When deploying a Node.js application on Hostinger, you can configure environment variables as part of the deployment process. Environment variables are commonly used to store sensitive data and configuration values such as database credentials, API keys, and application settings.
During deployment, you have two ways to add environment variables:
-
Import them from a .env file (recommended)
-
Add environment variables manually, one by one
Once all environment variables are added, you can confirm them and continue with building your application.
Before you start
Make sure you know which environment variables your application requires. If using a .env file, ensure it follows the correct format (for example: KEY=value).
Option 1 — Import environment variables from a .env file
Importing variables from a .env file is the fastest option, especially if you already use environment variables locally.
To import from a .env file:
- Start the Node.js application deployment process
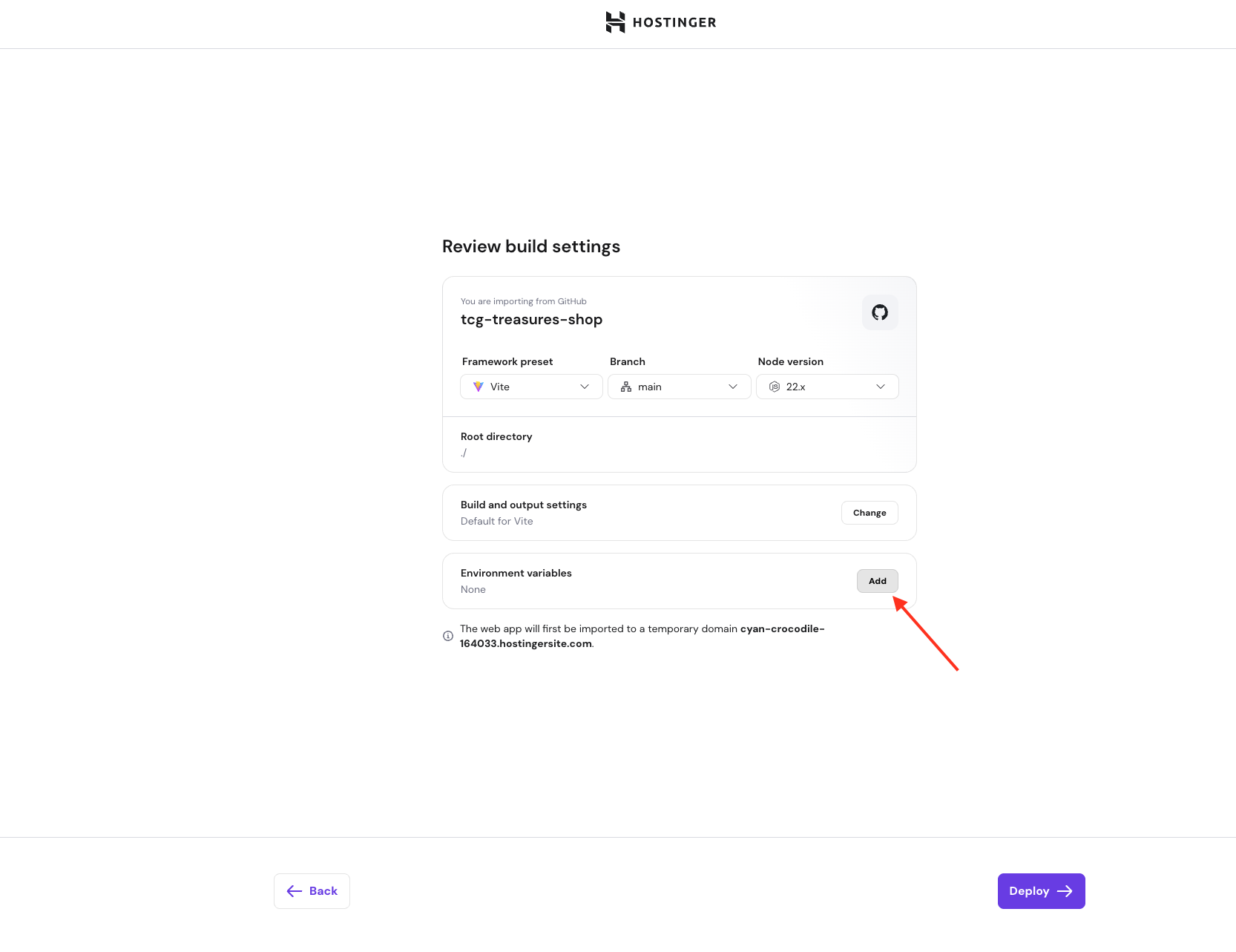
- At the Environment variables step, select Import from .env file
