Dec 26, 2025
Ariffud M.
7min Read
Creating an n8n workflow involves connecting apps and services through nodes to automate tasks. The process starts with a trigger that initiates a sequence of action nodes to manipulate data and execute commands.
While getting a simple workflow running is easy, creating one that’s reliable, secure, and easy to maintain requires more thought.
Implementing n8n best practices is essential for building dependable automations that prevent errors, protect sensitive data, and save you significant time on troubleshooting.
Here are proven best practices for building successful n8n automations:
A modular design involves breaking down complex, monolithic workflows into smaller, interconnected sub-workflows. Instead of having one giant workflow with dozens of nodes, you create several smaller ones, each responsible for a single task.
This approach is essential for scalability and makes your automations much easier to debug and maintain.
You can implement this in n8n using the Execute Sub-workflow node. This node lets one workflow trigger another, passing data to it and receiving results in return.
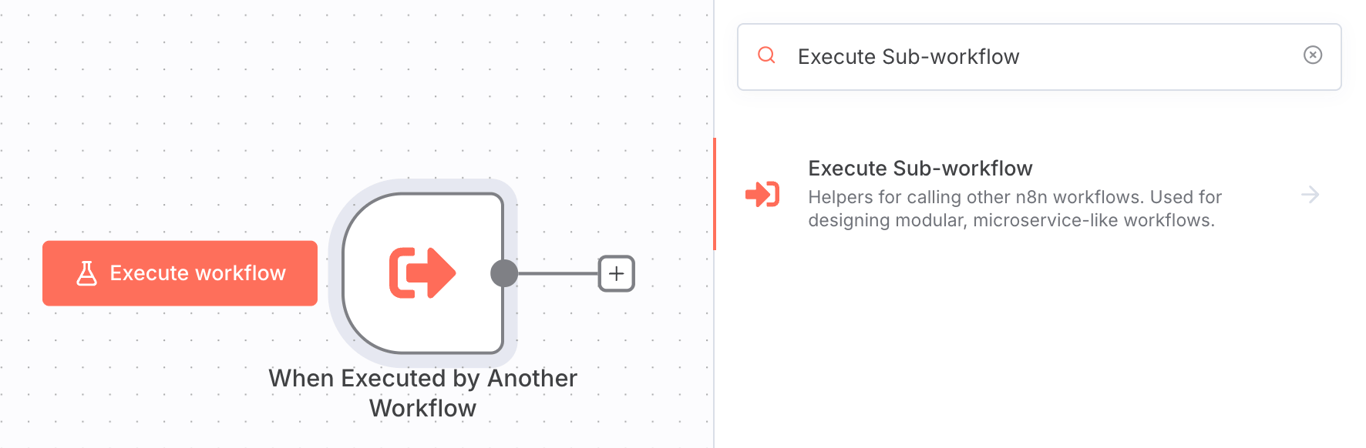
For example, imagine a workflow that processes new customer orders. Instead of building everything into one flow, you could create separate workflows for:
The main workflow would call each of these sub-workflows in sequence using the Execute Sub-workflow node. If the email notification fails, you only need to debug the small email workflow, not the entire order processing system.
Never assume the data entering your workflow is perfect. Incoming data from webhooks, forms, or other applications may be missing fields, be incorrectly formatted, or contain unexpected values.
Validating data at the beginning of your workflow prevents errors that can be difficult to trace later.
The easiest way to validate data is using the IF node. This node allows you to verify that the data meets specific conditions before allowing the workflow to proceed. You can check if a field exists, is not empty, or matches a particular format.
For instance, if a workflow triggers from a new user signup, you should add an IF node right after the trigger to check if the email field is not empty and contains an @ symbol.
