Dec 02, 2025
Amanda B. & Brian
8min Read
Encountering a “DNS server not responding” error can be frustrating, but it’s a fixable problem. The solutions range from simple steps to more advanced troubleshooting. Here’s what you can do to fix it:
The culprit of this error can be either on the server or the client side, so it’s best to try all the possible solutions starting from the top and moving on to the next if the issue persists.
Now, let’s explore in more detail how you can fix the issue.
Prefer a visual walkthrough? Check out this step-by-step video on how to fix the “DNS server not responding” error.
Here’s how to fix the “DNS server not responding” error on Windows and macOS:
Using a different web browser to visit the site that’s experiencing the domain name system (DNS) issue is the easiest solution to the error.
For instance, if you primarily use Google Chrome, try to access the web page using Safari, Microsoft Edge, or Mozilla Firefox.
If this method works, then your default browser is the one causing the error. In most cases, clearing the browser cache and updating it to the latest version will solve network connection issues.
Here’s how to update Chrome:
If the “DNS server not responding” error appears across different browsers, try the second method.
Troubleshooting network issues helps resolve DNS errors if they’re caused by connectivity issues. Try switching between different networks to check whether your internet connection is the problem.
Let’s say you encounter a DNS server error while connected to Wi-Fi. In that case, try using your mobile data instead. If you can access the web page just fine, it means the problem is with your Wi-Fi connection.
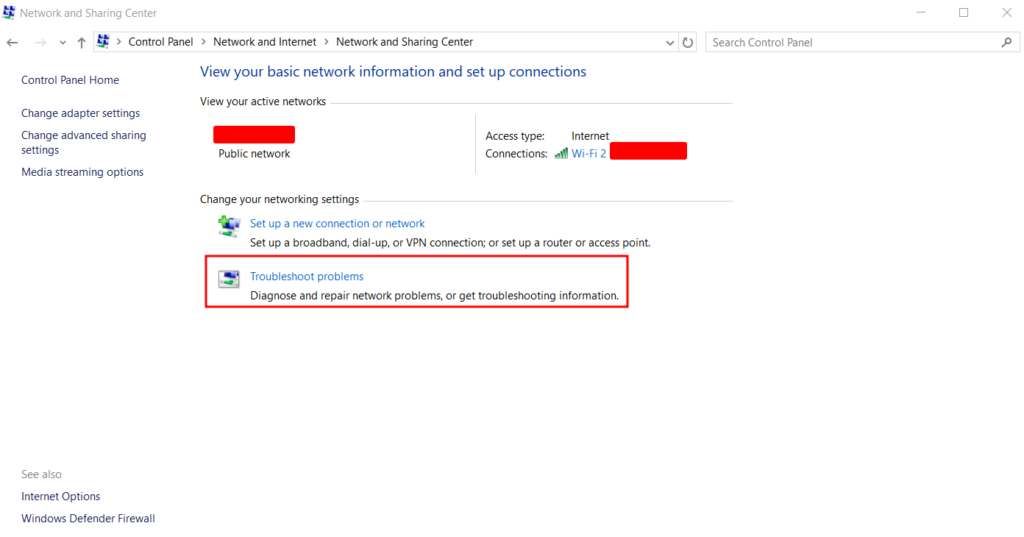
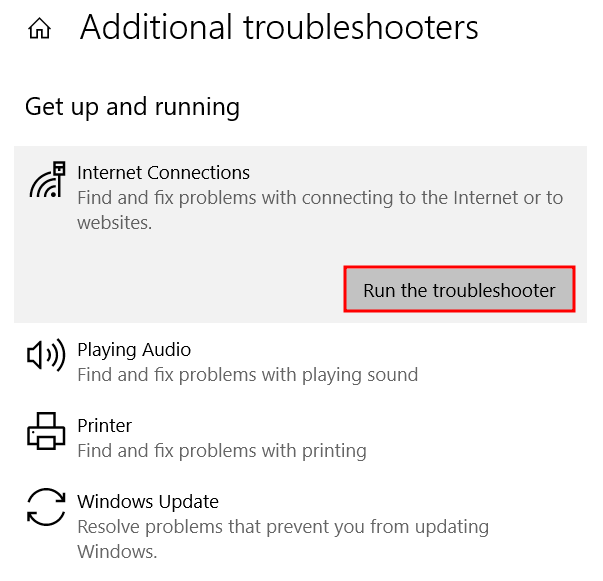
After identifying the problematic network, you can run the diagnostics tool on your computer to detect and fix internet connection problems:
Windows
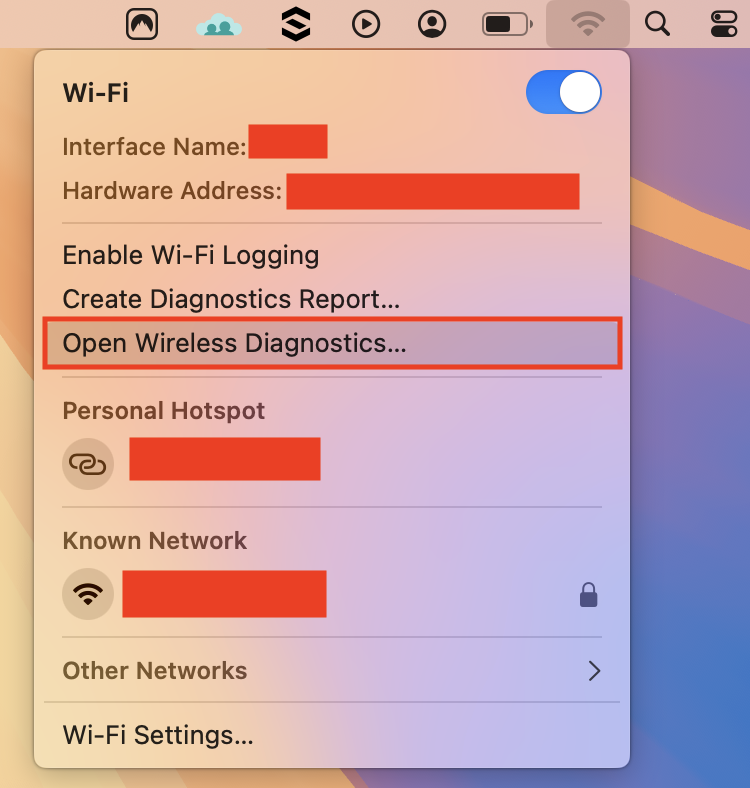
macOS
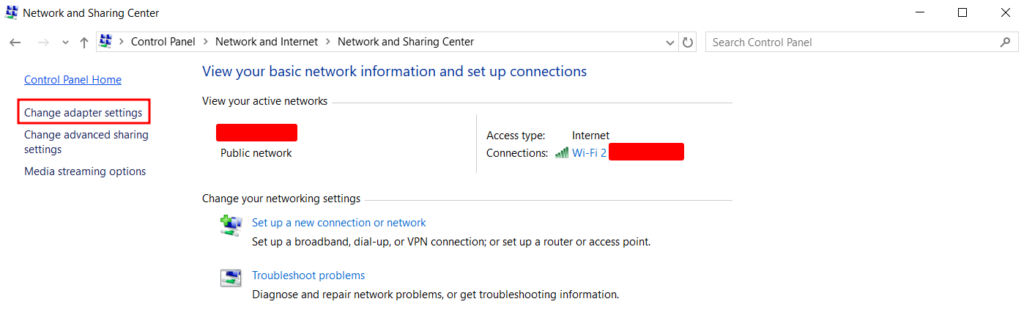
Disabling unused connections eliminates possible conflicts in your network, potentially fixing the DNS error. These include a virtual network, like a VPN, and a wired adapter, like an Ethernet connection.
