Dec 22, 2025
Domantas G.
14min Read
Drupal is a robust content management system (CMS) used to build all kinds of websites. Many well-established companies trust Drupal to run their high-traffic sites due to its versatile features and extensive modules.
That said, Drupal has a steeper learning curve than its competitors. Beginners may find building a website with this content management system challenging. In fact, without proper guidance, users may end up not utilizing all of Drupal’s capabilities.
However, there’s no need to worry ‒ our Drupal tutorial will cover everything you need to know in order to start. We’ll introduce you to the proper Drupal installation procedure and how to build a site using this CMS. We’ll also show you how to install modules, themes, and updates.

Drupal is a CMS that currently powers 2.2% of all websites whose CMS we know. Over the years, the PHP-based software keeps evolving due to a growing community of developers that have turned it into an open-source project. Today, Drupal is free to download under the GNU Public License.
Despite being mainly known for powering government and organization websites, Drupal can accommodate a wide variety of sites. That’s because it employs a vast collection of modules and themes to expand a website’s functionality and look.
Here is what you can expect when using this platform:
This tutorial will go over all the available features and attributes to help you decide whether to use Drupal. First, we’ll discuss the installation of the platform.
Before installing Drupal, there are a few things you have to take care of. We’ll go over them in the following sections.
Web hosting is a service that makes a website accessible on the Internet. By purchasing a hosting plan, you rent server resources to host the content of your website. Hosting prices vary depending on the service provider and the type of plans.
It’s essential to pick the right Drupal hosting provider, as it will significantly affect your site’s performance. A web host should provide you with enough resources and features to meet your site’s needs. Other important factors include security measures, guaranteed uptime, and customer support.
After finding the right hosting provider, choose the type of hosting. A hosting plan optimized for your site will save you money in the long run. Once your website has grown, upgrade to a plan with more resources and better scalability.
Most hosting providers offer hosting services that differ in the amount of allocated resources and customization flexibility. Here are some of Hostinger’s hosting plans:
Our Drupal hosting plans include everything necessary to build and maintain a Drupal site. With prices in the range of $1.39-$3.99/month, Hostinger’s Drupal hosting comes with servers optimized for Drupal, a one-click installer, and a dedicated support team.
Alternatively, opt for shared hosting if you’re planning to use a different platform. Hostinger’s shared hosting plans cost the same as Drupal hosting and include a WordPress installer.
Internet users use domain names to access websites on browsers without having to memorize the site’s IP address. If you want to know more, check our beginner-friendly guide about what domain name is.
The right domain name will help you build online credibility and boost the recognition of your brand. Therefore, make sure your domain is unique and memorable. Avoid symbols and hyphens as they can harm its readability.
Instantly check domain name availability.
You can check the chosen domain’s availability on Hostinger’s Domain Checker. If it is no longer available, view top-level domain or name alternatives using a domain name generator.
Once you’ve found the right domain, register it with a domain registrar and point it to your hosting server. If you purchase the domain name and hosting from the same web host as a bundle, you won’t need to do that.
Keep in mind that Domain Name System (DNS) records may take up to 24 hours to propagate globally. During this time, your site will be unavailable.

There are two ways to install Drupal – manually or by using an auto-installer. In this section, we’ll discuss both methods. Note that the steps listed in this tutorial are for the 9.x.x version of Drupal. However, they should apply to older core versions too.
The easiest way to install Drupal on your hosting server is by using the auto-installer feature. You can find it on your hosting control panel. For this example, we’ll install Drupal via Hostinger’s hPanel.
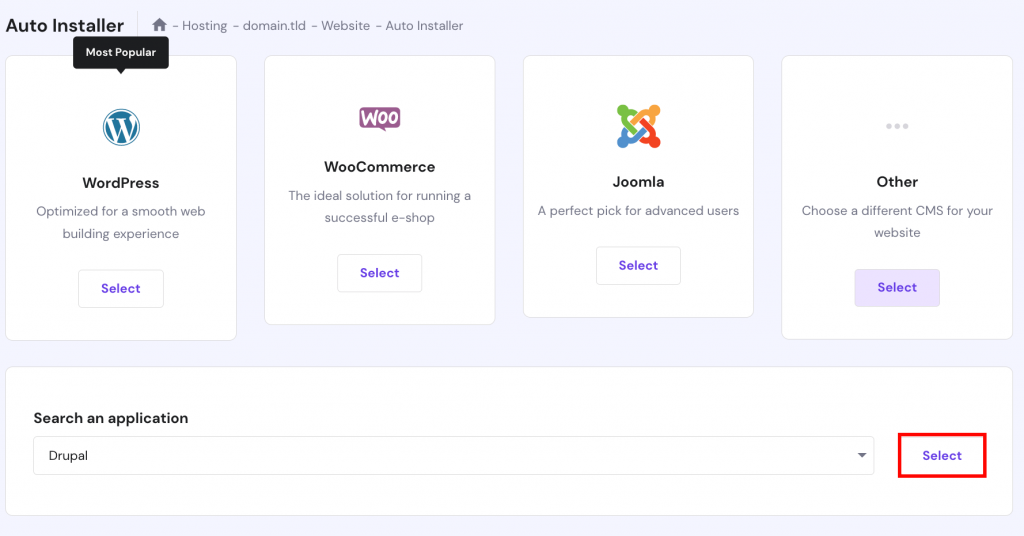
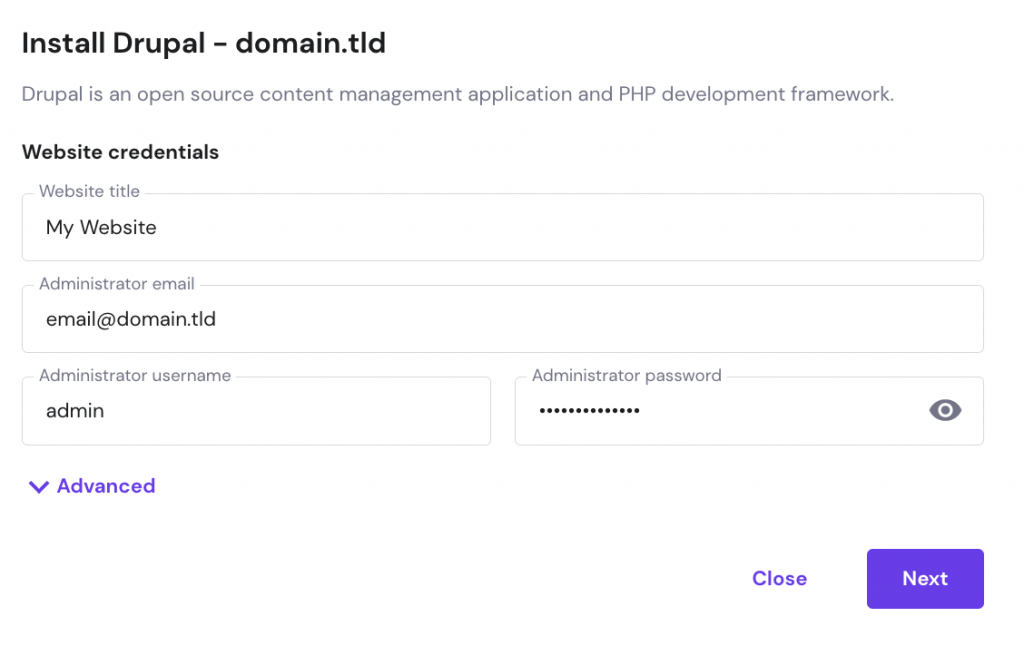
If your web hosting doesn’t include an auto-installer, you can install Drupal manually.
Developers generally prefer this method as it gives them more control over the installation, which is beneficial when installing Drupal on localhost or a VPS.
The following tutorial will show you how to install Drupal manually via hPanel.
