Oct 16, 2025
Ariffud M.
4min Read

The Linux shutdown command is used to power off, reboot, and schedule these tasks on Unix-based systems, offering a flexible way to manage system downtime.
You can use shutdown -h now to power off your machine immediately or shutdown -r now to reboot it. To schedule a shutdown, use an absolute time, like shutdown 22:30, or a relative time, such as shutdown +15.
Using the shutdown command is critical for system security. It provides a controlled way to apply crucial updates and security patches that require a reboot, all while warning logged-in users to prevent data loss.
The shutdown command lets you safely power off, reboot, and halt your system by communicating with systemd to initiate a specific target, like poweroff.target or reboot.target.
This process properly terminates all running services and notifies logged-in users.
The basic syntax for the shutdown command is:
shutdown [OPTION] [TIME] [MESSAGE]
Here’s a breakdown of its components:
To prevent new logins as a shutdown approaches, the command creates the /run/nologin file five minutes before the system goes down, but only if a time argument is used.
The shutdown command works similarly on both Ubuntu and CentOS. To run these commands on a virtual private server (VPS), you’ll first need to connect to it via an SSH client like PuTTY. We have a tutorial that explains how to use PuTTY to access your VPS.
To set a one-minute timer before shutting down your system, use the basic command:
shutdown
To shut down your system immediately, use the now argument:
shutdown now
To schedule a shutdown for a specific time, use the hh:mm format. For example, to shut down at 10:30 PM, you would use:
shutdown 22:30
To schedule a shutdown for a set number of minutes from now, use the +m format. The following command will shut down the system in 15 minutes:
shutdown +15
Finally, to display a warning message for any logged-in users, add your message after the time argument. For instance:
shutdown +15 "The server is shutting down for maintenance in 15 minutes. Please save your work."
To restart your VPS, add the -r (reboot) option to the shutdown command. This schedules a reboot for one minute in the future, giving you time to save your work.
shutdown -r
To reboot immediately, combine the -r option with the now argument:
shutdown -r now
You can also schedule a reboot for a specific time or after a particular duration:
shutdown -r 22:30
shutdown -r +15
To include a message with a planned reboot:
shutdown -r +15 “The server is rebooting in 15 minutes to apply updates.”
Here are a few other command options you should know:
For example, to halt the system, use:
shutdown -H
To cancel a scheduled shutdown in Linux, use the shutdown -c (cancel) command. This will immediately stop your previously scheduled shutdown or reboot task.
shutdown -c
Please note that you can’t use this command to cancel an immediate action initiated with +0 or now.
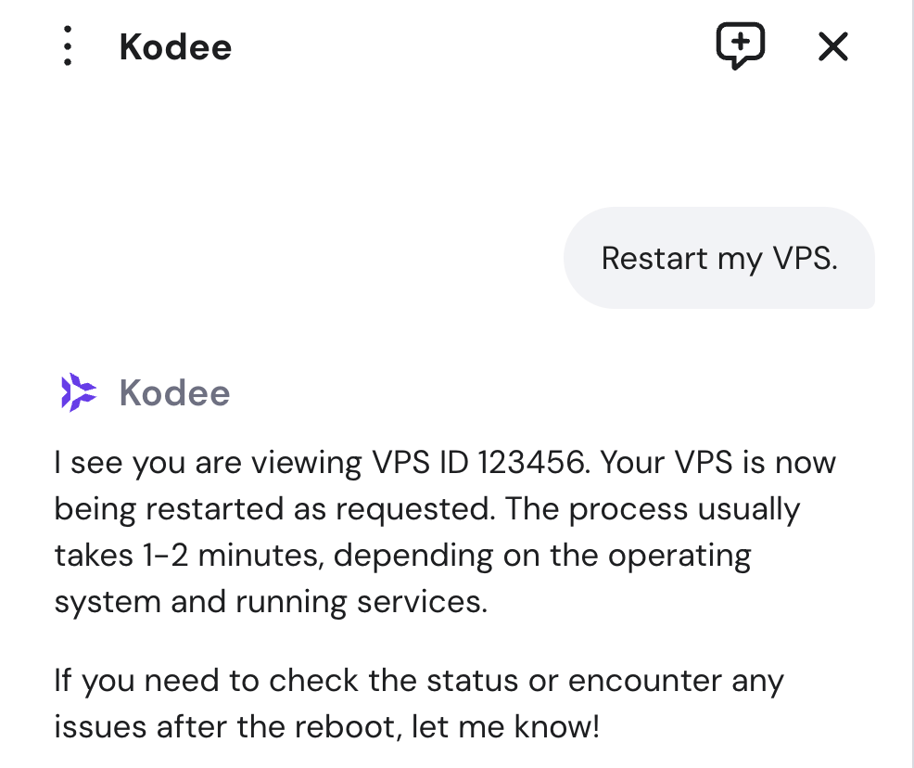
For Hostinger VPS users, you can use all the commands mentioned in this tutorial. However, there’s an even simpler way to manage your server’s power state.
Kodee, our AI assistant, can handle these tasks for you with a simple instruction. Navigate to your VPS dashboard, click the Ask Kodee button, and type a prompt like “Restart my VPS” or “Shut down my server.”
Kodee will handle the execution for you, confirming when the action is complete. This simplifies server management by removing the need to use the command line.

The shutdown command is important for security because it enables controlled and safe shutdowns, preventing data loss and file system corruption. Many critical system updates, especially security patches, require a reboot to take full effect.
By using the shutdown -r command, administrators can schedule these restarts during low-traffic periods. This approach minimizes downtime while keeping the system’s defenses up to date.
A controlled shutdown also sends warnings to logged-in users, helping prevent unexpected data loss and allowing all running services to close gracefully. This level of predictability is crucial for maintaining a stable and secure server environment.
Mastering the shutdown command is, therefore, a key part of improved VPS security. When you apply updates correctly and handle reboots methodically, your system remains reliable and resilient against potential threats.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.