Follow these steps to disconnect additional network connections on Windows:
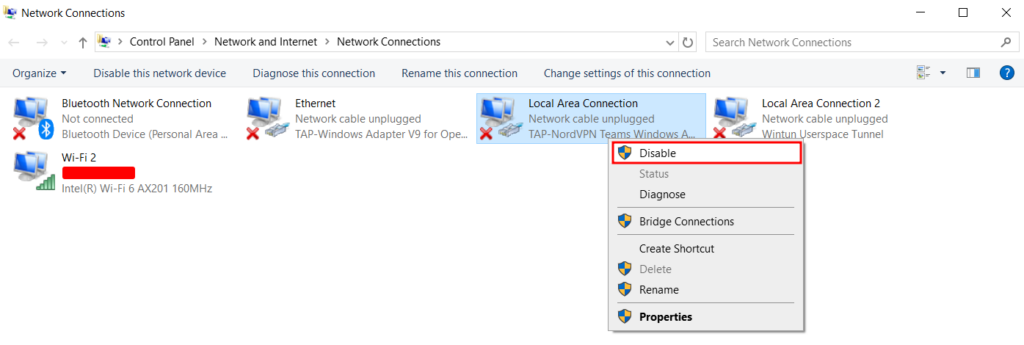
Here’s how to disable other network connections on macOS:
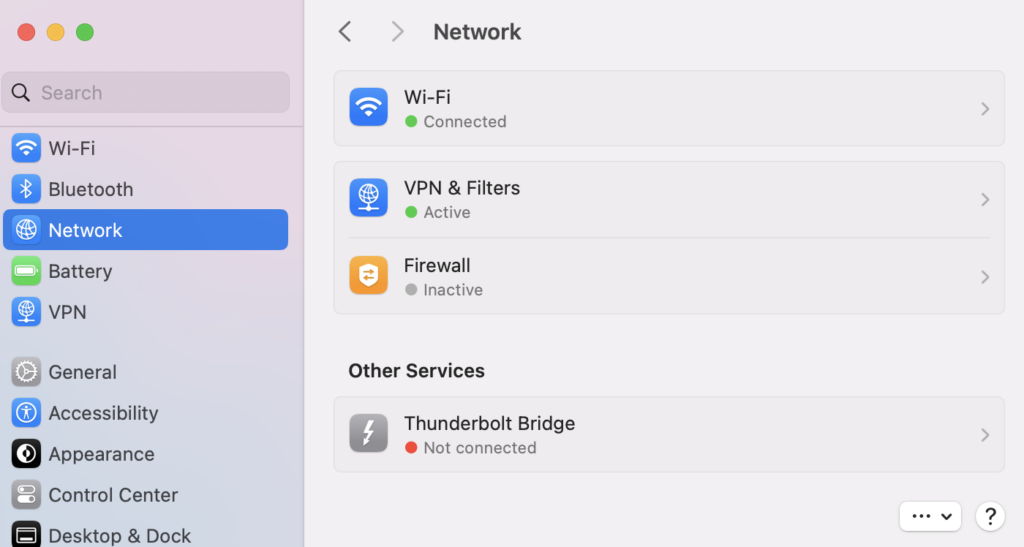

After disabling all unused connections, reload the web page and see if the DNS error message has been solved.
Restarting your internet router or modem resets several network settings, like the cache. A faulty router or modem configuration can also be the leading cause of the DNS server not responding and the connection failing.
Luckily, fixing this issue can be as simple as restarting your router or modem. Turn off the power button and unplug the power cable. Wait for at least 30 seconds before pressing the power button again to restart it.
If restarting doesn’t work, try to reset the router or modem to its default settings. Check the instruction manual of the device for the complete steps.
Flushing your system’s DNS cache forces your computer to fetch new DNS records when visiting a website. These records contain information about the visited site, like its domain name and the corresponding IP address, which helps your browser access the web page more quickly.
The problem happens when the DNS cache becomes outdated. Maybe the site has changed its IP address, or the domain has expired. Whatever the reason, incorrect DNS records will result in DNS errors.
