Feb 13, 2026
Ariffud M.
8min Read

WooCommerce Google Analytics integration connects your online store to Google’s tracking platform, enabling you to monitor conversions, product performance, and customer behavior.
Store owners use this data to identify top-selling products, find checkout drop-offs, and measure how well their marketing campaigns perform.
Connecting WooCommerce with Google Analytics 4 (GA4) takes four steps:
Once everything’s active, you can track metrics like conversion rates, add-to-cart events, and revenue by traffic source, all from your GA4 dashboard.
When using Google Analytics, you’ll in fact use Google Analytics 4 – the current and only supported version. Universal Analytics stopped processing data on July 1, 2023, so all new setups use GA4 by default.
Without a properly configured GA4 property, the WooCommerce plugin has nowhere to send tracking data. Complete this step before you install any plugins.
Follow these steps to create your GA4 property and get your Measurement ID:
If you already have a Google Analytics account, go to Admin → Create → Property and follow steps 4 through 9 above.
You’ll find your Measurement ID at the top of the Web stream details page. You can also access it later by going to Admin → Data collection and modification → Data streams → [your stream] → Measurement ID.
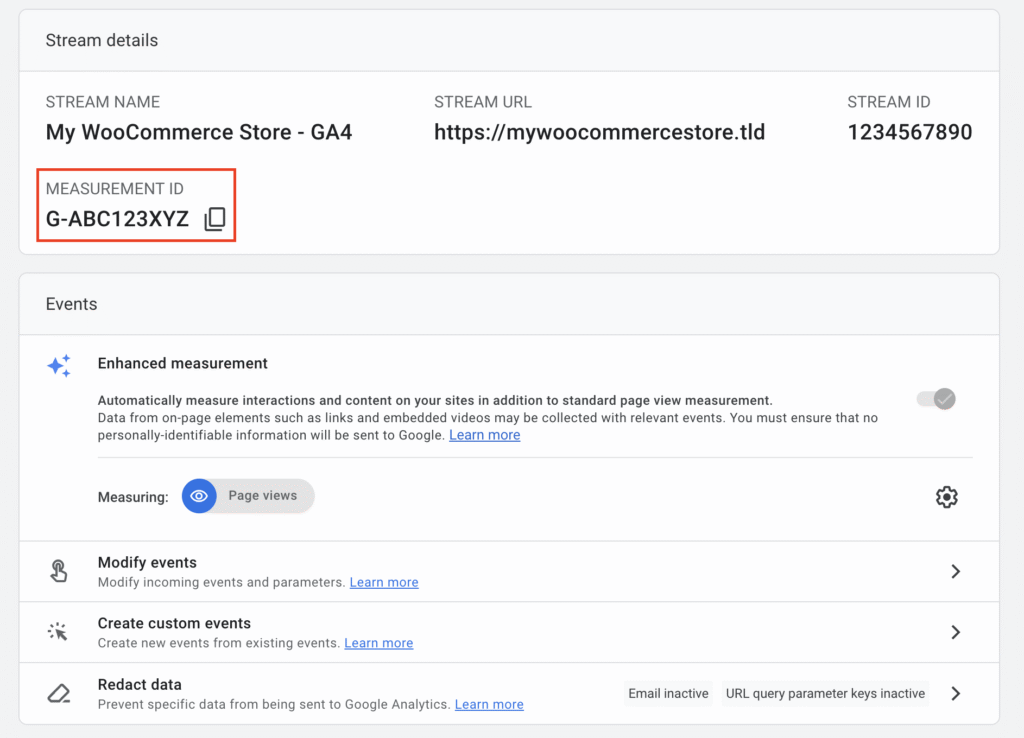
Keep this ID handy since you’ll need it during plugin setup.
Google Analytics for WooCommerce is the official free plugin for connecting GA4 to your store. WooCommerce (part of Automattic) maintains it, and you can find it on WordPress.org, where it has over 200,000 active installations.
Using the official plugin helps ensure compatibility with WooCommerce updates and gives you access to support from the WooCommerce team.
Here’s how to install the plugin from your WordPress dashboard:

You can also install the plugin manually by uploading a ZIP file:
A Pro version is available for $79 per year and includes features like user ID tracking, detailed checkout step events (payment method selected, billing email provided), coupon tracking, and order refund/cancellation monitoring.