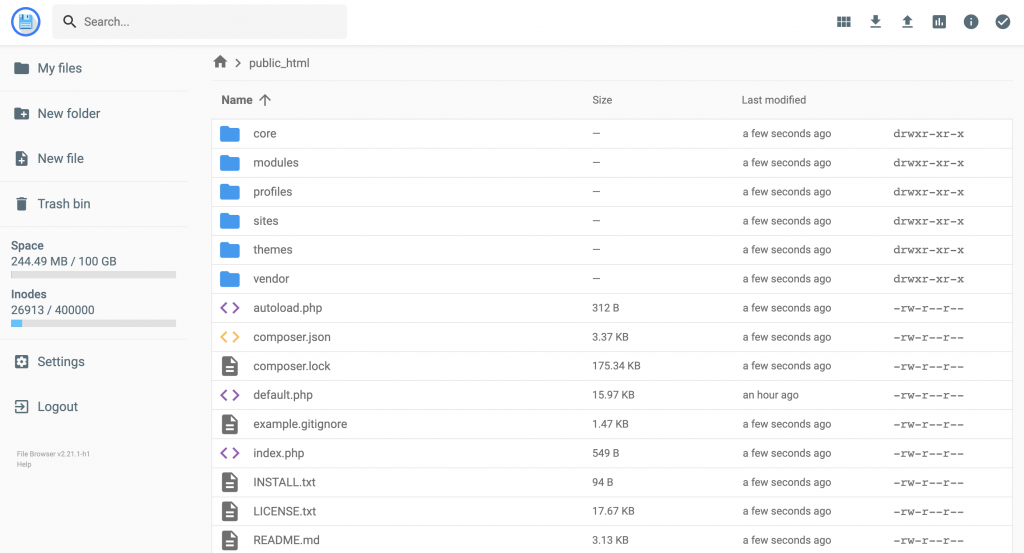
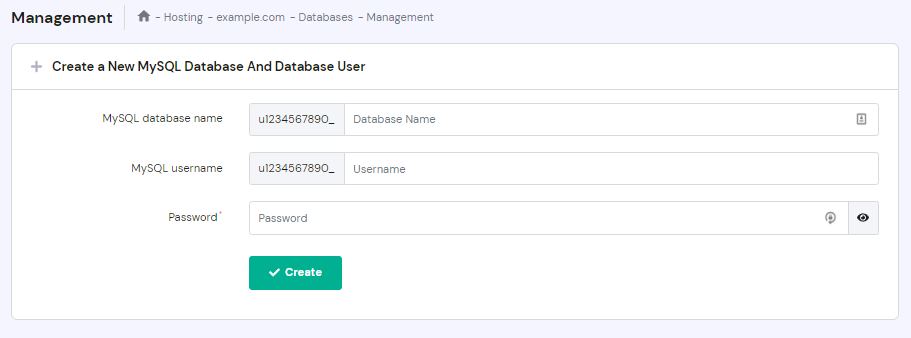
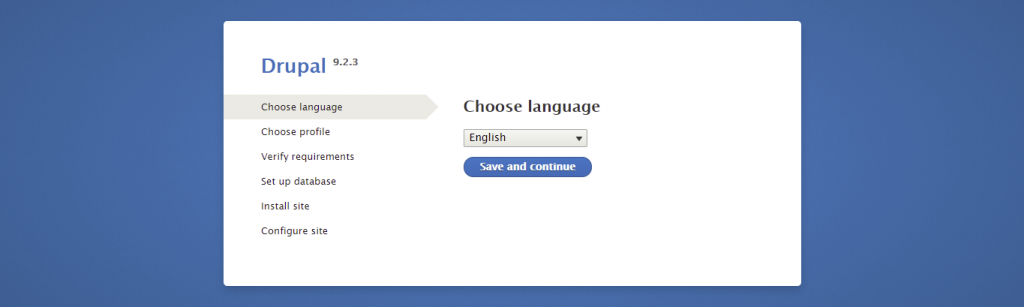
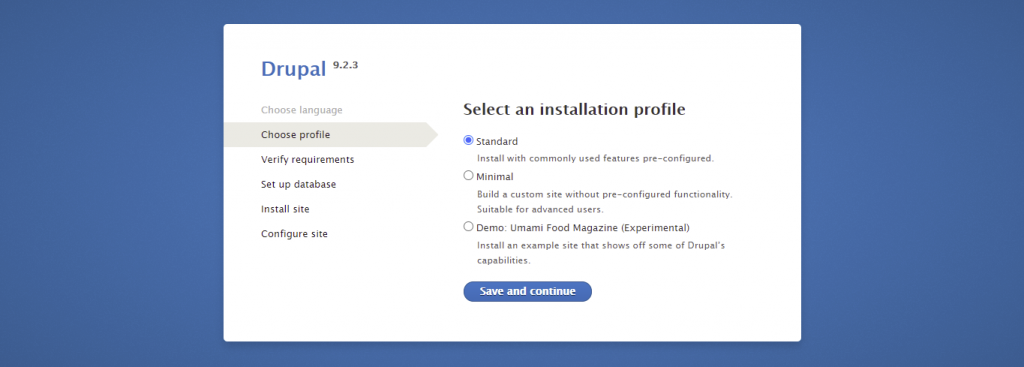
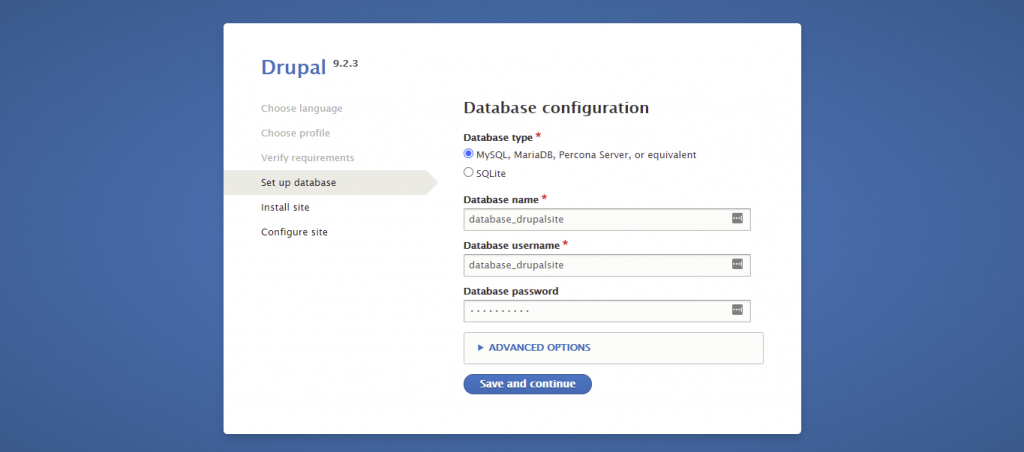
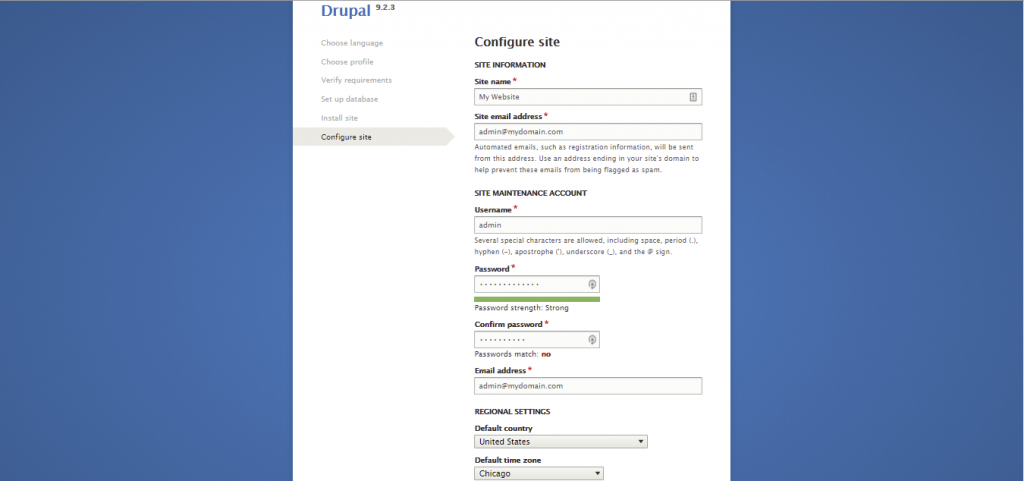
If you need to configure your Drupal database details, access the settings.php file. You can find it here: public_html/sites/default/.
Review your database credentials and information in the MySQL Databases section of the hPanel.
Hostinger VPS users can benefit from installing Drupal using our OS template. The OpenLiteSpeed Drupal One-Click automatically installs OpenLiteSpeed, Drupal and LSCache.
It also automates initial setup for components like PHP OPCache to reduce the time it takes to optimize a web server, making it a more convenient solution.
To do this, open your hPanel and click Manage on your server. After that, navigate to Operating System → Change Your Operating System → Applications. Choose the Drupal template from the drop-down menu.
After that, click Change OS and wait for the process to finish. Remember to back up your data before changing your VPS operating system.
