Jan 13, 2026
Simon L.
11min Read
Low-code development is changing the software landscape as businesses seek faster ways to build applications and solve complex problems.
With the global market growing to $101.7 billion by 2030 and 75% of new applications using these technologies by 2026, low-code trends point to massive growth.
This guide brings together 26 key statistics and insights that show how low-code platforms are reducing costs, cutting development time, and helping bridge the gap between what IT teams can handle and what businesses need.
Despite challenges with connecting systems, security worries, and the need for proper governance, these tools give non-technical staff the power to build solutions.
Want to understand how low-code is becoming essential for competitive businesses? Let’s look at the numbers behind this digital transformation.
Here are the most eye-opening statistics that show how low-code is transforming businesses in 2026:

According to our recent artificial intelligence statistics and trends research, AI is projected to contribute over $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, and the low-code market is set to benefit significantly. The statistics below show why businesses are rushing to adopt this technology.
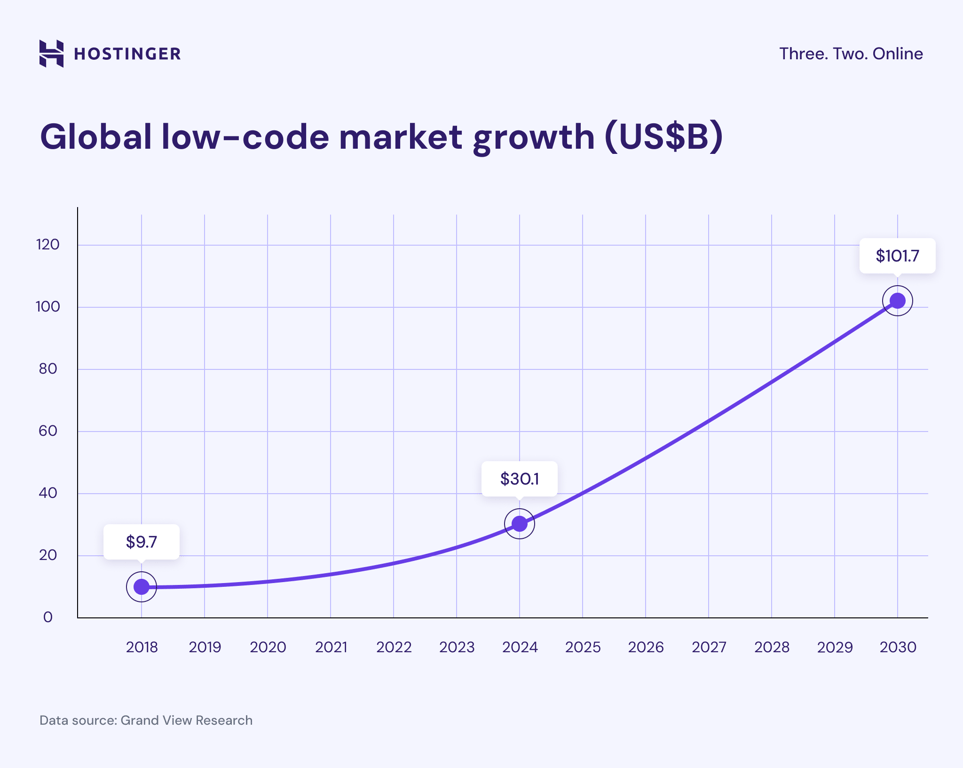
Low-code approaches are gaining momentum as organizations worldwide seek faster, more accessible application development options.
Set to grow at a compound annual rate of 22.3% between 2024 and 2030, this remarkable expansion shows no signs of slowing down. The market generated $30.1 billion in revenue in 2024 and is projected to reach $101.7 billion by 2030.
North America leads the charge, generating the largest revenue share in 2023 as businesses adopt these platforms to solve development challenges and speed up digital transformation.
The shift towards low-code approaches is being driven by two key factors: businesses need more automation, but they cannot find enough skilled developers.
Even though the IT workforce is expected to grow to 1.2 million developers by 2025, the talent gap remains significant. In 2020, 70% of companies couldn’t find the IT staff they needed, with thousands of positions left unfilled.