For most stores, the free version covers standard ecommerce tracking needs. If you’re unsure which one to choose, you can compare both versions on the WooCommerce Google Analytics comparison page.
Access the plugin settings by going to WooCommerce → Settings → Integration → Google Analytics in your WordPress dashboard. Enter your Measurement ID in the Google Analytics Tracking ID field.
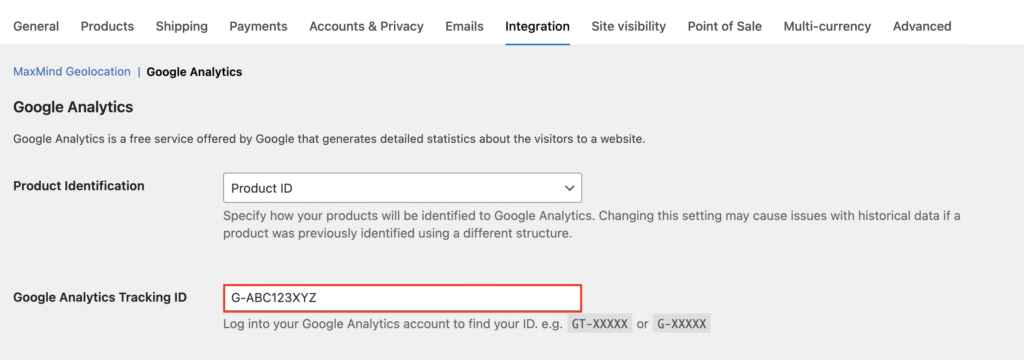
Configure the tracking options based on your store’s needs:
Click Save changes once you finish configuring the options.
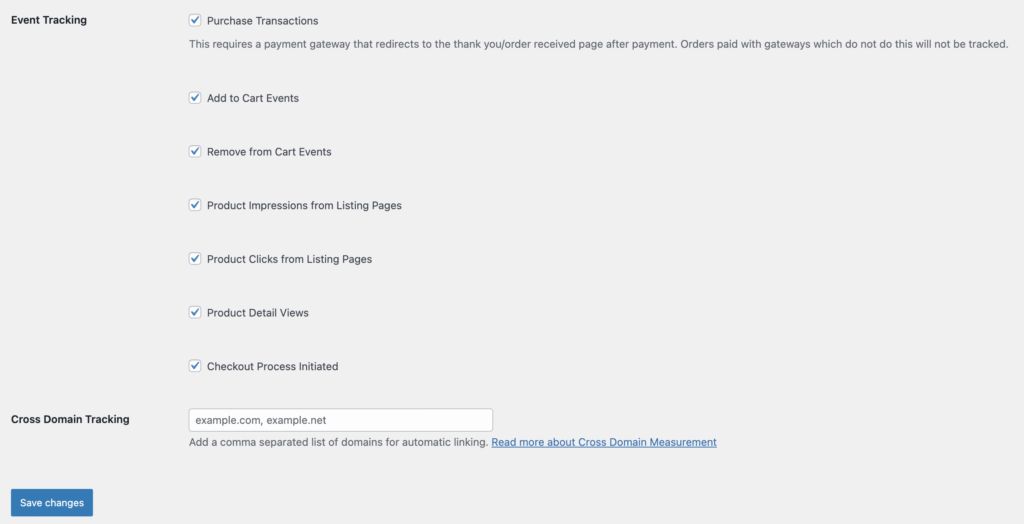
Note that the Pro version includes additional tracking for events like coupon usage, customer account activity, payment method selection, and order refunds.
If you’re using another Google Analytics plugin, like MonsterInsights, follow that plugin’s documentation for configuration steps.
GA4 can take 24 to 48 hours to display data after the initial setup. Reports won’t populate right away, so check again the next day if you see zeros across the board.
You can verify that tracking works using two methods.
