11 best PHP frameworks for beginner to advanced developers

PHP frameworks provide a foundation of prewritten code, libraries, and tools for building web applications.
They streamline development by handling repetitive tasks, offering a structured coding environment, and improving security.
With a PHP framework, developers can focus on the business logic of their application instead of rebuilding core features for every project.
Here’s a quick overview of today’s top PHP frameworks:
- Laravel. The most popular option, known for its elegant syntax and vast ecosystem.
- Symfony. A flexible, enterprise-grade framework built on reusable components.
- CodeIgniter. A lightweight framework known for its small footprint and speed.
- CakePHP. A rapid development framework that favors convention over configuration.
- Yii. A high-performance, component-based framework ideal for large-scale applications.
- Mezzio. A PSR-15 middleware microframework from the Laminas Project, suitable for modern API and web development.
- Phalcon. A unique framework delivered as a C extension for maximum speed.
- Slim. A microframework designed for simple, powerful APIs and web services.
- Flight PHP. A lightweight, zero-dependency microframework that’s gaining popularity quickly.
- Spiral Framework. A high-performance framework using a hybrid PHP/Go runtime for exceptional speed.
- Fat-Free Framework (F3). An extremely lightweight microframework suited for small projects.
Why should you use PHP frameworks?
You should use PHP frameworks to standardize your coding practices and automate common development tasks.
Without one, you’d need to create custom functions for database connections, session management, and input validation from scratch – a process that takes time and increases the risk of errors.
- Faster development. Frameworks offer reusable libraries for tasks like routing and authentication, which cuts down coding time.
- Stronger code structure. Most frameworks use the Model-View-Controller (MVC) or Hierarchical Model-View-Controller (HMVC) architecture. MVC separates data (Model), presentation (View), and control logic (Controller).
- Built-in security layers. Frameworks include tools that guard against common vulnerabilities such as Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), SQL injection, and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). For example, Laravel uses Eloquent’s prepared statements to prevent SQL injection.
- Better collaboration. Frameworks enforce coding standards and conventions, helping teams work consistently and speeding up onboarding for new developers.
- Large ecosystems and community support. Popular frameworks have active communities that provide plugins, packages, and extensions, expanding functionality without custom development.
What are the factors to consider when choosing a PHP framework?
The most important factors to consider when choosing a PHP framework include your project’s scope, your team’s expertise, and the application’s performance needs.
Not every framework fits every use case; a robust enterprise tool might be unnecessary for a simple portfolio site.
- Learning curve and documentation quality. Look for comprehensive, up-to-date documentation. A steep learning curve can delay your launch, so beginners benefit from strong tutorials and active community forums.
- Project type and size. Full-stack frameworks like Laravel work well for complex enterprise applications, while microframeworks like Slim suit simple APIs or microservices.
- Performance requirements. If speed is a top priority, consider lightweight or performance-focused frameworks such as Phalcon.
- Security features. Confirm that the framework provides built-in tools for input filtering and data encryption to handle sensitive data securely.
- Ecosystem and community support. A larger community means more third-party packages, better long-term maintenance, and easier troubleshooting.
- Modularity and extensibility. Select frameworks that let you load only the necessary components, keeping the application lightweight.
- Active maintenance. Review the framework’s GitHub repository for recent commits and releases to make sure it receives regular updates and security patches.
- Compatibility with hosting environments. Check that your hosting provider supports the framework’s requirements, including specific PHP versions or extensions.
- Server requirements and dependencies. Some frameworks have specific technical needs, such as minimum PHP versions, extensions, or server configurations. Make sure these requirements align with your planned infrastructure.
After reviewing these factors, you can explore the top PHP frameworks to find the best match for your project.
1. Laravel
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: Complex enterprise applications, rapid prototyping for startups, and team projects that need clear structure and strong testing tools.
Widely regarded as the most popular PHP framework today, Laravel is known for its elegant syntax that simplifies common web development tasks.
With more than 34,000 GitHub stars and over 470 million Packagist downloads, it leads PHP framework adoption by a wide margin.
