Dec 02, 2025
Ankit
14min Read

Navigating WordPress is not always simple, especially if you’re new to building websites. However, with the right guidance, managing your WordPress site can be less intimidating than it seems.
In this guide, you’ll explore the available tools for editing your site – from the default WordPress editor to page builder plugins – and learn how to update each section, including the header, footer, and content areas.
We’ll also share best practices to help keep your site secure and efficient while you make changes. By the end, you’ll feel confident handling your WordPress site like a pro. Let’s begin.
There are several ways to edit a WordPress website. Before we get into more detail, let’s briefly explore each method individually.
Ideal for: Block themes, holistic site design, beginners seeking visual control.
Think of the Site Editor as a canvas where every element from header to footer becomes a movable, customizable block within a cohesive system.
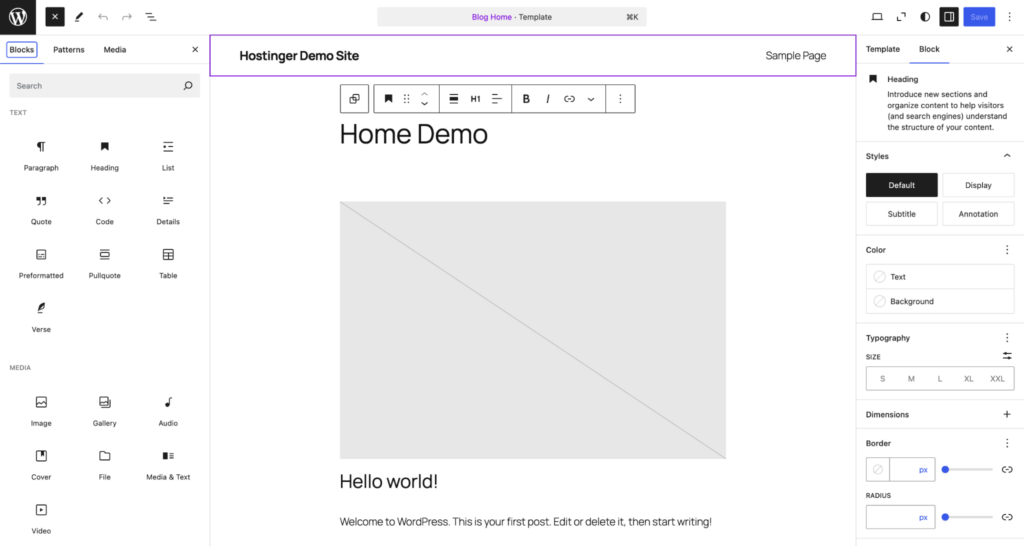
With the Site Editor, you can:
The only limitation is that the Site Editor requires you to be on a block theme. Users with classic themes won’t have access to this environment.
Ideal for: Classic themes, targeted adjustments, users who still run legacy WordPress themes.
The Customizer is the traditional way to edit WordPress sites built with classic themes. It offers a more structured approach to site editing.
For instance, it provides a live preview of changes, allowing you to tweak settings like site identity, colors, and menus before publishing.
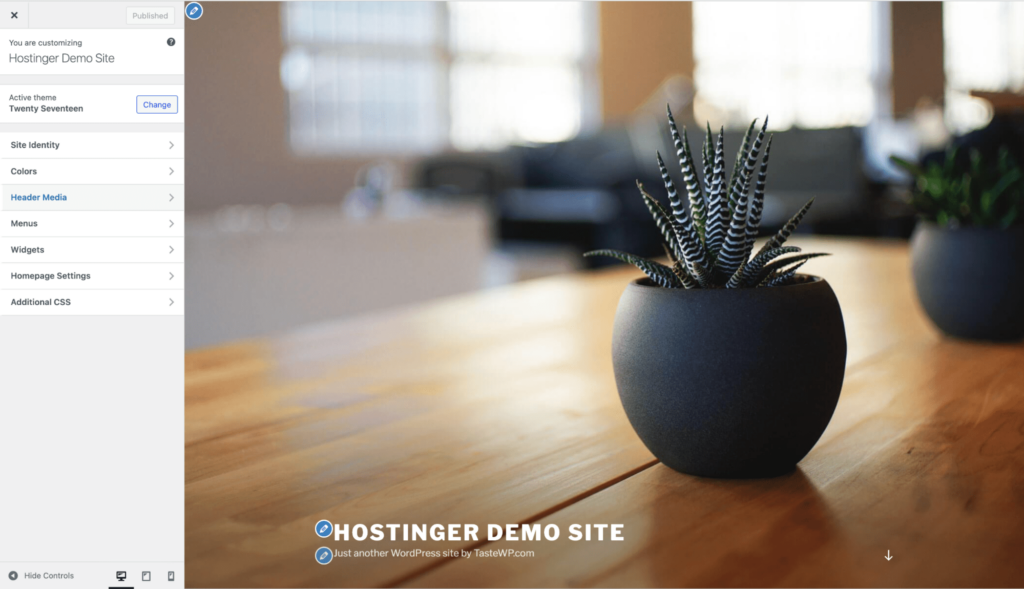

While the Customizer works with all traditional themes, it offers much less creative flexibility than the Site Editor.
You need to work within the customization options provided by the theme developer.
This complexity is further amplified by the fact that any advanced customization typically requires CSS knowledge. That can limit how far you can go in terms of customizing your website, depending on your technical skills.
Ideal for: Block and classic themes, beginner-to-advanced users.
Page builders (like Elementor, Beaver Builder, Divi, and many others) are third-party plugins that offer a drag-and-drop interface for designing custom layouts.
They provide pre-built templates, advanced styling options, and more flexibility than both the Site Editor and Customizer.
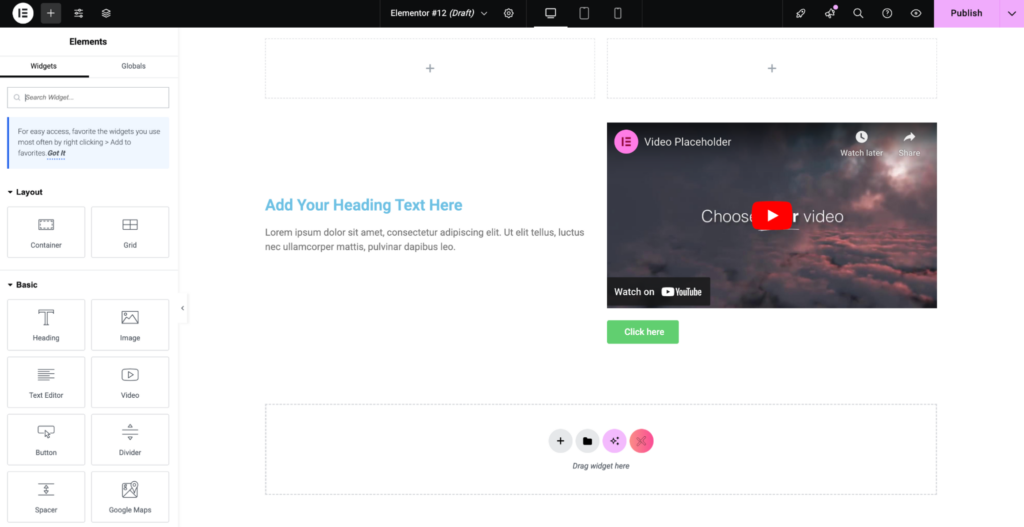
Page builders offer extensive template libraries, advanced styling controls beyond native WordPress capabilities, specialized modules for complex functionality, and responsive design for different device sizes.
They work with both classic and block themes, which make them a popular choice for users who want highly customized designs without coding.
However, premium page builder plugins can be expensive. Also, some of them may slow down website performance if not optimized properly.

In this section, we’ll examine simple ways to change the appearance of your theme, including adjusting colors, fonts, layouts, and spacing to match your style.