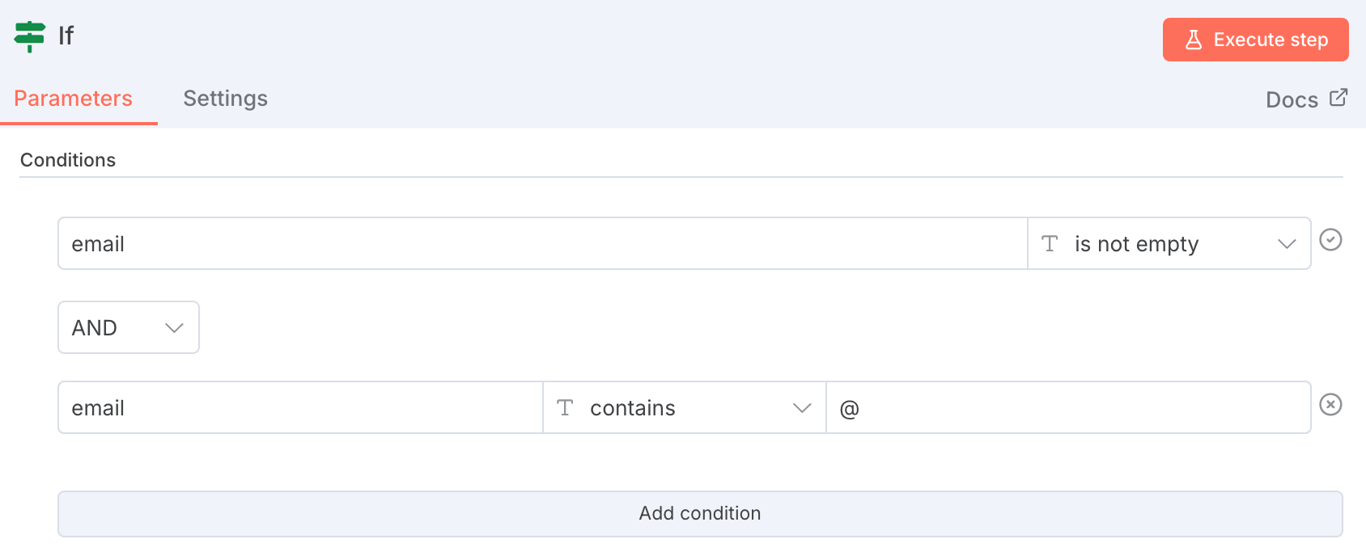
If the data is invalid, you can stop the workflow or send a notification to investigate the issue.
Workflows can fail for several reasons. An API might be temporarily unavailable, a database connection could time out, or data may arrive in an unexpected format.
Proper error handling prevents these issues from crashing your entire automation. A well-designed workflow should anticipate potential failures and manage them gracefully.
n8n provides several tools for error handling. First, many nodes have a Settings tab where you can enable Retry on Fail. This automatically retries a failed action, which often resolves temporary issues like network glitches.
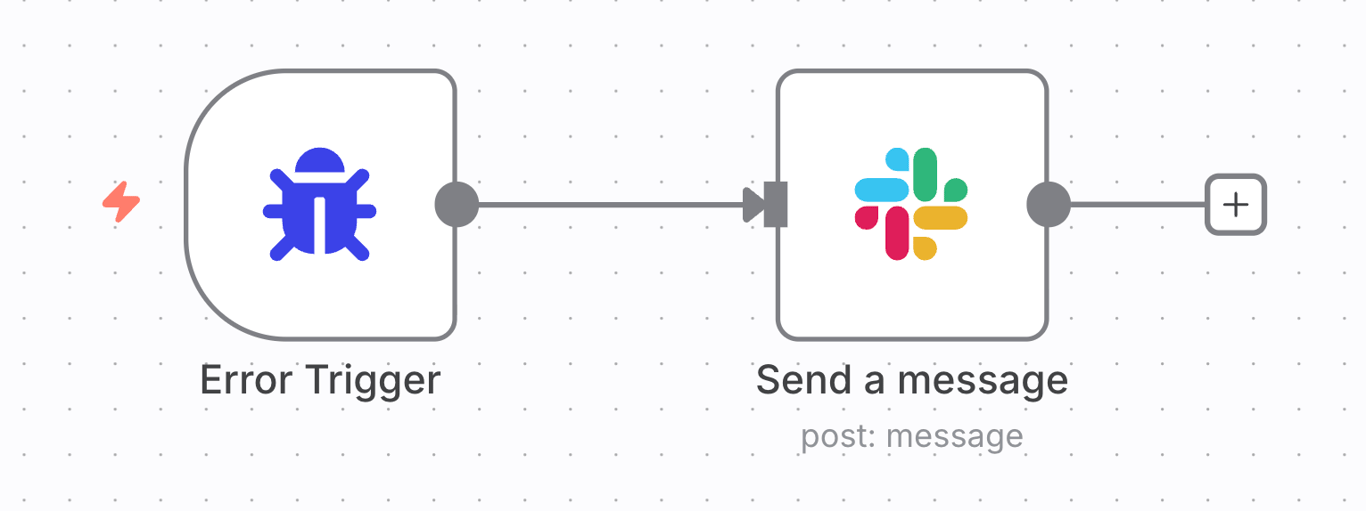
For more complex error handling, use an Error Trigger node. This lets you create a separate workflow that runs only when another workflow fails.