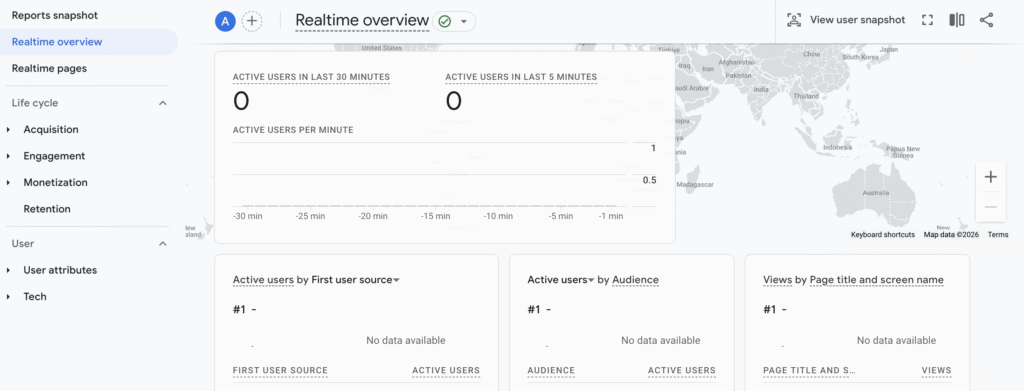
Use GA4 Realtime reports:
Use Google Tag Assistant:
If tracking doesn’t work as expected, check these common issues:
Your integration works correctly when GA4 shows active users, page views, and ecommerce events like add_to_cart and purchase.
In the Realtime report, you’ll also see user locations, active pages, and events as you browse your store.
GA4 tracks dozens of metrics for WooCommerce stores.
To understand store performance and customer behavior, focus on these six categories: conversion rate, add-to-cart and checkout behavior, purchase volume and revenue, user retention, device and browser performance, and geographic performance.
Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who complete a purchase out of the total number of sessions. For example, a store with 1,000 sessions and 30 purchases has a 3% conversion rate.
This metric helps you separate high-quality traffic from casual browsers. If a paid ad campaign drives lots of visitors but few sales, it often points to targeting issues or weak landing pages.
Track conversion rate by traffic source by going to Reports → Acquisition → Traffic acquisition. This helps you identify channels that bring in buyers, not just visitors. Invest more in sources with above-average conversion rates.
Add-to-cart events show how many visitors add products to their carts. Checkout data reveals where customers drop off, such as during shipping details, payment entry, or order review.
High add-to-cart rates combined with low checkout completion usually indicate friction in the checkout flow. Common issues include unexpected shipping costs, forced account creation, or too many form fields.
Use this data to prioritize improvements to the checkout process. If 60% of customers abandon the shipping step, test free shipping thresholds or show shipping costs earlier in the process.
Purchase volume counts completed orders, while revenue shows total sales value by product, category, or time period.
These metrics answer core business questions, such as how much your store sells, which products generate the most revenue, or whether sales grow month over month.
Compare revenue with traffic levels to spot opportunities. A product page with strong traffic but weak sales may need better images, clearer descriptions, or pricing adjustments.
User retention measures how many first-time visitors return within a specific period, like 7 or 30 days. GA4 retention reports compare new and returning users.
Returning customers cost less to convert than new ones. High retention usually signals customer satisfaction and effective email marketing or retargeting.
Low retention can point to issues with product quality, site experience, or post-purchase communication. Use these insights to improve follow-up emails, loyalty programs, or product recommendations.
Device reports break down traffic by mobile, desktop, and tablet. Browser reports show which browsers your customers use, such as Chrome, Safari, or Firefox.
Large conversion rate gaps across devices often reveal usability problems. If desktop converts at 4% but mobile converts at 1%, your mobile checkout experience likely needs attention.
Browser-specific issues can also hurt sales. For example, a broken payment form in Safari can stop customers from completing purchases. Review conversion rates by browser each month to catch issues early.
Geographic reports show the countries, regions, and cities of visitors. You can also review conversion rate, revenue, and session duration by location.
Location data helps guide marketing decisions. High traffic from Germany with low conversions may indicate a need for German-language product pages or euro pricing.
Use geographic insights to prioritize new markets, refine ad targeting, and adjust currency or shipping options for regions with strong potential.
Connecting GA4 to your WooCommerce store turns raw traffic into actionable insights. Store owners use this data to make smarter decisions and increase sales in several key ways.
Analytics data helps you spot opportunities, but search engine optimization (SEO) drives the traffic that makes those opportunities possible.
A well-optimized WooCommerce store ranks higher in search results and attracts more organic traffic. That traffic can turn into customers without relying on paid ads.
Optimizing a WooCommerce store for SEO covers three main areas: technical setup, on-page optimization, and content strategy.
Technical setup includes sitemaps, schema markup, and site speed. On-page optimization focuses on product titles, descriptions, and image alt text. Content strategy involves blog posts, category page copy, and FAQ sections.
Each of these elements helps search engines understand your store and match it with relevant search queries.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.