The Site Editor lets you modify your theme’s visual design through blocks, colors, typography, and spacing without writing code.
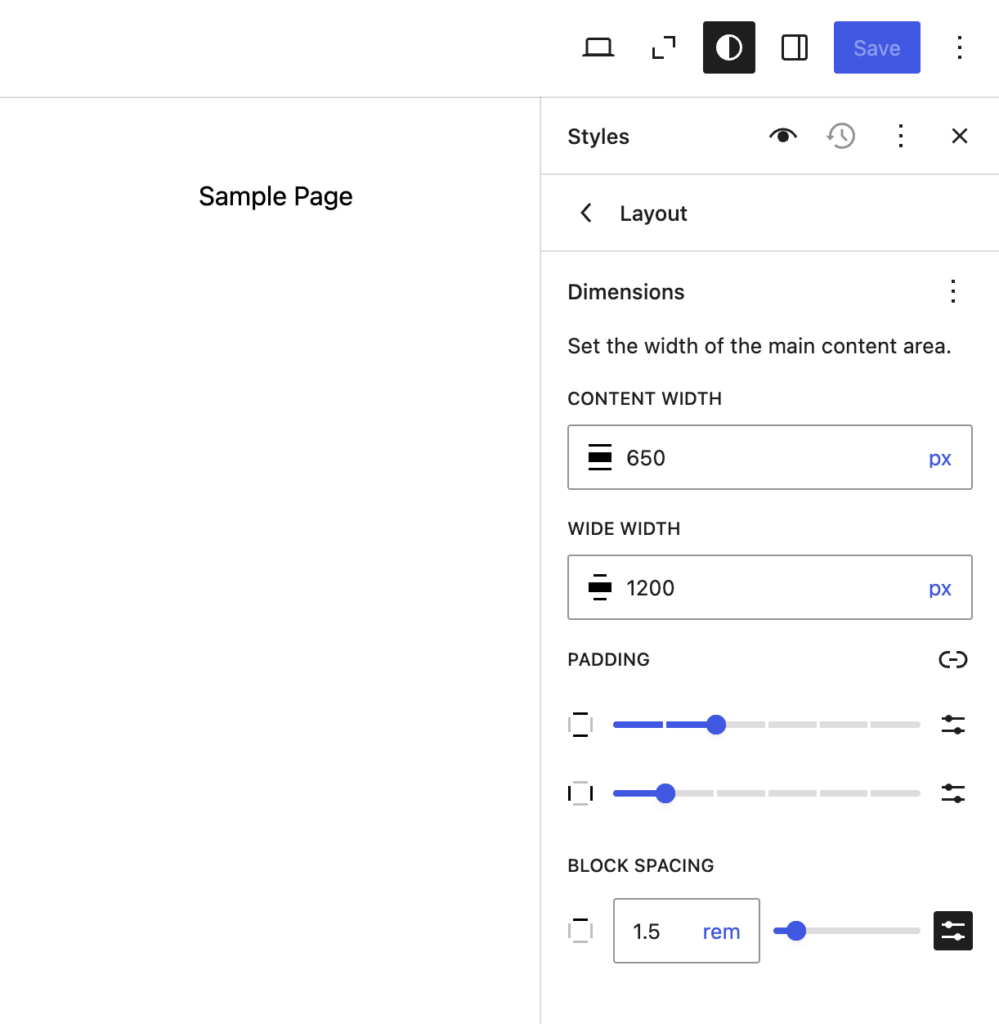
With Global Styles, you can adjust site-wide settings such as colors, typography, and layout. Here’s how:
Go to Appearance → Editor in your WordPress dashboard. Then, head over to the Styles section on the left panel.
Click the Edit Styles icon at the top of this panel to edit the presets. You can preview different color schemes and combinations before choosing a suitable option.
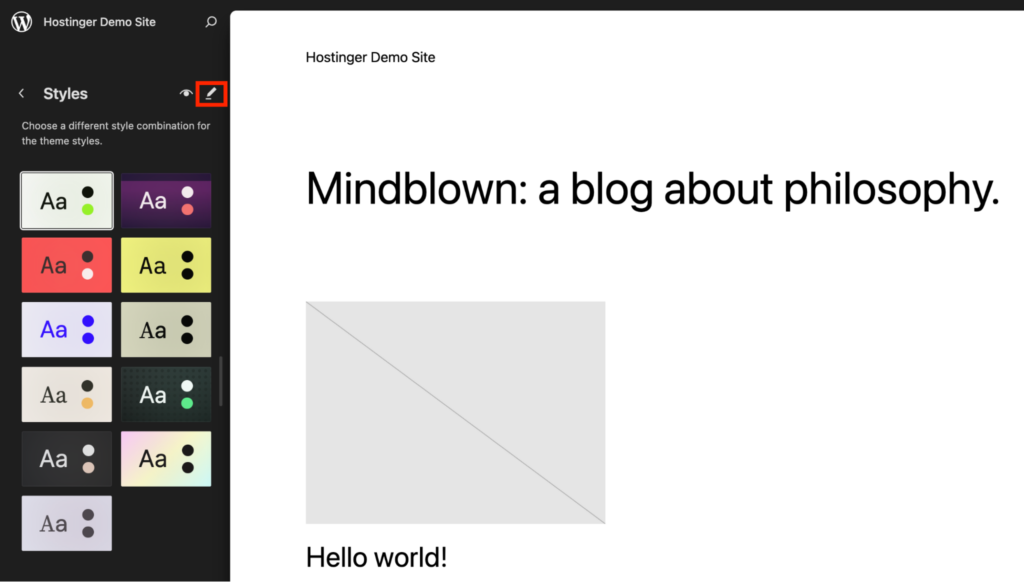
This will open the styles panel on the right of your screen. Access the Global Styles settings and make changes to your preferences.
Here’s what you can customize:
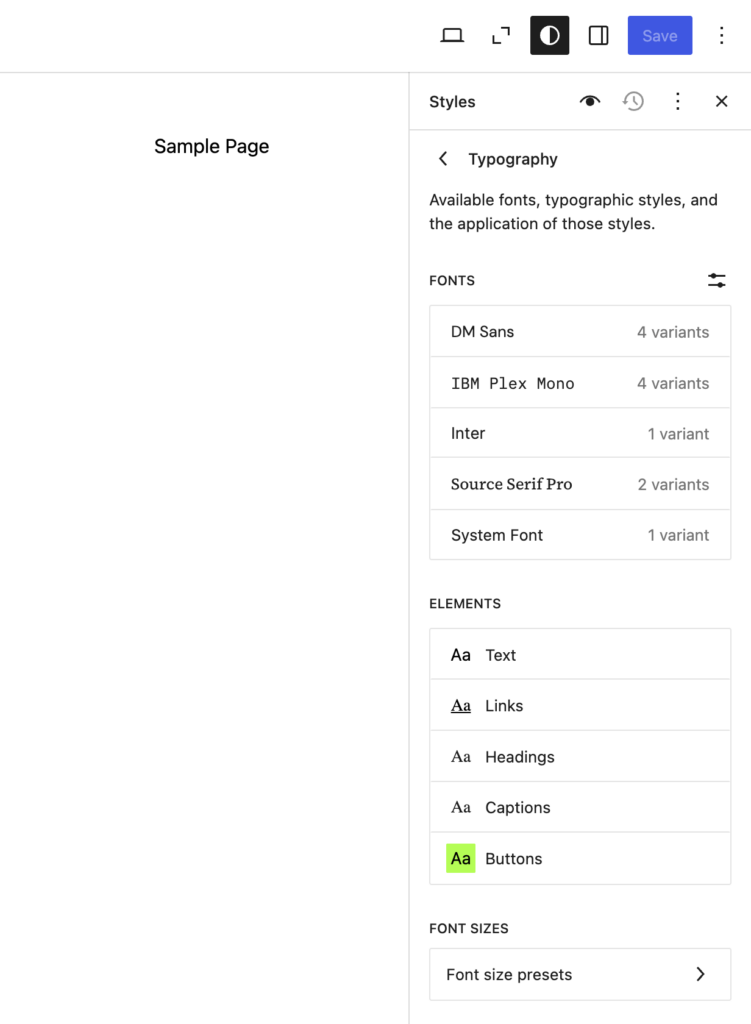

Customizer is the default editing tool for classic themes. Here’s how you can customize your WordPress theme with it:
Go to Appearance → Customize in your WordPress dashboard.
