May 09, 2024
Edward S.
6min Read
Git is a Version Control System (VCS) used by developers to facilitate collaboration. It is useful for coordinating work and tracking source code changes during the software development process.
When working in Git, developers utilize Git branches to add new features or repair bugs. A branch lets them make changes without affecting the original code. When a new branch is proven to work correctly, developers can merge it with the master branch.
This article will briefly explain what Git repositories and Git branches are. It will also teach you how to rename local and remote Git branches in case you misname one or want your project to be better organized. We’ll also mention some helpful commands.
Download complete GIT cheat sheet
Git is a Distributed Version Control System (DVCS) that provides all team members with access to the final version of a project. Git is designed with performance, security, and flexibility in mind to make project management easier.
When learning Git basics, you’ll run across the term repository. It acts like a folder for your project and contains all of its files as well as their revision history. Repositories can be private or public and can be shared with other people.
When you create a Git repository, a .git/ directory appears in the root of the project folder. Here, Git tracks changes of project files, stores objects, refs, and additional repository management information.
Be careful not to delete the .git/ folder on accident because doing so will result in the loss of your project’s history.
We recommend using GitHub as the centralized location for your repositories as its features facilitate collaboration and let users manage code more efficiently.
Git branches are isolated lines of your project’s development. They provide a way to work alongside your master branch, keeping it clear of clutter or any code that’s not yet finished.
A branch acts as a pointer to a commit – a snapshot of the changes you’ve made or wish to make. It is useful when you want to add additional features or fix a bug. It’s possible to create, delete, and list branches.
Branches also prevent unstable code from being merged with the master branch of a project.
Before we begin, make sure you’ve selected the branch you want to rename. Run this command to do so:
git checkout old-name
Replace old-name with the name of the appropriate branch.
If you want to see all of your local branches, input the following command:
git branch --list
When you’ve selected the right branch, follow these steps:
git branch -m new-name
git checkout master
Then, rename the branch by running:
git branch -m old-name new-name
git branch -a
Unlike renaming a local branch, it isn’t possible to rename a remote branch directly. Instead, you’ll have to delete the old remote branch name and push a new branch name to the remote repository.
The renaming process is simple – follow these steps:
git push origin --delete old-name
git push origin -u new-name
Alternatively, you can rename a remote git branch by overwriting it with the command below:
git push origin :old-name new-name git push origin –u new-name
Before creating a new branch, it’s essential to understand what Git commit is. It refers to a command that saves changes to a local repository. Git commit captures snapshots of changes happening within a specific project.
When you create a new local Git branch, Git establishes a new pointer to it.
With the concept cleared up, we can create a new local branch:
cd repository-name
git branch new-branch-name
git checkout -b new-branch-name
The -b option tells Git to run the Git branch command before Git checkout.
You can instead clone a branch and switch to it:
git checkout -b new-branch-name origin/new-branch-name
git checkout new-branch-name
git status
When a developer successfully adds new features, it is recommended to delete the Git branches used in development as they no longer serve a purpose and can clutter your code.
Note that Git will refuse to delete a branch containing commits that haven’t been merged into a remote branch or a repository.
To remove a local branch, use one of the following Git commands:
git branch -d branch_name git branch -D branch_name
The -d option (–delete) will remove your local branch if you have already pushed and merged it with the remote branch.
The -D option (–delete –force) will remove the local branch regardless of whether it’s been merged or not.
You can also remove a remote Git branch by specifying the names of both the remote repository and the branch. In most cases, the name of the remote repository will be origin, and the command will look like this:
git push origin --delete branch_name git push origin :branch_name
In Git, you can view any changes that you’ve made. To see them, enter the following command:
git log
For a more detailed summary, input this command:
git log --summary
These commands will return a list of every commit made within a repository.
If you’re looking for a specific commit, combing through all of them may be too time-consuming. Fortunately, there are a few flags that you can use to filter the output:
git log -n 3 – orders the results from the most recent.git log --after="2021-3-2" – returns a list of commits after the specified date.git log -S"# Introduction" – displays a commit containing particular content.git log -- filename – shows a list of commits inside a specific file path.To ensure an effective and efficient workflow, Hostinger offers seamless Git integration on the hPanel dashboard.