This gap between demand and available talent explains why low-code technologies are expected to power 75% of new app development by 2026, as organizations turn to platforms that enable non-technical employees to build applications.
Low-code has moved beyond being just another development tool and into being a key strategic asset, according to 81% of companies that consider low-code as strategically important.
This perspective is particularly true in the US and Europe, where business leaders see low-code as important for creating more agile and flexible IT operations.
Companies value low-code for different strategic reasons: 80% say it helps build applications faster, 79% believe it improves IT operations, and 79% think it’s vital for transformation projects.
For nearly one-third of surveyed companies, low-code isn’t just a supplementary tool – it’s at the core of how they develop software.
Regional adoption varies, with Africa leading at 34% and ASPAC close behind at 32%. This represents significant growth from previous years, especially in Europe, with 31%, where only 19% of companies used low-code strategies in an earlier study.
The growing skills shortage and demand for adaptable development approaches continue driving this global adoption.
As low-code platforms change how applications are built, they’re also changing who can build them.
This has led to the rise of citizen developers – employees with little to no coding experience who create apps using business-approved tools. These employees typically work in departments outside IT and use simple visual interfaces to build solutions for their specific needs.
Keep reading to learn how non-IT developers are changing application development and creating real business value.
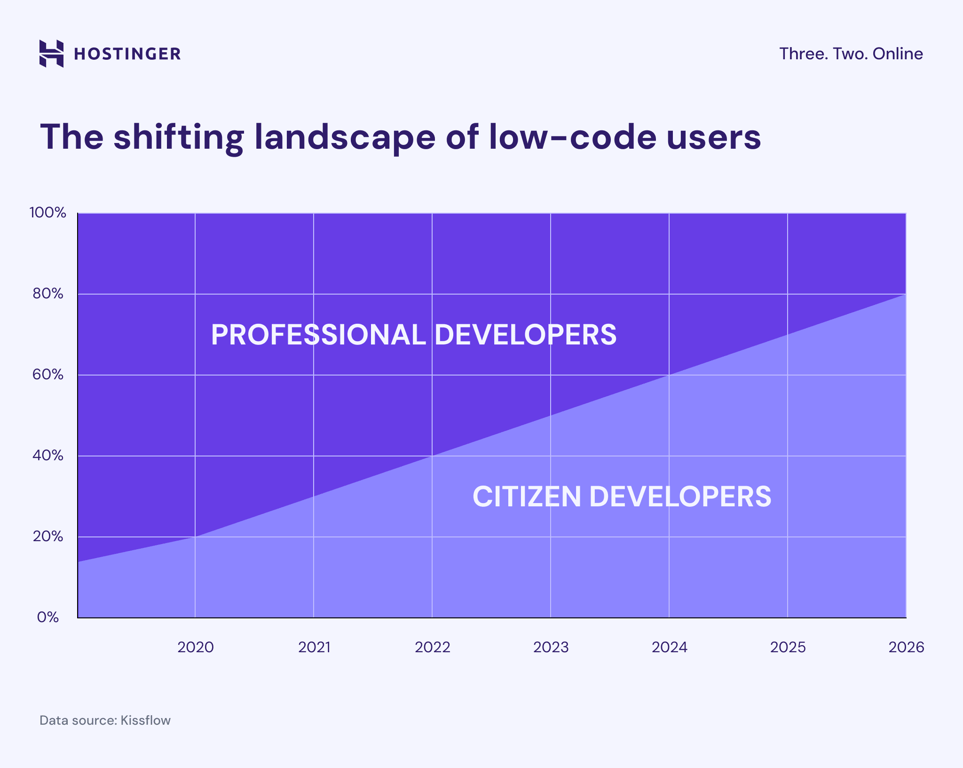
Traditional IT departments can no longer keep up with the growing demand for applications.
Software developer workloads continue to increase, with many engineers working 60-hour weeks and staying on call during weekends. New feature requests and product ideas often join a growing backlog of unfinished projects with no clear timeline for completion.
With 82% of companies struggling to hire qualified engineers, citizen development offers a practical solution, leading 84% of enterprises to adopt low-code and no-code platforms.
