Feb 19, 2026
Ariffud M.
5min Read

A domain name is the human-readable URL that visitors type into a browser to reach a website, such as example.com. Web hosting, on the other hand, is the server space that stores your site’s files, databases, and content so visitors can actually access it.
The domain is like a street address people use to find you, while hosting is the physical house where everything resides.
The main difference between a domain and hosting is in their functions: a domain identifies a website, while hosting makes it accessible on the internet.
To have a functioning website, you need both: a registered domain name to point visitors in the right direction and a hosting server to store and deliver the content.
Here are five other key differences between a domain name and web hosting:
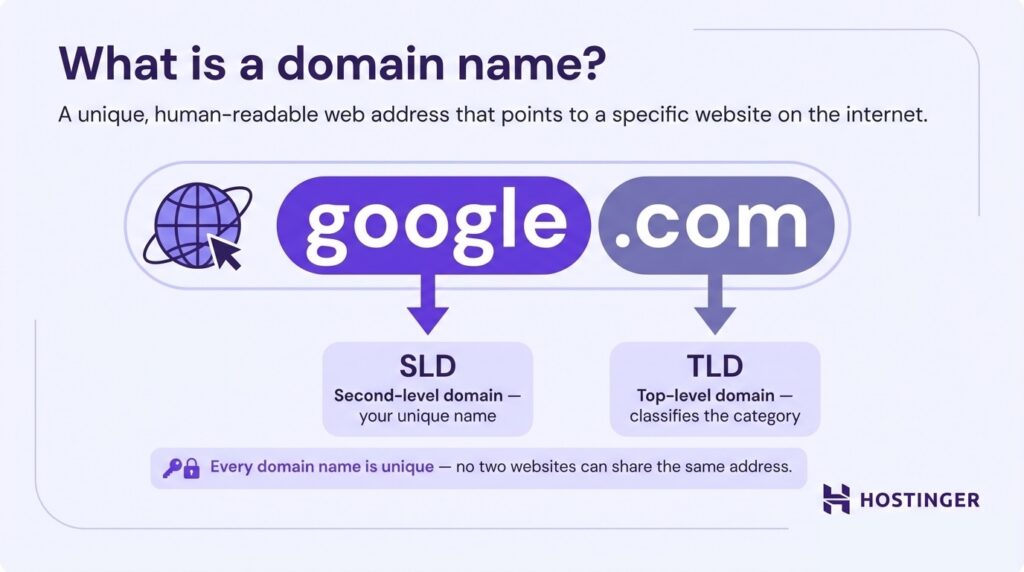
A domain name is a unique, human-readable web address that points to a specific website on the internet.
A domain has two parts: the top-level domain (TLD), which classifies its category or purpose, such as .com, .org, or .io, and the second-level domain (SLD), which is the unique name you register.
Let’s look at google.com, since it’s a domain we all use fairly often. Here, “google” is the SLD and “.com” is the TLD.
Every domain name works through the Domain Name System (DNS), a global directory that translates readable URLs into the numerical IP addresses (like 192.0.2.1) that servers use to communicate.
To secure a domain, you register it through an accredited registrar like Hostinger. Registration grants you exclusive use of that name for a set period, typically one to ten years.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the organization that oversees the domain system, requires registrants to provide accurate contact details, which are stored in a public WHOIS database unless privacy protection is enabled.
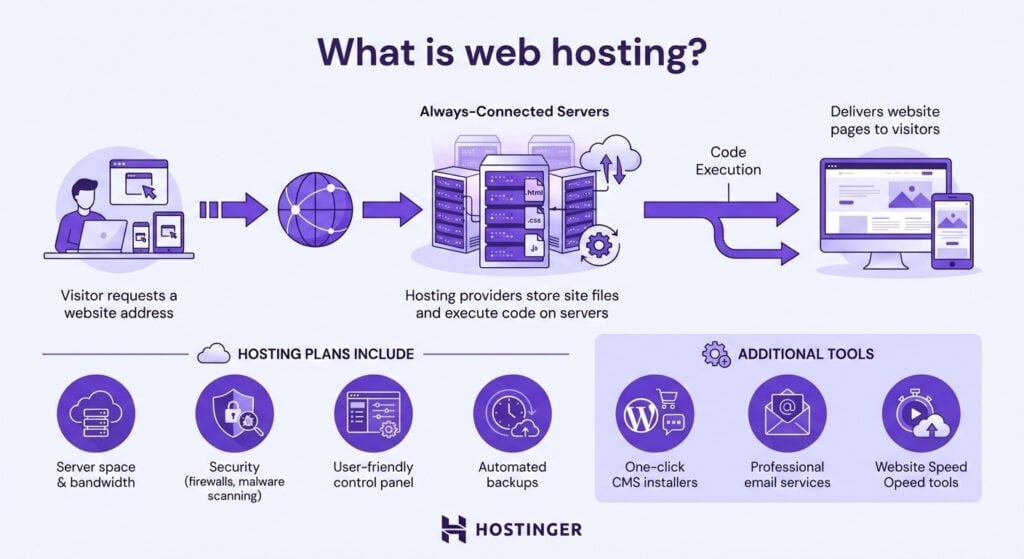
Web hosting is the service that makes a website available to anyone with an internet connection.
