Jan 21, 2026
Aris S. & Matleena S.
6min Read
AI agents, also known as autonomous software systems or intelligent digital assistants, are programs designed to independently perform tasks and make decisions to achieve specific goals.
Unlike traditional AI models, which often require constant human input, AI agents operate autonomously, handling everything from simple tasks to a series of operations.
Whether used in customer service as virtual assistants or in robotics for automated production, AI agents are proving their versatility and reliability. We’ll explore the key characteristics of AI agents, how they function, examples of AI agents in action, and the benefits they bring to businesses.
AI agents are intelligent systems capable of operating autonomously, meaning they don’t need continuous human intervention to complete tasks. Using their reasoning capabilities, they learn from previous interactions, make data-driven decisions, and perform real-world actions to accomplish specific goals.
Typical AI tools like machine learning models analyze patterns and predict outcomes based on data, but they don’t take direct action or adapt unless the prompt changes.
Meanwhile, AI agents are more than just data processing tools. They also integrate external tools, application programming interfaces (APIs), and computation platforms into their reasoning pipeline to overcome the limitations of traditional AI models.
Customer service chatbots and personal assistants like Siri or Google Assistant are examples of AI agents. These systems can handle tasks such as answering inquiries, gathering data from other sources, and setting reminders without manual human intervention.
Agentic AI is a complex system that involves multiple AI agents collaborating to achieve broader, more dynamic goals. It can be more proactive in coordinating systems, managing complex workflows, and learning from its actions to improve over time.
While similar and related, AI agents and agentic AI are distinct systems.
AI agents are designed to perform specific tasks and operate independently using their own reasoning. They also have less-advanced learning capabilities, mainly through feedback loops, heuristics, or updated context buffers.
The task scope of AI agents is narrower and limited to a specific goal within the given context. For example, an AI agent in customer support only answers questions or handles simple tasks like providing invoices. Meanwhile, agentic AI can analyze the user’s problem and notify the person in charge.
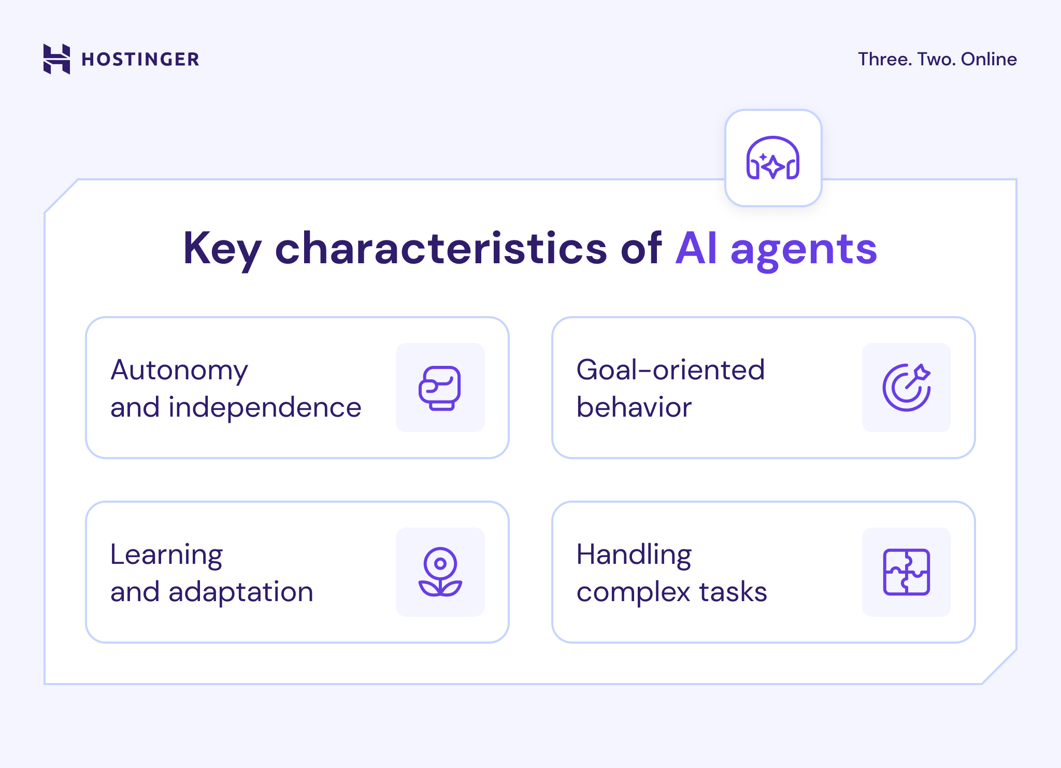
AI agents are defined by several key characteristics that set them apart from traditional software systems. These traits allow them to perform tasks autonomously and adapt to new challenges.
AI agents operate through a process of perception, reasoning, and action. This feedback loop allows them to perceive their environment, evaluate situations, and execute tasks toward achieving specific goals.
