Nov 09, 2024
Larassatti D.
5min Read
Nov 09, 2024
Larassatti D.
5min Read

When building a WordPress website with multiple team members, assigning user roles ensures your site’s security. Think of it like in a physical workplace – not everyone should be granted access to all areas.
Similarly, assigning roles on your WordPress admin dashboard gives each user the right level of access to do their job.
Let’s explore the different WordPress user roles and learn how to assign them to other team members. We will also guide you through editing permissions of each user role with a plugin.
A role defines a user’s access level. Meanwhile, permission defines the specific actions users can do on the website, like publishing a post, installing a plugin, or moderating comments.
In other words, roles contain a set of permissions. Therefore, assigning the correct role to each user is essential for ensuring:
Essentially, there are five WordPress default user roles. Activating a WordPress multisite will unlock an additional super admin role.

Here’s how each differs from the other:
1. Subscriber
Subscriber has the lowest control in WordPress. Granting users this role allows them to view published posts and manage their profile section on the dashboard.
This user role will be most beneficial if you want to create a membership WordPress website.
2. Contributor
Users with the contributor role can only add and edit their own content. They don’t have permission to publish. Once they’ve written the post, the site administrator or editor will review the content before making it live.
Therefore, this role is perfect for someone who wants to join a one-off collaboration with your site.
3. Author
As the name suggests, authors produce the site’s content. They unlock permissions that contributors don’t have, such as uploading media, creating, editing, publishing, and deleting posts.
That said, their access is limited to their own content management, meaning they can’t organize other users’ posts.