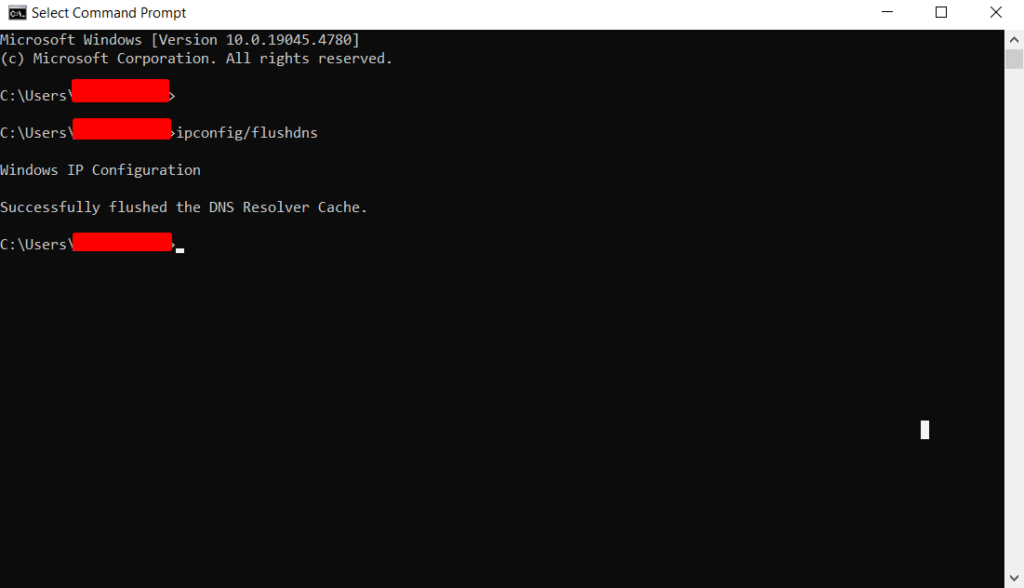
To fix this, try flushing the DNS cache on your device:
Windows
macOS
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
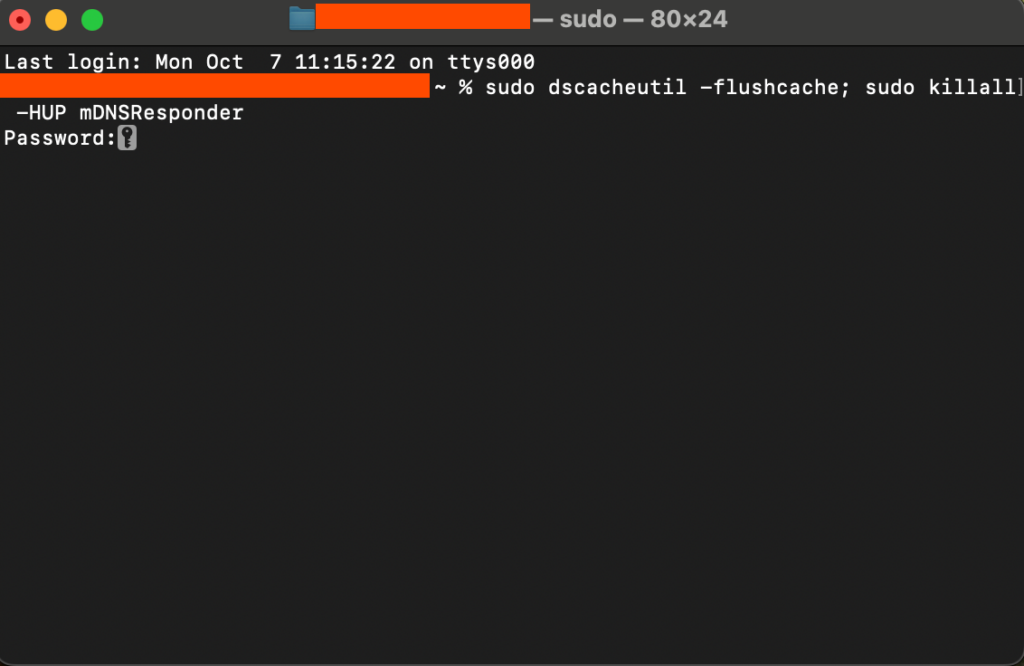
Keep in mind that older macOS versions require different command prompts.
Here’s the full list:
macOS Catalina, Mojave, High Sierra, Sierra, El Capitan, Mavericks, Mountain Lion, and Lion:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
macOS 10.10 Yosemite:
sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
macOS X Snow Leopard:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
macOS X Leopard and below:
sudo lookupd -flushcache
After running the commands above, the network adapter will refresh its DNS configuration.
Changing your DNS server address enables you to use the non-default resolver. By default, your home network obtains a DNS server address from your internet service provider (ISP), which is very likely experiencing downtime when your internet service stops working.
