Dec 22, 2025
Domantas G.
5min Read
When you install WordPress on your hosting account, the software adds a list of directories to your web server. From wp-admin that stores administrative files to the wp-content directory where themes and plugins are kept – these keep your pages up and running.
Aside from the core directories, WordPress also comes with the .htaccess file. In short, it is a configuration file that controls how your server is running. We will give you the details about this configuration file and information on how to locate it or create a new file entirely.
In particular, we’ll guide you through the process of locating your WordPress site’s .htaccess file in both Hostinger’s hPanel and cPanel. Please note that Hostinger no longer uses Apache as its main web server. Instead, LiteSpeed has become its drop-in replacement with .htaccess file support, and it is used for all Hostinger’s hosting services, including managed WordPress plans.
Download all-in-one WordPress cheat sheet
The .htaccess (hypertext access) is a critical WordPress core file used to enable or disable features of websites hosted on Apache. The .htaccess files are also referred to as server configuration files located in your WordPress root directory. By default, WordPress uses the .htaccess files to manage redirects and permalink structures.
Many WordPress plugins also use .htaccess files to operate, including most security plugins and caching plugins. These plugins modify and rewrite the .htaccess files to perform their functions.
The .htaccess file allows you to perform configuration changes per-directory basis, from altering your default index page to changing your website’s timezone. More advanced server configuration changes include the ability to:
Access this free .htaccess generator page to generate code snippets and set up more advanced rules on your site.
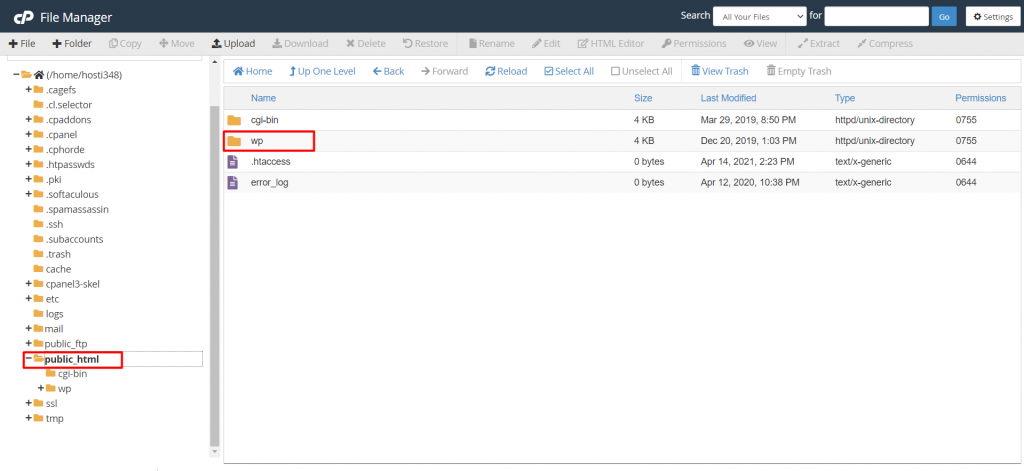
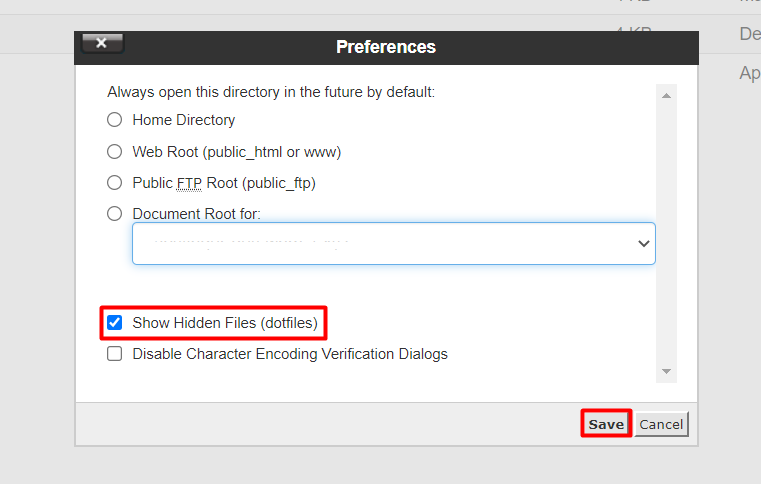
When you install WordPress on Apache Web Server, the .htaccess file is automatically added to your root directory, generally labelled as public_html or www. However, since the file is usually hidden, you will need to use the Show Hidden Files option to find it.
The following sections will walk you through the steps of locating your WordPress site’s .htaccess file in both Hostinger’s hPanel and cPanel.