The framework aims to make development a creative and enjoyable experience, rather than a frustrating one. Its large ecosystem includes tools that handle complex operations such as payment, billing, and server management.
Laravel also streamlines repetitive tasks like authentication, routing, sessions, and caching so developers can focus on business logic.
Its popularity benefits beginners as well, thanks to extensive documentation, tutorials, and learning resources.
The framework also offers Laravel Forge, a centralized platform for installing and managing application dependencies in your live environment.
Laravel key features
- Robust ecosystem. Includes tools like Laravel Homestead for local development and Laravel Forge for server management.
- Blade template engine. A powerful, lightweight templating engine that lets you write plain PHP in your views.
- Eloquent ORM. An advanced active record implementation that makes database interactions intuitive and readable.
- Built-in testing. PHPUnit is supported out of the box, with helper methods that enable expressive and consistent testing.
- Artisan console. A built-in command-line interface with helpful commands that speed up development tasks.
Laravel pros
- Extensive community support. Thousands of packages, tutorials, and forums make troubleshooting easier.
- Modern coding practices. Enforces clean code and modern PHP standards, which helps long-term maintenance.
- High security. Built-in protection against SQL injection, CSRF, and XSS.
Laravel cons
- Performance overhead. As a full-stack framework with many default features, it can be slower than lightweight alternatives.
- Frequent updates. The rapid release cycle, with major versions like Laravel 12 released annually, can introduce breaking changes that require maintenance work.
2. Symfony
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: Large-scale enterprise projects, complex applications that require long-term stability, and developers who want full control over configuration.
Symfony is a set of reusable PHP components and a web application framework designed to speed up the creation and maintenance of web applications.
It’s widely used in enterprise environments because of its stability, sustainability, and strict adherence to PHP standards.
The framework is modular, so you can use the whole stack or select specific components such as the HTTP library or template engine.
This flexibility makes Symfony the foundation for major projects, including CMSs like Drupal and ecommerce platforms like Magento.
Symfony uses Twig, a fast template engine with a concise syntax for defining your project’s frontend. Twig also auto-escapes output by default, providing XSS protection without manual intervention.
Its built-in debugging tools also provide detailed insights into each request to help you confirm your application works as intended.
Symfony key features
- Component-based system. Choose from over 100 standalone components to include only what your project needs.
- Twig template engine. A fast, secure, and flexible engine with a concise syntax for defining templates.
- Debugging toolbar. A built-in toolbar that offers detailed information about request processing and database queries.
- Database independence. Through Doctrine, Symfony provides powerful database tools and a structure that works independently of the database engine.
Symfony pros
- High flexibility. You can build anything from small microservices to large enterprise applications.
- Interoperability. It adheres to the PHP Standard Recommendations (PSR), ensuring compatibility with other libraries.
- Long-term support. Stable release cycles make it a reliable choice for multi-year projects. LTS versions receive extended support – for example, Symfony 7.4 will receive security fixes until November 2028.
Symfony cons
- Steep learning curve. Its extensive features and abstract concepts make it harder for beginners to master.
3. CodeIgniter
- Type: Full-stack / Lightweight framework
- Best for: Beginners learning MVC architecture, simple to medium-sized applications, and projects hosted on shared servers with limited resources.
A powerful PHP framework with a minimal footprint, CodeIgniter is designed for developers who want a simple and elegant toolkit for creating full-featured web applications.
It’s known for its speed and for avoiding strict coding rules or complex configuration.
The framework is flexible, supporting both MVC and non-MVC design patterns to fit different team sizes and project needs.
Larger teams can streamline development with its MVC structure, while solo developers can work without it.
Its strong performance makes it ideal for lightweight applications that need to run well in modest PHP hosting environments.
CodeIgniter also includes solid security tools, such as context-sensitive escaping and protection against cross-site scripting.
CodeIgniter key features
- Small footprint. CodeIgniter 4 is approximately 1.1 MB in size, plus an additional 1.6 MB for the user guide, facilitating quick setup and deployment.
