Dec 26, 2025
Aris S.
6min Read
GitLab is a remote platform that serves as a comprehensive DevSecOps platform and Git repository manager. By integrating the entire software development lifecycle into a single application, it allows teams to progress faster from the planning to the monitoring stage without juggling multiple disparate tools.
Understanding GitLab requires looking at its core components:
Let’s explore each of them in detail, starting from the features that make GitLab a comprehensive development platform.
GitLab functions are built-in features that enable end-to-end software lifecycle management, eliminating the need for third-party solutions. They work together to create a seamless flow from code creation to production deployment.
Source Code Management is the practice of tracking modifications to a code repository, which GitLab implements by providing a robust Git-based version control system.
GitLab SCM tracks every change made to the project, allowing developers to roll back to previous states if a bug is present. It also supports branching, which enables team members to work on isolated features asynchronously without disrupting the main codebase.
When it’s time to merge these branches, the system detects conflicts automatically, preventing code overlaps that could cause errors.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) is a methodology for automating the building, testing, and deployment of code. GitLab streamlines this by providing Auto DevOps, a feature that automatically detects your project’s language and structure to create a pipeline template.
GitLab allows you to set up multiple custom runners, which are agents that execute jobs, to automatically run tests whenever code is committed.
Additionally, the pipeline blocks broken code from being merged, which helps detect errors early and ensures the main branch remains stable.
Once tests pass, your GitLab CI/CD pipeline automatically deploys the application to staging or production environments, streamlining the release process.
GitLab provides Kanban or Scrum-style project management boards that integrate with version control. This allows developers to link changes they made directly to the issues they resolve, creating a transparent audit trail and efficient teamwork.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| Issues | Discrete tasks or bug reports that need resolution. | Tracks day-to-day work and individual assignments. |
| Issue boards | Visual boards that organize issues into lists based on status, like To Do, Doing, and Done. | Visualizes workflow status similar to Kanban or Scrum for better task organization. |
| Milestones | A collection of issues and merge requests to be completed by a specific date. | Tracks progress toward a specific deadline or a release goal. |
| Epics | A collection of related issues and milestones that span across projects. | Helps product managers plan high-level roadmaps and long-term goals. |
GitLab security features automatically scan your application code throughout the development lifecycle to improve compliance and reduce vulnerabilities before deployment. They not only ensure end users are safe, but also help avoid last-minute patches.
The main GitLab security features comprise:
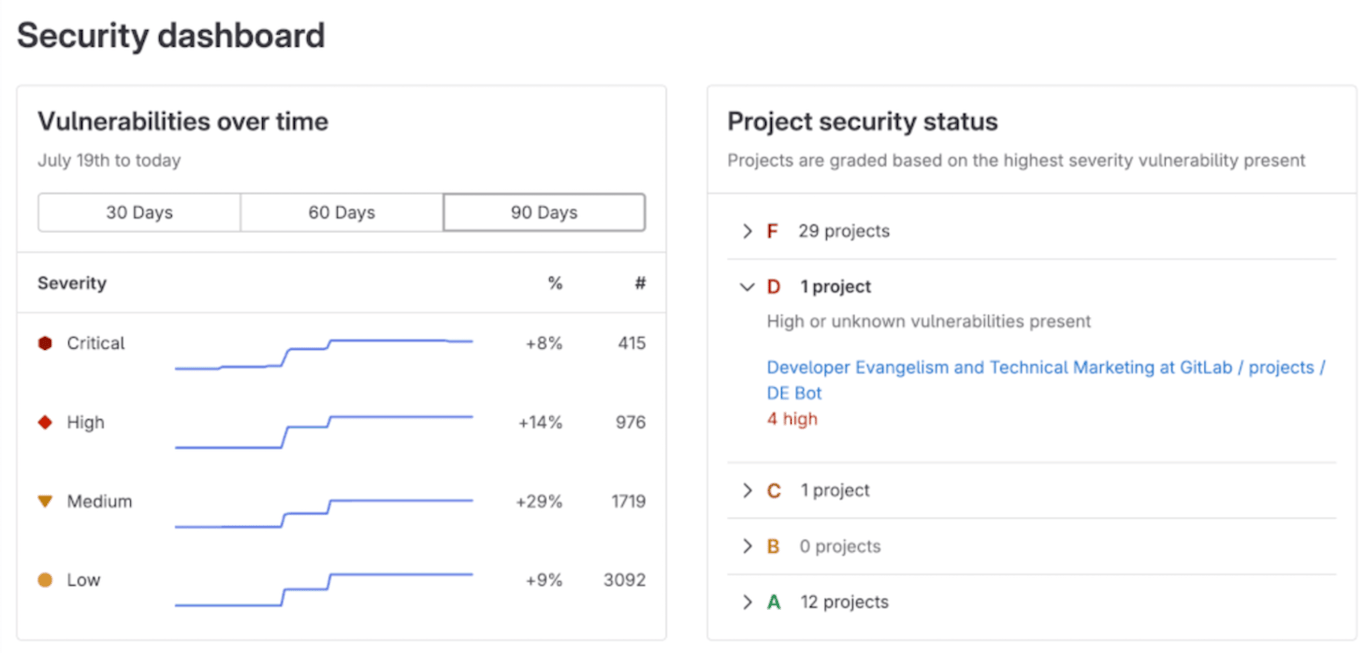
For enterprise users, GitLab offers a centralized Security Dashboard that provides a comprehensive view of vulnerabilities across all projects, enabling security teams to triage and manage risks effectively.
