Dec 22, 2025
Jordana A.
5min Read
A URL redirect is a server function that sends users from one URL to another, typically using HTTP status codes like 301 or 302 redirects.
Also known as domain forwarding, a simple URL redirect helps direct visitors to the correct website. This helps prevent duplicate content, allowing you to change your site’s structure without impacting rankings.
Domain redirection is a straightforward process:
When done correctly, a URL redirect can boost search engine optimization (SEO) by passing link authority from old pages to new ones. This helps maintain rankings and prevents broken links, which helps improve user experience.
The result? Little to no traffic loss during migration.

To set up a URL redirect, you must meet the following requirements:
This section will cover four domain redirection methods, starting with the most flexible. Choose the one that best suits your needs.
This method works best for configuring advanced redirects. It lets you implement complex redirect rules and manage multiple redirects, giving you more control over your website’s URL structure.
The real advantage of using the .htaccess file is its flexibility. It lets you manage redirects based on specific conditions, like certain URL patterns or user agents, making it ideal for complex needs.
You can use a File Manager or FTP client to locate and modify the .htaccess file. In the following steps, we’ll explain how to do it hassle-free with Hostinger’s File Manager:
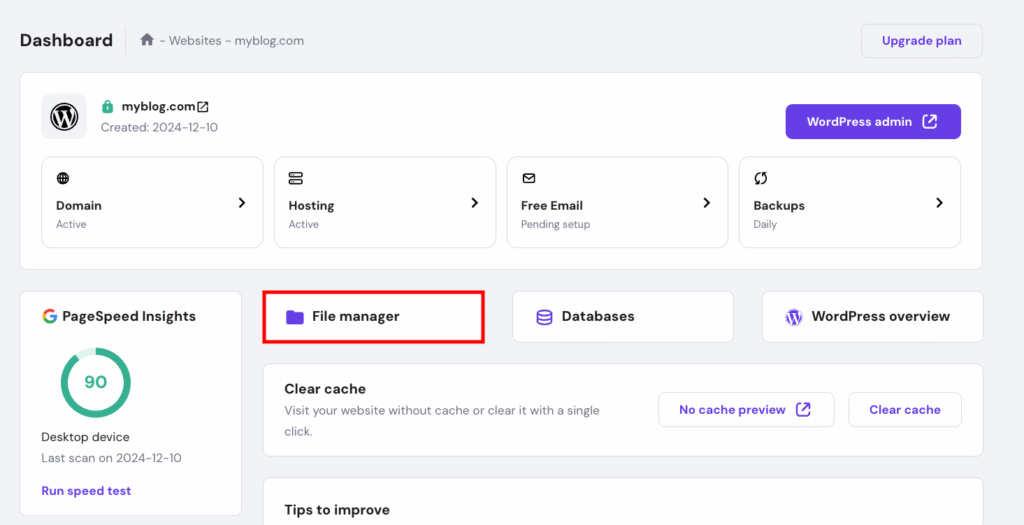
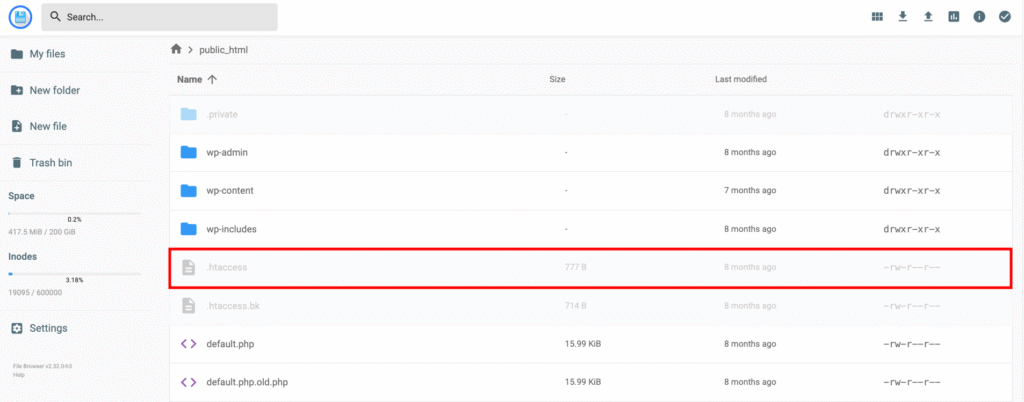
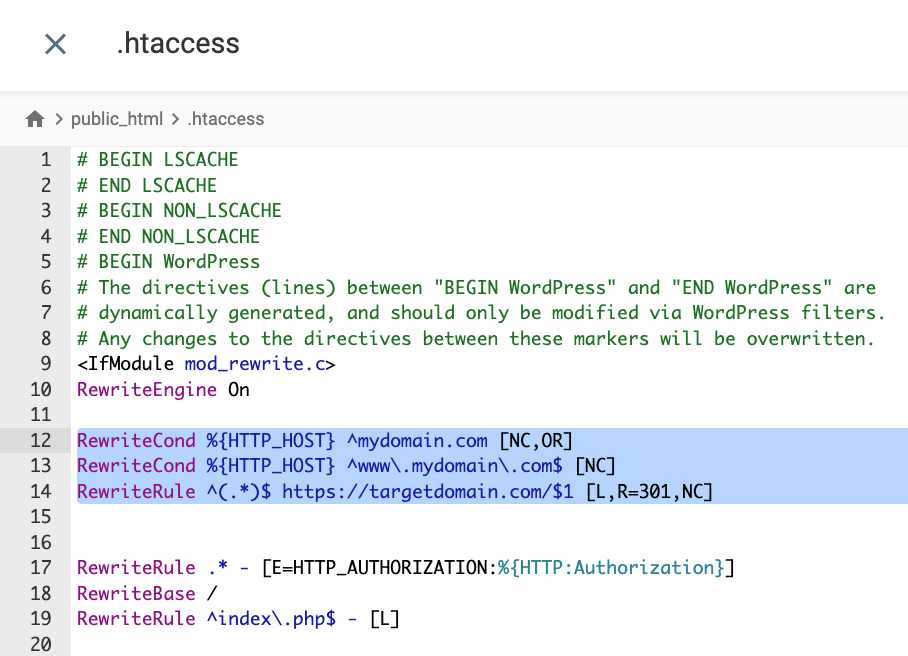