You should now be redirected to the home page, which has a left sidebar with different customization options. These options depend on the theme you’re customizing.
In general, you’ll see these options:
Elementor and Beaver Builder are powerful page builder plugins that help you design your website and change your theme.
First, you’ll need to complete a simple setup process:
Once this is done, you’re ready to begin customizing your page.
We’ll use Elementor for this walkthrough.
Click Elementor from the dashboard sidebar → Theme Builder → Customize.
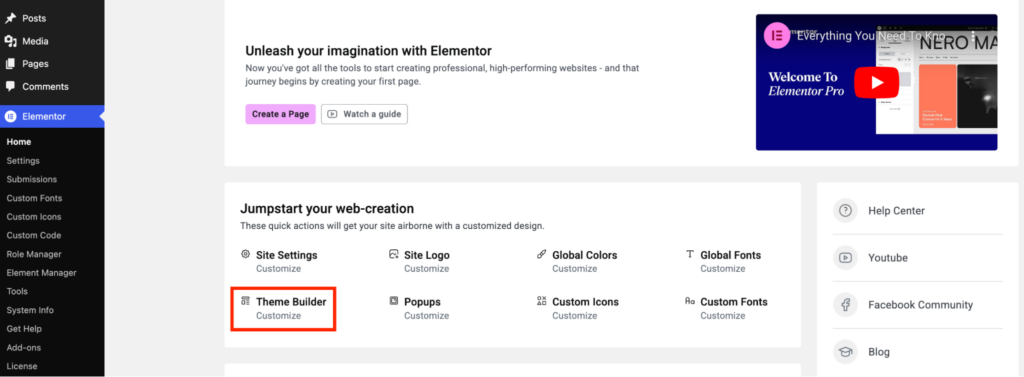
You’ll be redirected to the theme builder page, where you can customize individual parts of your theme.
Here’s what you can customize:
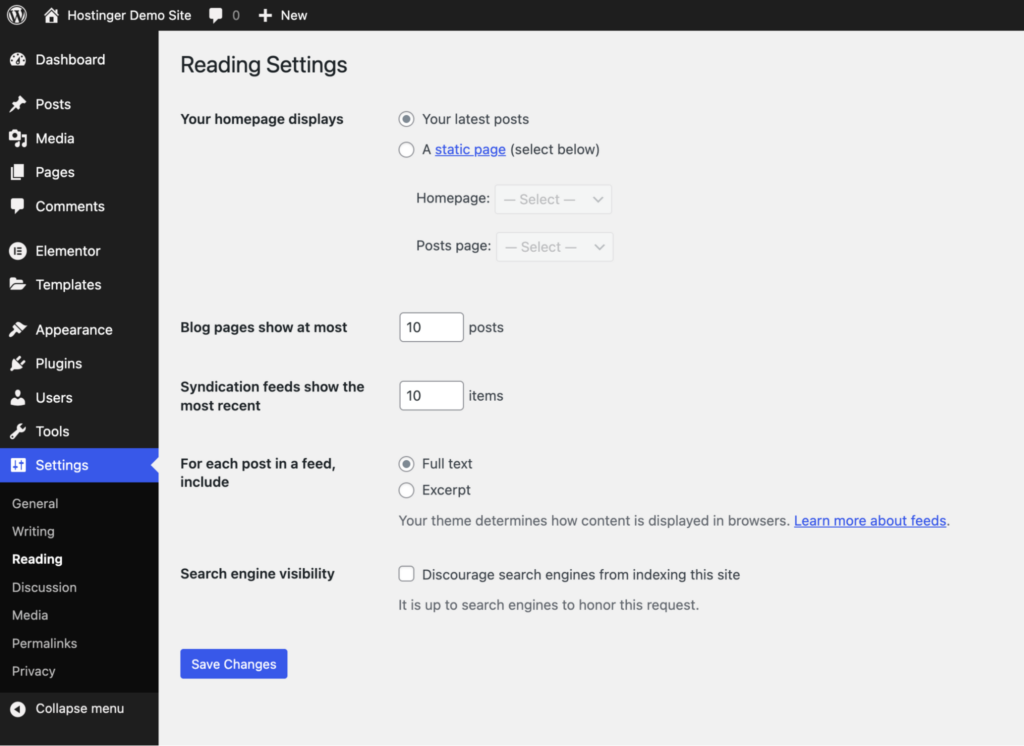
WordPress lets you pick any page as your homepage. Here’s how you can configure it.
Go to Settings → Reading on your WordPress dashboard. Under Your homepage displays, choose Your latest posts or select A static page. Click Save Changes.
Now, let’s look at different ways to edit your WordPress homepage.
Here are the steps to edit your homepage using the Site Editor:
Go to Appearance → Editor on your WordPress dashboard.
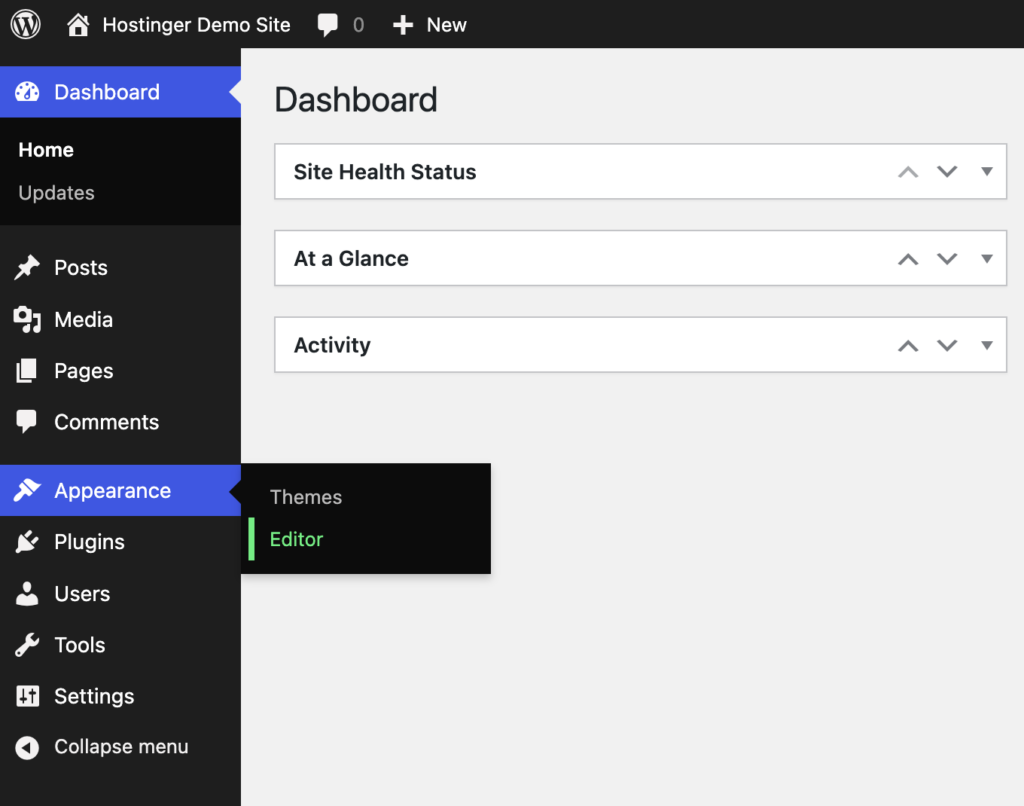
You should now see the homepage on the right with the design options on the left.