Follow these steps to deploy a Git repository from hPanel:

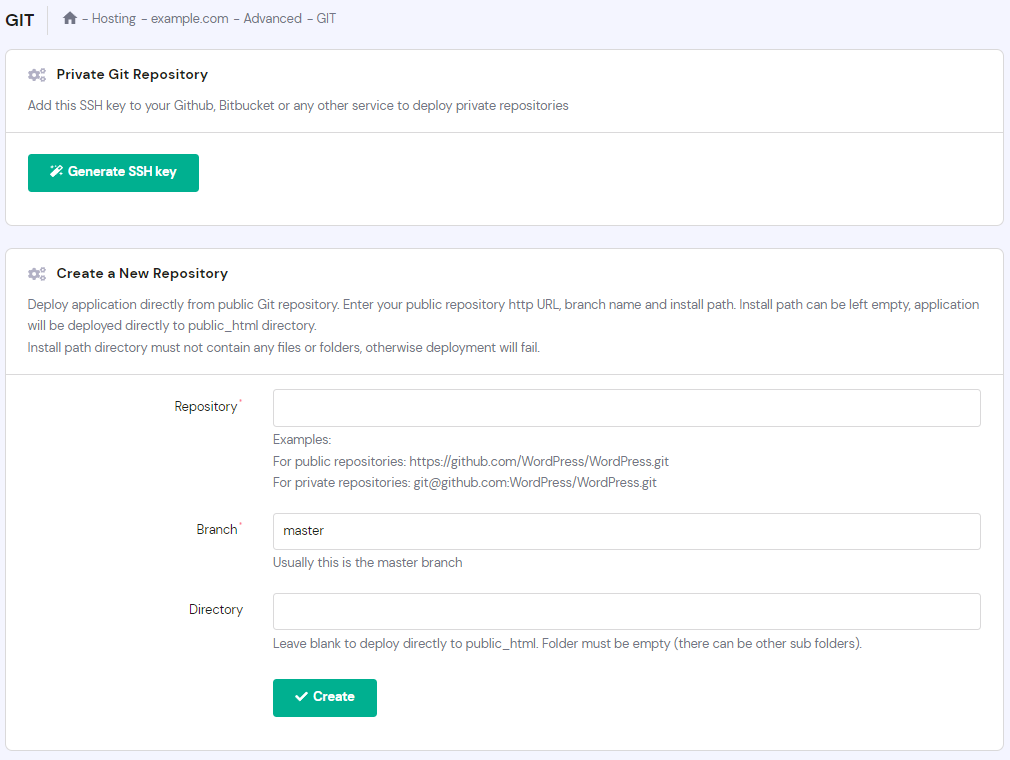
Cloning a repository lets you download the complete source code of the repository to your computer, thus making an identical copy of it.
To do so, you’ll need to use the Git clone command. You’ll also have to specify the URL of the repository. Begin by following the steps below:
git clone https://github.com/user-name/your-repository-name.git
For SSH, input this:
git clone ssh://github.com/user-name/your-repository-name.git
cd your_apps
git status
Once you have cloned a repository to your computer, any changes you make won’t affect the original.
For more information on how to use Git and related subjects, check out these links:
Git is a tool used by developers to facilitate collaboration during software development. By using Git branches, one of the system’s most important functions, users can implement new features without interfering with the source code.
This article has demonstrated how to manage Git branches with different commands, such as renaming or creating a branch, listing existing ones, and deleting them.
We hope you found this tutorial helpful. If you have any questions, leave them in the comment section.

No, in order to rename a remote Git branch you need to delete the old branch name, and then push the correctly named branch to the remote repository.
Run the command git branch -m to rename a local Git branch.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.
Comments
September 15 2019
Thank you for taking the time to write such a clear tutorial!
September 23 2019
Nevermind