Dec 02, 2025
Ariffud M.
7min Read

NGINX is a high-performance web server widely recognized for its stability, rich features, and low resource consumption. As a reverse proxy, it acts as an intermediary for client requests to back-end servers, enhancing the security, performance, and scalability of web applications.
In this article, you’ll learn about the NGINX reverse proxy server, its role in modern web architectures, and the steps to set it up. We’ll guide you through the installation and configuration process to ensure your applications run more efficiently and securely.
An NGINX reverse proxy is a server configuration that directs incoming traffic to various back-end servers based on URL, ensuring efficient load distribution and resource accessibility.
An NGINX reverse proxy server extends beyond simple traffic redirection, playing a crucial role in boosting web application performance. It adeptly manages both dynamic and static content, routing them to suitable servers for optimal processing and delivery.
With NGINX Plus, users gain access to enhanced features such as superior load balancing, extensive monitoring capabilities, and strengthened security measures.
In Kubernetes environments, NGINX excels as an ingress controller, orchestrating external access to services – a key component in deploying scalable cloud-native applications.
Furthermore, NGINX enhances network efficiency through its API gateway functionality, which simplifies network traffic management and ensures reliable routing to upstream services.
Learn how to temporarily and permanently redirect traffic using NGINX with our comprehensive guide.
At its core, the NGINX reverse proxy acts as a bridge between client devices and back-end servers, such as LiteSpeed or Apache, managing incoming requests in a reverse proxy setup.
Request Handling Process
When a client device sends HTTP requests to your web application, these requests first reach the NGINX reverse proxy server. NGINX then examines the request’s details, such as URL and headers, to determine the appropriate handling.
For static content requests, NGINX optimizes delivery by serving content from its cache, significantly reducing load times. Meanwhile, dynamic content requests requiring real-time processing are forwarded to the appropriate back-end server.
Decision-Making for Back-End Server Forwarding
NGINX uses various load balancing methods to decide which back-end server to forward requests to, such as:
Advanced Configurations
For complex scenarios, you can configure NGINX rules based on request headers, content type, and even custom code modules, allowing for precise forwarding decisions.
This adaptability enables NGINX to efficiently direct traffic to web and application servers and functions as a forward proxy for outgoing requests when configured to do so.
Before setting up an NGINX reverse proxy on a virtual private server (VPS), ensure you have the following essentials in place for a smooth and effective configuration:
We’ll guide you through configuring an NGINX reverse proxy on a Hostinger VPS running an Ubuntu 22.04 distribution. It should work on later versions of Ubuntu as well.

To set up an NGINX reverse proxy, you first need to install the NGINX server on your VPS. Follow these steps to get NGINX up and running:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install nginx -y
sudo systemctl status nginx
The output should indicate that the NGINX service is active (running), similar to the following example:
● nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-01-01 12:34:56 UTC; 2min 22s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Main PID: 1234 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 1152)
Memory: 5.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─1234 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
└─1235 nginx: worker process
If your VPS has a firewall configured, you also need to allow traffic to NGINX. For Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) systems, enable traffic on appropriate ports with:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'
When you’re installing NGINX, the system automatically sets up several essential directories and files for its configuration and operation.
Organizing NGINX configuration files is crucial for tailoring its functionality to suit specific needs, such as managing diverse workloads and efficiently directing requests to several servers.
Basic NGINX Configuration File Structure
The core configuration file for NGINX is nginx.conf, found in /etc/nginx/. This file contains global settings and includes directives to pull in additional configurations from other files and directories:
Important NGINX Directives
To effectively utilize NGINX, you need to familiarize yourself with its key directives:
To configure NGINX as a reverse proxy, you need to create a new configuration file. This file will contain the server blocks and directives needed for routing requests. Follow these steps:
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
sudo nano example.com
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://your_backend_server_ip;
proxy_set_header Host $host; # Forwarded host
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}Replace your_backend_server_ip with your back-end server’s actual IP address.