Here’s how to find and edit your .htaccess file via Hostinger File Manager:

If you use cPanel, the process is more or less similar:
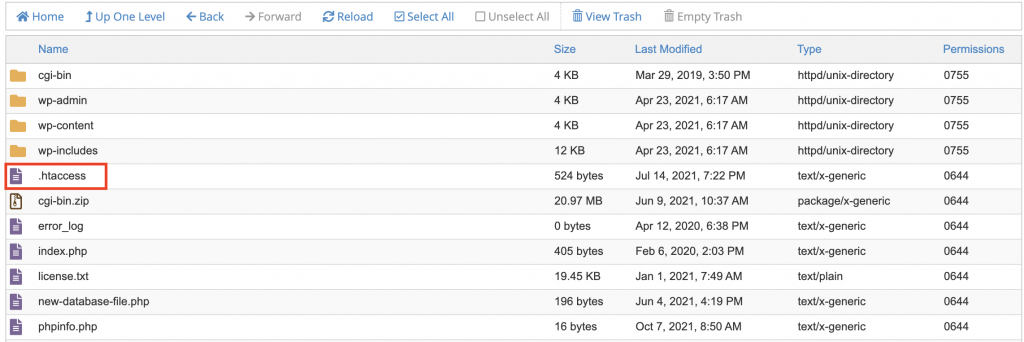
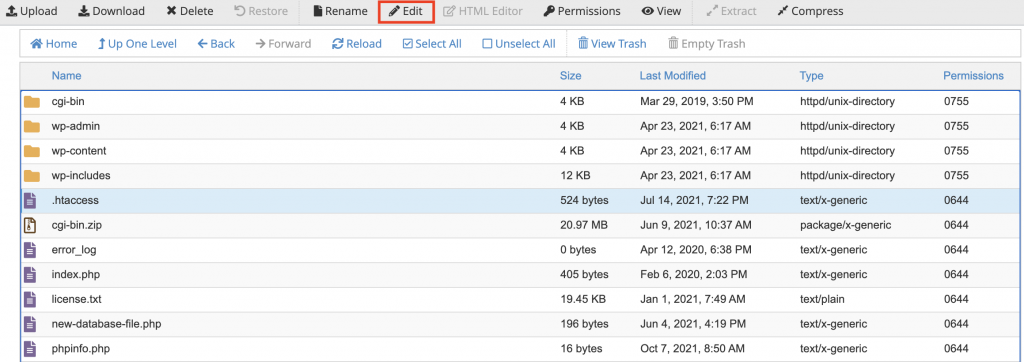
Now that you have located your .htaccess file, you can start editing the file. Start adding code snippets above or below the existing code to enhance the functionality of your WordPress site. However, before you make any configurations, there are several factors worth paying attention to:
There are a few instances where your WordPress installation will not include the .htaccess file by default. Alternatively, a broken plugin might corrupt this server configuration file and disrupt your site. In these cases, you will need to create a new file from your hosting control panel manually.
hPanel users will locate the New file button on the left sidebar menu on your File Manager page.
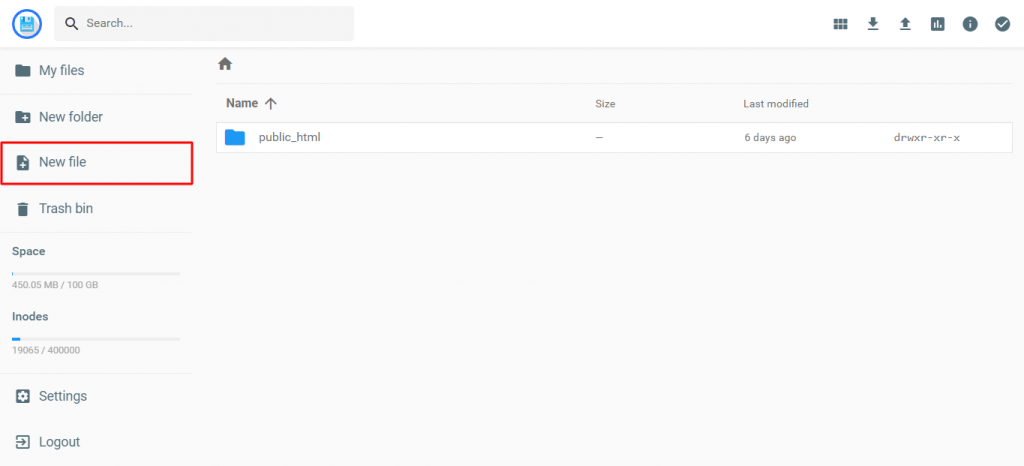
If you use cPanel, choose the New File button on the upper-left corner of your screen.