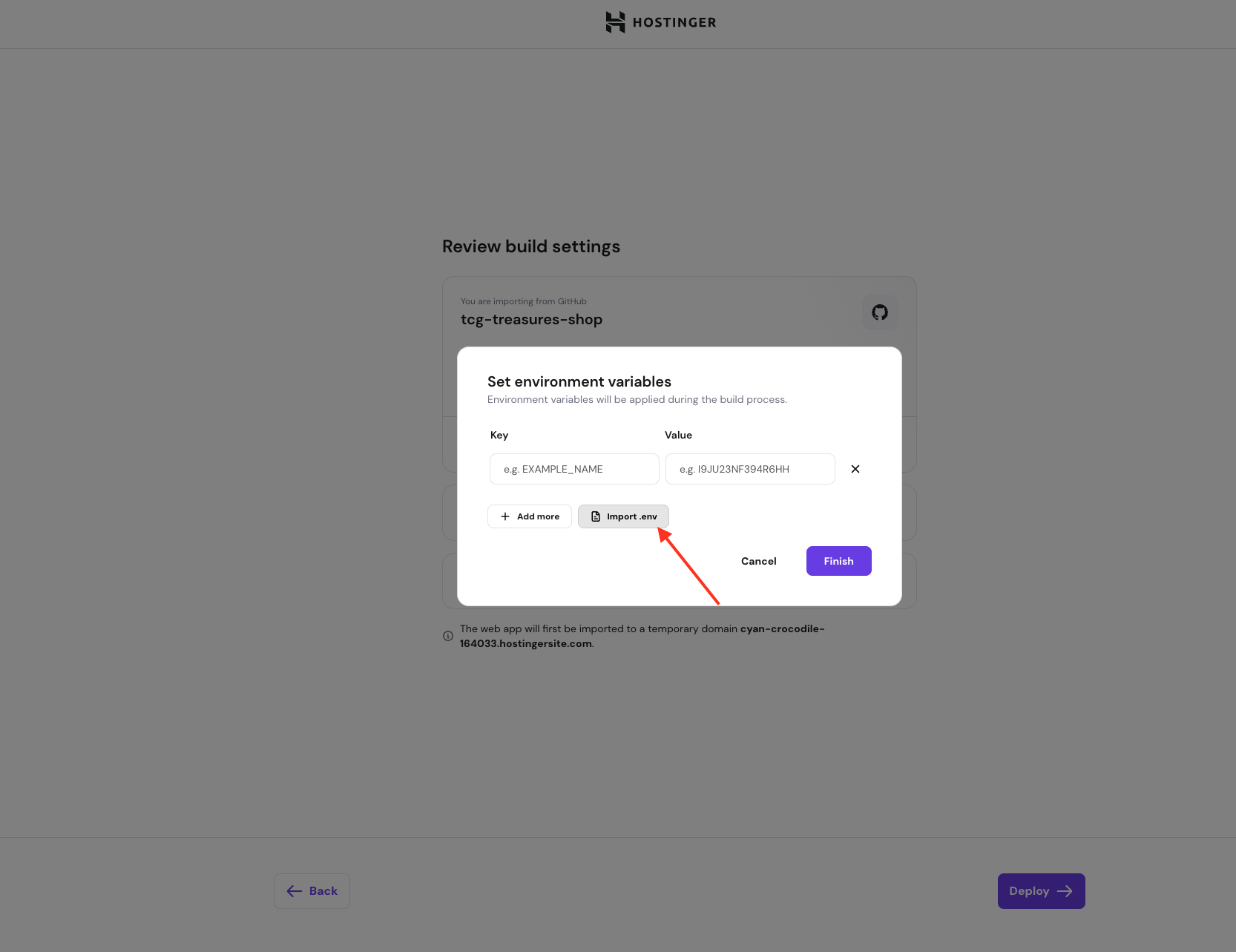
- Upload your .env file or paste its contents into the input field
Your .env file should follow this format:
DATABASE_URL=mysql://user:password@host:port/database
API_KEY=your_api_key_here
NODE_ENV=production- Review the imported variables to ensure all required variables are present and there are no typos
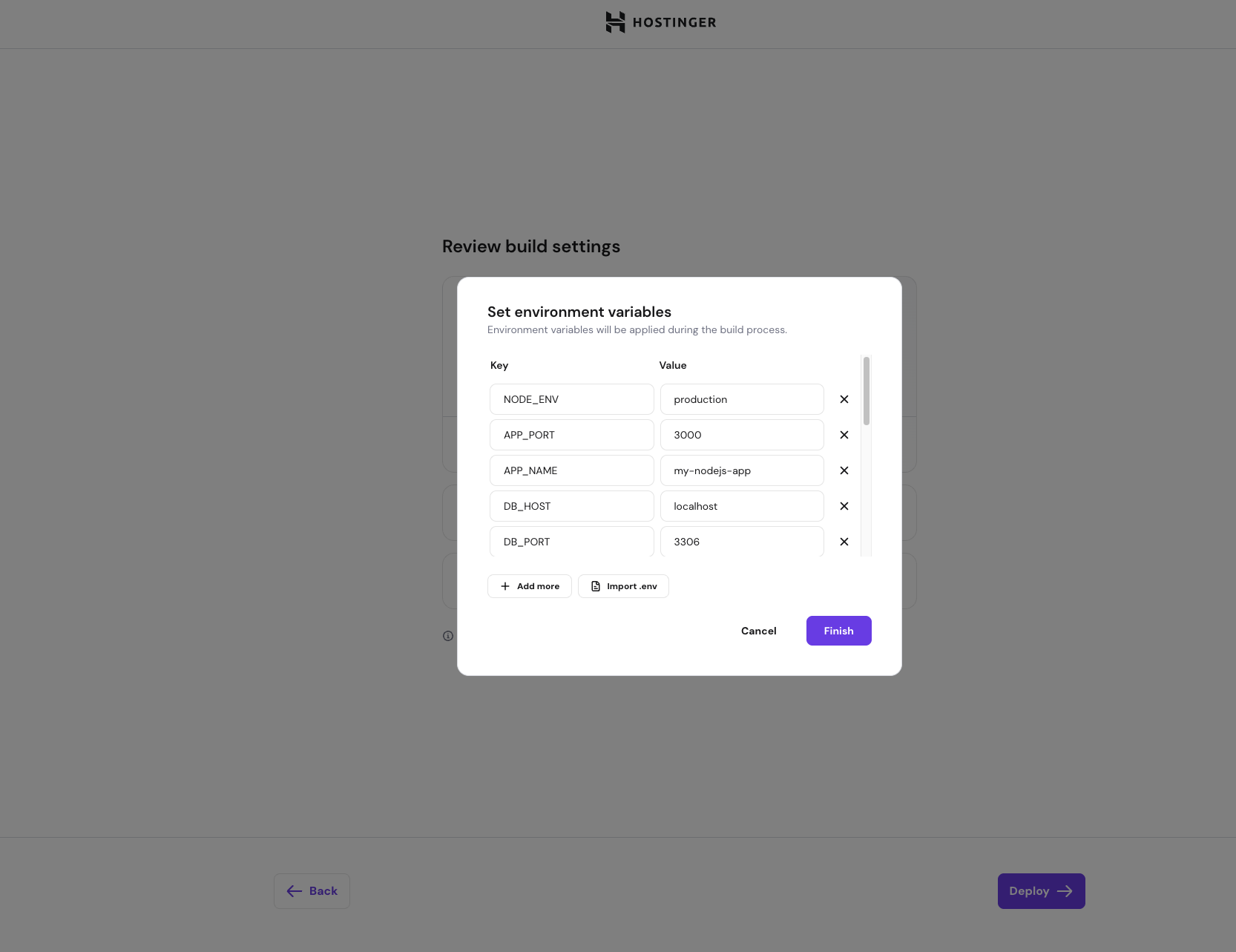
- Click Confirm to save the environment variables
Option 2 — Add environment variables manually
If you only have a few variables or don’t use a .env file, you can add them manually.