With IT teams struggling to keep pace with the growing backlog of development requests, it’s expected that citizen developer apps will grow at least 5 times faster than what traditional IT departments can support.
Given this trend, 70% of new applications shipped by large enterprises are expected to use low-code and no-code development platforms by 2025. This shift represents a fundamental change in how business software is created and deployed.
Organizations are increasingly turning to department-level teams to build their own tools, as 72% of IT leaders report being blocked from strategic work due to project backlogs.
Companies are finding value in equipping both developers and business staff with low-code tools to build applications faster and create custom workflows.
As a result, developers outside formal IT departments are expected to account for 80% of the low-code user base by 2026, up from 60% in 2021.
This trend is being driven by organizations seeking to automate more business processes and create systems that can be quickly adapted as business needs change.
Currently, 41% of organizations are actively working with citizen developers, and another 20% are either evaluating or planning to implement citizen development programs.
This approach helps companies reduce costs, enhance transparency, and combat uncontrolled app sourcing by business users.
The impact is significant as 80% of companies now consider non-technical developers critical to their success. This trend will continue, with 53% of business decision-makers expecting further growth in apps built by non-IT teams.
IT departments frequently face an impossible situation: endless requests for custom applications with limited resources to fulfill them.
As a result, 71% of organizations using citizen development have accelerated application development by at least 50%, with 29% seeing delivery times improve by 100% or more.
The impact on backlogs is impressive, with the majority of developers being able to focus on complex, higher-priority projects.
As businesses increasingly adopt low-code solutions and empower non-IT developers, they’re seeing significant returns on their investments. Let’s explore the most compelling benefits driving this shift.
Traditional application development is often measured in months, creating bottlenecks for businesses needing digital solutions.
Low-code platforms dramatically change this equation, often reducing development time by up to 90%. As a result, 72% of users develop applications in three months or less.
This efficiency allows 80% of organizations to free their developers for higher-level projects, enabling businesses to respond quickly to market changes without expanding their development teams.
Businesses face constant pressure to innovate quickly while managing limited IT resources and involving business stakeholders in digital initiatives.
Up to 84% of enterprises have adopted low-code development tools specifically to reduce strain on IT resources, increase speed-to-market, and better involve business decision makers in digital asset creation.
The results have been impressive, with 91% of low-code users reporting significant improvements in IT agility and innovation capabilities.
Building applications through traditional development methods is not only time-consuming but also expensive for organizations.
Research shows that low-code solutions can cut development costs by up to 70% compared to traditional methods, allowing companies to break even within just 6-12 months.
The long-term impact is substantial, with businesses seeing a potential 260% ROI over three years, as demonstrated by one financial services company’s 300% increase in new product launches.
A striking 90% of developers who adopt low-code platforms report maintaining fewer than five application requests in their monthly backlog.
This backlog reduction occurs because business users can create their own applications after minimal training, transferring responsibility away from overburdened IT teams.
The impact is particularly valuable for non-urgent “long-tail” requests that would otherwise never reach the top of the priority list.
Traditional software development cycles often struggle to keep pace with rapidly evolving business requirements.
Current usage shows that low-code platforms can make software development 10 times faster than traditional processes, allowing organizations to focus more on design and user experience.
This allows business experts to lead automation projects instead of waiting for technical teams who might not fully understand the business needs.
While low-code platforms offer significant benefits, organizations still face obstacles when using these tools. According to our AI in business study, 38% of companies struggle to align AI tools with their existing systems, making it essential to understand these potential roadblocks.
Let’s explore the key challenges businesses face and how to address them effectively.