- Loose MVC architecture. It follows the Model-View-Controller pattern but lets you bend the rules when needed.
- Built-in security. Offers protection against XSS and CSRF attacks, along with input validation tools.
- Excellent performance. CodeIgniter 4 can handle around 1,874 requests per second on PHP 8.5, thanks to its lean core, which minimizes overhead compared to other lightweight frameworks.
CodeIgniter pros
- Easy to learn. Clear documentation and a simple structure make it beginner-friendly.
- Fast execution. The lightweight core keeps applications sprinting even on modest hosting plans.
- Minimal configuration. You don’t need the command line or complex configuration files to get started.
CodeIgniter cons
- Slower release cycle. Updates and new features arrive less frequently than in Laravel or Symfony.
- Less rigid structure. Its flexibility can lead to messy code in large teams if strict internal standards aren’t enforced.
4. CakePHP
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: Rapid application development (RAD), commercial applications that need speed, and developers who prefer convention over configuration.
CakePHP is one of the original PHP MVC frameworks. It simplifies common web development tasks by providing an all-in-one toolbox to help you start quickly.
The framework follows a “convention over configuration” approach, meaning it makes assumptions about your setup to save time.
For example, a UsersController automatically maps to a users database table and a User model without requiring any configuration files.
Because CakePHP handles much of the configuration, you can focus on your application’s logic instead of defining every setting manually. It continues to evolve with maintained coding guidelines that all users follow.
CakePHP also offers a vast library ecosystem, including one of the most comprehensive collections of reusable components. It’s a strong option if you need rare features or support from an active developer community.
CakePHP key features
- Code generation (Bake). A command-line tool that generates application code to speed up prototype creation.
- Built-in batteries. Provides validation, database access, caching, and authentication out of the box.
- Scaffolding. Automatically creates basic Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) views for your database tables.
- Security features. Includes input validation, CSRF protection, form-tampering protection, and SQL injection prevention.
CakePHP pros
- Rapid development. Conventions and scaffolding tools let you build a functional prototype in minutes.
- Clean MVC conventions. Enforces a strict directory structure that keeps code organized in large projects.
- Active community. A loyal user base contributes to plugins and offers many support channels.
CakePHP cons
- Restrictive conventions. Deviating from the framework’s strict rules can be difficult if your project requires a unique structure.
- Lower performance. Slower than lightweight frameworks because of its larger feature set. It can handle only around 73 requests per second, compared to CodeIgniter’s 1,800+.
5. Yii
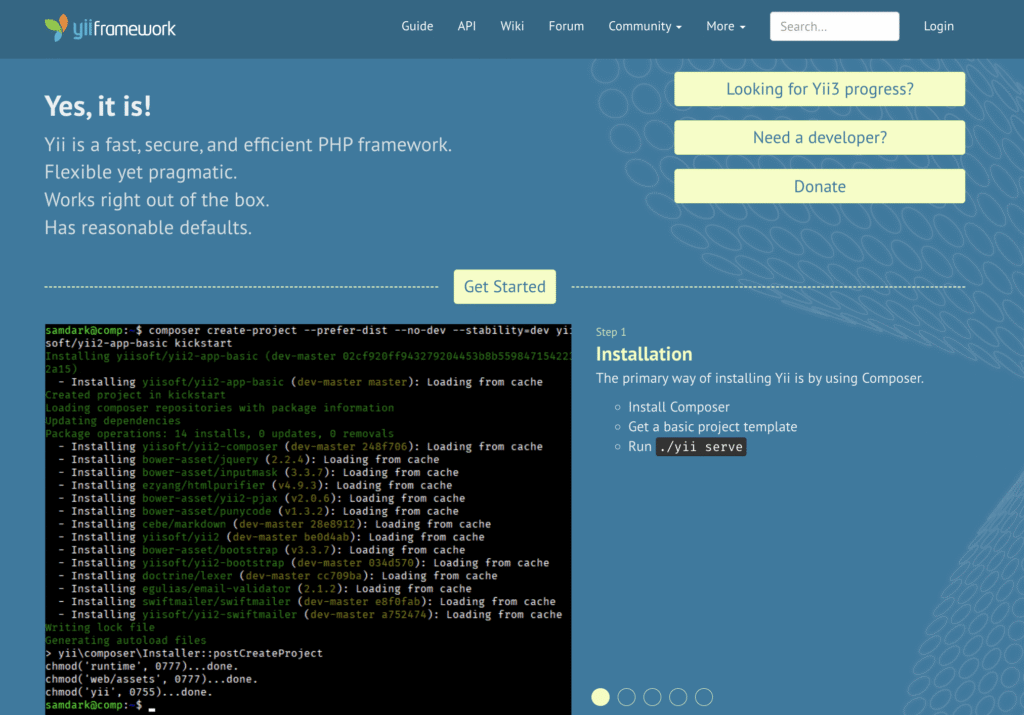
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: Large-scale ecommerce systems, high-traffic portals, CMSs, and forums.