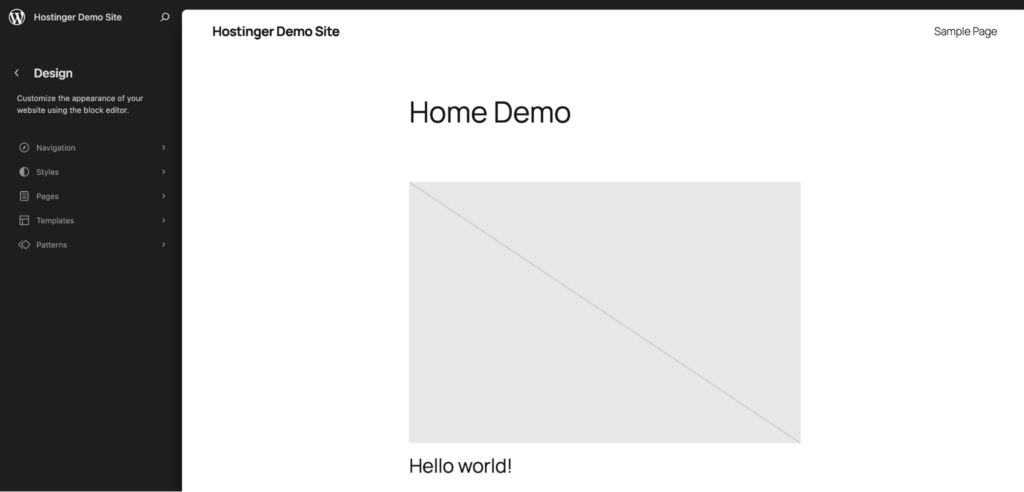
Click on the homepage. You can now edit the page visually by clicking individual elements.
Press the + icon on the top editing panel beside the WordPress logo to add new blocks, patterns, and media. Here are some essential elements of a good homepage:
Remember to save your progress and apply the changes by hitting the Save button in the top-right corner.
Here’s how you can edit your homepage on a classic theme using Customizer.
Go to Appearance → Customize in your WordPress dashboard.
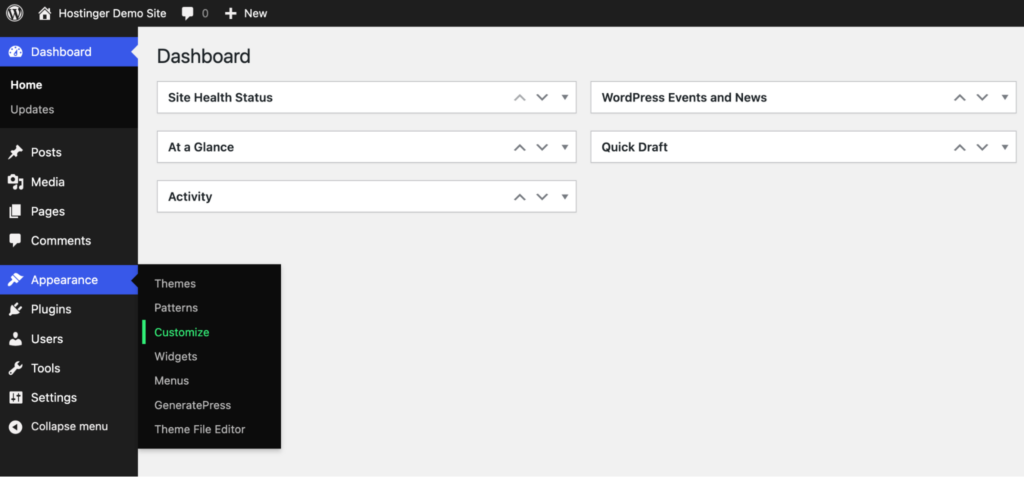
Open Homepage Settings from the editing panel on the left part of your screen. Choose a specific page or the latest posts as the homepage if you haven’t already defined it.

Here’s what you can edit on your homepage:
To edit the homepage with Elementor, you must first create a page with it and set it as the Home Page via Settings → Reading → A static home page.
Go to Pages → Add New Page.
Then, click on Edit with Elementor at the top of the page.
You can now customize your homepage using the modules available on the left panel.
Once this page has been set as the homepage, you should now see an Edit with Elementor button when you visit the homepage while logged in. This lets you edit the homepage with Elementor whenever you want.
You can either start with one of the pre-made templates to speed up the process or open a blank canvas to design everything from scratch.
Begin by organizing your homepage’s elements in order of importance so visitors immediately understand what matters most. Elementor makes this easy with its drag-and-drop interface and specialized sections:
What makes Elementor useful for beginners is that you can see every change instantly as you make it. You can also customize everything from spacing to colors by clicking directly on any element and using the side panel options.
Headers and footers function as your site’s structural framework. They appear on every page of your site to create consistency and orientation.
Headers typically include your site’s navigation system, making content easy to explore. Footers, on the other hand, include essential trust elements like contact information and links to legal documentation.
Together, they create an experience that helps visitors confidently navigate your site regardless of which page they’re viewing.
Let’s explore how to edit your website’s header and footer.
The Site Editor offers multiple templates for your site’s header and footer. Here’s how to edit these elements:
Go to Appearance → Editor in your WordPress dashboard.
Click Patterns from the editing panel on the left.
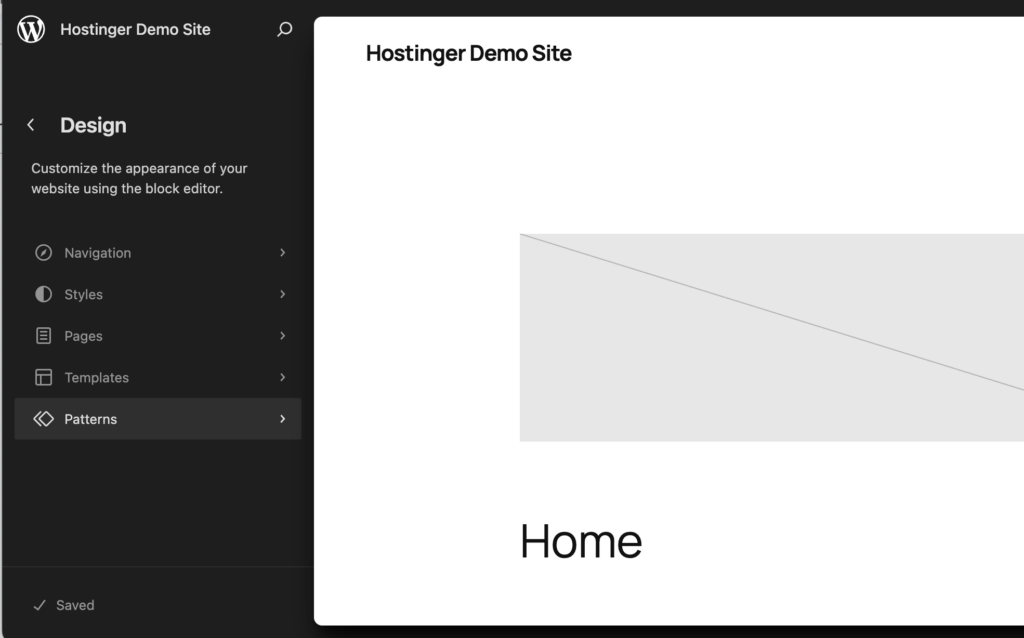
Go to Header to see all available designs. Open any of these designs to edit headers.