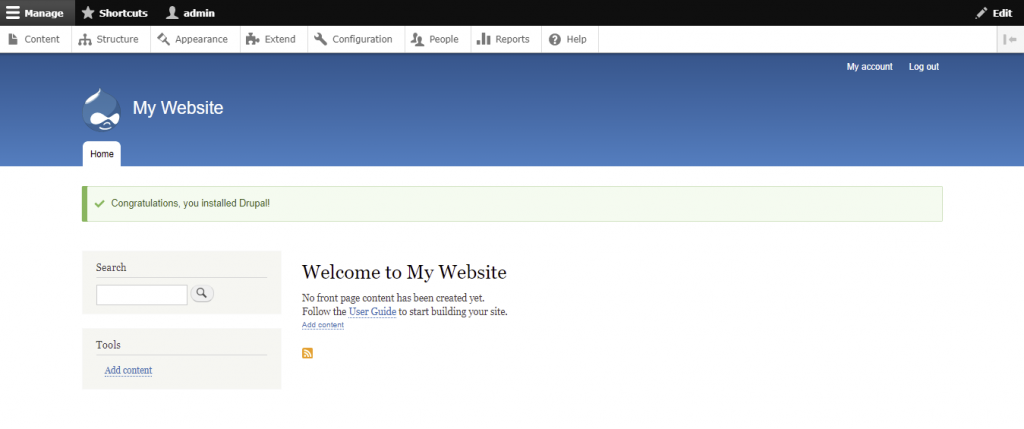
After successfully installing Drupal, we can proceed with the steps of building a site on the platform. The following section will discuss the navigation of the Drupal admin dashboard and how to create website elements, such as pages and menus.
The Drupal admin dashboard is accessed by logging in. You can access the login page via https://your-site-address/user/login.
Once logged in, click Manage at the top left corner of the page to view the following menu items:
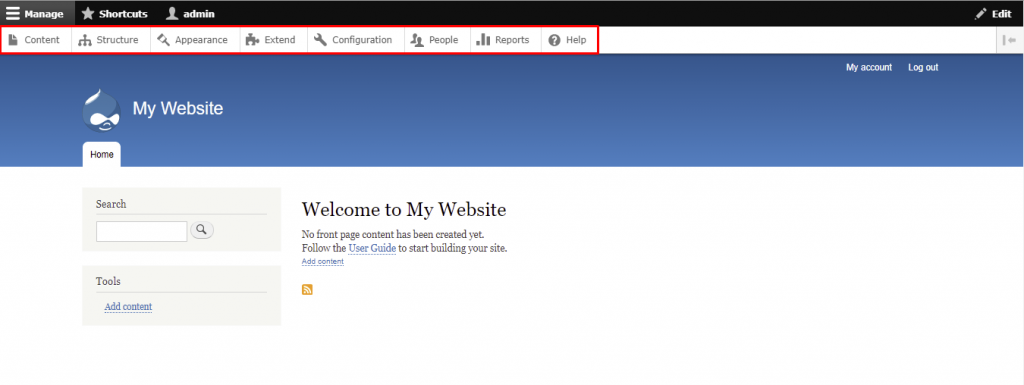
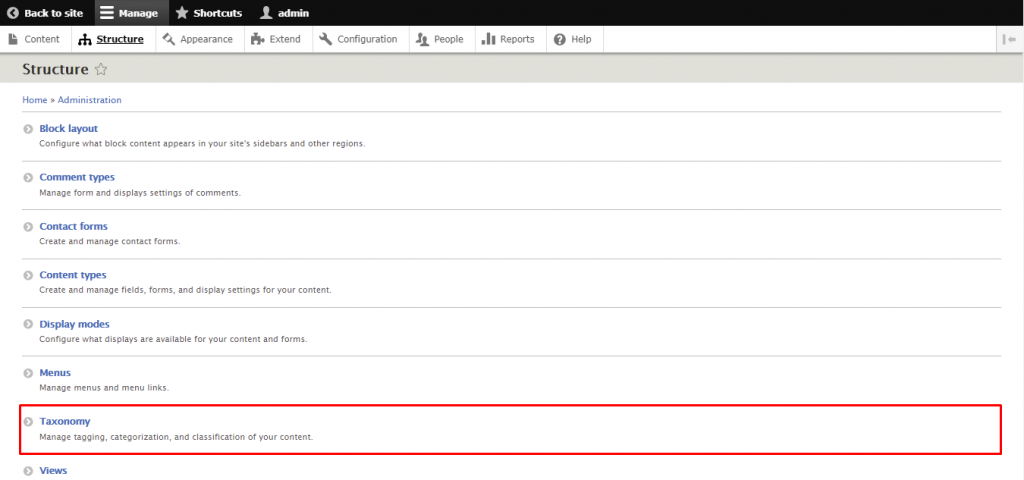
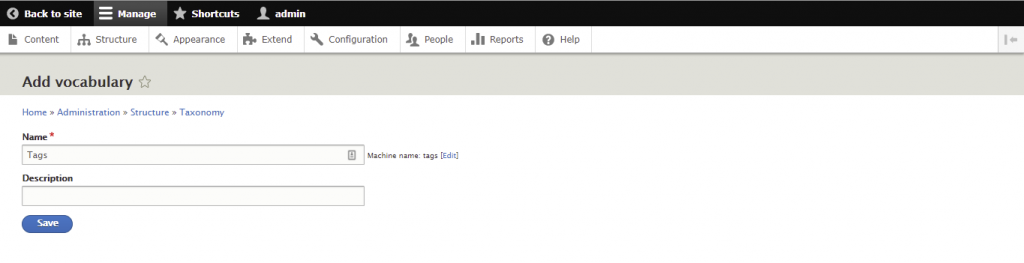
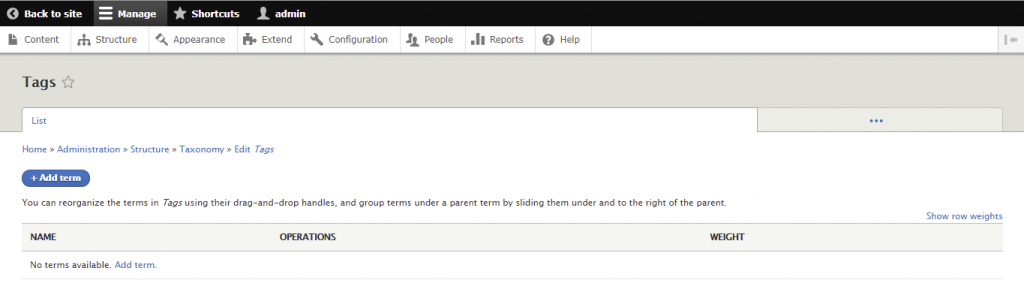
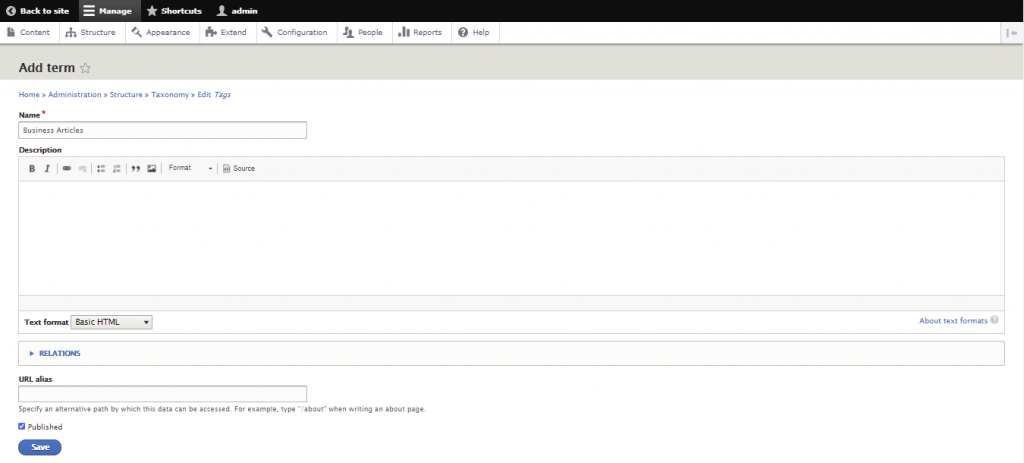
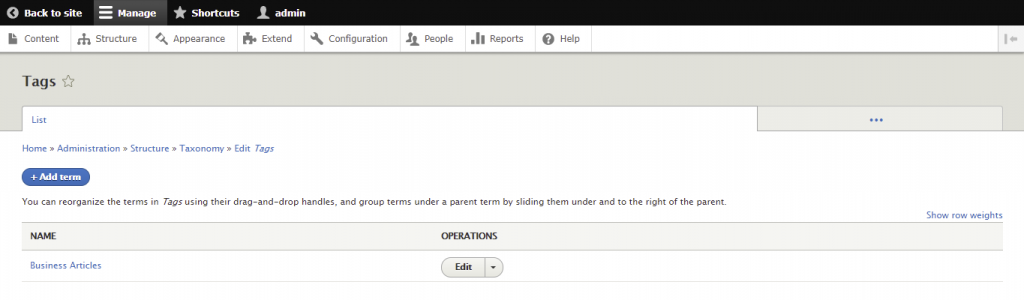
A taxonomy is used to classify website content. In Drupal, taxonomies comprise entities called terms, which are words that describe specific content within vocabularies. A vocabulary may have a flat or hierarchical structure depending on the type of content.