Yii is a generic, component-based web programming framework designed for high performance across a wide range of applications.
It works exceptionally well for complex systems where extensibility and speed matter, such as portals and forums.
The framework offers a robust set of capabilities and supports numerous extensions, facilitating rapid development. For example, it provides Gii, a code generator that automates model creation, CRUD operations, and module generation.
Yii also includes strong security features, such as user-based authentication controls and SQL injection prevention.
While it isn’t the most beginner-friendly framework, its documentation and active community support make the learning process easier.
Yii key features
- Gii code generator. A web-based tool that automatically generates models, controllers, and forms.
- Extensive library. Includes built-in support for internationalization, caching, and tiered caching schemes.
- Database Access Objects (DAO). Provides an efficient way to interact with databases and manage migrations.
- Security-focused. Defaults protect against SQL injection, XSS, and cookie tampering.
Yii pros
- High performance. Its lazy loading and component-based architecture minimize memory usage, making it efficient for demanding applications.
- Highly extensible. You can customize nearly any part of the core code to fit your needs.
- Short development time. Automation tools significantly reduce boilerplate code.
Yii cons
- Steep learning curve. Its extensive features and strict object-oriented design can overwhelm beginners. The component architecture also requires an understanding of behaviors, events, and Active Record relations to work efficiently.
6. Mezzio
- Type: Micro-framework
- Best for: Modern API development, PSR-compliant applications, and teams migrating from Laminas MVC or Zend Framework.
Mezzio is a PSR-15 middleware microframework from the Laminas Project, designed for building modern, standards-compliant PHP applications.
It follows PSR-7 (HTTP messages), PSR-15 (middleware), and PSR-11 (container) standards, ensuring strong interoperability with other PHP libraries.
The framework’s minimalist architecture provides developers with full control while maintaining enterprise-grade reliability.
Mezzio supports multiple routers (FastRoute, Laminas Router), dependency injection (DI) containers (Laminas ServiceManager, PHP-DI, Symfony), and template engines (Twig, Plates, Laminas View), letting you choose the components that best fit your workflow.
Mezzio key features
- PSR-15 middleware. Build PHP applications using PSR-7 and PSR-15 standards for maximum interoperability.
- Laminas components. Access more than 100 loosely coupled Laminas components that you can use independently in any PHP application.
- Flexible architecture. Select your preferred router, container, and template engine without being locked into a framework.
- Laminas ecosystem. Full compatibility with Laminas tools for validation, forms, and database abstraction.
Mezzio pros
- Standards compliance. Built entirely on PSR standards, ensuring long-term interoperability.
- Modular design. Use specific components, like the input validator or mail handler, without loading the entire framework.
- Modern architecture. Middleware-first design aligns with modern PHP practices and simplifies testing.
Mezzio cons
- Requires PSR knowledge. Developers unfamiliar with PSR-7 and PSR-15 patterns will face a learning curve.
- Smaller community. Offers fewer tutorials and community resources compared to Laravel or Symfony.