To add environment variables manually:
- Start the Node.js application deployment process
- At the Environment variables step, click Add
- Enter the variable name (for example, DATABASE_URL)
- Enter the variable value
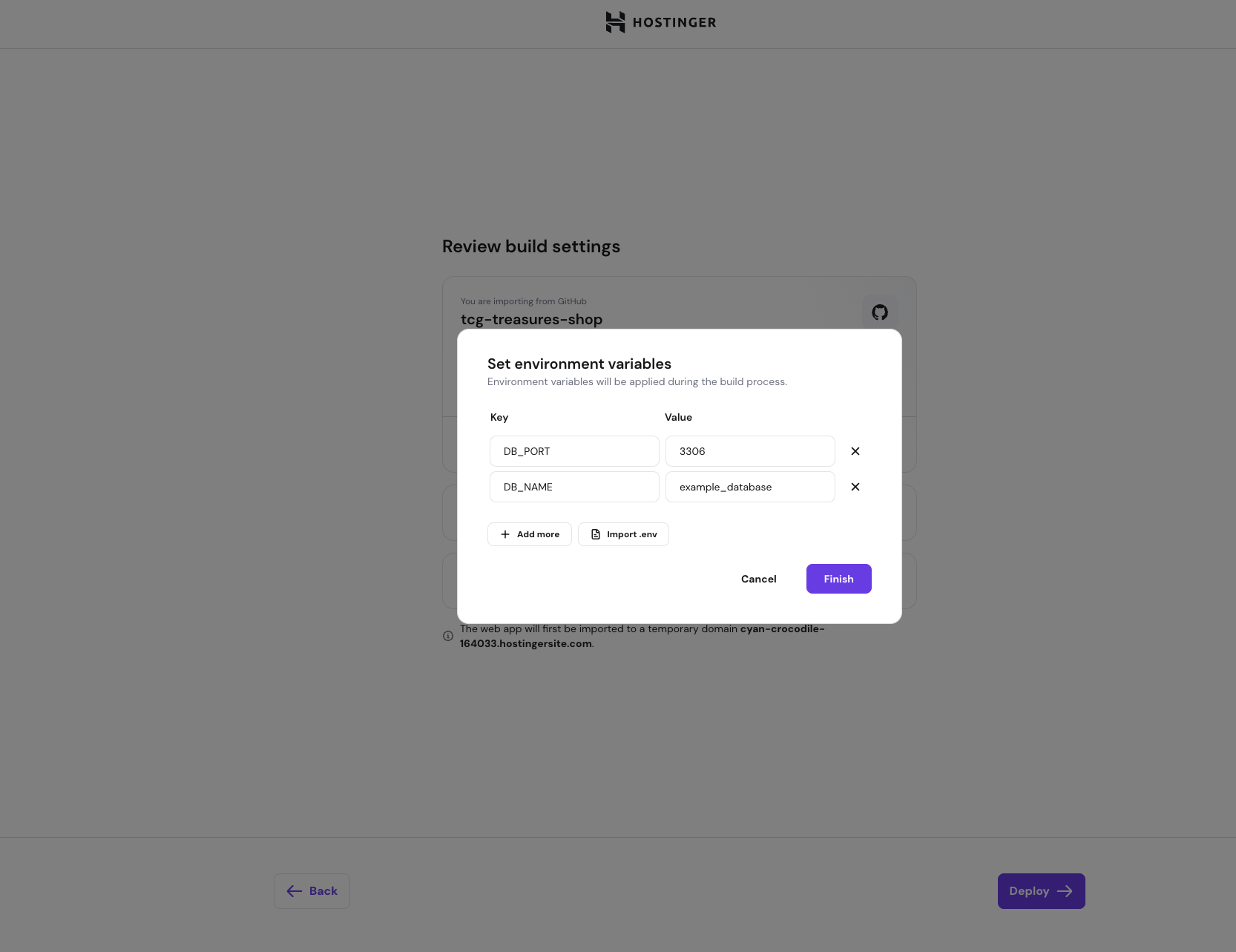
- Repeat the process for each environment variable
- Review the list of environment variables
- Click Confirm to save them
NOTES:
- Environment variables added during deployment are not stored in your repository.
- If you update environment variables later, you may need to redeploy your application for changes to take effect.
- Never commit sensitive data such as API keys or passwords directly into your GitHub repository.