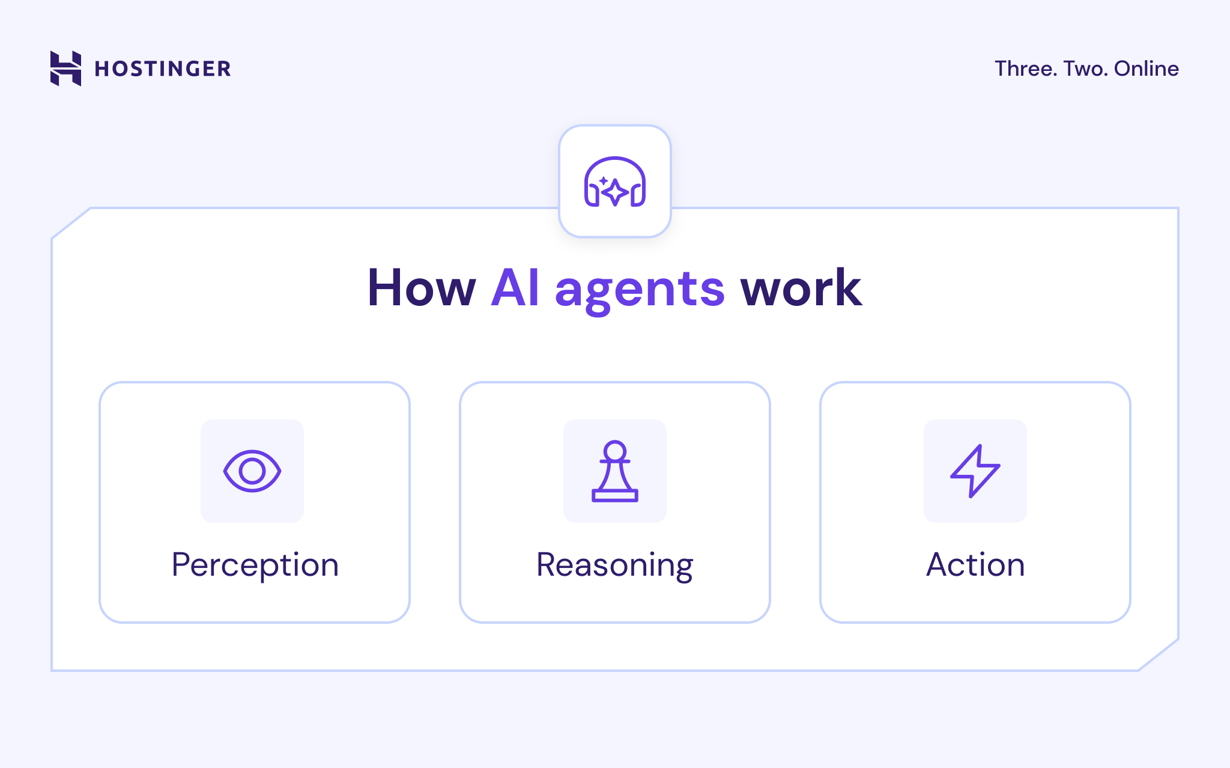
The first stage of an AI agent’s operation involves “perceiving” its environment. This is how the agent “sees,” “reads,” or “hears” user inputs, such as text, images, voice commands, and real-time data from external sources.
For instance, a voice assistant uses speech recognition to perceive a user’s command, such as “Set an alarm for 7 AM.” An AI agent’s ability to “perceive” its environment is what allows it to be reactive and respond to dynamic situations.
Note that the quality of input matters for the AI agent. By tuning your prompt, you provide more information, details, and context that help it “reason” more accurately about the actions it should take.
The AI agent processes the collected data and evaluates actions it must take to achieve its goal. It typically uses a large language model (LLM) as the reasoning engine to interpret queries, plan multi-step solutions, and respond.
The agent’s ability to reason is what allows it to go beyond simple, one-step commands and execute more complex tasks.
In a self-driving car, an AI agent perceives data such as the car’s speed, brake temperature, road conditions, and distance to the vehicle in front. Based on this data, it decides whether to apply the brakes, how much pressure to use, and when to release them.
After reasoning through the information, the agent makes an informed decision and takes real-world action.
The action an AI agent takes depends entirely on its goal. For example, a scheduling assistant agent might send a meeting invitation to multiple participants, while a data reporting agent generates an automated report based on its analysis.
Given their narrow scope, AI agents’ actions vary depending on how you engineer your prompt. They’ll be able to follow a chronological course of action if you provide step-by-step instructions, but may struggle to execute a series of actions if given only a simple line of command.
This ability to initiate and carry out tasks in the real world distinguishes AI agents from traditional, generative AI tools. This capability is valuable for automating intricate processes and managing multi-step workflows.
AI agents are used in many industries to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and provide innovative solutions. Let’s look at a few examples of AI agents in action:

Chatbots are widely used in customer service to provide instant, ’round-the-clock support. These agents can handle common inquiries, resolve issues, and even guide users through troubleshooting processes.
A more advanced AI assistant, like Hostinger’s Kodee, takes this a step further by integrating the model context protocol (MCP) to access data from external sources.
This enables Hostinger users to manage their virtual private servers (VPSs) and WordPress sites only by chatting with the assistant.