7. Phalcon
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: High-performance applications, systems with heavy loads, and environments where resource usage must stay low.
Phalcon is a full-stack PHP framework delivered as a C extension, setting it apart from every other framework on this list.
Due to this architecture, the framework loads into RAM as a web server module, resulting in exceptionally fast execution speeds.
Even though its core is written in C, developers still work with Phalcon through standard PHP classes and don’t need to know C.
The framework is lightweight and follows the MVC pattern, so users can load only the modules and libraries they need. This keeps development clean while maintaining high performance and low resource overhead.
One consideration is that Phalcon has a smaller community than Laravel and offers fewer learning resources.
Phalcon key features
- Low overhead. Since it loads as a server module, it doesn’t need to interpret core files on each request.
- Volt template engine. A fast, developer-friendly template engine built directly into the framework.
- Memory management. Optimized for efficient memory usage, allowing more concurrent requests on the same hardware.
- Asset management. Includes tools for managing CSS and JavaScript, including minification.
Phalcon pros
- High speed. As a C extension, Phalcon eliminates interpretation overhead, leading to significantly faster execution times and lower latency.
- Feature-rich. Includes ORM, caching, queuing, and other necessary components despite its performance focus.
- Resource efficient. Ideal for reducing cloud hosting costs where CPU and memory usage affect billing.
Phalcon cons
- Installation requirements. Installing the extension requires root access, which isn’t available on many shared hosting plans. Phalcon v6, currently in development, will address this limitation by offering a pure PHP option.
- Debugging difficulty. Because the core is compiled in C, debugging internal framework issues can be harder.
8. Slim
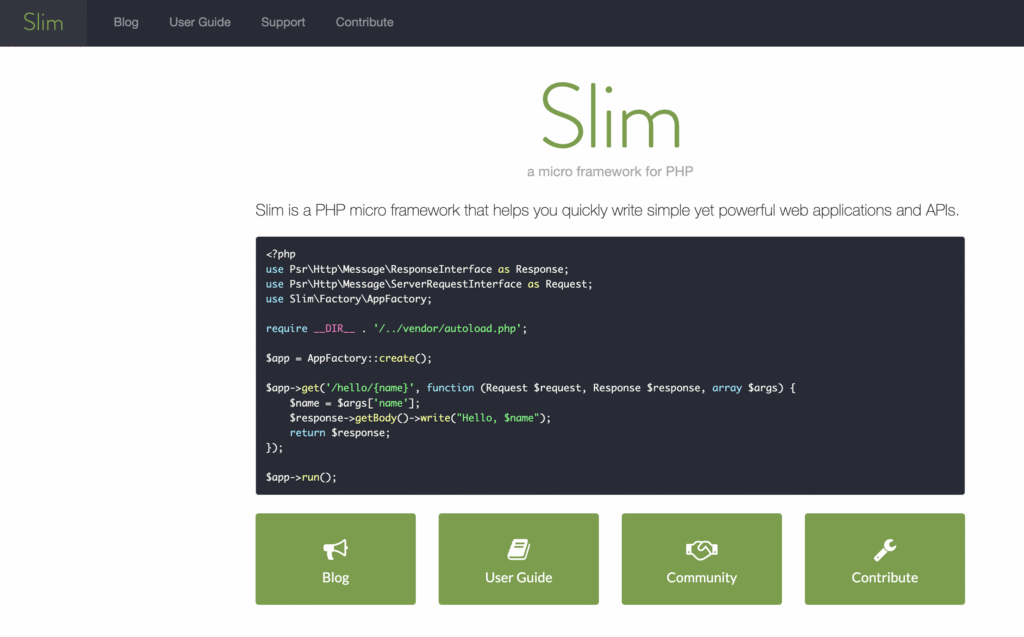
- Type: Micro-framework
- Best for: RESTful APIs, microservices, and small web applications that don’t require full-stack features.
