Dec 02, 2025
Aris S.
4min Read
Your computer’s hosts file maps a domain name to its IP address. If you experience an unreachable web page or want to block a specific website, editing the hosts file can be the solution.
In this article, you will learn how to edit the hosts file in Windows, macOS, and Linux. Before getting into the steps, we’ll explain what a hosts file is exactly so you understand why learning to modify it can be a useful skill.
A hosts file is a configuration in your operating system that maps a domain name to its corresponding internet protocol (IP) address.
It works similarly to a domain name system (DNS) server, which translates a website’s domain into its IP address so your web browser can access it.
The difference is that your operating system will prioritize the host file over the DNS server. If information about the corresponding IP address is unavailable locally, your internet service provider will use the DNS server.
Editing the hosts file means manually adding a domain or hostname and its IP address. It can be helpful in several scenarios:
Remember that changes in the hosts file will only apply to your local computer. For example, you must wait for DNS propagation to finish before your website is accessible on other systems.
Before editing your hosts file, make sure you have information about the website you want to add, including its domain name and IP address. Since the steps to obtain them differ depending on the web hosting provider, check their documentation or contact support.

Here are the steps to edit the hosts file in a Windows system. The procedure should work for the newer versions of the operating system, like Windows 11 and 10:
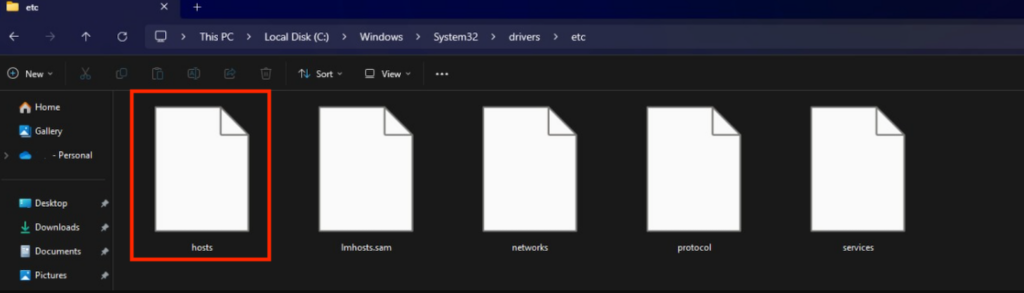
185.185.185.185 domain.com
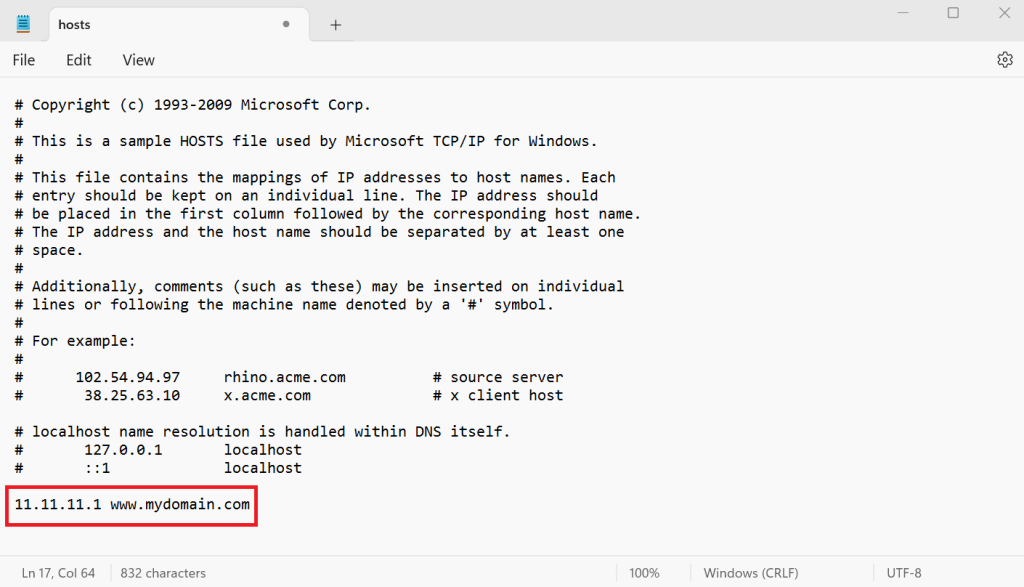
To disable a setting, add a hash sign (#) at the beginning of the line, like # 185.185.185.185 domain.com. This is safer than deleting the entry since you can easily reactivate it by removing the symbol.
The easiest way to edit the hosts file in macOS is using commands via Terminal. Here are the steps:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
185.185.185.185 domain.com
If you prefer using a graphical user interface, follow these steps instead. Note that the interface might be different depending on your operating system version:
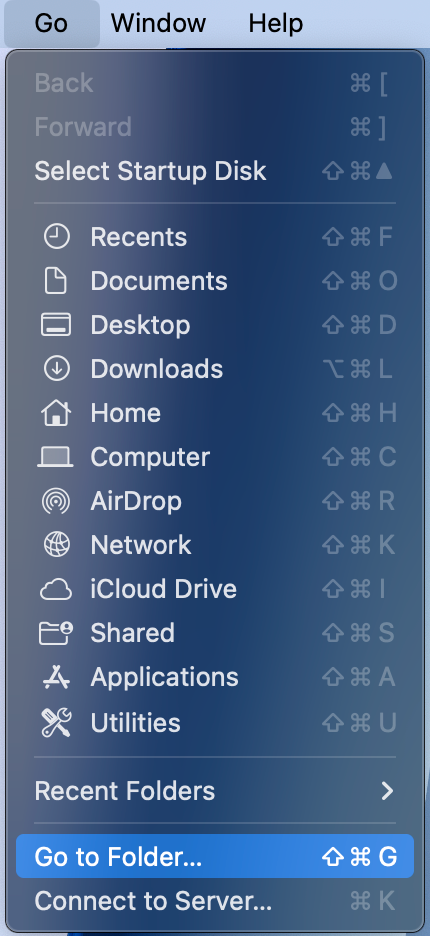

In Linux, you can edit the hosts file using the graphical interface or commands via Terminal. For this tutorial, we will use Terminal since it is more efficient and works the same way regardless of your distribution:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
185.185.185.185 domain.com
Your operating system’s hosts file resolves a domain or hostname to its IP address. Editing this file is helpful if you want to block a specific site or explicitly map a website to its address for accessibility on your local machine
In this article, we have explained how to edit the hosts file in popular operating systems. For Windows users, navigate to C:WindowsSystem32Driversetc using File Explorer and edit the file using Notepad.
Meanwhile, the steps to edit the hosts file in macOS and Linux are similar. Open Terminal and run sudo nano /etc/hosts to open the file. After adding the domain and its corresponding IP address, hit Ctrl + X, Y, and Enter to save the changes.
In Windows, you can find the hosts file by navigating to the C:WindowsSystem32Driversetc path using Explorer. For macOS and Linux, the file is located in the /etc/hosts directory. You can access it using Terminal or applications like Finder in macOS.
The hosts file is an essential networking component of operating systems. Due to its importance, you can find this file in any modern operating system, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Modifying the hosts file ensures your website is accessible since you explicitly add the IP address to its domain name or hostname. Moreover, you can block or redirect malicious websites by assigning other IP addresses to their domain names.