You can configure this error workflow to send you a detailed alert via Slack or email, log the error to a spreadsheet, or even attempt a corrective action. This turns an unexpected failure into an actionable notification.
A workflow that seems obvious today can be confusing three months from now, especially when you need to make changes. Documentation provides context, explaining the “why” behind your logic. It’s essential for team collaboration and for your future self.
n8n has a built-in Sticky Note feature that lets you add comments directly on the workflow canvas.
Use these notes to explain complex parts of your workflow, describe the data structure at a specific point, or leave reminders about why you chose a particular setting.
It’s good practice to add a sticky note at the beginning of every major logical section of your workflow.
For example, in a data processing workflow, you might add notes like “Fetching raw data from API,” “Filtering for active users,” and “Formatting data for database insertion.”
Your workflows will often need to connect to various services using API keys, tokens, or passwords. Hardcoding these secrets directly into your nodes is a significant security risk.
If you share your workflow or if someone compromises your account, a bad actor could expose your credentials.
To prevent this, always use n8n’s built-in credentials manager. When you configure a node that requires authentication, n8n will prompt you to create new credentials.
This stores your sensitive information in an encrypted format, separate from the workflow logic itself. To secure the n8n automation platform, it references these credentials by an ID, so the actual secret is never visible in the workflow’s code.
For instance, when setting up a Google Sheets node, instead of pasting your API key into a field, n8n will prompt you to connect your Google account.
n8n then handles the OAuth2 flow – a process that grants access without sharing your password – and stores the tokens securely.
Not everyone on your team needs the ability to edit or execute every workflow. Unrestricted access can lead to accidental changes to critical production workflows or unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Implementing proper access control is a key element of securing your automation environment.
n8n offers user management features that let you assign roles and permissions to different users. For self-hosted instances, you can configure owner, editor, and viewer roles.
For more granular control, n8n’s enterprise plans offer role-based access control (RBAC). You can define custom permissions for who can create, modify, or execute specific workflows.
Follow the principle of least privilege: only grant users the minimum level of access they need to perform their jobs.
For example, a team member who only needs to monitor workflow results should have view-only access, not the ability to edit the workflow.
Activating a new workflow without testing is like deploying code to production without running it first.
A minor misconfiguration can lead to significant problems, such as sending incorrect emails to thousands of customers or deleting the wrong data from a database. Testing in a safe environment is a non-negotiable step.
One effective strategy is to create a duplicate of your production workflow for testing. In this test version, replace production data sources with sample data.
For example, instead of writing to your main customer database, have the workflow write to a test table. Instead of emailing actual customers, send the emails to your own inbox.
If you have a self-hosted setup, you can deploy n8n on a separate staging server dedicated to testing. This completely isolates your testing environment from production, providing the highest level of safety.
Once you’ve confirmed the workflow runs as expected, you can deploy it to your production instance.
The world of APIs and software is constantly evolving. A service your workflow relies on might update its API, or developers could discover a security vulnerability.
Keeping your n8n instance and its nodes up to date ensures you have access to the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches.