Slim is a PHP microframework that helps you build simple yet powerful web applications and APIs quickly. It’s minimalist by design, removing the overhead of full-stack frameworks and focusing solely on handling HTTP requests.
Its main strength is request handling. Slim uses a powerful HTTP router to map route callbacks to specific HTTP methods and URIs.
Another valuable feature is its middleware system, which lets developers run code before and after the Slim core processes a request – useful for tasks like security filtering or logging.
Overall, Slim is well-suited for building HTTP request–driven applications or RESTful APIs with minimal setup. It’s easy to learn, offers strong documentation, and has an active community.
Slim key features
- PSR-7 support. Fully compatible with standard HTTP message interfaces, ensuring interoperability with other PHP tools.
- PSR-15 middleware. An easy-to-use middleware layer for manipulating request and response objects, such as for logging or authentication.
- Dependency injection. Supports any PSR-11 container implementation to manage external dependencies cleanly.
- Powerful routing. Handles both standard and custom URL matching with parameters and patterns.
Slim pros
- Extremely lightweight. Minimal core code results in speedy response times.
- Easy to learn. You can understand the framework structure quickly compared to most alternatives.
- Flexible. You start with a minimal setup and add only the libraries you need after installing Composer.
Slim cons
- No batteries included. It lacks built-in features such as database ORM or templating, so you must integrate these features yourself.
9. Flight PHP

- Type: Micro-framework
- Best for: Lightweight APIs, rapid prototyping, and developers who want zero-dependency simplicity.
Flight PHP is a fast, extensible PHP microframework with zero external dependencies. It requires PHP 7.4 or higher and prioritizes simplicity without compromising power.
Flight gained strong momentum in 2024–2025, thanks to active development and the addition of modern features, including route groups, middleware, and dependency injection handlers.
It supports clean routing, middleware, and DI and can power anything from simple single-file projects to well-structured applications.
The framework is also 100% unit tested, making it reliable for production use despite its minimalist footprint.
Flight PHP key features
- Zero dependencies. Requires no external packages, just PHP.
- Simple routing. Intuitive route definitions with support for groups and parameters.
- Middleware support. Easily add authentication, logging, or custom logic.
- Extensible architecture. Override or extend framework methods to match your project’s needs.
Flight PHP pros
- Ultra-lightweight. A minimal footprint enables fast execution and easy deployment.
- Beginner-friendly. Simple API helps new developers start building quickly.
- Actively maintained. Receives regular updates, with new features added throughout 2024–2025.
Flight PHP cons
- Limited built-in features. Like most microframeworks, you must add ORM, templating, and authentication yourself.
- Smaller community. Offers fewer tutorials and packages than microframeworks like Slim.
10. Spiral Framework
- Type: Full-stack framework
- Best for: High-performance enterprise applications, microservices, real-time applications, and projects that require speed and scalability.
Spiral Framework is a high-performance PHP framework built on a unique hybrid runtime architecture.
Unlike traditional PHP frameworks, Spiral integrates with RoadRunner, an application server written in Go. RoadRunner keeps your PHP code in memory between requests, rather than reloading it each time.
This design results in significant performance improvements. By eliminating bootstrap overhead on each request, Spiral with RoadRunner achieves significantly higher throughput than traditional PHP-FPM setups.
The framework supports more than sixty PSR-compatible components and has been battle-tested in production for over a decade.
Spiral takes inspiration from frameworks like Spring and ASP.NET, making it a flexible choice for developers building scalable enterprise systems.
It supports multiple architectural patterns, including MVC, HMVC, CQRS, and event-driven designs.
Spiral Framework key features
- RoadRunner integration. A high-performance application server that handles HTTP, gRPC, WebSockets, and queue processing.
- Long-living processes. Keeps PHP code in memory to eliminate the overhead of bootstrapping on every request. This approach mirrors how Java and C# applications work, enabling PHP to compete with traditionally faster runtimes.
- Cycle ORM. A flexible DataMapper ORM with dynamic schema mapping. Unlike Active Record (Eloquent), DataMapper separates business logic from persistence, which improves testability in complex applications.