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^mydomain.com [NC,OR]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www\.mydomain\.com$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://targetdomain.com/$1 [L,R=301,NC]Remember to replace mydomain.com and targetdomain.com with the correct web addresses.
To configure 302 Temporary Redirect, replace the R’s value with 302 instead.
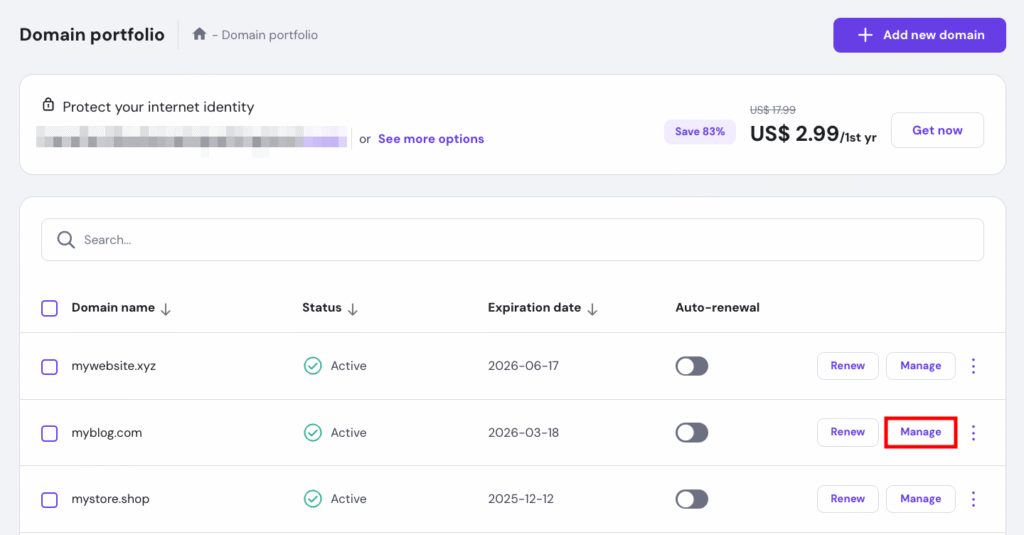
Most hosting providers allow users to set up redirects through domain settings, making this method the easiest and most user-friendly option. Here’s how to redirect a domain through Hostinger‘s hPanel:
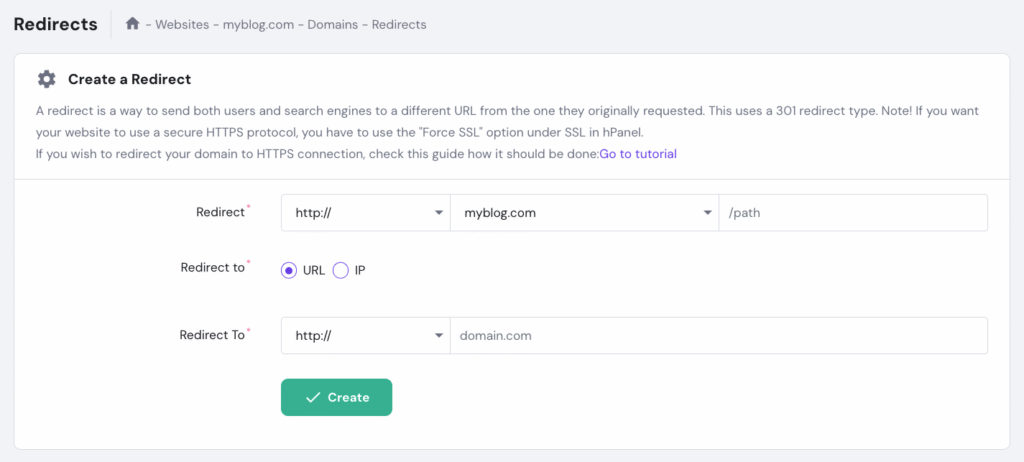

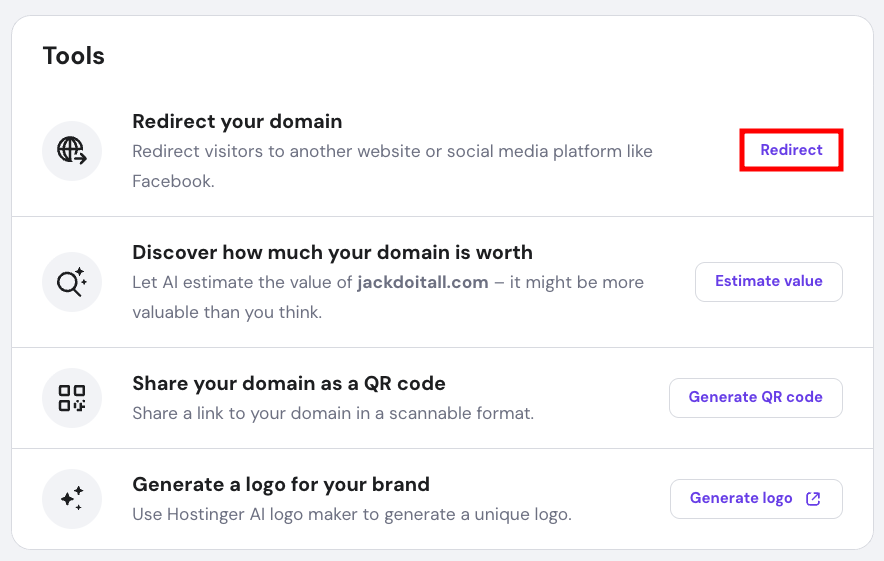
If you don’t have a hosting plan, you can still redirect your domain using Hostinger’s domain forwarding feature. While technically a form of forwarding, it functions like a redirect by sending visitors from your domain to another website.