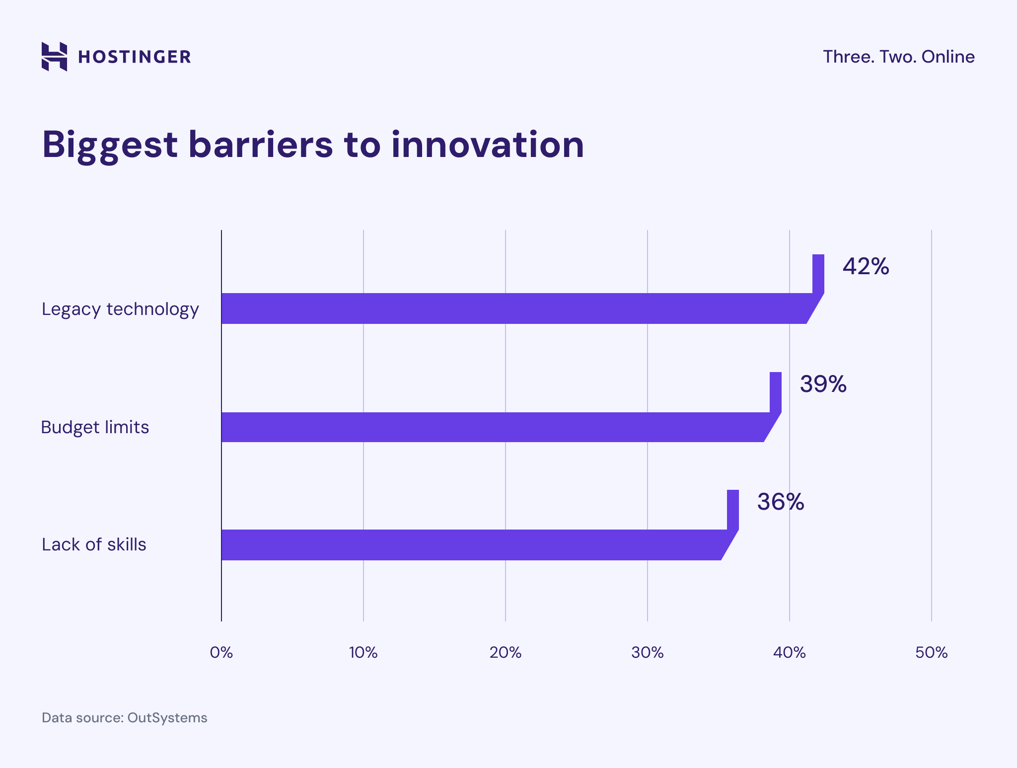
Many businesses still run critical operations on older systems that weren’t designed for today’s digital platforms.
Modernizing outdated software is a top priority for 73% of organizations, which makes sense since 42% of businesses identify legacy technology as their most significant barrier to innovation, more than budget limitations (39%) or lack of skills (36%).
While 55% of organizations find that low-code platforms help them update legacy systems affordably, older systems often lack modern APIs or data formats, making them difficult to integrate with new low-code tools.
When non-technical employees build applications without proper oversight, they may bypass approval processes or create solutions that don’t meet company standards.
Without proper governance, these well-intentioned efforts often create technical debt that IT teams eventually must address.
To mitigate these risks, companies need a citizen developer framework that defines which apps need IT collaboration, establishes approval processes, and assigns maintenance responsibilities. This approach ensures that low-code development empowers innovation while maintaining organizational standards.
While low-code platforms provide features that enhance development speed, they often come with constraints when users attempt to extend beyond out-of-the-box functionality.
According to research, 39% of business leaders report limited customization capabilities as a significant challenge, with the same percentage believing low-code tools are not suitable for advanced problems.
These limitations can lead to oversimplified solutions for complex business problems or specific use cases. Many organizations address this by adopting hybrid approaches – selecting platforms that allow custom coding while still maintaining the speed advantages of low-code development.
Despite being marketed as simple development tools, 41% of business leaders find low-code platforms more complicated to implement and maintain effectively than initially expected.
While these platforms aim to make development accessible to everyone, they still require expert developers for complex tasks like back-end APIs, infrastructure management, and advanced front-end customizations.
This complexity, combined with the limitations of pre-built components, can lead to situations where even minor application changes require significant reworking.
As generative AI (GenAI), which can create text, images, and code from simple prompts, is used more with low-code tools, new challenges are appearing alongside the benefits.
While 40% of organizations see building apps with GenAI as essential to their strategy, security and governance concerns are the most significant barriers, affecting 62% of these companies.
These issues are compounded by shortages in talent and skills (45%) and a lack of proper technology (18%). Even though 38% of businesses claim to understand AI in app development well, these problems can slow down low-code adoption across company departments.