You can temporarily solve this problem by switching to public DNS server addresses, such as:
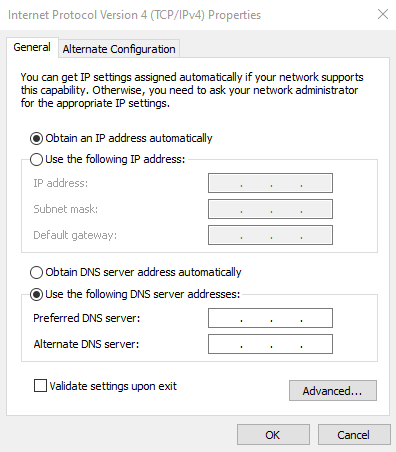
Here’s how to change your DNS address on Windows:
If you’re a Mac user, follow these steps:
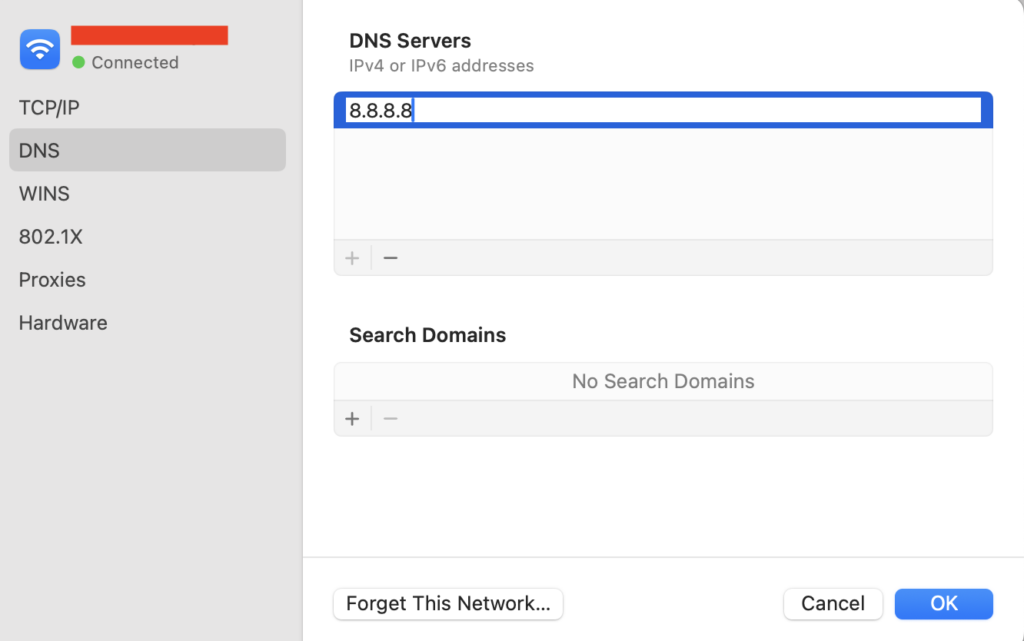
After changing the DNS settings, restart your Windows or Mac computer, and see if your internet access has been restored.
Disabling Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) forces your system to access websites using the older IPv4 address. This can resolve the DNS issue because some sites might not support the newer protocol.
Here’s how to disable IPv6 on your Windows computer:
For Mac users, do the following:
However, with this method, IPv6 connections still work for local networks. If you want to deactivate IPv6 completely, open the Terminal app and run the following command:
networksetup -setv6off Ethernet && networksetup -setv6off Wi-Fi
This will disable IPv6 on both wireless (Wi-Fi) and wired (Ethernet) networks.
Restarting your PC in safe mode resolves the DNS issue if the problem lies within your operating system. Sometimes, certain software, files, or network drivers might block DNS connections.
To figure out whether that’s the case, run your PC in safe mode – a stripped-down version of your OS, where non-essential processes and components are disabled.
Here’s how to restart your Windows computer in safe mode:
On a Mac device, the steps are a lot simpler:
If your network connection works in safe mode, it means third-party apps might be causing the DNS server isn’t responding error.
While there’s no way to know for sure which software is at fault, it’s most likely your firewall or antivirus program.
Disabling antivirus and firewall apps ensures these tools aren’t interfering with your internet connection and causing issues. Try disabling them to see if they’re causing the issue.
To deactivate Microsoft Firewall Defender, open the Start menu and click the Settings icon. Next, head to Update & Security → Windows Security → Firewall & network protection.
