches your specific use case and priorities.
A report from Ioplex shows that around 201 million companies – about 67% worldwide – now use generative AI tools powered by LLMs. Adoption spans industries, with retail and ecommerce leading at a 27.5% usage share.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.