Despite the promise of easier development, technical gaps remain a significant challenge for low-code adoption.
A lack of technical skills among non-IT employees worries 41% of companies, with another 40% concerned about insufficient IT knowledge among their staff.
This reflects a broader trend where 93% of IT leaders face modernization challenges due to staffing and tool shortages, with 82% emphasizing the need to train staff and improve old processes to get the full benefits of low-code tools.
As companies tackle adoption challenges, the low-code landscape continues to change in exciting ways. Understanding these emerging trends is vital for businesses wanting to stay competitive in today’s fast-changing digital environment.
Faster, more accessible approaches are gradually replacing traditional development approaches as companies modernize their digital systems.
By 2025, 50% of all new applications will be created using no-code or low-code technologies. This major shift is driven by hyperautomation, which combines AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation with low-code platforms.
These tools help companies connect automation systems across departments, handling complex processes that older tools couldn’t manage. As these automation trends continue, 30% of enterprises are expected to automate over half of their network activities by 2026.
As low-code technology matures, it’s evolving into industry-specific solutions with pre-built templates and compliance features.
The impact is already visible across multiple sectors – healthcare providers use these tools for better patient care and virtual doctor visits, educational institutions create virtual classrooms and administrative systems, and retailers design apps like mobile storefronts and loyalty programs.
This industry-focused approach is making low-code accessible even to organizations without extensive technical resources.
The gap between tech and business teams is shrinking as low-code tools create new ways to work together, with 59% of low-code projects involving direct teamwork between IT and business departments.
The benefits go beyond better collaboration, with 40% of low-code users seeing faster development and lower costs.
Organizations using low-code find their projects cost 53% less and finish 56% faster than traditional development, showing how these platforms can both unite teams and save money.
Companies are finding new ways to update their systems, with 58% of IT professionals transforming legacy systems using low-code applications.
This change reflects the growing importance of low-code, with 75% of IT professionals seeing it as a trend they can’t miss and 45% feeling a new urgency to adopt it.
By making system updates cheaper and more flexible, low-code gives organizations solutions that can overcome outdated technology while adapting to new requirements.
When business teams need solutions, they often wait for IT departments to help them. But no-code and low-code tools can cut development time by up to 90%, greatly speeding up how quickly business applications can be created and launched.
IT departments benefit too, with 80% believing that low-code platforms let developers focus on more complicated, higher-value work.
This shift allows companies to work on strategic projects while still handling everyday business needs.
As organizations pursue digital transformation, low-code platforms have become essential tools for enhancing efficiency and driving innovation.
The business benefits are clear. Low-code platforms speed up development by up to 80%, allowing companies to respond faster to market changes and customer needs.
This speed advantage translates to significant cost savings by reducing the need for specialized coding expertise and decreasing development time.
Low-code development has transformed from a niche solution into a mainstream approach that’s changing how businesses create applications.
The benefits are compelling – development time reduced by up to 90%, costs cut by 70%, and practical ways to bridge the gap between what IT teams can handle and what businesses need.
By empowering citizen developers and fostering collaboration between technical and business teams, low-code platforms help companies overcome talent shortages while speeding up digital changes.
Despite challenges like security concerns, integration difficulties, and the need for proper governance, the low-code trends are clear: these platforms are must-have tools for businesses that want to thrive.
The future of low-code and no-code platforms looks increasingly AI-driven, with tools being able to create advanced apps from simple prompts. By 2026, these platforms will build 75% of new apps, allowing citizen developers to create custom solutions while freeing IT teams for more complex projects.
Low-code solutions speed up digital transformation by cutting development time by up to 90%. When employees create their own solutions without technical developers, businesses can launch more digital projects while adapting faster to market changes, freeing IT teams for more complex work.
The future of software development looks increasingly low-code. As AI improves, these platforms are expected to power 75% of new apps by 2026. With companies needing faster digital changes, low-code will keep changing how businesses solve problems and create software.
Platforms like Hostinger Horizons, Softr, and Budibase are great examples of no-code and low-code solutions. Hostinger Horizons’ prompt-based development approach makes it particularly simple for non-technical users to describe what they need in plain language and have the platform build it.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.