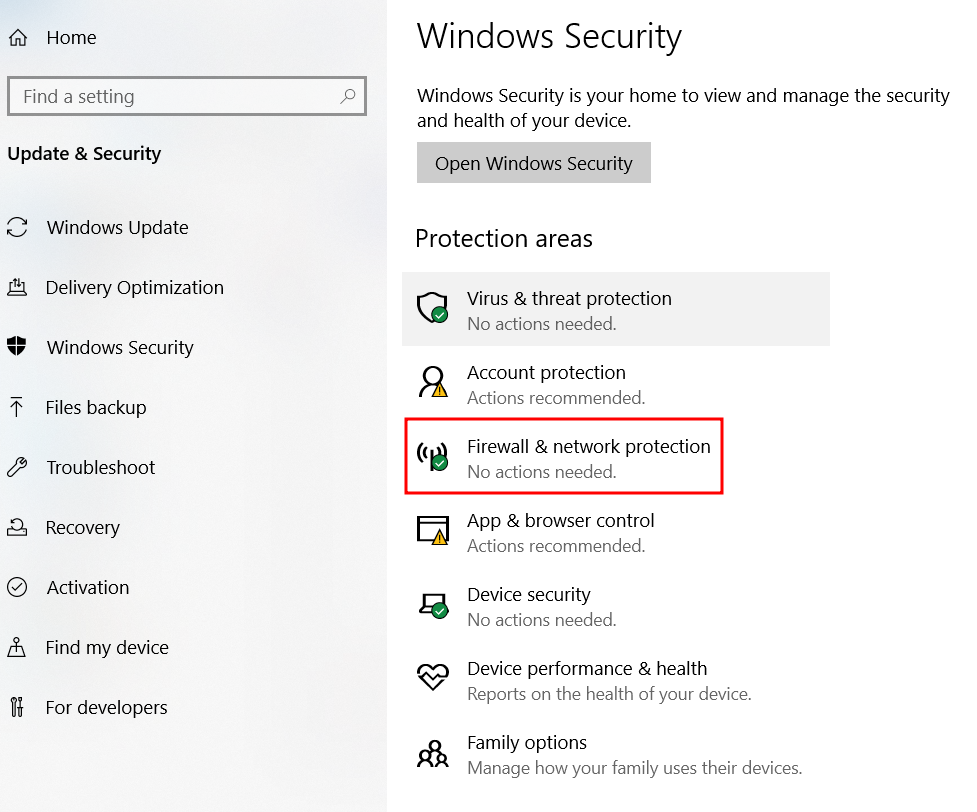
You will see three profiles: domain, private, and public network. Simply open each option one by one, and toggle off the button under Microsoft Defender Firewall.
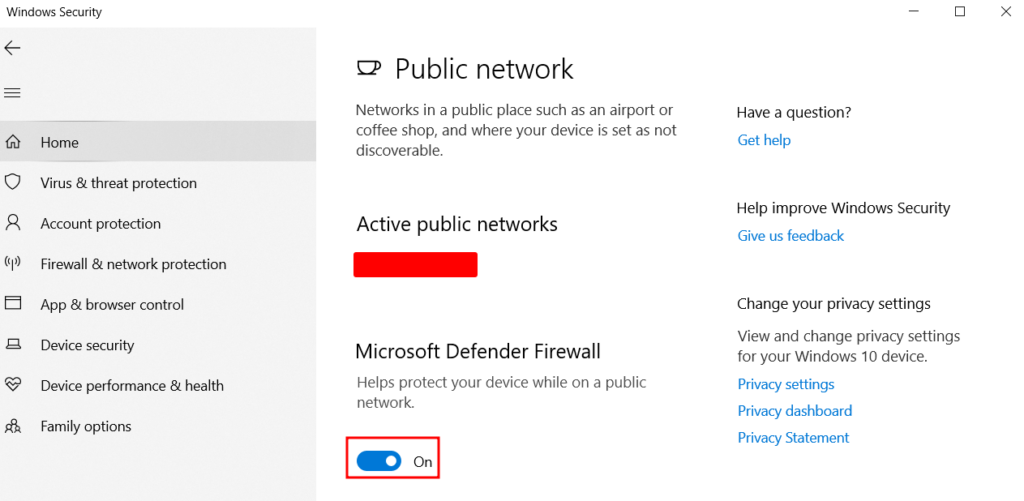
If you want to disable third-party antivirus and firewall apps you’ve installed, head to Virus & threat protection from the left sidebar.