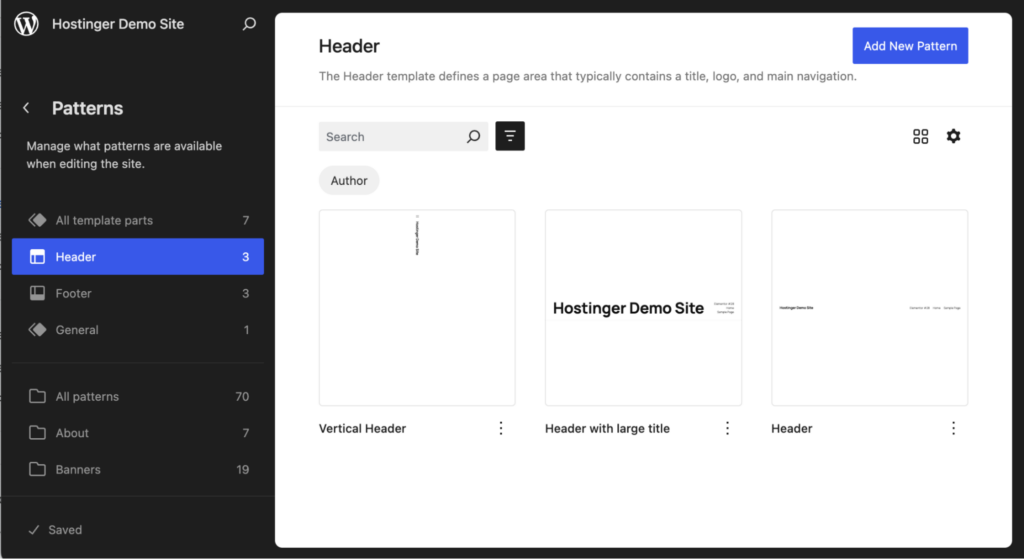
Alternatively, go to Footer to see all available footer designs.
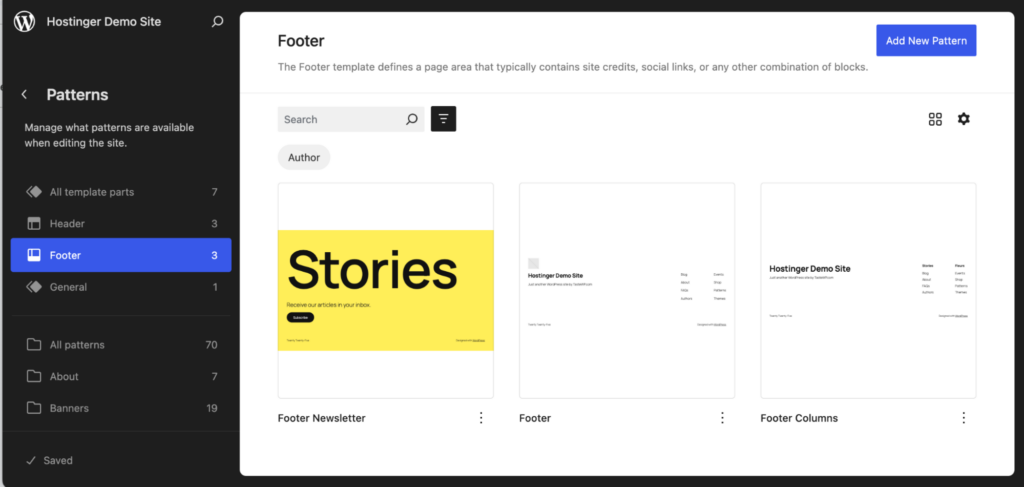
Click Add New Pattern → Add New Template Part on the top-right corner to create a new header or footer design.
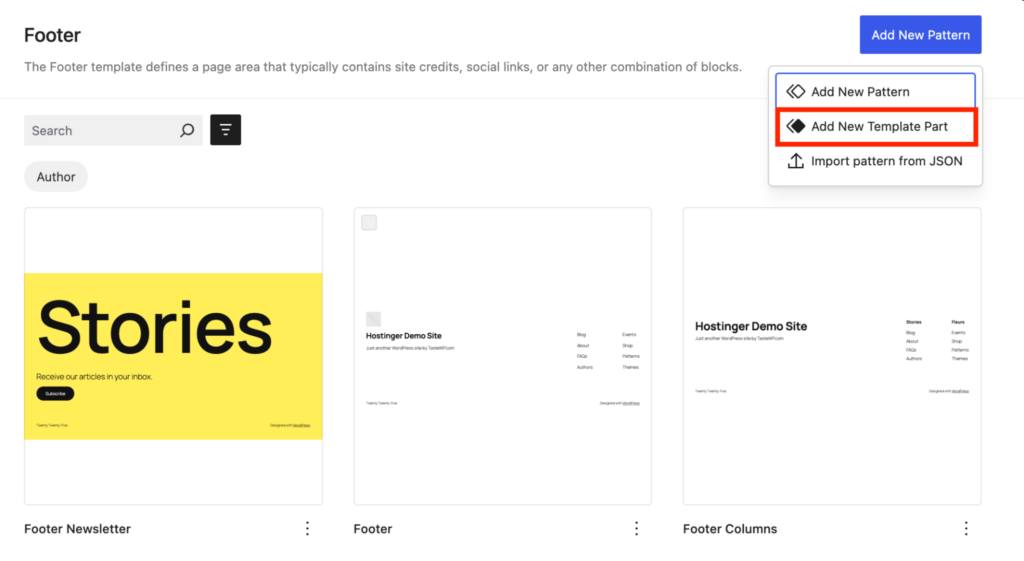
Choose whether you want to design a header or footer element. Then, add a name, select the type of template part, and click Add.
Here, you’ll find all the editing tools you need to design this new element. You can add new blocks or media as you like.
Classic WordPress themes split header and footer customization across two interconnected systems.
The Customizer handles visual styling (colors, layout, sizes), while the Widget Areas let you add functional content blocks like menus, search bars, and contact information.
To access these systems, go to Appearance → Customize, then look for Header or Footer options in the sidebar menu.
Click on Header Builder in the left sidebar to access design controls for your site’s top navigation area. You’ll immediately notice that header options vary dramatically between themes.
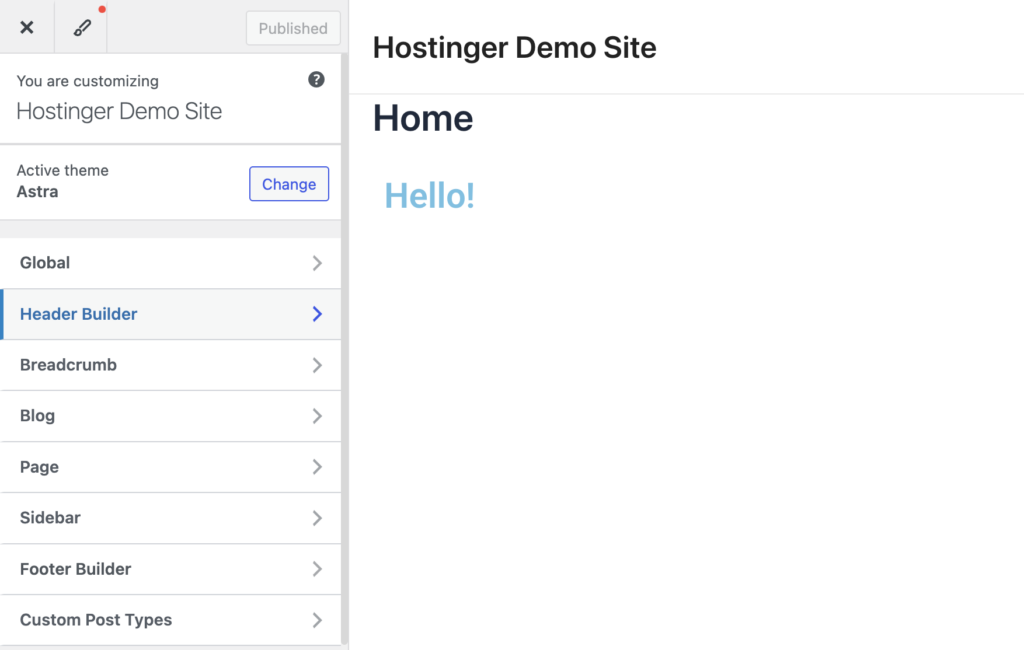
For this guide, we’re using the Astra theme because it offers exceptional header customization flexibility, revealing the full potential of WordPress headers.