Behind the scenes, a hosting provider maintains specialized, always online machines called servers that store your site’s files, execute its code, and deliver pages to every visitor who requests them.
A hosting plan typically bundles server space with bandwidth, security features such as firewalls and malware scanning, and a control panel for managing files and settings.
Most providers also offer tools like one-click CMS installers, email services, and automated backups.
The server handles every visitor request. When someone types a domain name into a browser, the hosting server locates the corresponding files and delivers them to the visitor’s device so that the page can load.
A domain name identifies where a website is located, while web hosting stores and delivers the website’s content. The domain serves as the entry point for visitors, and hosting provides the infrastructure that keeps the site running.
Here’s a comparison table to clarify their roles:
| Feature | Domain | Hosting |
| Definition | A unique URL address used to locate a website | A service that stores website files on a server and makes them accessible online |
| Purpose | Replaces numerical IP addresses with a memorable name for user navigation | Keeps a website live and delivers content to visitors’ browsers |
| Function | Acts as a pointer that directs browsers to the correct server | Acts as storage that holds and serves files, images, and databases |
| Provider | Sold by ICANN-accredited domain registrars | Offered by hosting companies that operate and maintain web servers |
| Cost | Typically $10–$20/year, depending on the TLD | Varies widely based on plan type, from $2/month for shared hosting to $90+/month for dedicated servers |
| Renewal | Registered for 1–10 years – requires periodic renewal | Paid as a monthly or annual subscription |
| Uniqueness | Globally unique – no two websites share the same domain | Not unique – multiple websites can share the same physical server (on shared, cloud, and VPS hosting) |
| Independence | Can exist without hosting (domain parked or redirected) | Requires a domain for visitors to reach it |
| Components | Consists of a second-level domain and a top-level domain (SLD + TLD) | Consists of server hardware, CPU, RAM, disk space, and bandwidth |
| Examples | .com, .net, .org, .io, .store | Shared, cloud, VPS, and dedicated server hosting |
Yes, you need both a domain and hosting. A domain without hosting means the browser has no files on a server to retrieve. Though you can forward a domain to an existing page, like a social media profile, this isn’t a website. And hosting without a domain means visitors have no memorable address to reach your site.
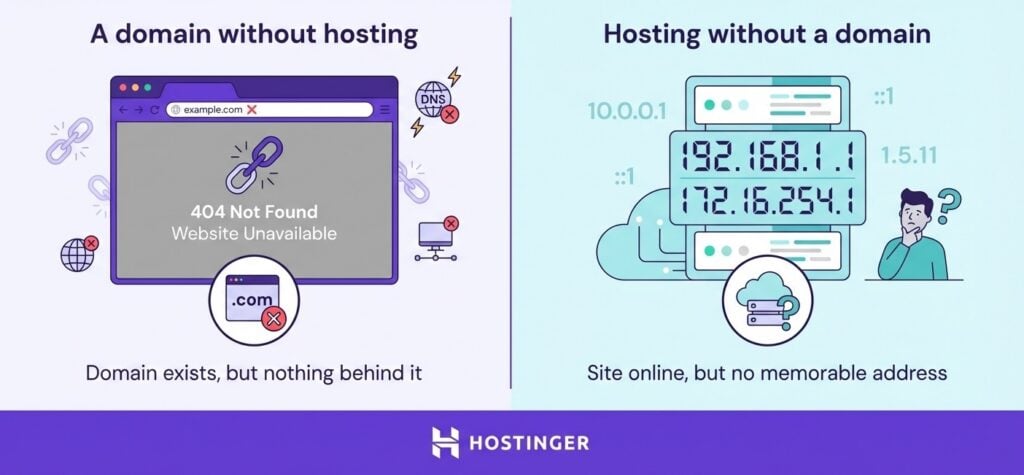
If you register a domain but skip hosting, visitors who type your URL will see a registrar placeholder page or a DNS error. The domain exists in the system, but there’s nothing behind it.
