Sep 19, 2025
Domantas G. & Tashia T.
6min Read
A content delivery network (CDN) is a system of distributed servers that deliver web content from the users’ closest server locations.
Here’s how a CDN works in simple steps:
A CDN improves website performance by reducing loading times, increasing reliability, and ensuring content is available even during traffic spikes. It also enhances security with features like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection and secure data delivery.
This makes CDNs valuable for websites that handle large volumes of content, such as ecommerce brands, news and media sites, streaming and gaming platforms, educational websites, high-traffic blogs, and government or nonprofit portals that require reliable access for users worldwide.
When choosing a CDN service provider, consider factors like cost, network coverage, ease of integration with your website, and the level of support they provide. You’ll also want to weigh advanced features such as caching, real-time analytics, and scalability to ensure the CDN meets your current and future needs.
Continue reading to learn how CDN works, the benefits of using a CDN, and what you should know before choosing one.
Download glossary for web beginners

In short, a CDN speeds up your website by delivering content from servers that are closer to your users. It relies on two key components to work effectively:
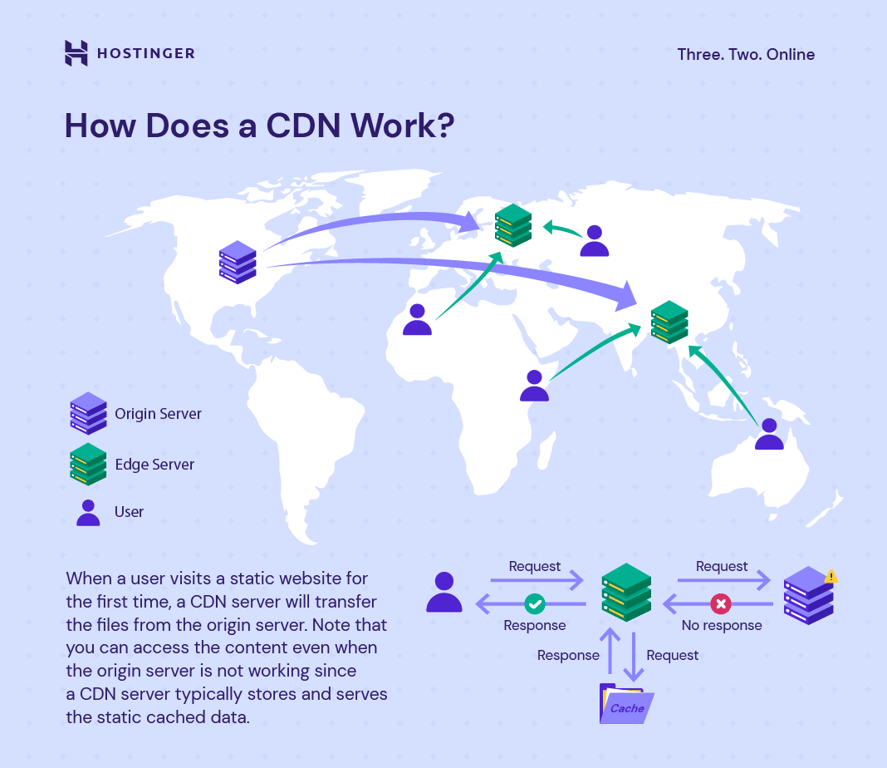
To illustrate how a CDN handles user requests, imagine you run an ecommerce store hosted on an origin server in New York. With a CDN in place, a customer in Tokyo can access your site faster through the following process:
With this information in mind, let’s continue exploring the benefits of using a CDN and why it’s essential for your website’s performance.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of why implementing a CDN is a smart move for any website:
One of the biggest expenses in web hosting is bandwidth. A CDN reduces these costs by distributing website content across multiple servers or points of presence, which lowers the amount of data your origin server needs to handle.
CDNs also use website caching, which stores static files on edge servers for faster access. This reduces the workload on your main server and cuts bandwidth usage.
Static content consists of files that remain the same for every user who visits your website. Examples include images, videos, HTML pages, CSS stylesheets, and JavaScript files. Because these files don’t change, they can be easily cached on edge servers for faster delivery.
In contrast, dynamic content changes based on factors like user accounts or location, so it can’t always be cached. Advanced CDNs use smart routing and optimized networks to deliver dynamic content efficiently.
Put simply, CDNs combine caching, load balancing, and optimization technologies to speed up your website while reducing server load and bandwidth costs.
One of the biggest contributors to high bounce rates is latency, which is the delay between a user connecting to a site and the web page content appearing on the screen. Latency usually happens due to:
You can resolve or greatly reduce many of these issues by using an effective CDN. Implementing website optimization strategies will also improve site speed and performance.
Combined, these efforts also help search engines better understand your site. As a result, your ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) will improve, increasing site traffic.
If you chose WordPress as your website creation platform, check out our practical guide on how to speed up WordPress websites, which complements using a CDN.
A CDN enhances web hosting security by diverting traffic away from the origin server to edge servers, effectively making the main server less visible to attackers.
If all data transfer happens through a single web server, your website becomes more vulnerable to malicious actors, such as DDoS attacks and other security threats.
DDoS attacks involve coordinated requests sent from multiple locations, often using bots, with the goal of overwhelming the origin server and causing it to crash. These attacks can last for hours or even days, making the hacked website inaccessible.
CDNs also maintain SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data and ensure secure transfers. While people often still call them SSL certificates, modern certificates use the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, which is more secure and reliable than the older SSL protocol.
These certificates protect information by allowing only the intended recipient to access it, and they change your website URL from http:// to https://.
With Hostinger, you don’t need to worry about setting this up separately, as all of our web hosting plans include free SSL/TLS certificates, giving you secure, encrypted connections right from the start. You can also choose to purchase additional certificates from trusted authorities like Let’s Encrypt if needed.

In addition to faster content delivery, content availability – or redundancy – is essential. This means ensuring your website stays accessible even during heavy traffic or hardware failures.
High traffic or server issues can cause downtime that most websites cannot afford. Since a CDN distributes traffic across multiple servers, it reduces the load on your origin server and prevents interruptions, keeping your site online and functional at all times.
If some servers experience outages, other operational servers automatically handle the traffic, ensuring continuous access for users.
Certain types of websites and online services gain the most from this CDN advantage, including:
Key elements to consider when browsing different CDN services are your budget and requirements, including anticipated needs in case of future growth.
Here’s is a list of features good CDN services should have:
Different CDN services offer various features and benefits. While some providers include basic domain name system (DNS) services for free, others offer premium DNS options that improve website performance, security, and traffic management by efficiently directing users to the nearest server.
Known to be one of the most reliable CDN service providers, Cloudflare falls into the latter category.
We offer an in-house CDN solution for clients subscribed to Business Web Hosting plans and above (excluding VPS). By enabling Hostinger CDN, you’ll gain access to edge servers distributed across Europe, Asia, North and South America, South Africa, and Australia.
While the exact steps to set up a CDN may vary by provider, here’s a general guide to get you started:
A CDN does more than speed up content delivery – it strengthens your overall web hosting strategy. When combined with a reliable hosting plan, a CDN improves user experience, reduces server load, and protects your site from cyber threats such as DDoS attacks.
To further boost your website’s performance, be sure to optimize other essential web hosting features, including hosting plans, website caching, and advanced security measures.
Together, these tools create a solid foundation for a fast, secure, and scalable website that can handle growing traffic and maintain high availability.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.