In contrast, neglecting updates can leave your system vulnerable and may cause nodes to stop working if they become incompatible with the services they connect to.
The n8n team releases updates frequently, including performance improvements and support for new apps and services.
If you use n8n Cloud, the platform updates automatically for you. For self-hosted users, it’s important to check for new n8n versions and apply updates regularly.
As you refine and improve an automation, you’ll make many changes. Versioning is the practice of saving distinct copies of your workflow at different stages of development.
This creates a history of your changes and provides a safe method for rolling back to a previous version if an update causes issues.
While n8n has a built-in version history for workflows, a simple and effective manual method is to duplicate your workflow before making significant changes.
You can rename the cloned workflow with a version suffix, like Customer Onboarding_v2 or Daily Report_v2.1.
This practice is invaluable when experimenting with new logic, especially as you iterate on concepts from a structured n8n tutorial.
If your changes don’t work out, you can delete the new version and revert to the last known good one without having to manually undo your work.
When you only have a few workflows, it’s easy to remember what My Workflow 3 does. But as your collection grows, generic names become harder to manage.
Using clear, descriptive names for both your workflows and the nodes within them is crucial for maintaining consistency and clarity.
A good workflow name should describe its purpose, such as Sync New Customer Contacts to Postgres DB or Generate Weekly Social Media Report. This immediately tells you what the automation does without the need to open it.
The same principle applies to nodes. Instead of leaving nodes with default names like HTTP Request, rename them to describe their specific actions, such as Get User Data From API or Post Message to #sales Channel.
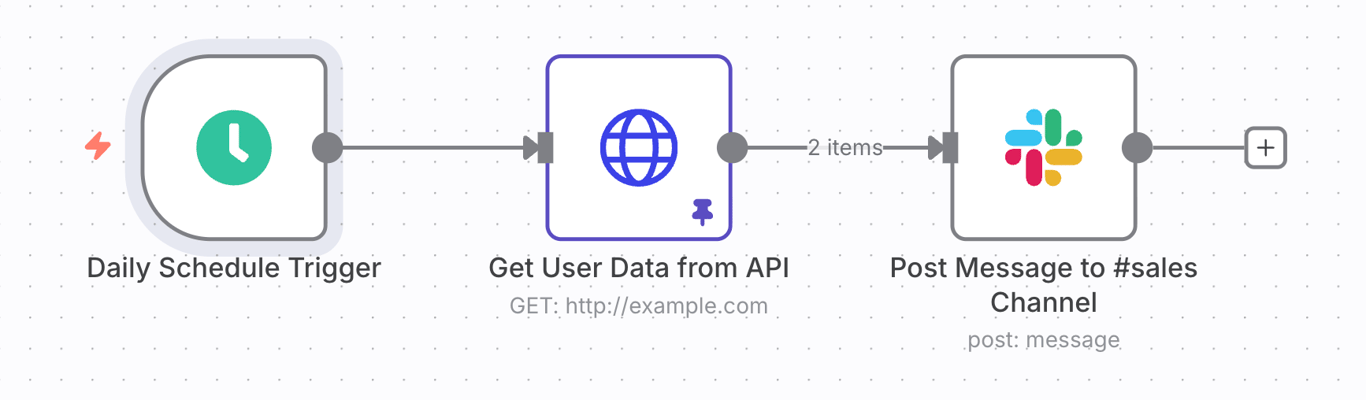
This makes the flow of logic on the canvas much easier to follow at a glance.
Seeing best practices in action makes them easier to understand.