If you purchase hosting without a domain, your site is technically online but accessible only via the server’s raw IP address – something no visitor will remember or trust.
Both services serve a distinct role, and a website only functions when they work in tandem.
You can purchase a domain name and web hosting together as a bundled package from the same provider, or buy them separately from different companies.
Many hosting providers, including Hostinger, offer domain registration alongside their hosting plans, while standalone registrars focus solely on domain sales.
Buying both from the same provider has practical advantages:
That said, bundling has some drawbacks:
We recommend an integrated solution for most website owners, especially beginners who want to launch their websites quickly without manually configuring DNS records.

A domain name and a web hosting server form a complete system when connected.
Using the house-and-address metaphor, the address (domain) brings visitors to your front door (your website’s homepage), while the house (hosting) holds everything they came to see, like rooms, furniture, and decorations (your pages, content, and images).
DNS settings, especially the nameserver records, link the two. They tell the internet which hosting server is responsible for a domain.
The process works in four steps:
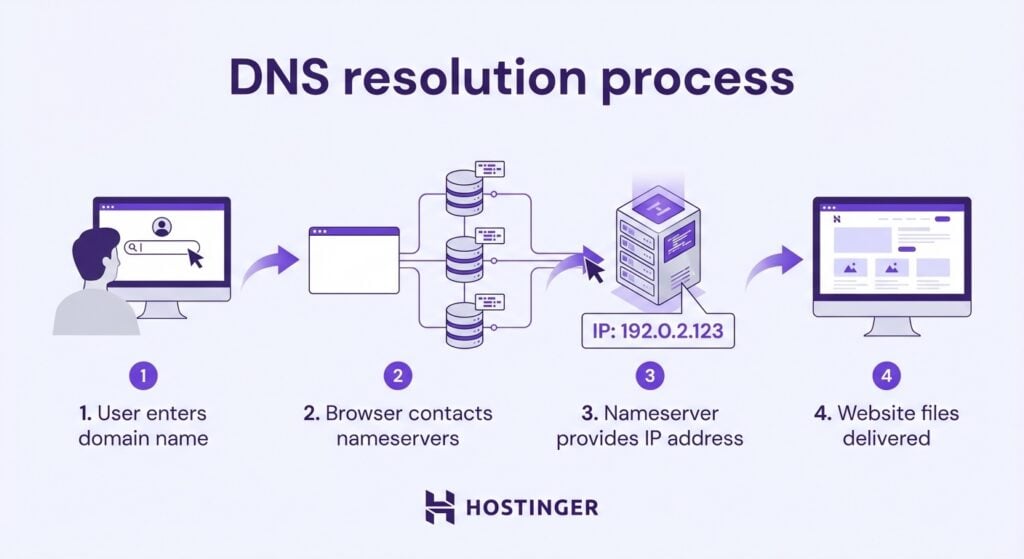
Every live website depends on a domain and hosting working in tandem: one to be found, the other to deliver what visitors came for.
Getting both ready for your site takes five steps.
For a complete walkthrough of each stage, read our guide on how to make a website, which covers platform selection, design, and content setup in detail.
Comments
December 17 2020
Thank admin, I appreciate your effort, you have quality content on your website, I have bookmarked for future pursue. Keep it up Truly decent and intriguing post. I was searching for this sort of data and delighted in perusing this one. Continue posting. A debt of gratitude is in order for sharing Usually, I never comment on blogs but your article is so convincing that I never stop myself to say something about it. You’re doing a great job Man, Keep it up. very interesting, good job and thanks for sharing such a good blog.
May 15 2022
Hi This article contains excellent definition and very useful, I really appreciate.
May 18 2022
Happy to hear it was helpful!
February 24 2024
Thanks for this article. This is educational.
February 26 2024
Hi there! Glad to hear that!