Nov 19, 2025
Brian & Ariffud M.
6min Read

When you move or delete WordPress content, broken links damage your SEO and frustrate users unless you set up 301 redirects in WordPress.
These redirects automatically route visitors from outdated URLs to the correct pages, preserving your search rankings and eliminating 404 errors.
Three of the most effective methods to set up 301 redirects in WordPress are:
A 301 redirect in WordPress is a permanent forwarding code that tells browsers and search engines that a web page has moved to a new URL.
When a user or search engine crawler tries to access the old URL, the server responds with a 301 Moved Permanently status code and automatically routes them to the new location.
This process is crucial for user experience and SEO because it prevents 404 Not Found errors and passes link equity (ranking power) from the old URL to the new one.
You should create 301 redirects to preserve SEO value, maintain a smooth user journey, and effectively manage your site’s architecture.
Specifically, these redirects help you:
You should use 301 redirects when a page has moved permanently to a new URL to transfer link equity and preserve SEO value.
Setting up a redirect using a WordPress plugin typically involves the following steps:
Popular WordPress redirection plugins are AIOSEO and 301 Redirects. AIOSEO is a comprehensive SEO suite that includes redirection in its premium plans, while 301 Redirects is a dedicated, lightweight tool often used specifically for this one function.
Setting up a 301 redirect using AIOSEO requires purchasing the AIOSEO Pro or Elite version.
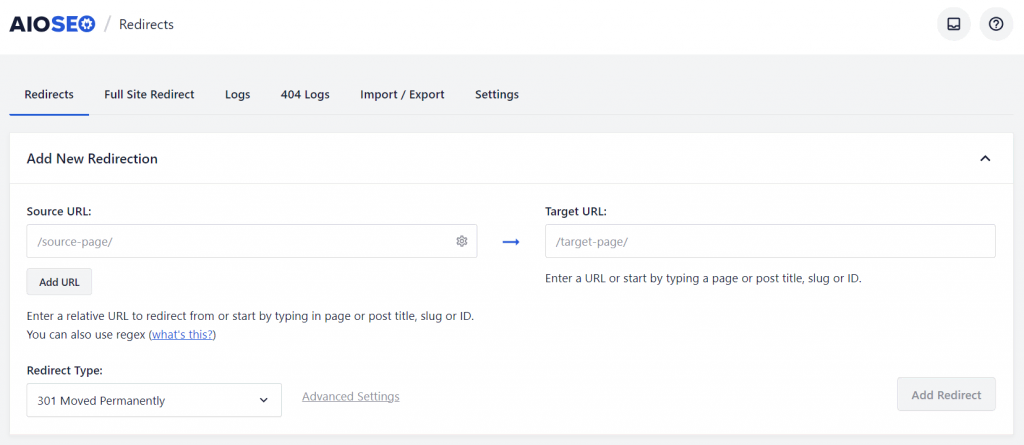
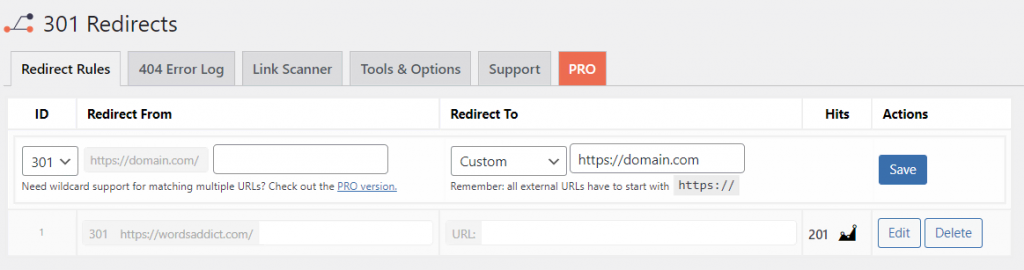
To set up a 301 redirect using the 301 Redirects plugin, follow these steps:
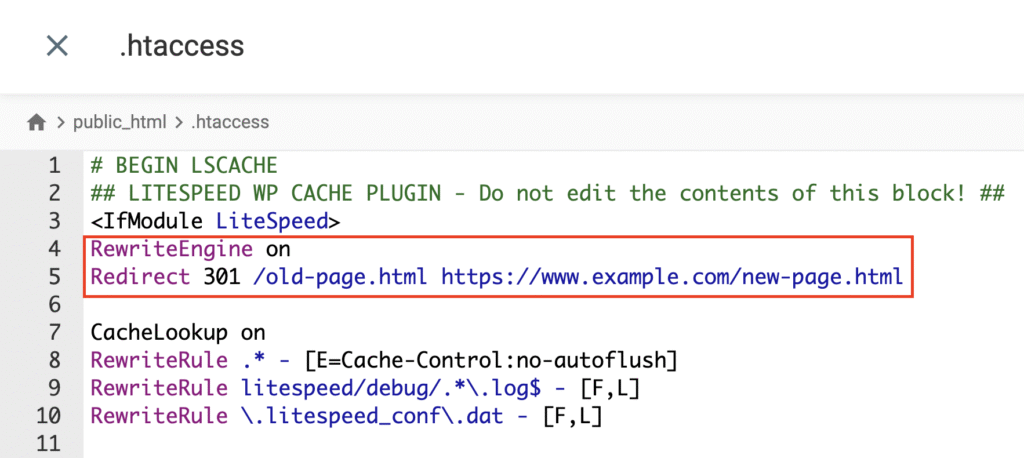
To create a 301 redirect manually by editing the .htaccess file, you must access your server files directly. This method is faster for the server as it processes the redirect before loading WordPress.
Important! This method only works on Apache and LiteSpeed servers. Some WordPress hosting providers use NGINX servers, which don’t have .htaccess files. If you don’t see this file in your root directory, check your hosting control panel for built-in redirect tools instead.
Redirect 301 /old-page.html https://www.example.com/new-page.html
To implement a 301 (permanent) redirect using a PHP script, use the header() function to send the correct HTTP status code and the new location.
The PHP redirect method is useful if you want to perform a redirect from a specific template file or logic within your theme.
<?php
// Permanent 301 Redirect
header("HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently");
header("Location: https://www.example.com/new-target-url");
exit();
