Aug 27, 2024
Leonardus N.
6min Read
Aug 27, 2024
Leonardus N.
6min Read

To understand the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error fully, you have to know how DNS works. When you type a website address such as hostinger.com, your computer sends a DNS request to get the IP address of the web server that hosts the website.
The lookup process can be quick if the browser or internet service provider has already stored the IP address in its cached files. If it can’t find the matching address in the DNS entries, it will go through the DNS domain name resolution process to get the IP address.
Sometimes, the website may have moved to another IP address, but the system is still storing the old cached address. The browser will get the outdated address from the cache, so the domain name cannot be resolved, and the error message will be triggered.
However, there are other possible causes for this error too. This includes network configuration, browser or internet settings, and DNSSEC application.

| Error code | ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED |
| Error type | DNS |
| Error variations | NET::ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED The webpage is not available The site can’t be reached |
| Error causes | Cached data Network settings Enabled DNSSEC Firewall or antivirus software misconfiguration Browser settings |
If you prefer a visual tutorial to guide you through the process, follow our video tutorial on how to fix ERR_NANE_NOT_RESOLVED.

Important! Before proceeding, check the domain name on Hostinger’s WHOIS database to see if it hasn’t expired or been suspended.
Since there are several possible causes for the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error, we will discuss six different methods to fix it. These include simple fixes, such as clearing browser cache and data, and more technical ones, like modifying the hosts file and disabling DNSSEC.
One of the most common causes of the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error is outdated cache. Therefore, it’s best to start by flushing the DNS cache on your operating system.
The DNS flush method differs depending on the operating system – we have a complete DNS flush tutorial for Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux. In essence, it’s as simple as using the Windows command prompt window or the terminal on Linux and macOS to execute a command.
We recommend periodically clearing and renewing the DNS cache to prevent security vulnerabilities such as DNS spoofing and behavior tracking.
The Google Chrome browser also stores DNS data to boost page load speed on revisits. However, an outdated entry in the DNS cache could trigger the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error message if the website has moved to a different IP address.
Clear the host cache on Google Chrome by following these steps:
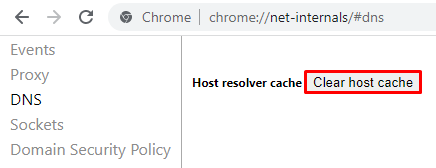
We also recommend periodically clearing browser cookies from Google Chrome. Browser cookies can block your internet DNS, triggering the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error message.
Check our complete guide on how to clear browsing data on various browsers.
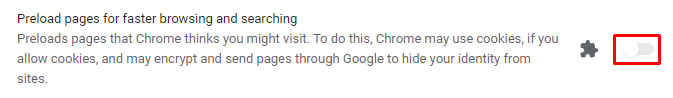
Another Google Chrome setting that’s worth checking is the page preloading service. This feature prefetches the resources of web pages related to sites you have already visited, including DNS preloading.
The main goal is to improve user experience as the prefetched page will load faster. However, this feature is also known to cause the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Thus, it’s best to disable the prediction service to prevent the error from happening. Moreover, prefetching the pages uses your internet bandwidth and takes up local resources.
Follow these steps to do so:
A firewall or security software can block the internet connection and cause the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED DNS error, especially if you accidentally misconfigured it. Resetting your firewall settings is a possible quick fix.
Follow these steps to do so on a Windows computer:
Another possible cause of this error is that the DNS server is not working properly. Therefore, when you try to access the website, the DNS query can’t be resolved.
In this case, using one of the following DNS server addresses from Google and Cloudflare public servers should solve the problem.
| DNS Server | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| 8.8.8.8 | 2001:4860:4860::8888 | |
| 8.8.4.4 | 2001:4860:4860::8844 | |
| Cloudflare | 1.1.1.1 | 2606:4700:4700::1111 |
| Cloudflare | 1.0.0.1 | 2606:4700:4700::1001 |
To do so, you need to configure the DNS server on your computer. Here are the steps to change the DNS address on a Windows computer:
If you’re using macOS, here are the steps:
If you’re using the Linux operating system, you’ll have to use the terminal to change the DNS address.
sudo nano /etc/resolv.confnameserver 8.8.8.8nameserver 8.8.4.4sudo chattr +i /etc/resolv.confThere’s a hosts file in your computer that contains domain names and their IP addresses. When you visit a website, the computer will first look at the hosts file to find a matching domain name and IP address. The system will only send a DNS request if it doesn’t find any matches.
Adding the website’s IP address to the hosts file can fix browsing problems caused by the DNS. It’s also useful for finding out the error source. If you can access the website after adding the domain name and its IP address to the host file, the problem was coming from your side.
Check our complete guide for editing the hosts file on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
In summary, find the hosts file in the Windows system folder and open it using Notepad. As for Linux and macOS, use the terminal and a text editor to open and edit the file.
Problems with your internet connection and WiFi router can be another reason why the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error occurs.
There are two tests you can do to confirm this. The first one is reaccessing the website using a different, stable internet connection.
For example, create a mobile hotspot from your mobile phone and use that to connect your computer to the network. Revisit the website and see if it loads normally. If that is the case, there’s a chance that the previous internet connection is the root cause of the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Another option is adding various devices to the same internet connection and using them to open the same website. If all devices show the same error, then the internet connection must be the main issue.
Turn off the router and disconnect the power supply. Wait for at least 30 seconds before reconnecting the power and turning on the router again.
Keep in mind that the router takes a while to become fully functional. Wait until the internet light turns green before connecting your computer to the network and testing it again.
If you have tried all methods above and the error persists, check the domain on WHOIS to see if DNSSEC is enabled.
It’s an additional layer of protection that uses cryptographic signatures. While it protects the access to the DNS records from unauthorized users, it can also prevent the domain from propagating properly, and thus triggering the error.
If that’s the case and it’s not your domain or website, there’s not much you can do other than inform the website owner about the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED DNS error. However, if it’s your domain or website, disable DNSSEC from your domain account.
If you use Hostinger, disable DNSSEC by accessing your domain configuration panel.
The ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error happens because the system can’t find the correct IP address or the computer is storing old and outdated information.
Clearing cached data from your system is the primary method to fix the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
However, there are other ways to solve this problem as there can be other contributing factors. Here is a recap:
If none of these methods fixed the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error on your website, contact your hosting provider’s customer support team for further assistance.
Take a look at the following frequently asked questions about the error.
Yes, the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error is a common issue that occurs when your browser is unable to resolve the DNS address of a website you are trying to access. The cause of this issue is often due to your internet connection, DNS server, or the website’s domain name configuration.
One way to prevent the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error is to ensure that the domain name is correctly spelled and that the DNS server is functioning properly. Another way is to clear the browser cache or try accessing the website from a different browser or device.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.