Jan 21, 2026
Aris S.
7min Read
Website caching is a method of improving page load time by storing temporary, ready-to-use copies of web content in a more easily accessible location. Its primary purpose is to minimize data transfer and reduce the load on the website’s host server.
Without caching, a visitor’s browser must request content like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and images from the website’s host server each time they visit. Caching speeds up this process by storing these resources closer to their location so that the browser doesn’t need to redownload all the required data from the host.
Website cache can be client- or server-side. Client-side caches are located in the user’s local device’s web browser, while the server-side ones are on a server specifically used for storing temporary data, like a content delivery network (CDN).
While important for website performance, caches can cause errors if not managed properly. Regularly purging them on the client and server sides will help avoid issues while keeping optimal page responsiveness.
Dive deeper into website caching, how it works, why it is important for your site, and how to properly clear it to avoid errors.
Caching makes a website more efficient by reducing the need to repeatedly fetch data from the server. The general process of serving cached pages involves several steps:
This system of hits and misses ensures that a website can serve pages quickly while still being able to update content when necessary.
Cached pages are served faster because the browser or server doesn’t need to request data directly from the origin server.
Instead of going through the entire process of retrieving and assembling a page from scratch with every visit, caching allows the website to load quickly by reusing previously stored data. This is especially impactful for static pages that rarely change.
For a user’s web browser, this means retrieving a page’s elements from their own computer’s local disk, which is significantly faster than waiting for a response from a remote server.
In addition to local storage, caches can reside in a CDN, a remote proxy server located close to the users.
Website caching is a critical part of a website optimization strategy because it directly impacts performance, user experience (UX), and even search engine rankings. It helps websites load faster and more efficiently, benefiting both the site owner and the visitor.
Here’s why caching is important:
Given its benefits, caching has become an essential feature of a website.
Depending on the storage location, there are different types of website cache, each useful in different situations and implemented at various points within a website’s delivery pipeline. In general, they fall into two broad categories: client-side and server-side.
Client-side caches store elements like HTML pages, CSS stylesheets, images, and multimedia content on the visitor’s local machine. They are also referred to as browser caches because they reside and are managed in the web browser.
Web browsers often automatically flush these caches to ensure you have the most up-to-date data about the visited website, but users can also manually purge them as needed.
Website owners can also manage them through server-side cache storage settings and HTTP headers like Expires and Cache-Control. Using versioning, like styles-3.css or /app-1a32c159b.js, site admins can force browsers to download new files even with long cache durations.
The main issue with browser caching is the potential for outdated content if assets have changed, but the client still stores the old temporary data. Also, storage space on the user’s device is limited.
Server cache is an umbrella term covering various caching types that store content on a remote location, such as the website’s host or a proxy server. Website owners control server cache without end-user input.
This caching type can store static content, such as HTML pages and images, and dynamic content generated by databases.
There are subtypes of caching that fall into the server cache category:
Clearing your website’s cache is vital to ensure users see the most up-to-date version of your site. While caching is designed to speed up loading speed, outdated data can sometimes cause visitors to see old versions of your website or issues like inaccessibility.
For WordPress websites, you typically clear the cache using a caching plugin like LiteSpeed Cache, WP Rocket, or WP Super Cache.
The steps to clear WordPress cache differ depending on the plugin you use. Typically, you can do this by accessing the plugin’s settings menu on the WordPress admin dashboard and selecting the type of cache you want to purge.