The first step of creating a taxonomy is to add the required vocabularies and each of their terms. You can then attach taxonomy terms to content entities, setting up listing pages to classify them.
Here are the steps to create a new taxonomy in Drupal:
Drupal has two core content types – article and basic page.
The article content type, formerly known as story, is used to create content like press releases and blog posts. Entries of this content type feature on the site’s homepage and allow comments.
Meanwhile, the basic page type is employed for static content that requires minimal to no updates, like an About Us page. A basic page isn’t featured on the site’s homepage and doesn’t allow comments by default.
Additionally, Drupal has four optional content types, which you can activate by enabling the Book, Blog, Forum, and Poll modules:
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create both articles and basic pages.
Let’s start by creating an article:
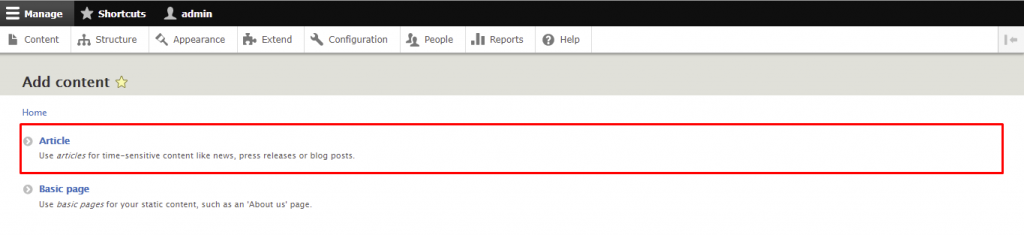
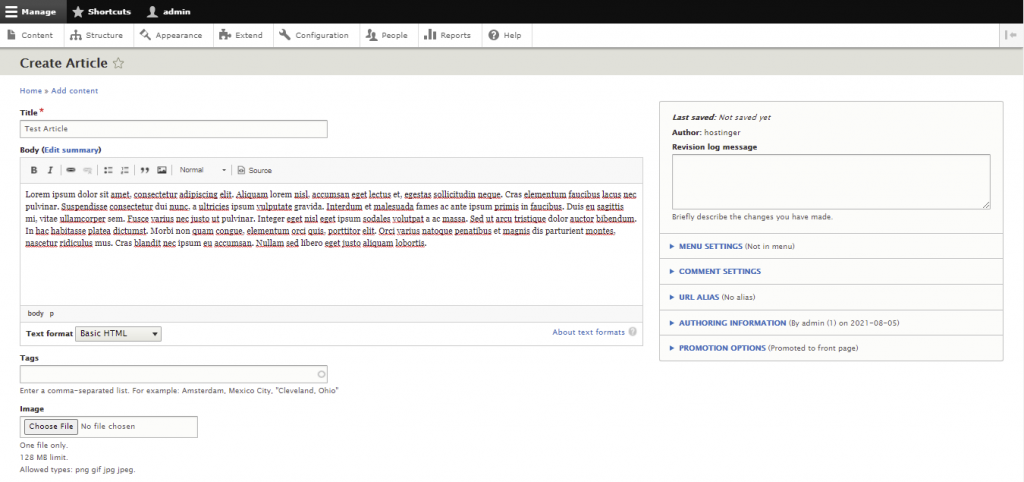

Now, let’s try to create a basic page. Here are the steps to make an About Us page:
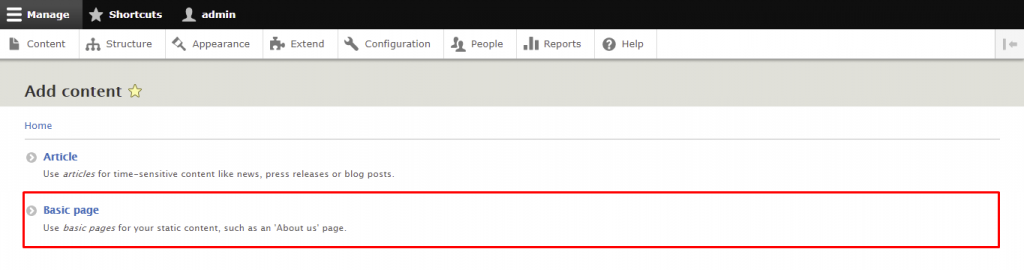
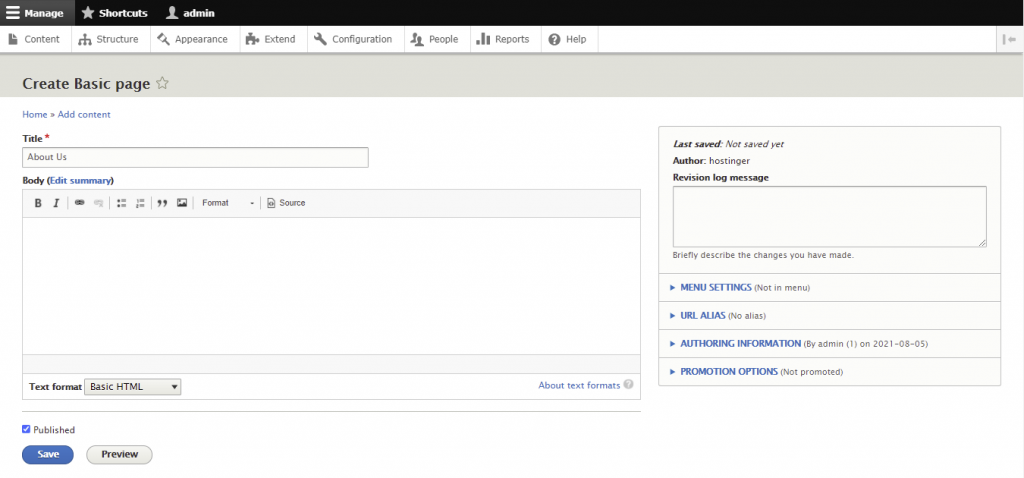
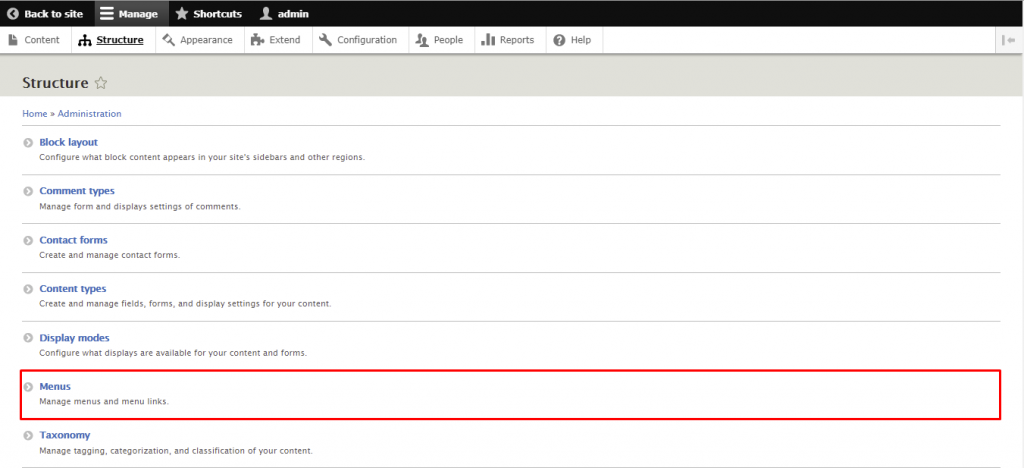
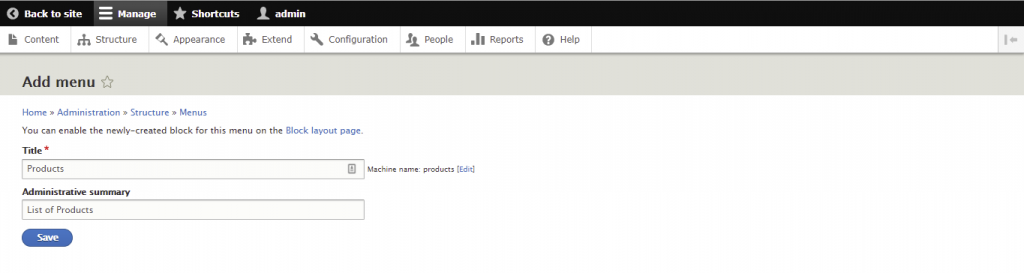
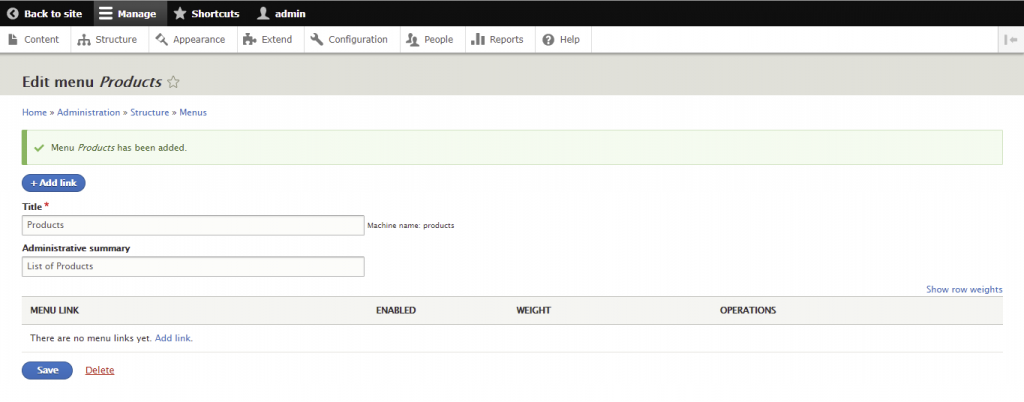
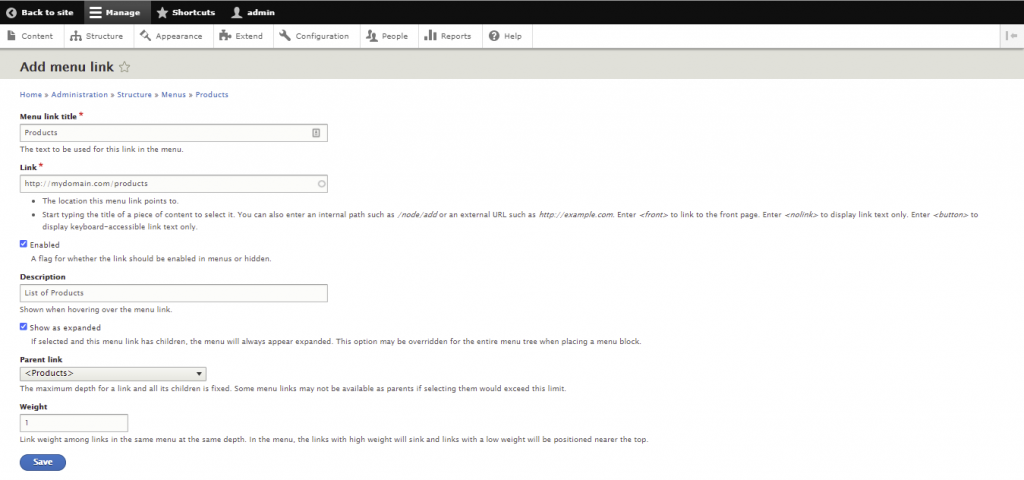
Menus are useful for categorizing and structuring the site. While Drupal already has several of them by default, you can also add custom menus.
The following steps will show you how to create one:
Blocks are boxes of content that are rendered in a region. For example, you can add a user login form (block) to the website footer (region).
This functionality, provided by the Block core module, is part of the core of Drupal 8. Use it with the Custom Block and Place Block modules to incorporate blocks on any page.
Here are the steps to place a block in Drupal:
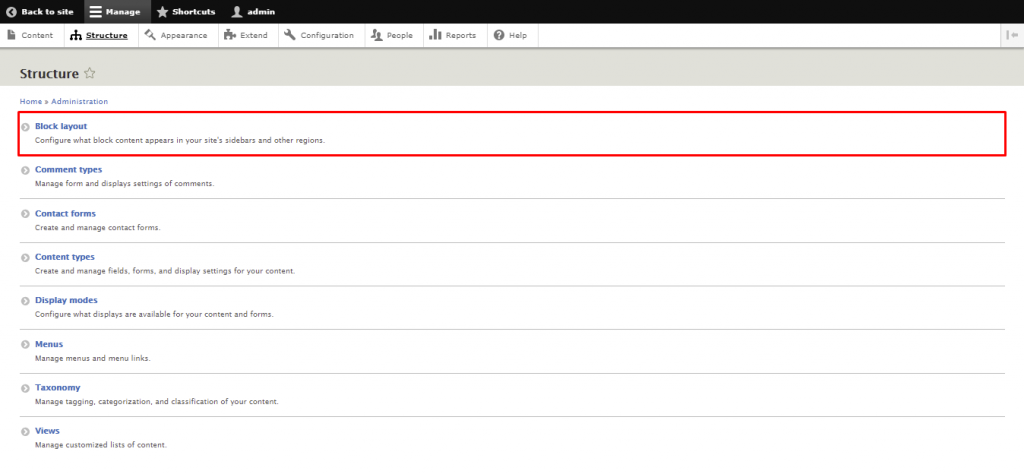
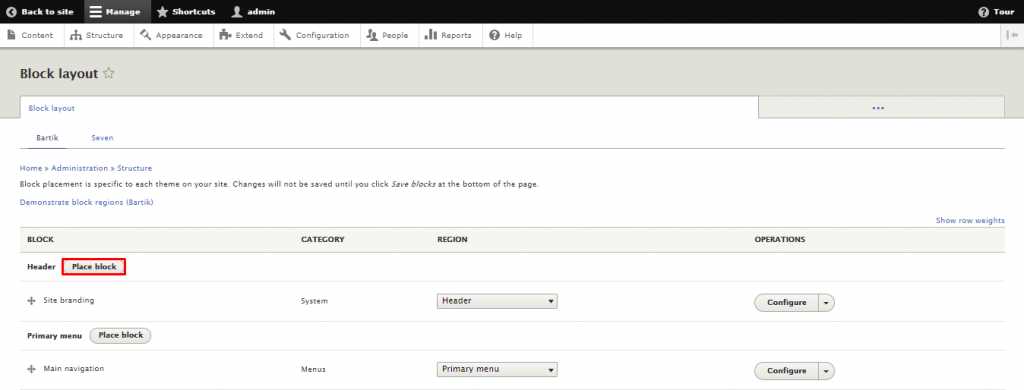
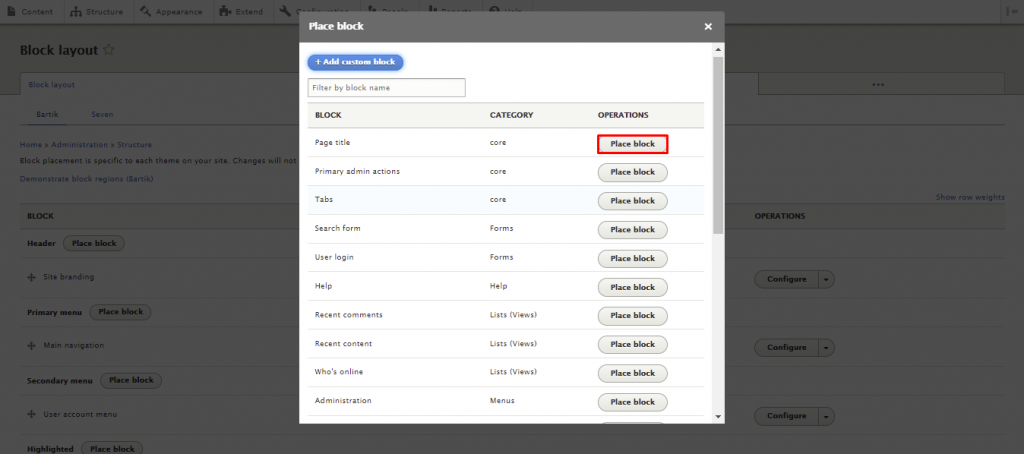
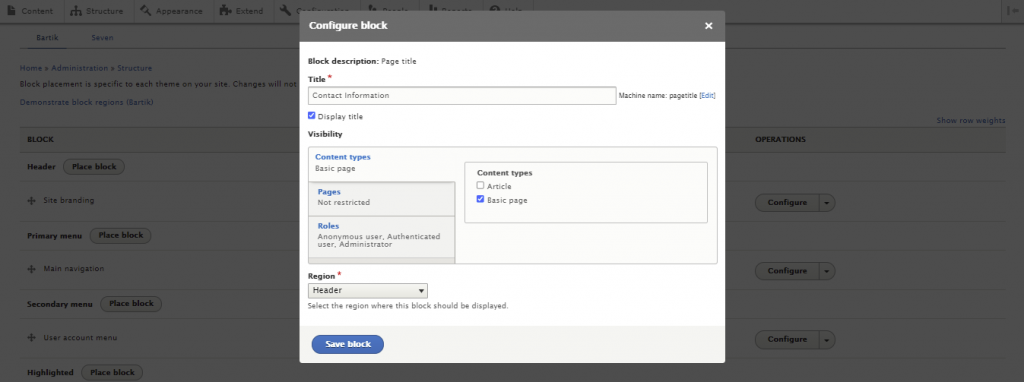
A Drupal module is a collection of files that extends a site’s functionality. Drupal has two types of modules ‒ core and contributed modules.