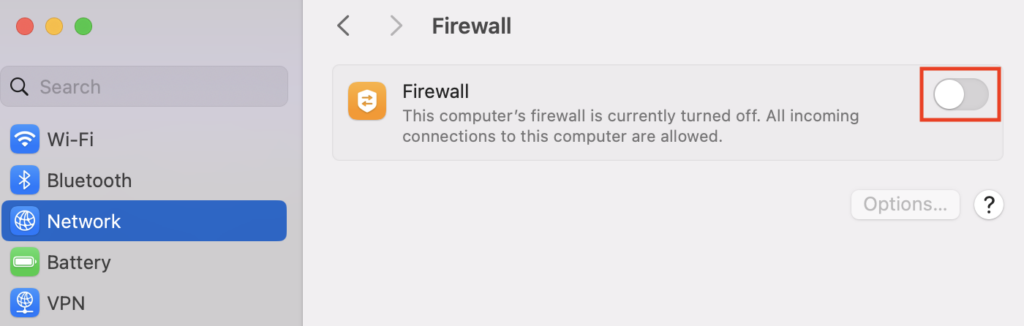
On a Mac computer, you can turn off the built-in firewall by accessing the Apple menu → System Settings → Network. Select Firewall, then toggle off the button.
For third-party antivirus and firewall programs, you will have to open each app and deactivate it manually.
Updating network adapter drivers ensures that the devices connected to your computer’s network interface, such as routers, printers, and Ethernet cables, are using the latest and most tested settings.
When their drivers are outdated or corrupted, these devices won’t be able to communicate with the network adapter, leading to connectivity issues. Updating them will help fix the issue.
Here’s how to update the network adapter driver of your active connection (usually Wi-Fi):
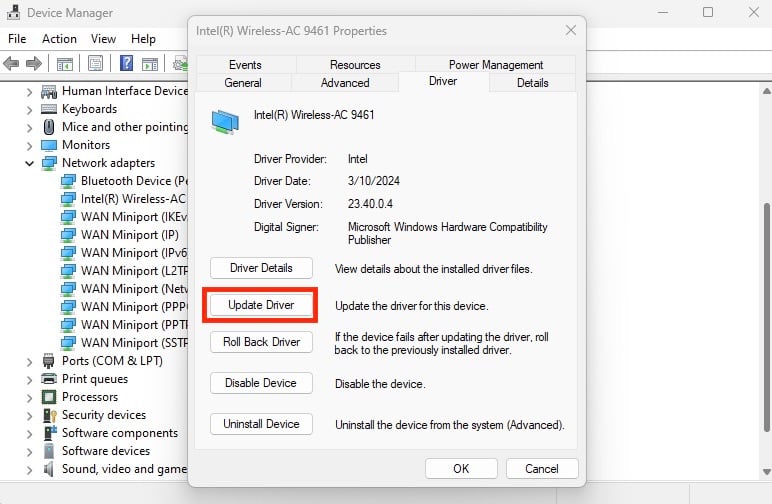
Not sure which one is the correct driver? Go ahead and update every network adapter on the list. If your network driver is already up-to-date, but you still see the DNS server error, try to uninstall it and then reinstall it again.
The cause of the “DNS server not responding” error message is that the DNS of the domain you want to reach is unavailable, or your browser cannot connect to the internet. It commonly happens for these reasons:
If the “DNS server not responding” error returns after trying all the solutions, consider alternative fixes. Bar in mind that these might not be applicable for all operating systems and may only work for as a temporary workaround. Here’s what you can try:
You can use another device to access the problematic website to see if the issue is related to your system. Another solution is to disable the peer-to-peer feature in your Windows computer that might conflict with the DNS.
If you are connected to your organization’s network, check with the administrator if it is experiencing an issue. This is because its configuration might override your system’s settings, potentially causing the error.
If none of these fixes work, ithe problem might be on the website’s end, typically related to the domain configuration. Notify the website owner and wait until the issue is resolved.