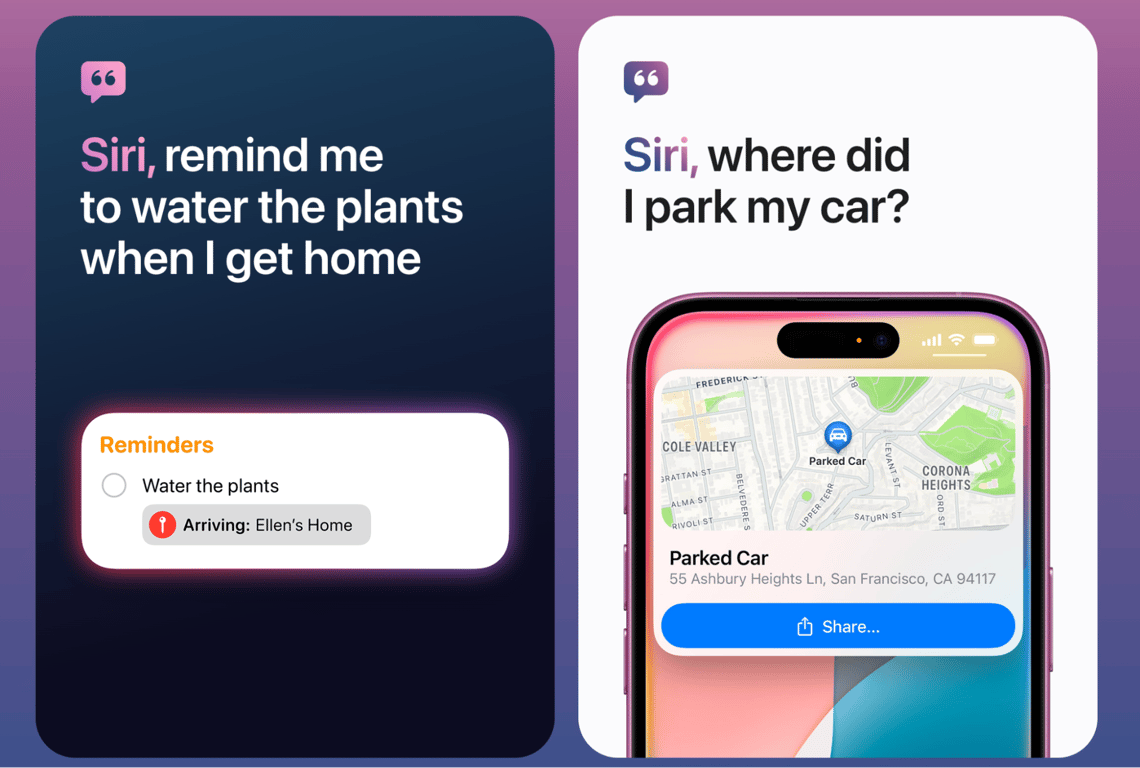
Personal assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Amazon Alexa are AI agents that manage various tasks, from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices.
They help users by performing actions based on natural language commands, improving productivity and convenience. These agents are constantly learning from user interactions, improving their responses and expanding their functionality over time.
AI agents are also deployed in data analysis to uncover trends and insights from large datasets. For instance, stock market analysis bots track market fluctuations and provide real-time recommendations for investment decisions.
These agents use complex algorithms to analyze vast amounts of financial data, offering insights that would be difficult for humans to process manually. They also adapt future behaviors based on past insights to make better decisions.
AI-powered robots are used in manufacturing to automate tasks such as assembly, inspection, and packaging. Examples of such robots are factory robots tasked with assembling products or performing quality control in production lines.
These robots can perform complex actions with precision, enabling companies to operate more efficiently, reducing human error, and increasing productivity.
AI agents help developers code faster and smarter by suggesting improvements, generating snippets, and identifying errors. For example, a coding copilot can debug functions, create boilerplate code, or automate repetitive tasks, learning from the developer’s patterns to improve over time.
AI coding platforms like Hostinger Horizons make it easy to integrate these AI assistants into workflows, helping developers save time, maintain consistency, and focus on higher-level problem-solving.

As businesses continue to look for ways to increase efficiency and reduce operational costs, AI agents are expected to play a critical role in automating routine tasks, streamlining workflows, and providing intelligent decision-making.
The continuous evolution of AI agents should allow them to handle increasingly complex tasks. Instead of serving as a workplace assistant, they will be a key component of future AI ecosystems and business operations across different industries, like robotics.
Not only are AI agents becoming “smarter,” but they are also becoming more accessible. For example, many developers use AI-powered coding tools to help streamline complex tasks like debugging.
Individuals can also easily build an AI agent using n8n, a low-code, open-source automation platform. This allows them to create a personal assistant for their daily tasks, like scheduling meetings and setting up reminders.
Platforms like Hostinger Horizons make it even easier for individuals and small businesses to build and customize AI agents for daily tasks, such as scheduling meetings, sending reminders, or automating routine website management, without needing advanced technical knowledge.

All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.