If the theme has header presets, you’ll see them here. Depending on the theme, you can also add custom elements and widgets to the header.
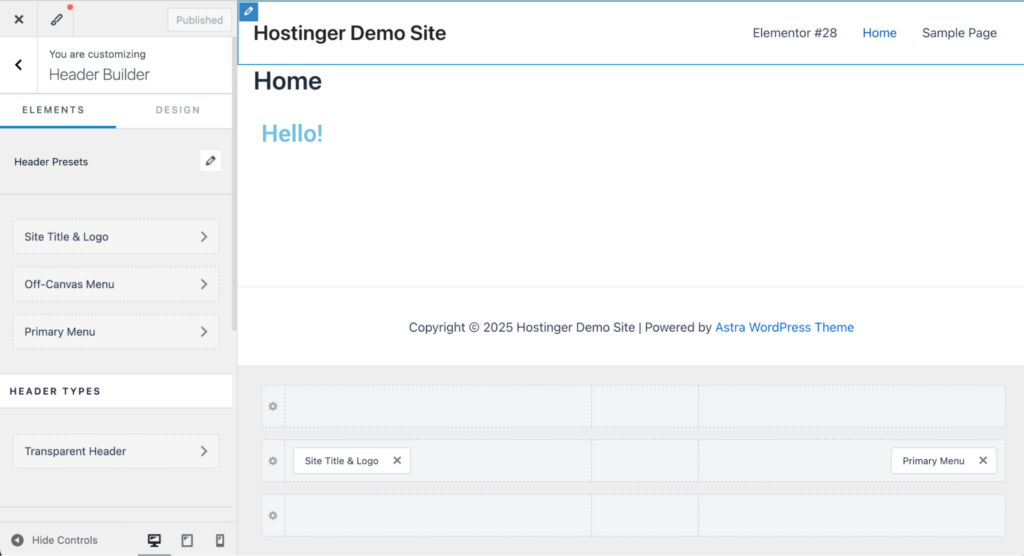
Now, go back to the main menu and click Footer Builder to find all available footer options.
Within the Footer Builder, you’ll typically discover these key options to edit the footer:
Some themes support multiple widgets, while others allow only a few. Here’s how you can add additional widgets and buttons to the Astra footer:
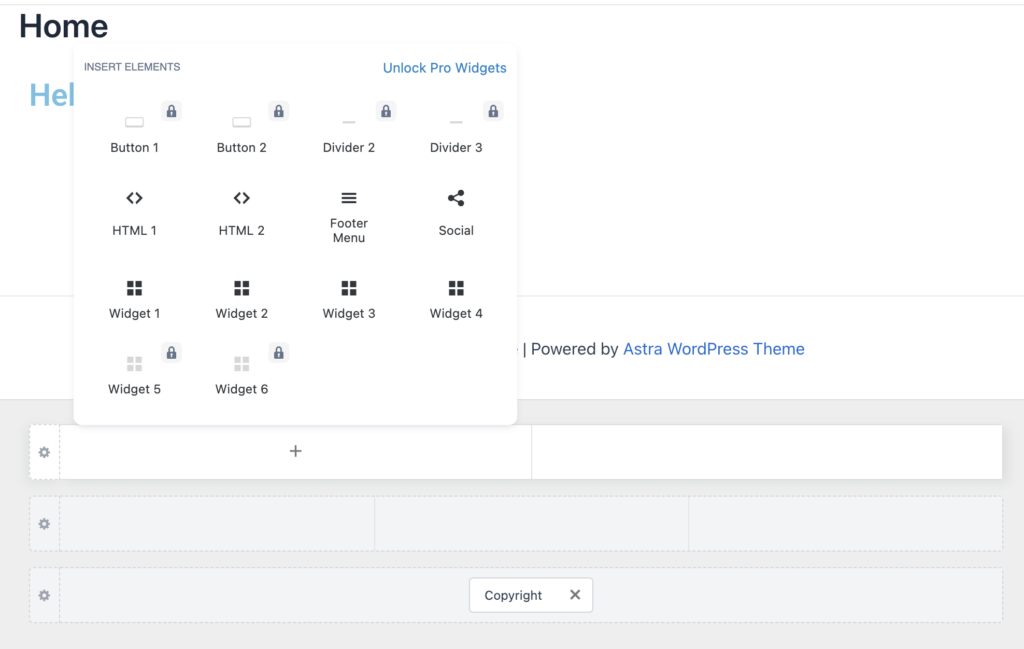
To edit your site’s header and footer with a page builder like Elementor, use the Theme Builder again.
From the dashboard, click Elementor → Theme Builder → Customize.
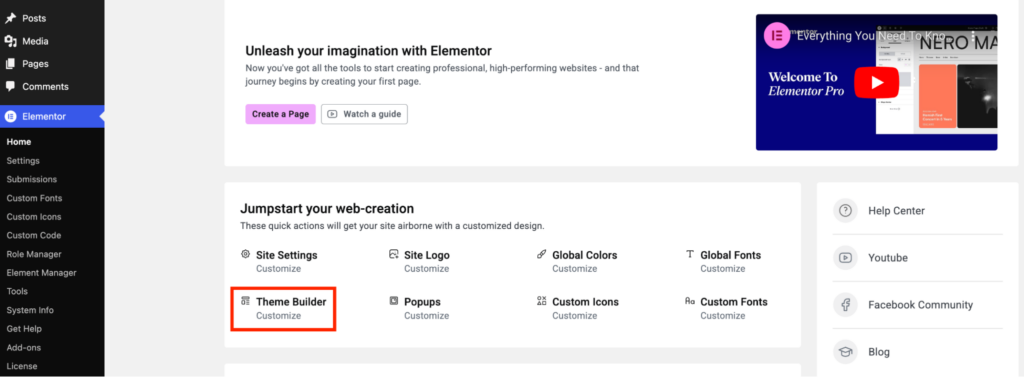
On the next page, select Header or Footer from the left sidebar based on what you wish to edit. For this demonstration, let’s edit the Footer.
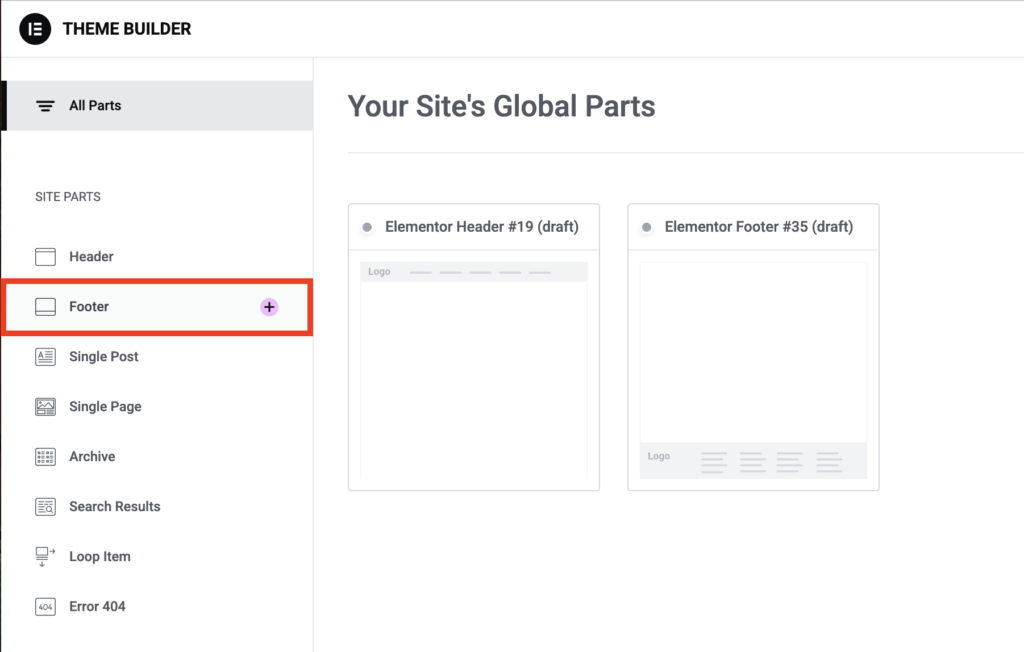
Elementor makes it easy to create footers with the help of pre-built blocks.