With this in mind, assigning the author role is perfect for regular contributors on your site.
4. Editor
Above the authors, editors hold high-level access to manage the website content. They can approve comments, organize the media library, and edit pages.
The editor’s permission is limited to content management and overseeing the work of other users and contributors. Editors can’t access the installed themes and plugins, approve updates, or tweak site settings.
Assigning this role to your site’s content manager, team leaders, and senior contributors is the ideal scenario.
5. Administrator
The administrator role holds the highest position in the hierarchy. This means administrators have complete control over every aspect of the website, including managing users and changing critical website configurations.
When you create a new WordPress website, this role will be assigned to you by default.
6. Super Admin
There will be an additional super admin role specifically for WordPress multisite networks. It functions equally as the administrator, but the scope is elevated to multiple websites, hence the term super.
Super admins have permission to perform administrative tasks within the network, such as adding or deleting websites, installing a WordPress theme or plugin, and organizing content. They also have complete control over all the network’s users.
You can add a wide range of functions to your website using WordPress plugins. Depending on the plugin’s features, you may find some extra user roles when it’s activated. Here are a few plugin examples, along with the roles they include:
WooCommerce (for adding eCommerce functionality)
Easy Digital Downloads (for selling digital products)
Yoast SEO (for optimizing your website for search engines)
Slice WP (for building an affiliate marketing program)
Assigning user roles in WordPress is totally simple. However, note that you can only do it if you are an administrator. Here’s how:
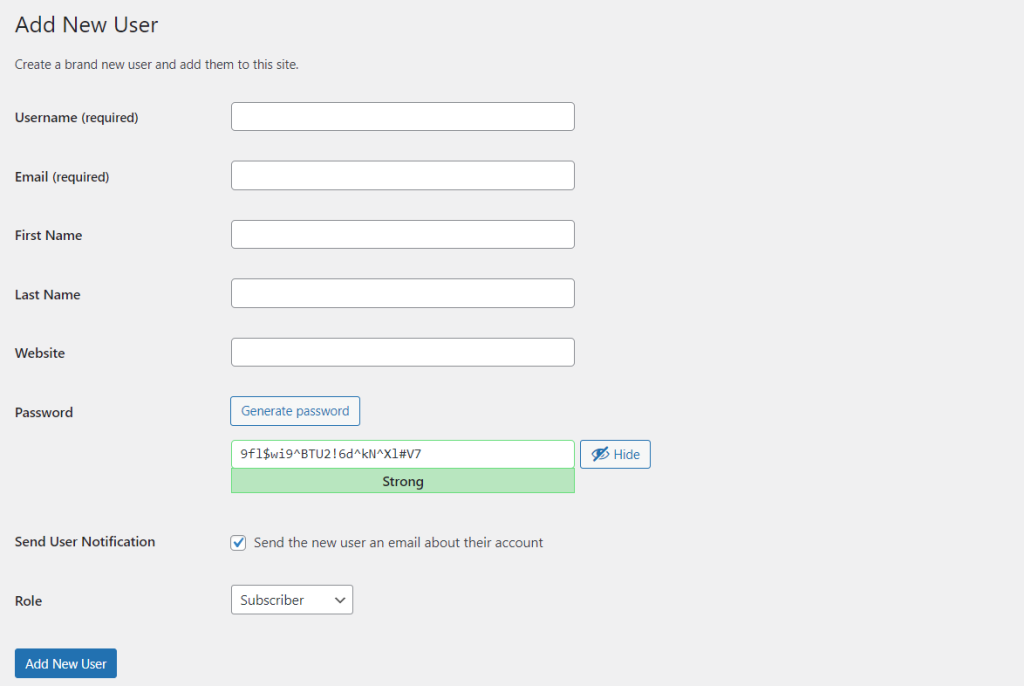