Drupal includes core modules with essential functions by default. For additional tools, install contributed modules from the module downloads page or create your own modules.
In this section, you will learn how to install a module via the administrative interface and Drush.
While this method is the easiest way to install Drupal modules, it only works for contributed modules. Refer to the Drush tutorial in the next section to install custom modules.
Follow these instructions to install a module using the administrative interface:
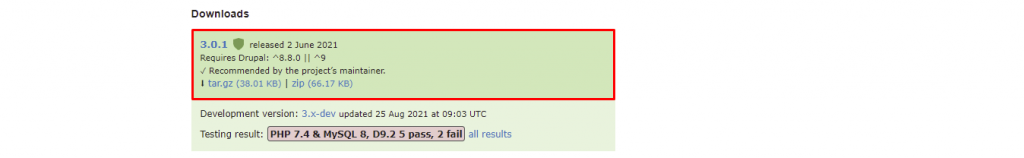
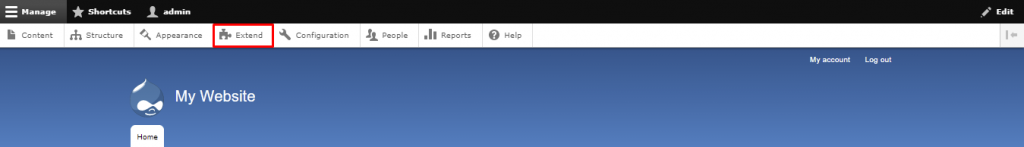
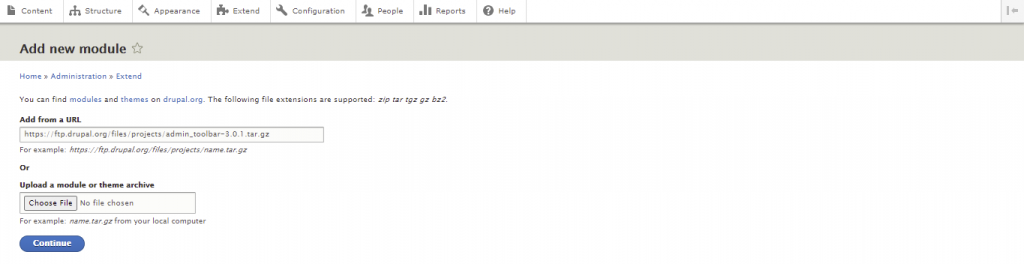
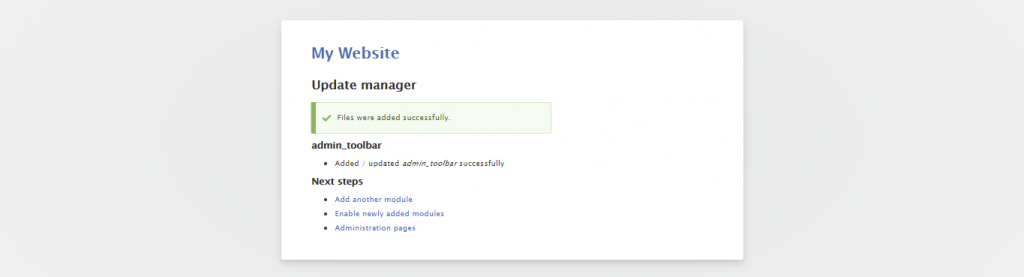
Important! If the Add new module button is missing, enable the Update Manager core module from the Extend menu. Changing the default theme to Seven via Appearance also works in some cases.
Here are some of the most popular contributed Drupal modules:
Drush is a command-line shell for managing Drupal. It provides a way to perform admin tasks without using Drupal’s backend. That said, operating Drush requires technical knowledge, so it may be unsuitable for beginners.
The first thing you need to do is install Drush on your Drupal project. Run the line below from your root directory to install Drush via the Composer dependency manager tool.
composer require --dev drush/drush
Keep in mind that this will only work for users with root access, meaning that you have to be on a virtual private server to install modules using Drush.
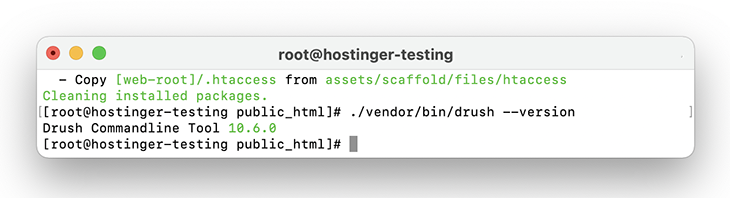
Execute the following command to check whether the installation process was successful:
./vendor/bin/drush --version
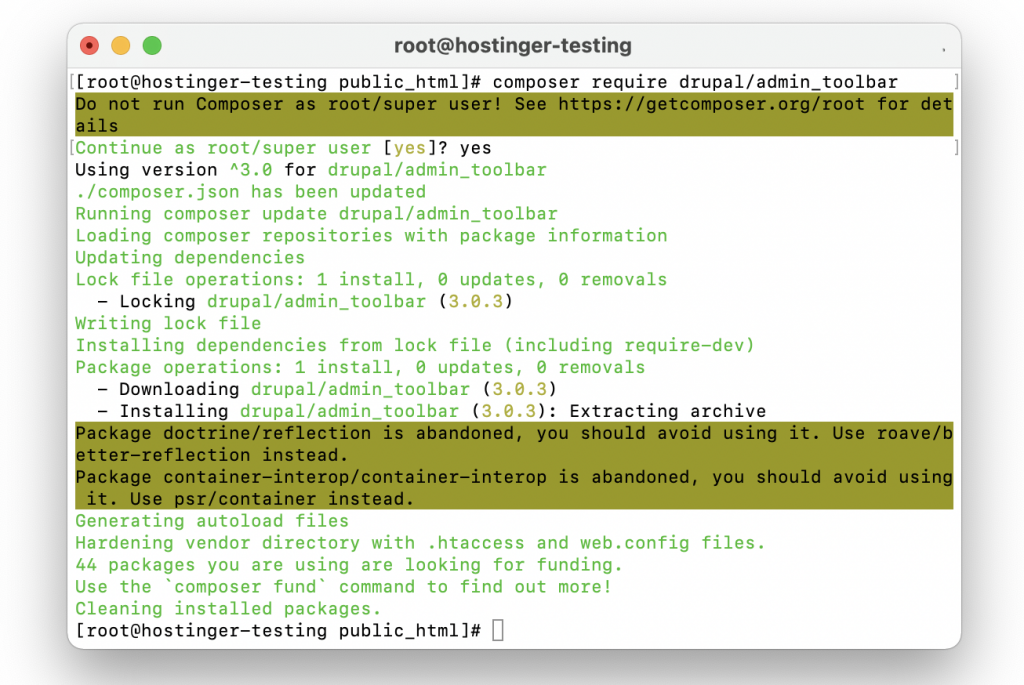
Now that you have Drush set up, use it to install a Drupal module by following this tutorial:
composer require drupal/admin_toolbar
drush pm:enable admin_toolbar
Setting up an appealing look for your site is essential, as it will leave a good impression on visitors. Using an aesthetically pleasant theme is one way to do it.
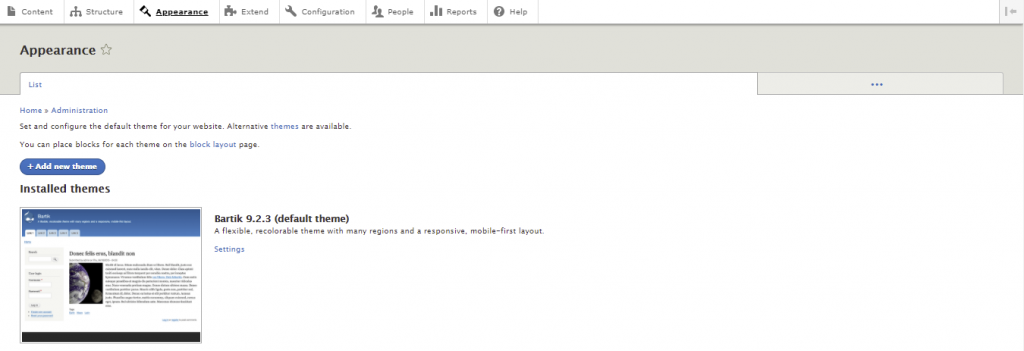
You can view installed Drupal themes via the Appearance tab.