Enter .htaccess as the file name, then insert the code below:
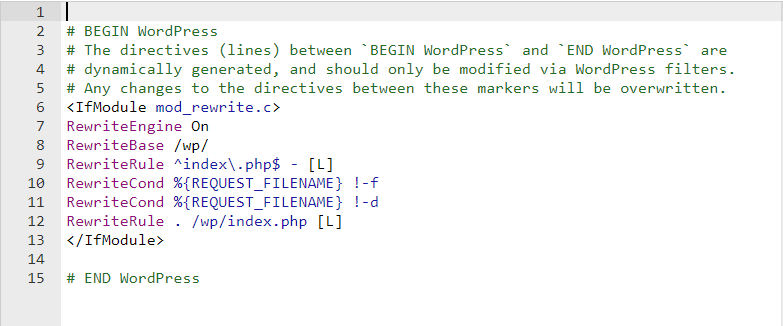
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPressOnce you’ve added the code, press Create to save your changes. Keep in mind that the code is universal for all WordPress sites. However, other content management systems (CMSs) will have different code for their .htaccess files.
Aside from the method above, you can also use a text editor such as Notepad to create a .htaccess file, then upload it to your web server using an FTP client.
The .htaccess file is a configuration document for use in WordPress websites. This file plays an important role in keeping your site accessible, as it determines how the server runs and functions.
Every WordPress installation will include a .htaccess file that you can access through your hosting control panel or FTP client. When you host multiple sites, your web server will also have multiple .htaccess files.
By making full use of your .htaccess files, you can perform various configuration changes on a per-directory basis. This includes blacklisting or whitelisting specific IP addresses, redirecting traffic from HTTP to HTTPS, and setting up a password on every directory.
In this guide, you have learned how to locate the .htaccess files on your server. If the .htaccess files are not present for some reason, you need to manually create one and upload it to your server. Simply create a new file in the public_html directory, label it as .htaccess, and fill out the default code.
Give it a try, and should you have any further questions, please leave them in the comments below.
WordPress Multisite
Headless WordPress
WordPress REST API Tutorial
How to Use Xampp
What Is WordPress Heartbeat
How to Become a WordPress Developer
Best WordPress Frameworks
How to Perform a WordPress Search and Replace in the Database
Learn more about WordPress .htaccess from these frequently asked questions.
To edit .htaccess in WordPress, access the file via an FTP client or File Manager, then make changes using a text editor. It’s important to back up the file before editing and to use proper syntax to avoid errors.
The default WordPress .htaccess file is a configuration file used by Apache web servers to control website access and URL structure. It includes rules for WordPress permalinks and security settings to help prevent unauthorized access and protect against malicious attacks.
Comments
January 23 2018
Thanks for the awesome article
February 15 2018
No problem! It's great to hear that you found it useful! :)
February 21 2019
Thanks, you gave easy and right method ?
July 31 2019
Great resource :)
November 29 2019
Great Job!!!!!!!!!!!
June 20 2020
Hello. I can!t reach my website through https://................./wp-login.php adress. I have uploaded htaccess file, wp-config.php file separately but they are not making a difference. Please help me, I am not a code writer:( Thanks a lot
July 14 2020
Hey Aylin! To open your website through wp-admin you will need to have an active SSL certificate on your domain name. :) Please make sure you have SSL installed, and then you can try accessing the page via HTTPS again!
June 27 2020
Thanks. Very helpful
December 20 2020
Hey!! I accidently deleted my .htaccess file and now my categories section is blank. Even though al categories are there in categories link. but not showing in post editor Could you please help me solving this? Screenshot for ref - https://imgur.com/a/PmHASV7
February 09 2021
Hi, John! If this happened after removing the .htaccess file, first thing I'd suggest would be looking into it's restoration options. A lot of hosts will have the option to restore one file only. For Hostinger plans, you'll find it from hPanel -> Backups :)
January 19 2021
Great resource :):)
February 08 2021
AHHH thank you, saved me so much time waiting for hosting support.
August 04 2021
Thank you so much. I have just spend 10 agonizing hours trying to get my Wordpress site back up. I tried renaming htaccess, renaming plugins, reinstalling WP and keeping only the content files etc etc. Nothing worked .... until I read this! And this did the trick. Now I am back up and trying to troubleshoot what went wrong in the first place.
April 30 2024
Please help me to restore my account back from forbidden error
May 08 2024
Hello! For assistance with account restoration, we recommend reaching out to our Customer Success Team directly. They'll be able to provide personalized assistance and help resolve the issue promptly ?
August 04 2025
What would need to be in the .htaccess if you have created a custom react app to host on hostinger? The app will be static of course
September 11 2025
Hi, William! Usually when you’re hosting a custom React app on Hostinger, your .htaccess file in the project’s main directory would look like this:
RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d RewriteRule ^.*$ index.html [L]This helps prevent 404 errors by telling the server that if it cannot find the requested file or folder, it should serve the index.html file instead.