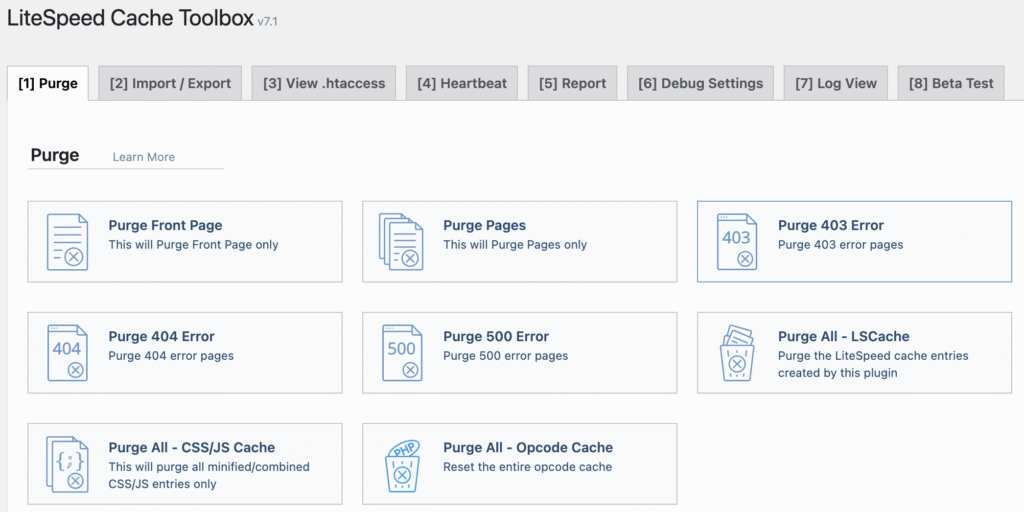
Commonly, you have the option to purge all caches or temporary data of specific pages or posts. For a more detailed guide, check out our tutorial on how to clear WordPress cache.
For non-WordPress sites, you can often clear the cache directly through your hosting control panel.
The steps for clearing your cache differ depending on your hosting provider and control panel. For example, cPanel users can do this by opening their websites’ data using the File Manager feature and deleting the cache folder, typically named tmp or cache.
Meanwhile, Hostinger web hosting solution users can use hPanel’s built-in Cache Manager feature:

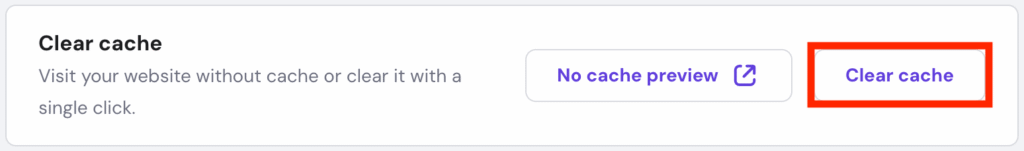
If you wish to clear a specific page’s cache on your Hostinger website, follow these steps:
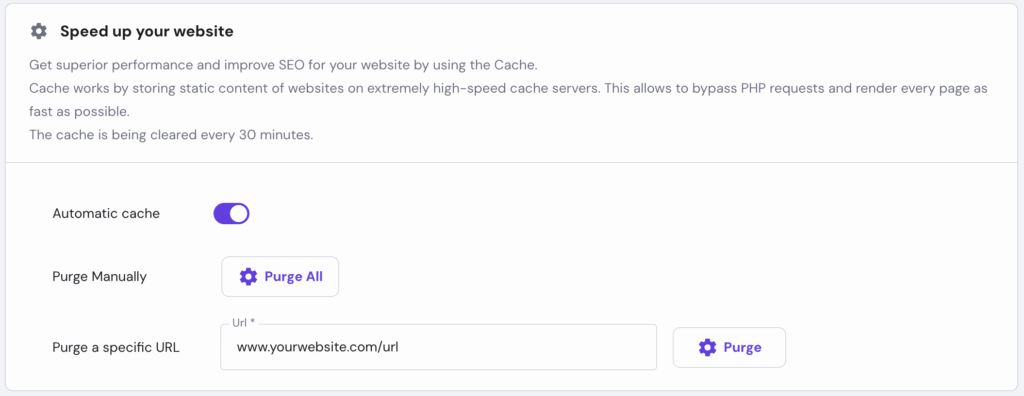
After enabling the Automatic cache feature, you won’t need to manually purge your website’s cache since our system will do it every 30 minutes. It ensures your pages remain up-to-date and helps avoid errors.

If updates aren’t showing, the culprit can often be the visitor’s cached files, not your server. Therefore, you may need to ask them to clear their own browser caches.
Visitors can clear their browser’s cache manually through its settings, typically from the History menu. You can find a complete guide in our How to clear browser cache tutorial.