Important! Always be cautious when appointing another user as an administrator. Once assigned, they have the full right to do everything on the admin dashboard, including changing configurations or deleting the entire site.
If you want to change the role of an existing user, do this instead:
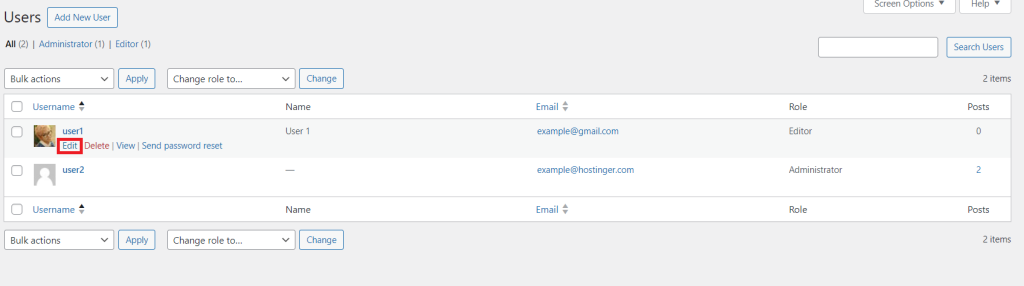
You can modify the five default user roles with a plugin if you need more detailed permissions.
If you need a guide, we have a separate tutorial for installing a WordPress plugin.
Follow these steps to customize an existing user role:
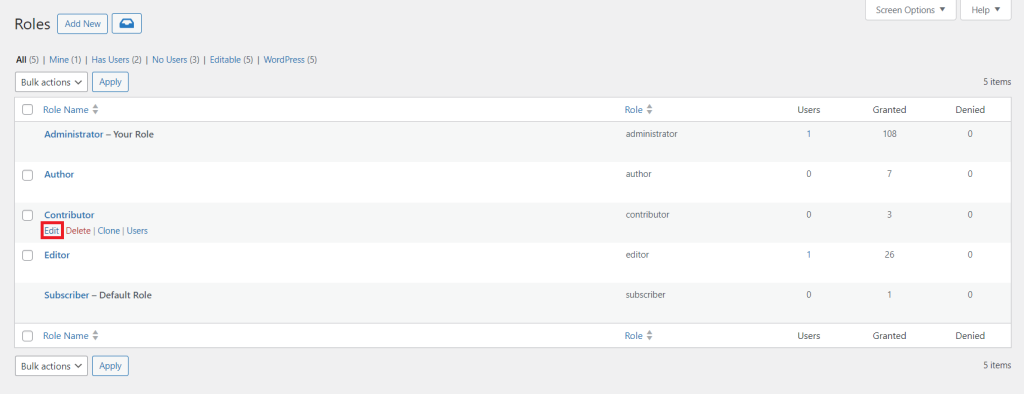
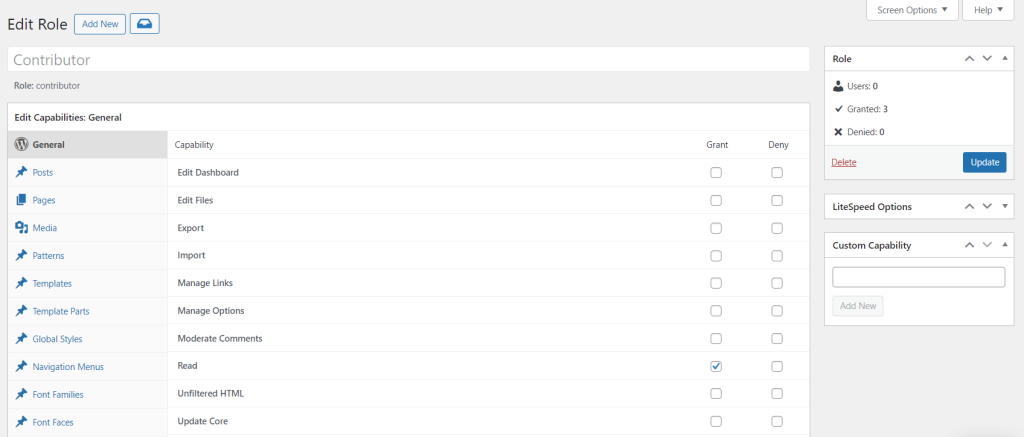
Aside from tweaking permissions for the default user roles, you can add custom ones with the same plugin. Here’s how:
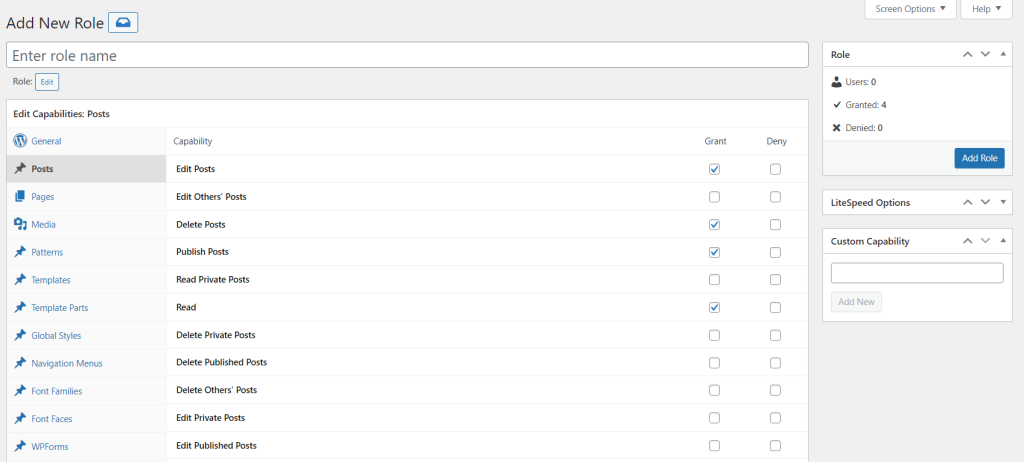

Assigning roles to multiple users on your WordPress site lets you restrict access, delegate tasks effectively, and help ensure your site remains secure. To recap, here are the six default roles in WordPress:
Apart from these, you can also create custom user roles by activating a plugin.
We hope this article helps you understand how to manage user roles in WordPress. If you have further questions, don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.
By default, WordPress has five pre-defined user roles: subscriber, contributor, author, editor, and administrator. If you’re running a WordPress multisite network, there will be an additional super admin role.
WordPress default settings allow users to have only one role at a time. You can assign multiple roles by activating a WordPress user role editor plugin like Members or PublishPress Capabilities.
Note that only administrators can grant WordPress user access. If you are one, go to User → Add New Users from the WordPress admin dashboard. Fill in the username and email, select a user role, and then hit the Add New User button to finish.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.