Here’s how:
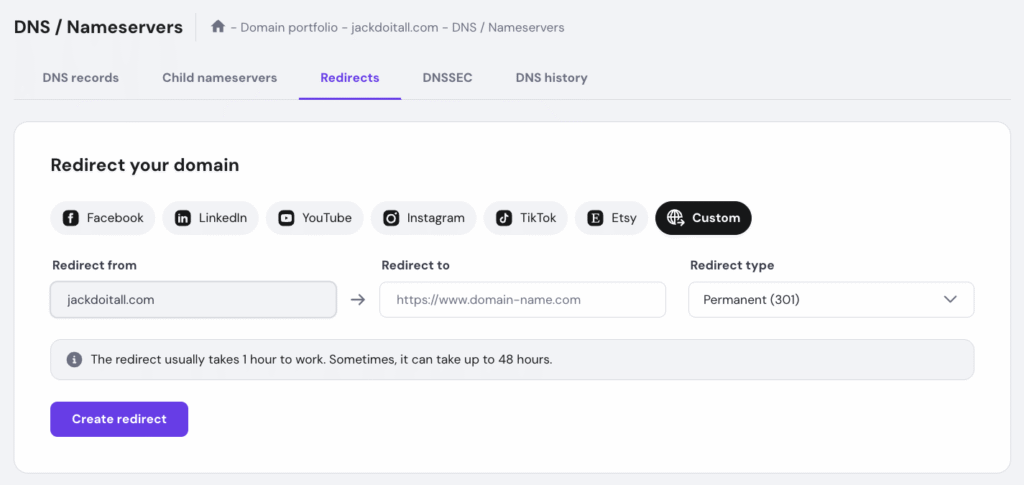
The domain name system (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses. When a user enters a domain name into their browser, the DNS system finds the matching IP address for that domain and directs the user to that website.
To redirect domains with DNS records, create CNAME or A records linking the old domain to the new destination’s domain or IP address.
Here’s how to do it using a Hostinger account:
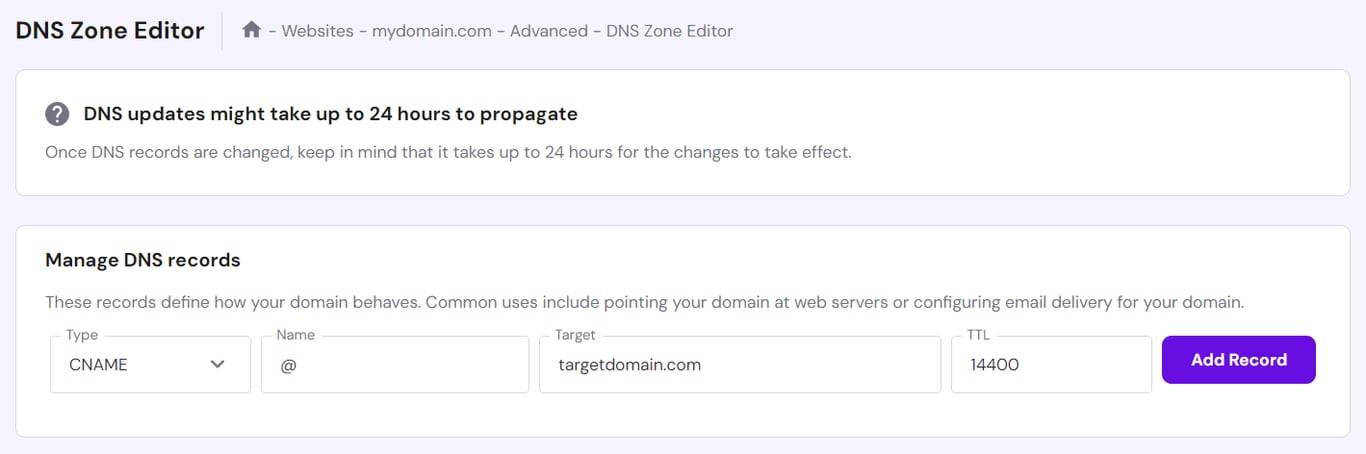
DNS propagation takes up to 24 hours to complete. Once it’s done, the old domain will redirect visitors to the new web address. You can monitor your propagation status by location for domains using Hostinger nameservers.