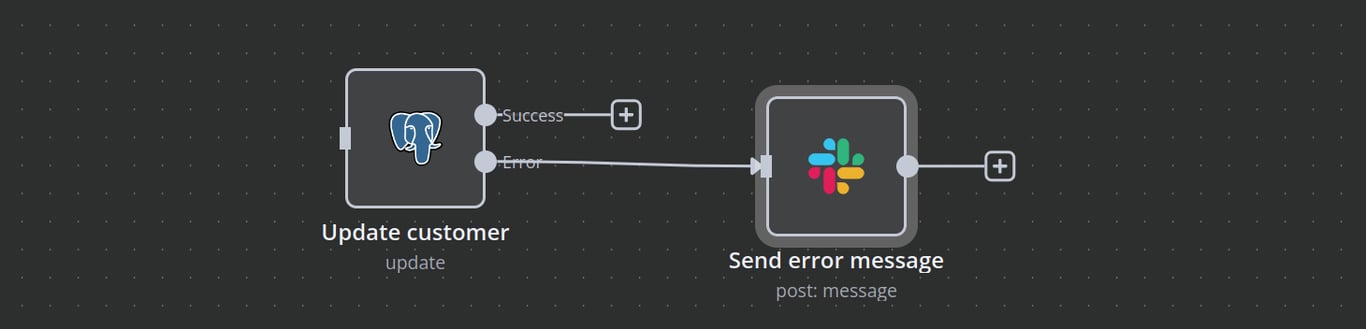
For example, a customer data synchronization workflow keeps CRM and database records aligned. It applies data validation by using an If node to check if a customer record already exists before creating a new one.
The workflow also includes robust error handling, using On Error settings to send an immediate Slack or email alert if the database update fails.
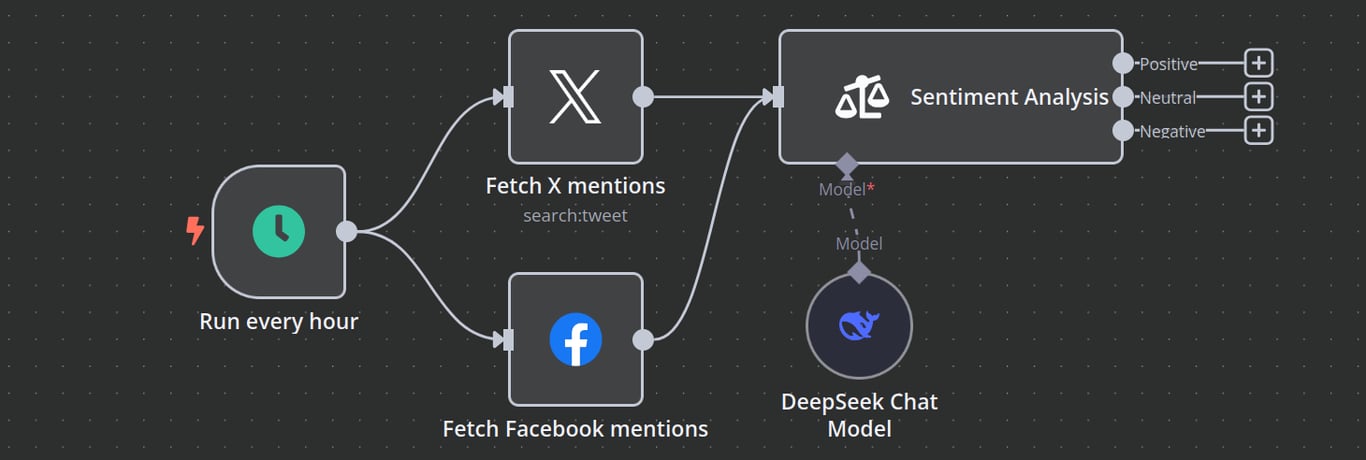
Social media automation workflows involve breaking down a complex process into smaller, dedicated tasks, such as content scheduling, engagement tracking, and analytics reporting.
For instance, an engagement tracking workflow applies logic by using AI sentiment analysis to categorize social media mentions as positive, neutral, or negative before sending them to the appropriate team via Slack or email.
For more inspiration, explore other workflow examples that showcase creative and efficient automation solutions.
No, you don’t always have to create a workflow from scratch. Building a high-quality workflow that applies all these best practices is much easier when you start with a pre-built template.
Using a template from n8n’s official website is a great way to save time and learn how to structure workflows effectively. These pre-built solutions often already incorporate best practices like error handling and proper credentials management.
You can import a template and customize it to meet your specific needs, giving you a significant head start. Before building your next automation, check out the best n8n templates to see if someone has already solved a similar problem.

All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.