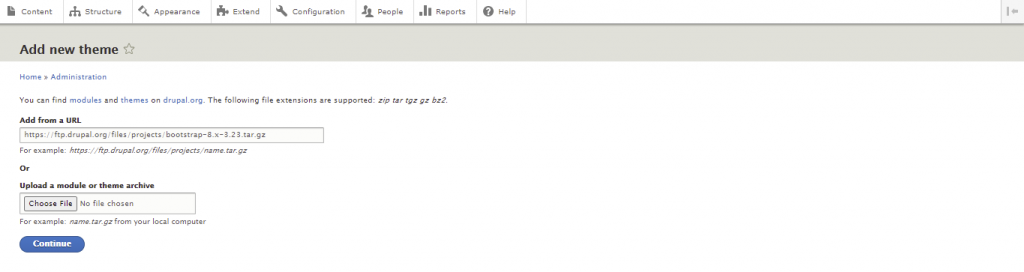
Many online sources offer third-party themes to choose from. However, the official Drupal Theme downloads page is the most reliable source, containing over 2,900 themes.
The theme directory has useful filters to narrow down a search based on compatibility as well as development and maintenance status.
Here’s how to install a Drupal theme:
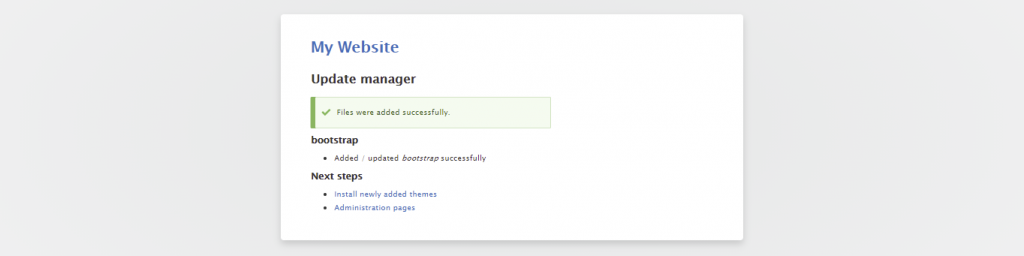
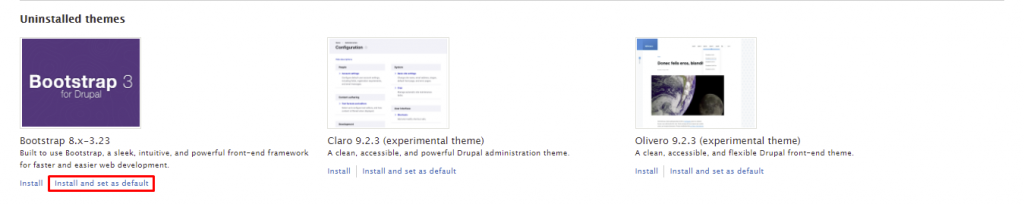
With Drupal, you can set up a fully functional blog site. However, the Blog module is no longer included with the core software, starting with Drupal 8. Therefore, you’ll have to download and install the contributed module manually.
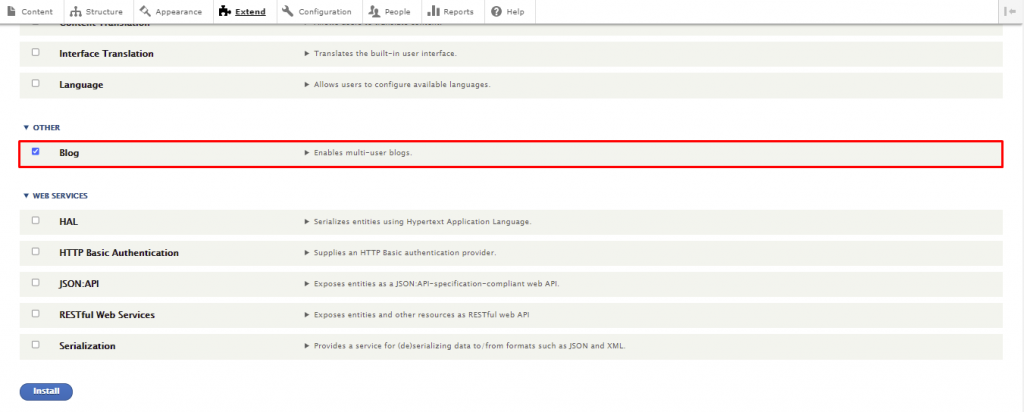
Once installed, the blog module will appear on the Extend menu. Check the box next to Blog and click Install to enable the module.
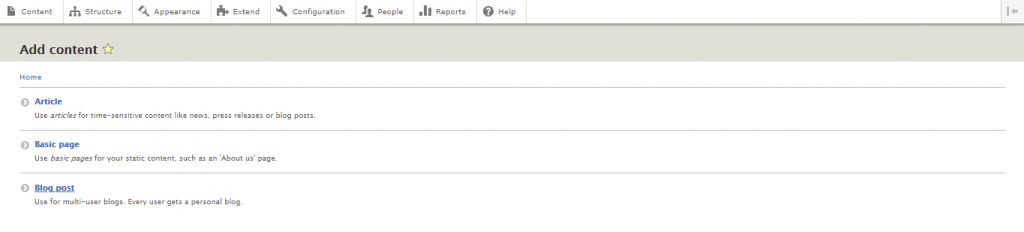
When you navigate to Content -> Add content, you should see a new content type called Blog post. Select it to create a blog entry.
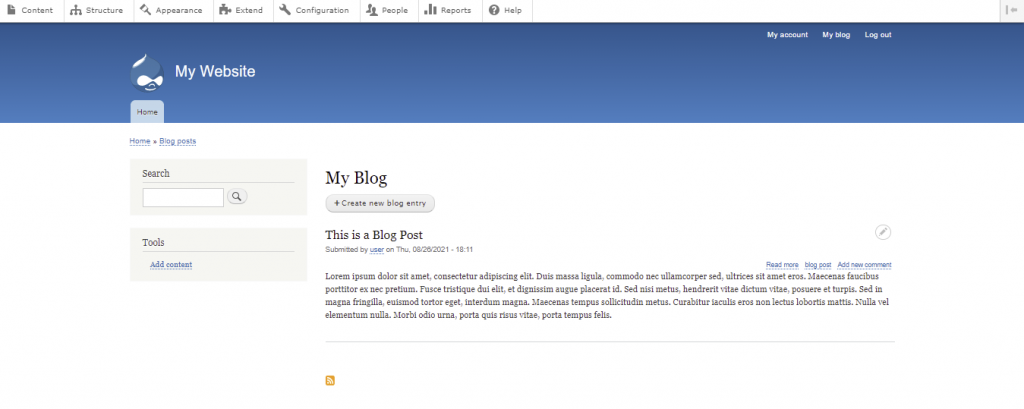
Add the title, body, and tags for the post. Click on the Comment Settings menu on the right side and choose Open to allow comments. If another user wrote the blog post, add their account name to the Authoring Information settings.
Once you’re done, check the Publish box and hit Save to create a new blog post. Your blog post should now be visible under the Blog section of your homepage.