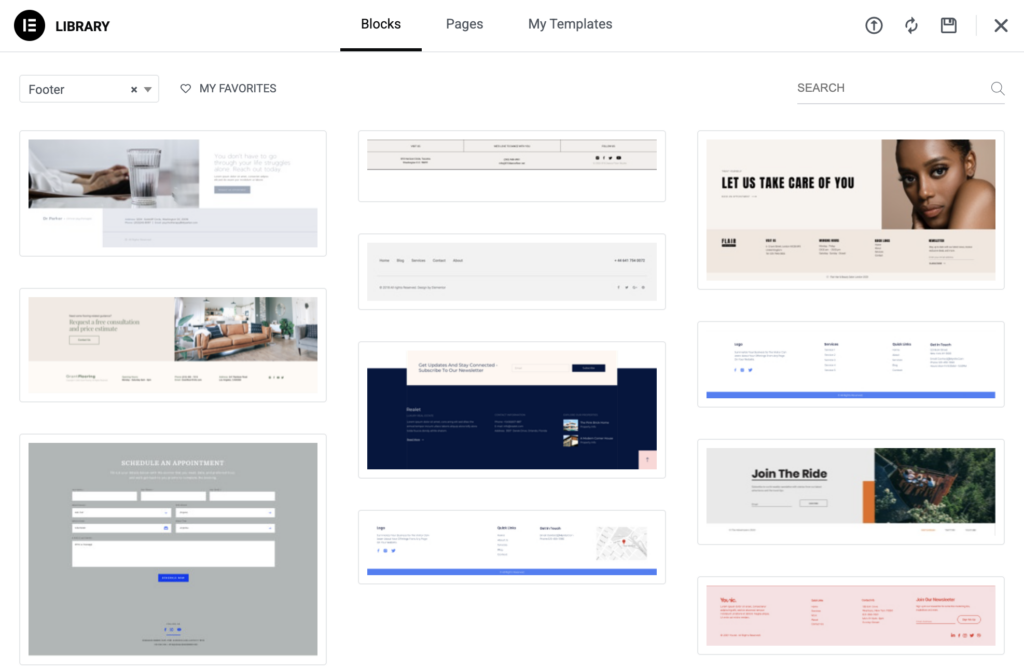
If you decide to close the pop-up, you’ll have a blank space to create your footer. You can drag and drop the elements into your Footer section to build it from scratch.
A well-structured navigation menu improves the user experience. Let’s explore how to create and customize navigation menus using the three WordPress editing methods.
The Site Editor handles navigation menus through a dedicated Navigation block system. Here’s how to create and customize your menu:
Go to Appearance → Editor in your WordPress dashboard.
Click Navigation to access customization options for the navigation menu.
Here, you’ll be prompted to allow editing of the navigation menu. Click Edit, and you can now customize the menu.
You can add new items to the list and link to existing pages. If you want to remove a menu item, click on the three dots beside the menu item and hit Remove <item name>.
Customize this block by changing the layout, color settings, spacing, and typography.
You can also create a dropdown menu by nesting items under a parent page. Drag them slightly toward the right side to create a nested submenu.
The Customizer offers a dedicated menu interface to edit your navigation menu. Here’s how:
Go to Appearance → Menus in your WordPress dashboard.
You’ll find the options to create a new menu. Add a name to your navigation bar and click Create Menu.
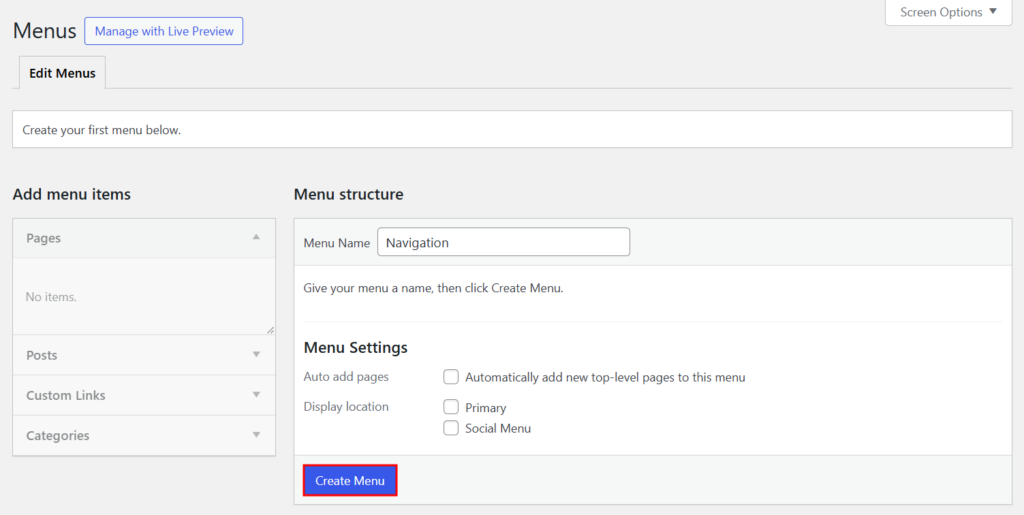
Select Pages or Posts to add items to this menu. You can also add Custom Links or post Categories.
Choose where you want to display this menu by selecting its location:
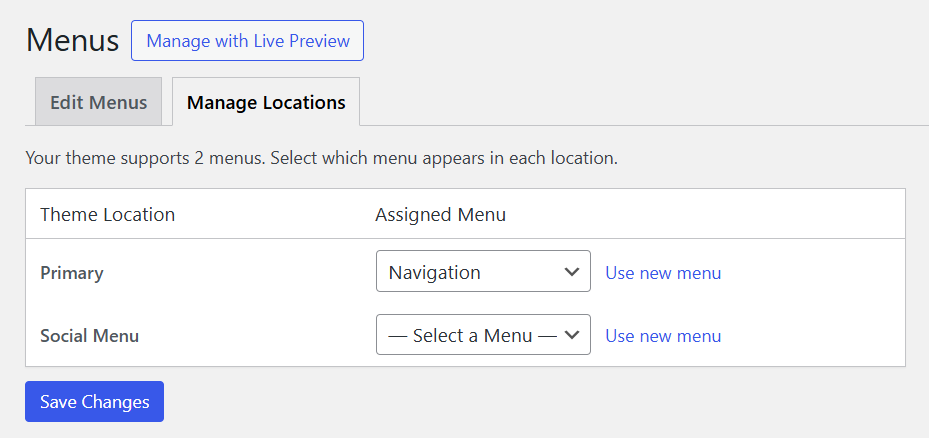
Preview the navigation and Save Changes to apply it to your website.
You can also create a nested menu with multiple items. Go to Appearance → Customize in your WordPress dashboard.
Press Menus to see all available menus.
The left editing panel will show you all the items added to your menu. Hover over an item and move it slightly right to automatically nest it as a submenu under the parent item.