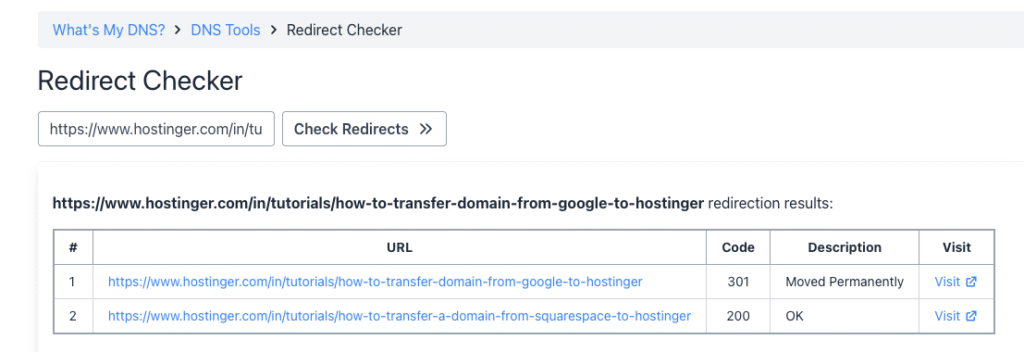
After setting up the redirect, test it by entering your old domain in different browsers and devices to make sure it leads to the correct URL. You can also use free online tools like What’s My DNS or WhereGoes to verify it’s working properly.
If the domain redirect doesn’t work, try the following troubleshooting tips:
If the error persists, contact your hosting provider or domain registrar for assistance. Hostinger’s Customer Success team is available 24/7 to assist you with any redirection issues.
There are two main types of redirects: 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary). Not every situation benefits from a 301 redirect domain setup, so it’s important to understand which type to use to protect your SEO performance.
Also known as a permanent redirect, 301 redirect is commonly used when moving a website to a new domain. It passes on link equity and maintains links coming from other websites, allowing you to retain the old domain’s search ranking. This redirect type is also unmasked, meaning visitors will see the URL change in their browsers.
Want to set up 301 redirects in WordPress? Check out our step-by-step guide covering all the available methods.
A 302 redirect is a temporary redirection method often used in the short term for purposes like heavy website maintenance or A/B testing. Although it won’t pass on SEO value to the target URL, visitors will still see the URL change in their browsers.
A masked redirect or URL frame shows the destination content while retaining the original URL in the browser’s address bar. This redirection type creates the illusion that the content is on the original domain when it’s actually elsewhere.
Although many marketers use masked redirects for affiliate marketing or branding purposes, they can negatively impact SEO in the long run. Search engines might identify them as duplicate content, which can harm the destination domain’s SEO authority.
For these reasons, not all hosting providers and domain registrars support masked redirects. That said, you can edit the .htaccess file to set up a masked redirect manually.
Redirecting domains is a common practice during website rebranding or restructuring, domain consolidation, or protocol change. Redirects allow visitors to access the correct website, even if they enter the wrong web address or click on an outdated link. It also helps preserve SEO authority and prevent broken links.
You can redirect multiple domain names to the same website. It’s also possible to redirect each one to a specific page on the destination domain.
When done correctly, redirects don’t hurt your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts. In fact, 301 redirects pass most of a page’s link equity to the new URL, making them essential for maintaining rankings when moving content, changing domains, or fixing broken links.