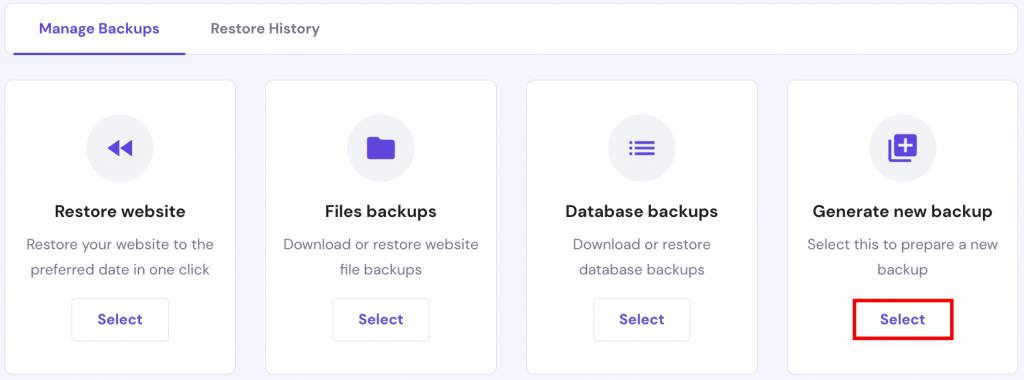
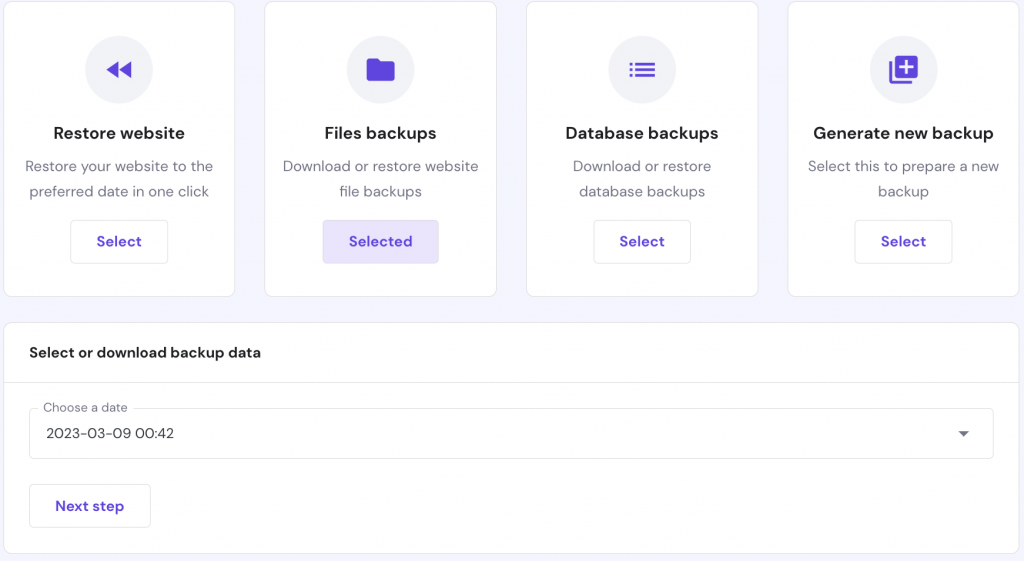
Regularly backing up your Drupal site helps keep data safe in case of a software or hardware malfunction. If something goes wrong, a backup will let you restore the site without losing important data.
The following tutorial will show you how to back up your Drupal files using Hostinger’s hPanel:
In Drupal, updates and upgrades are two different things. An update means installing a newer minor version of Drupal, such as updating the core to 9.2 from 9.1. Meanwhile, upgrading refers to major changes, like replacing Drupal 8 with version 9.
In this section, we will go over the steps of updating Drupal. Before starting, we strongly recommend switching your site to Maintenance mode. Doing so will prevent visitors from accessing the site during the update process.
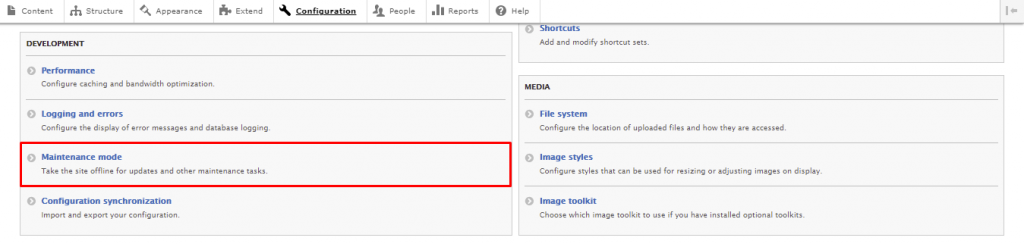
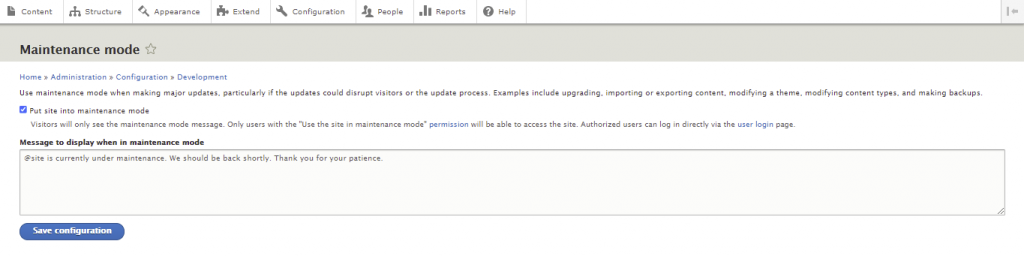
With this out of the way, navigate to Reports -> Available updates to see if a Drupal core update is available.
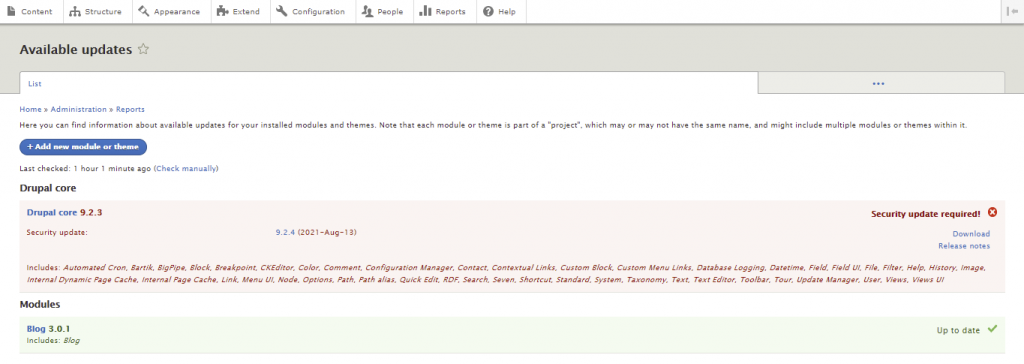
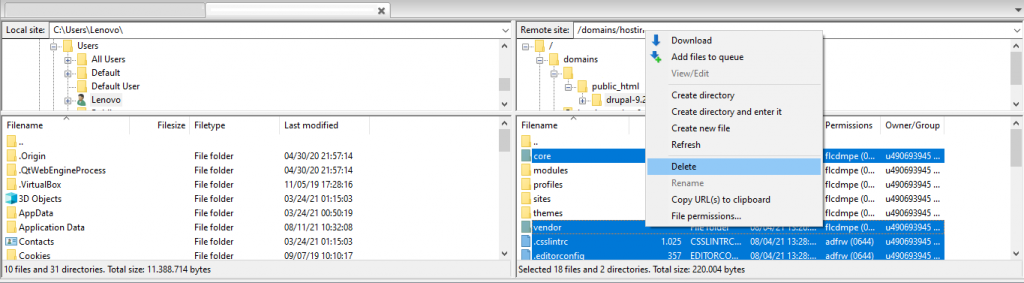
There are a few ways to update Drupal. You can use SSH or FTP to update the platform manually or employ Composer to automate the process. If you’re a beginner, we recommend using an FTP client like FileZilla.
Here are the steps to update Drupal using FTP:
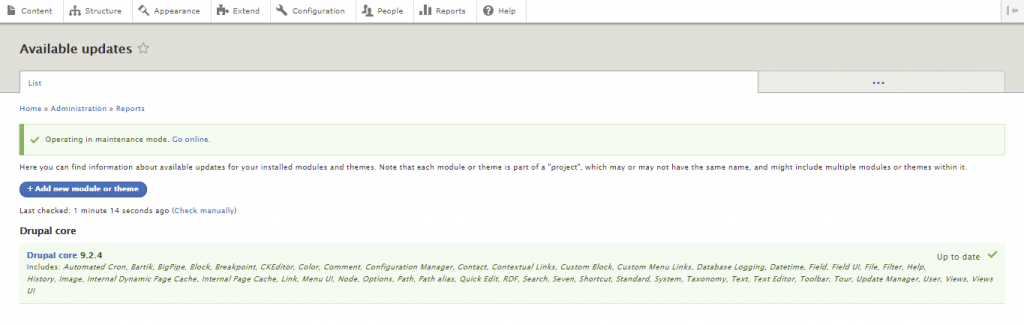
Drupal is a highly customizable CMS that can power all kinds of websites. It supports a wide array of modules and themes to streamline the web development process and extend its functionality.
This article discussed the steps to build a new site on Drupal, from installing the platform to setting up themes and modules. We also covered other essentials, such as creating a blog, backing up a site, and updating Drupal.
Consult the official Drupal documentation to learn more about the CMS. It will take some time and effort before you can fully utilize it.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions in the comment section below should you require additional information. Good luck.
Comments
January 25 2018
Thank you for this informative read, I have shared it on Twitter.
February 22 2018
The official White House website (https://www.whitehouse.gov) also uses Wordpress !
February 27 2018
Hey Jon, Yep, they migrated to WordPress not a long time ago :)
December 21 2020
Hostinger is working good with our drupal site https://www.examtray.com. It is better to chat with them for instant solutions. But you will get problems upgrading your drupal site as the modules become incompatible. When compared to wordpress sites, drupal maintenance is difficult any one should agree.