GitLab is an excellent platform for a wide range of users, from hobbyists to global corporations, because its architecture scales well to meet different needs.
Since GitLab is open-source, individual developers should use GitLab because it reduces costs for tools and centralizes their workflow.
GitLab’s free tier offers a generous amount of storage and CI/CD compute minutes, which can be expanded using paid add-ons.
Since this plan is cloud-based, freelancers and students can build, test, and host portfolio projects without separate hosting or testing services.
In a team environment, GitLab is helpful because it streamlines collaboration and enforces a high standard of code quality.
Features like Merge Request Approvals ensure that code is already peer-reviewed before being merged, while Code Owners automatically assign reviewers based on ownership and expertise.
This asynchronous workflow is vital for distributed teams, ensuring everyone stays aligned without constant meetings. Since GitLab’s premium plans all let you onboard unlimited licensed users, it’s excellent for a team of any size.
At a larger scale, GitLab benefits companies and enterprises by enhancing security compliance and offering robust scalability.
GitLab provides audit trails for every change, making it easy for organizations with strict governance to review each development stage in detail, ensuring compliance.
Furthermore, enterprises can self-host GitLab on easily scalable infrastructure, such as a Cloud platform or a Linux Virtual Private Server (VPS) environment. This allows companies to seamlessly scale up their hardware resources as their project expands.
For companies that prefer a managed solution, the dedicated plans are also available. The GitLab team will provision your GitLab instance on a single-tenant host and fully handle the deployment as well as the recurring maintenance.

While GitLab’s features are excellent for a wide range of users, other platforms might fit your specific needs better. For example, your existing tech stack or team may work better with another solution.
GitLab has a strong focus on being a complete, self-contained DevOps platform that can be self-hosted. Meanwhile, GitHub is primarily a Software as a Service (SaaS) platform known for having the world’s largest open-source community.
With that in mind, GitLab is more suitable for organizations that prioritize data sovereignty and want to host their own code on private infrastructure for maximum control. While GitHub also offers enterprise solutions, its primary strength lies in public open-source collaboration and social coding, making it the go-to for community-driven projects.
GitLab is excellent for teams that want a tool-agnostic CI/CD solution built directly into their repository. On the other hand, Bitbucket is recognized for its extensive integration with the Atlassian ecosystem, allowing it to work seamlessly with tools such as Jira, Confluence, and Trello.
Given their differences, GitLab is a better choice for teams that want a single application for the entire DevOps lifecycle without relying on heavy external integrations. While Bitbucket is powerful, it is best for teams that are already heavily invested in Jira for project management or other Atlassian tools.
Using GitLab brings various advantages that directly impact the efficiency and security of your software production:
While GitLab helps improve your development efficiency, consider the effort and time invested to manage the platform, especially if you are self-hosting it. While GitLab offers managed services, they are only available in the cloud-based and managed plans.
With this in mind, it’s crucial to use a feature-rich GitLab hosting platform. For example, Hostinger offers the intuitive hPanel that streamlines the server-side administration of your GitLab infrastructure. You can also ask our AI assistant Kodee for help and manage your server directly.
GitLab is a powerful, all-in-one DevSecOps solution that offers comprehensive tools centered around automation, collaboration, and version control. Whether you are a solo developer or a business owner, this platform is an excellent solution to elevate your software development efficiency.
To start using GitLab, decide whether you want to self-deploy it or use its cloud-based plan. While cloud plans offer simplicity, self-hosting is excellent if you want flexibility and scalability because you use your own infrastructure.
When self-hosting GitLab, choose a reputable and reliable hosting provider, like Hostinger. After setting up the server, check out our step-by-step guide to learn how to install GitLab on your Linux VPS. Once finished, you can start exploring the platform and all its features.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.