When it comes to SEO and redirects, problems usually happen only if they’re excessive or set up incorrectly. Too many redirects can slow your site and confuse search engines, which may harm SEO. The key is to use them sparingly, point to the most relevant pages, and include them in your regular SEO audit process to keep everything running smoothly.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
April 24 2017
Hello! Is the hostinger redirect is a 301 type? Thank you!
April 25 2017
Hello, Yep, that's correct. Of couse, you can use 302 redirect if you wish.
April 29 2020
Has the menu system changed? I don't see this menu.
April 30 2020
Hey, Stuart, in order to find this menu, go to your hPanel -> press Manage on the domain where you will be adding Redirects -> Scroll down a bit and you will find the Redirects option.
May 23 2021
Experiencing the same problem as Stuart, I can't see this menu at the end of the "Domain Overview" page or anywhere else
May 27 2021
Hi Alex, To find the menu, go to your hPanel -> press Manage (on the domain where you will be adding Redirects) -> Scroll down a bit and you will find the Redirects option.
July 28 2021
Where would I look to see if a meta refresh is set up? I've checked the site's header code and also the header.php file but I am stumped. The issue is that I have a domain redirected but I can't find where it's redirect is set up. Checked domain DNS (not set up), checked add on domain and cPanel redirects (also not setup), checked .htacess and index.php (not there) so now I am trying to see if a meta refresh is set up but I can't find that either. It seems possible though as it takes at least 4 seconds to wait for the redirect to happen. Thanks for any help
September 17 2021
Hi Tess, for meta refresh, check the section of your page using Inspect Tool. Additionally, make sure to look through parked domains section on your control panel and the database of your website to see if you can find the redirect. Good luck!
August 19 2021
When you redirect via your cpanel, does the old site have to remain active for a period of time until this redirect propagates to the internet, or does it happen immediately where you can take the old site down right away??
September 20 2021
Hi Dave! If you set the redirect well, the redirection from control panel should be immediate. However, if the old website goes down (e.g. domain expires, it's removed from a hosting plan, etc.), the redirect will disappear. This doesn't mean that you cannot remove the old website's files and associated data, you can surely do that as they're not reflected online anymore - just make sure to keep the domain name alive and added to your hosting plan :)
June 17 2022
How can I use redirect websites to get backlinks?
July 14 2022
Hey! If you wish to redirect website while maintaining the backlinks, you would need to use 301 redirect ?
June 25 2022
I want to use url frame redirection option how to do that
July 01 2022
If you wish for your website's content to be reflected on another domain without creating a redirect from one domain to another, you can simply park the domain. You can learn how to do it here! ?
June 11 2023
i've redirected my domain using the 301 redirect in the panel and when i access the root of the domain, it correctly bounces to the new url. but if i click on a previously indexed page from google, it gives a 404 instead of redirecting to the new domain. how do you fix it so that ALL URLs from the old domain are sent to the new domain? thanks!
September 02 2023
Hello. I'm trying to redirect not only the main domain but also all the pages under that domain. I tried using a path of "/*" to catch everything but it does not work. What can I use to establish a wildcard redirect?
September 08 2023
Hello there. I would highly suggest trying to set up the redirects via Cloudflare using their bulk redirects feature.
October 23 2023
I have several domains with you. Two domains have hosting packages and the third doesn't. One of my hosting packages allows subdomains. I set one up and uploaded a website to it. The subdomain site displays correctly. I've redirected the domain (the one without a hosting package) to the subdomain. Everything works great except I can't mask the redirected URL. When I set the redirect my only type options were 301 and 302. I need the URL FRAME type to mask the transfer URL. Remember there is no hosting attached to the domain so I can't mask with HTML code. So how do I mask the domain?
November 07 2023
Hi there! I apologize URL masking without hosting is not available in Hostinger. If you want to mask the URL, one possible solution is to consider purchasing a hosting package for the domain that you want to redirect. This will allow you to set up the necessary configurations and use HTML code to mask the URL ?