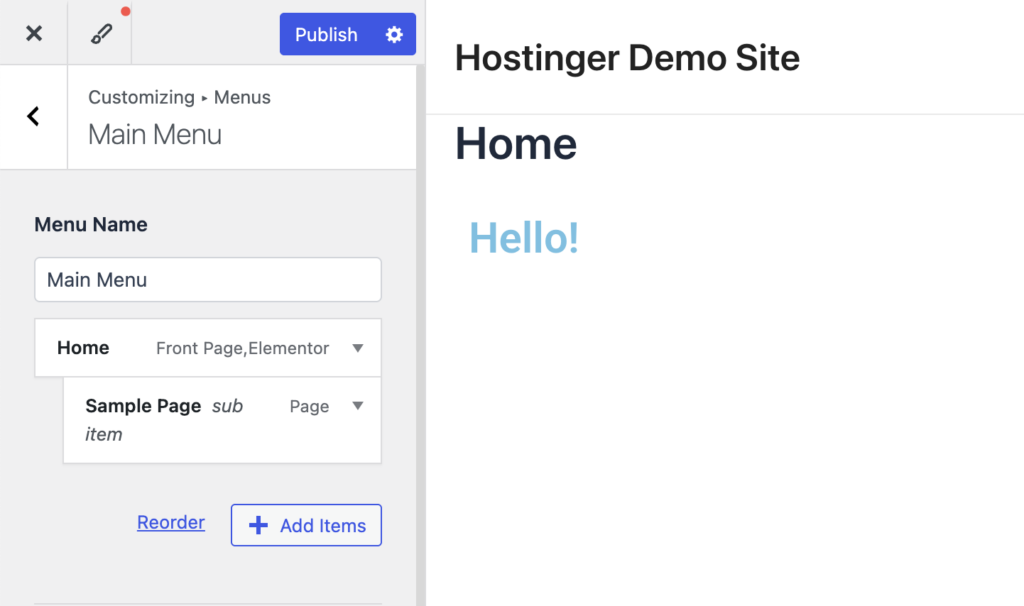
Page builders usually provide their own navigation menu modules with enhanced styling options. Here’s how to create and customize a navigation menu in Elementor:
Go to Elementor → Theme Builder in your WordPress dashboard.
Go to Header in the Theme Builder options to begin editing your site’s navigation. This critical entry point serves as both your brand’s first impression and your visitor’s primary orientation system.
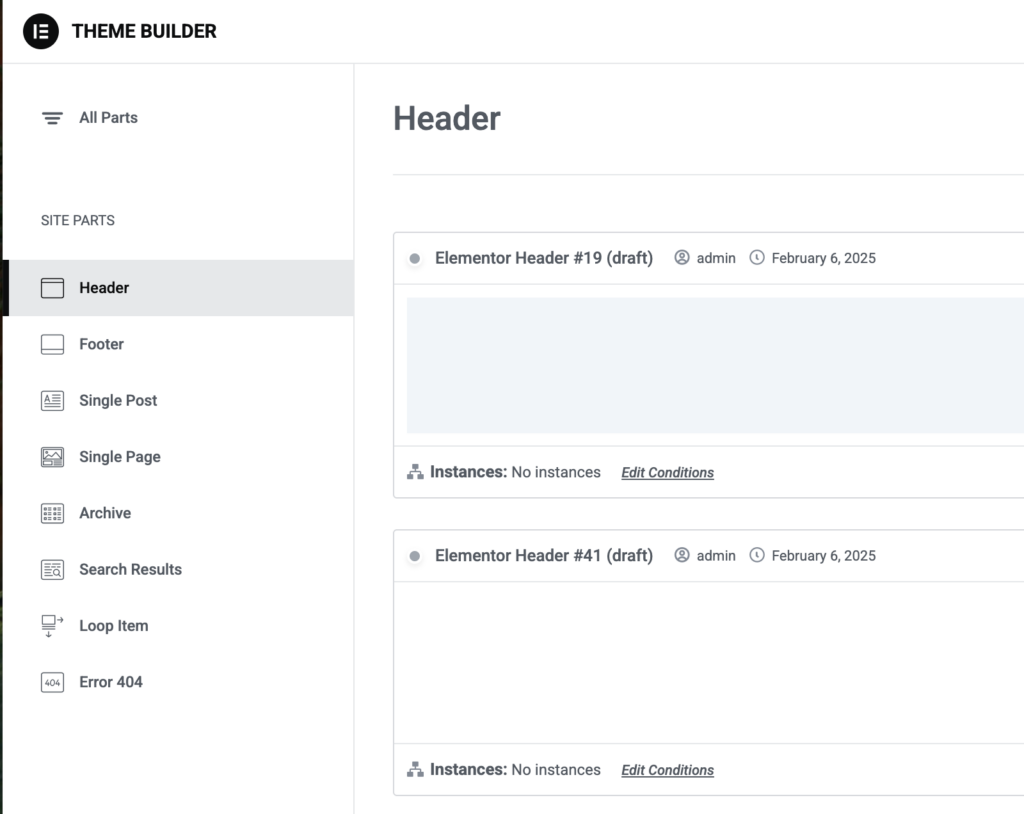
You can now drag and drop the elements to the menu bar. If you wish to use one of the menus you’ve already created, drag the WordPress Menu element.
To customize the items displayed by this module, you need to go back to the WordPress Dashboard → Appearance → Menus as we did in the Customizer section.
However, you can add other custom elements included with the page builder, such as buttons, images, icons, and login buttons.
Your site title is important for branding and SEO. It appears in browser tabs, search results, and your website’s header. The most straightforward method to edit your site title in WordPress is through the admin settings.
Go to Settings → General in your dashboard.
Here, you’ll find these key fields:
Add your desired title, tagline, and icon, then click Save Settings to apply these changes.
You can customize both the site title and tagline along with the logo from the Site Identity section in the Customizer.

Open the Site Identity tab.
Remember that any changes in your site title can impact your website’s SEO performance. So, make these edits thoughtfully to avoid any dips in your organic visibility.
An SEO-friendly site title is concise and relevant to the website, so aim to include your main keyword in the title.
Some themes offer additional options to customize the site title’s appearance, such as font settings, colors, and positioning. Check your theme’s documentation for theme-specific customization options.
WordPress uses the Block Editor (Gutenberg) as its default tool for creating and managing content inside pages and posts. It follows a block-based approach, where each paragraph, image, button, or other content element is treated as a separate block that can be customized.
It’s important to understand the difference between the Block Editor and the Site Editor:
To get started, create a new page on WordPress by clicking Pages → Add New Page.

Alternatively, create a new post by clicking Posts → Add New Post.
Search for specific blocks by their exact WordPress names, such as lists, featured images, or columns. Then, click on your chosen block to insert it.
You can customize each block differently, for example:
Here are some aspects to consider when creating your pages and posts:
Also, before you publish, take a moment to optimize these final elements that significantly impact performance:
These practices create the foundation for content that performs well technically and delivers exceptional user experiences.
If you have coding knowledge, you can customize a WordPress site by editing its core files. However, editing code directly comes with risks, so it’s important to apply changes carefully to avoid breaking your site.
These are some of the most commonly edited WordPress files for customization:
Follow our best practices when editing code on these files to avoid unwanted errors:

Editing a WordPress website is not hard when you understand how to use the tools available.
In this guide, we covered various ways to edit your WordPress site’s theme, title, header and footer, pages, posts, and even code.
So, whether you’re making small content updates or redesigning your entire site, we hope you find this guide useful.
If you can’t edit your WordPress site, check your user permissions and see that you’re logged into your dashboard at yourwebsite.com/wp-admin as an administrator. Conflicts with plugins or themes can also block edits, so try disabling them or switching themes. Some themes may not work with certain page builders which can also cause issues. Go through these steps one by one and find out what is blocking your progress.
To enable Full Site Editing (FSE) in WordPress, use a block theme that supports it. In your dashboard, go to Appearance → Themes, search for Full Site Editing themes, and activate one. Then, navigate to Appearance → Editor to access the Site Editor and modify your site’s structure.
Yes! WordPress is designed to be user-friendly, even for beginners. The Site Editor (for block themes) lets you visually edit headers, footers, and templates. The Block Editor (Gutenberg) allows you to create and edit pages and posts using an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. You can also use the Classic Editor (for classic themes) or Page Builder Plugin (for both block and classic themes).