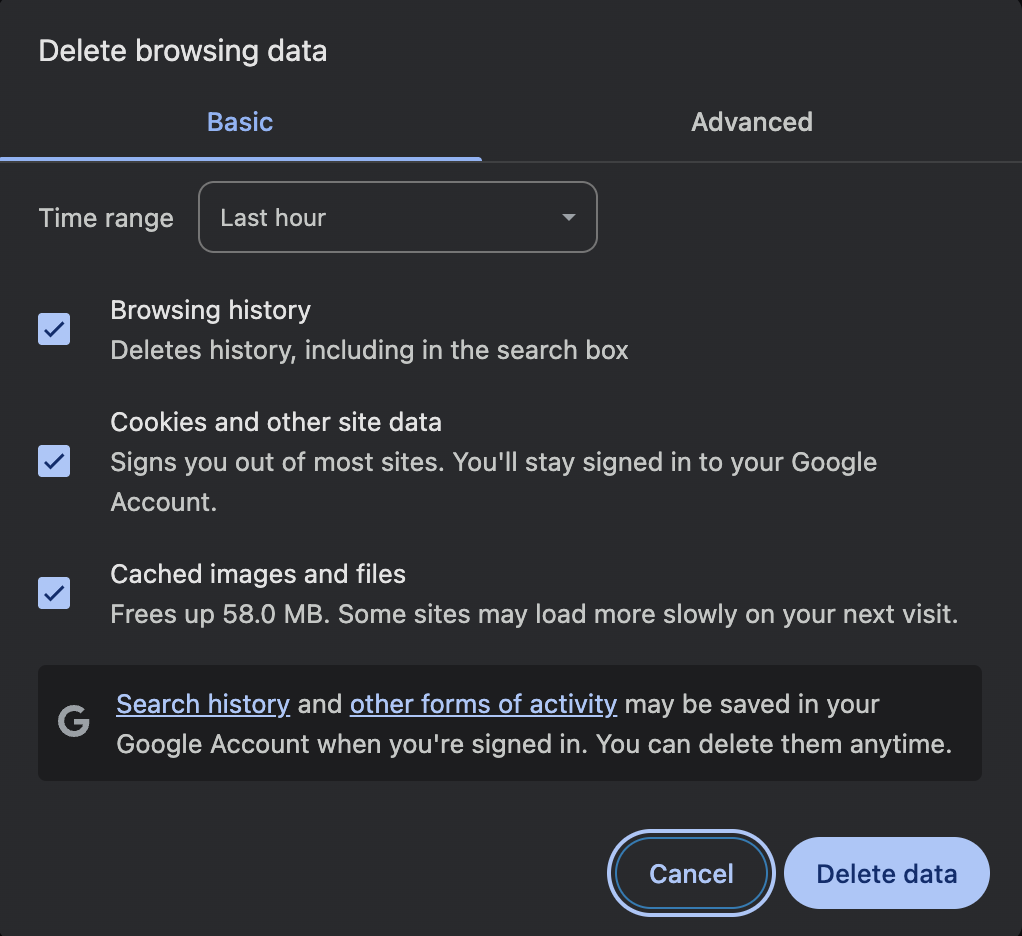
Alternatively, users can perform a hard reset to force the browser to load the visited web page directly from its origin server.
To try it out, open your web browser and press Ctrl + F5 if you use Windows or Cmd + Shift + R if you use macOS.
Caching delivers faster load times, stronger SEO signals, better UX, and higher conversion rates. Treat it as a base layer in your optimization plan, then measure the difference.
To see the direct impact of caching, you can use a website speed test tool like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights. Try running a test before and after clearing your site’s cache to see the difference in load times and other key metrics.
Caching won’t fix a bloated site by itself, but it will give you instant, compounding gains. However, caching is a key component of a broader strategy in building a fast and user-friendly website.
Beyond caching, other strategies can further optimize your site’s performance and offer bigger benefits. For example, optimizing images and assets on your page enables visitors’ web browsers to load them quickly.
Also, minify your site’s CSS and JavaScript to allow the host server to serve user requests more efficiently. In addition, store and distribute static data using a CDN to speed up your website for global audiences.
Make caching your first move for speed, as it delivers quick, measurable wins. Then keep the momentum: test, tune, and layer in image optimization, leaner scripts, and a CDN for sustained gains in SEO, UX, and conversions.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.