Configuring Load Balancing
To set up a load balancer, define an upstream block and use proxy_pass within your server block to distribute traffic among multiple servers:
upstream myapp1 {
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp1;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
# Additional settings...
}
}Handling Static Content
For efficiency, serve static content directly from NGINX using a separate location block:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://your_backend_server_ip;
# Proxy settings...
}
location /static/ {
root /path/to/static/files;
expires 30d;
}
}
Fine-Tuning Proxy Directives
Customize how NGINX interacts with your proxied servers using various proxy_ directives to enhance performance and manage proxied requests effectively:
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
http {
proxy_cache_path /path/to/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=my_cache:10m max_size=10g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
proxy_cache my_cache;
}
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
proxy_buffering off;
}
location / {
proxy_pass https://backend.example.com;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend.example.com;
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
}
Once done with your NGINX reverse proxy configuration; it’s time to enable the settings, test for syntax errors, and apply the changes. Here are the steps:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
Alternatively, Hostinger VPS customers can use Kodee to confirm their NGINX configuration. Open the Kodee AI Assistant menu from your VPS dashboard’s left sidebar, then type your prompt like this:
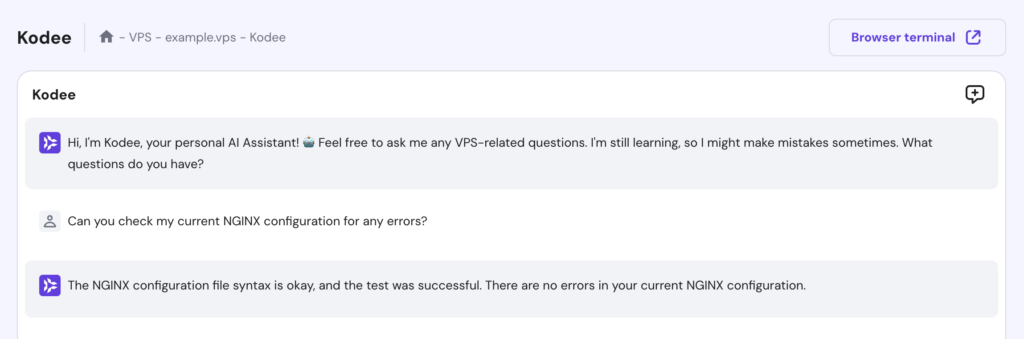
If any NGINX reverse proxy issues are detected, it will indicate where they are, so you can troubleshoot and correct the errors.
Reload or Restart NGINX
To apply your configuration changes, you can either reload or restart the NGINX server.
sudo systemctl reload nginx
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Restarting is sometimes required for more significant changes or troubleshooting NGINX errors.
In this guide, you’ve learned how to set up NGINX as a reverse proxy server, covering installation, configuration, and testing.
By managing and distributing incoming requests evenly, you ensure your server is optimally utilized, and your web applications run smoothly. Use these steps as a starting point to enhance the performance, security, and scalability of your server environment with NGINX.
This section will answer the most common questions about NGINX reverse proxy servers.
Using an NGINX reverse proxy server can improve performance by balancing traffic across multiple web servers. It also enhances security and scalability within data centers, making it ideal for managing web applications.
Yes, you can use NGINX as a reverse proxy for multiple back ends, even those employing different technologies like Apache Tomcat. This setup enhances resource allocation and boosts other servers’ performance.
When configuring an NGINX reverse proxy, use SSL to secure data transmission. Given its role as a single point of entry, it’s crucial to enforce robust security measures. Also, ensure proper configuration of WebSockets to maintain secure, real-time communication.
Yes, using NGINX reverse proxy caching can reduce load times and server demand by storing copies of frequently accessed resources. This is particularly handy for microservices and virtual hosts, streamlining content delivery and enhancing user experience.
Comments
April 24 2020
One of the simplest and most helpful guided, loved it.
April 24 2020
Hey, glad it helped!
October 22 2020
Doesnt work at all. All I get is connection errors.
February 02 2021
Hi there, Simon! Can you clarify what errors you're getting? You can always contact our Customer Success team from your Hostinger account, they'll be happy to have a look!
March 20 2022
It works !!! Excellent !!!