?>Please note that the exit() function is critical. It stops script execution after the redirect, preventing any additional code from running that could interfere with the redirect.
For Hostinger WordPress hosting customers, you can set up a 301 redirect in hPanel safely without manual coding.
This server-level approach is simpler than editing .htaccess manually and includes error checking to prevent syntax issues.
For a detailed walkthrough, read our guide on how to set up a redirect in Hostinger.
Other types of redirect codes include HTTP 302 (Found), 303 (See Other), 307 (Temporary Redirect), and 308 (Permanent Redirect), as well as non-HTTP methods like meta refresh and JavaScript redirects.
These codes serve specific technical purposes distinct from the standard 301.
A 302 redirect is a temporary redirect that signals a web page has moved to a different URL for a short time.
Search engines follow 302 redirects but treat them differently than 301s – they may temporarily index both the old and new URLs and won’t transfer full link equity to the new location, since the move is expected to be reversed.
Use this when you are temporarily updating a page or running a brief A/B test.
A 303 redirect is an HTTP status code that means “See Other.” It instructs the browser to use a GET request to a new URL to retrieve the resource, rather than using the original method (like POST).
It is commonly used after a successful form submission (like a credit card payment) to prevent the browser from re-submitting sensitive data if the user refreshes the page.
A 307 Temporary Redirect is an HTTP status code that tells a browser to temporarily go to a different URL to find the requested resource, without changing the request method.
Unlike 302, a 307 redirect guarantees that the method (POST or GET) remains the same. This is intended for temporary alterations where you plan to return the content to its original URL soon.
A 308 redirect is a permanent redirect similar to 301, with one key difference: it preserves the HTTP request method.
If the original request was a POST, it remains a POST (unlike 301, which converts it to GET). This is useful for API endpoints and form submissions that have permanently moved to a new location.
Fixing broken links with 301 redirects is a critical first step in technical site maintenance. Once your URL structure is secure and users and search engines can see the right content without hitting dead ends, the next priority is improving your site’s visibility and rankings.
You should now focus on optimizing your content, page speed, and site architecture to drive more organic traffic.
To move forward, explore our complete guide on WordPress SEO tips, which shows you how to master basic SEO steps, optimize on-page elements like titles and images, improve technical factors like site speed, and maintain your site’s performance over time.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.