- Built-in security. Includes encryption, CSRF protection, RBAC authorization, and token-based authentication.
- Microservices ready. Offers native support for gRPC, message queues, and Kubernetes-compatible health checks.
Spiral Framework pros
- Exceptional performance. The hybrid PHP/Go architecture delivers faster response times than traditional frameworks.
- Scalable architecture. Provides built-in tools for queues, event broadcasting, and container orchestration.
- PSR compliance. Works with most PHP Standard Recommendations and widely used libraries.
Spiral Framework cons
- Steeper learning curve. The long-living process model introduces concepts that differ from traditional PHP development. Developers must also understand memory management and worker lifecycles – concepts that are unfamiliar to those coming from PHP-FPM environments.
- Server requirements. Depends on RoadRunner, which may not be available in shared hosting environments.
11. Fat-Free Framework (F3)
- Type: Micro-framework
- Best for: Very lightweight applications, developers who want total control, and rapid prototyping of small tools.
Fat-Free Framework is a powerful yet easy-to-use PHP microframework to help you build dynamic web applications with minimal effort.
Its codebase is extremely lightweight at approximately 85KB, and its modular design lets you load only the components you need.
Getting started requires only a web server and a copy of the framework – no Composer, cURL, or complex configuration is needed.
This simplicity makes F3 highly accessible for developers who want to start coding immediately without managing a large directory structure.
Despite its lightweight core, Fat-Free is extendable through optional plugins for tasks like unit testing and image processing.
It also supports multiple databases, including MySQL, SQLite, and MongoDB, providing flexibility in how you store and manage data.
Fat-Free Framework key features
- Multi-database support. Connects to MySQL, SQLite, MSSQL, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL.
- Built-in cache engine. Offers a multi-protocol cache engine to improve application performance.
- Zero dependencies. Doesn’t require Composer or complex directory structures to run.
- Optional plugins. Extends the small core with plugins, such as for unit testing and image processing.
Fat-Free Framework pros
- Ultra-lightweight. Adds almost no overhead to your application, resulting in fast performance.
- Flat learning curve. Its simplicity makes it easy to master quickly.
- Portable. With no complex installation requirements, it’s easy to move between servers.
Fat-Free Framework cons
- Risk of disorganized code. The lack of a rigid structure can lead to messy code in larger projects if not managed carefully.
What should you build next with your PHP framework?
Once you select the right PHP framework, the next major step in building a dynamic application is connecting your project to a database.
The framework provides structure and logic, while the database stores your actual content and user information.
Almost every useful feature in a web application, whether a login system, product catalog, or content management dashboard, relies on database-driven functionality.
Mastering how your framework interacts with data is important for moving beyond static pages.
To start with the fundamentals of database interaction, learn how to connect PHP to MySQL.
This knowledge forms the foundation you’ll use when working with your framework’s tools, such as Laravel’s Eloquent or Doctrine in Symfony.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.

Comments
October 03 2018
If you are looking framework for performance, go for Yii.
November 06 2018
Yii is pretty great. Though I've heard that Phalcon is the fastest PHP framework and beats most others in benchmarks by a large margin.
October 18 2018
I agree. This list of PHP frameworks is really good and their usage is quite simple (especially once you get the hang of it).
February 19 2019
I miss Adive framework for PHP7 :P
May 16 2020
I think the best php framework is Laravel. Especially the route, resource function is very good.
November 03 2020
I initially had trouble understanding some PHP frameworks, but now I find them super simple.
February 17 2021
Web application development helps us in understanding hard matters. Thank you for sharing this wonderful post. keep sharing such blogs with us.
December 13 2021
Hey, Thank you for sharing these PHP frameworks. Laravel is the best suited framework for building web applications.
March 20 2022
Great article. I wish you had included Trongate though. I used it recently and found it lightweight, fast and easy to use.
March 22 2022
Hey John! It looks like it's a new framework - we haven't tested it yet, but we'll surely consider it for a future update of the article - thanks :)