Feb 24, 2025
Ariffud M.
9min Read
Feb 24, 2025
Ariffud M.
9min Read
Imagine a visitor is about to make a significant purchase or access a service on your website. Instead of reaching the desired page, they’re greeted with a frustrating message: 503 Service Unavailable. For them, it can be a deal-breaker.
It’s even worse for the website owner who’s risking lost traffic, missed sales, and potential reputation damage as visitors might not return in the future.
Although the 503 error is often temporary, addressing it quickly is crucial. In this article, we’ll explain what the 503 Service Unavailable error means, explore its common causes, and guide you through actionable steps to fix it. By the end, you’ll know how to troubleshoot the error and apply preventive measures to make sure it doesn’t happen again.
The 503 Service Unavailable error is a temporary HTTP response status code indicating that the server can’t handle the request at the moment. This often occurs due to resource limitations, scheduled maintenance, or back-end issues. It typically resolves once the underlying problem is fixed.
503 Service Unavailable falls under the 5xx HTTP status code category, representing server-side issues. Unlike permanent errors such as 404 Not Found, the 503 error indicates that the server is functioning but unable to complete requests.
Behind the scenes, a client (such as a web browser, app, or API client) sends a request to the server for a webpage, API resource, or other content. The server (usually a web server like Apache or NGINX) recognizes the request, but something prevents it from being processed correctly.
Instead of delivering the requested resource, the server sends back an HTTP 503 response, informing the client that the service is currently unavailable.
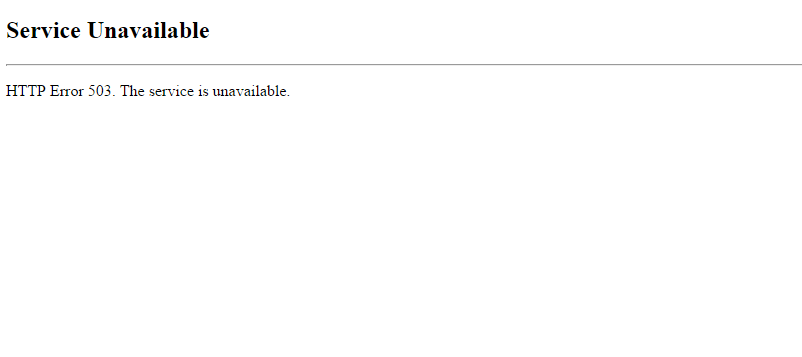
Some possible causes of the 503 Service Unavailable error include:
| Error code | 503 Service Unavailable |
| Error type | Server-side error |
| Error variations | 503 Service Unavailable Error 503 Service Unavailable 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable HTTP Error 503 HTTPS Error 503 HTTP Server Error 503 HTTP Error 503. The service is unavailable. The server is temporarily unable to service your request due to maintenance downtime or capacity problems. Please try again later. |
| Error causes | Excessive traffic or insufficient resources to handle requests Temporary downtime for maintenance or updates Issues with backend systems Incorrect server or application configurations Malicious DDoS attacks Faulty security settings or overly restrictive rate-limiting policies |
While 503 Service Unavailable is a server-side issue, website visitors can try a few quick fixes, such as:
For website owners, we’ve outlined six proven steps to resolve the 503 Service Unavailable error. Start with the first method, and if the issue persists, try the next steps until the problem is fully resolved.
The first step is to analyze whether your server has sufficient resources to handle the current traffic or tasks.
Servers process requests using resources like CPU, RAM, bandwidth, and disk space. When these resources are maxed out, your website’s performance can degrade, triggering errors like 503.
Website owners can monitor resource usage through their hosting provider’s control panel.
For example, on Hostinger’s web hosting, cloud hosting, and Managed WordPress plans, open hPanel to access your website’s dashboard. Then, go to Hosting Plan → Resource Usage to view metrics such as disk space, inodes, CPU, memory, bandwidth, and I/O (throughput).
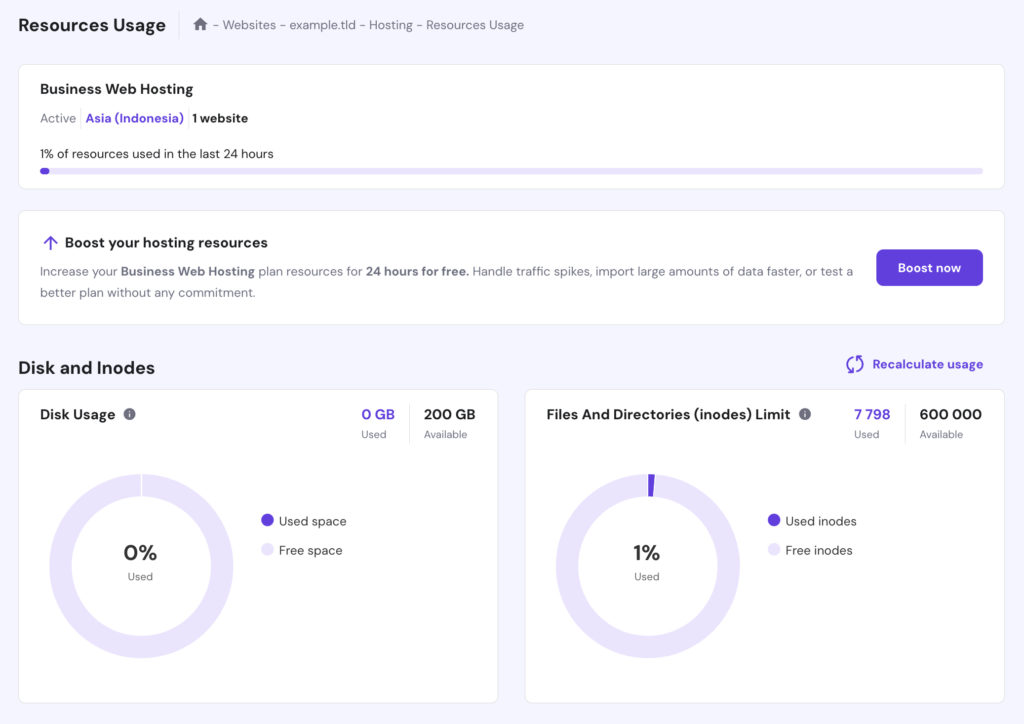
If your website consistently exceeds disk space, inodes, or memory limits (represented by a red line on graphs), you need to optimize resource usage or upgrade to a higher-tier plan with more CPU, RAM, and bandwidth.

If you host your website on a Linux virtual private server (VPS), run commands like top, htop, or vmstat in the terminal to monitor running processes and resource usage in real time. If you identify processes consuming excessive CPU or memory, terminate them using commands like kill or pkill to free up resources.
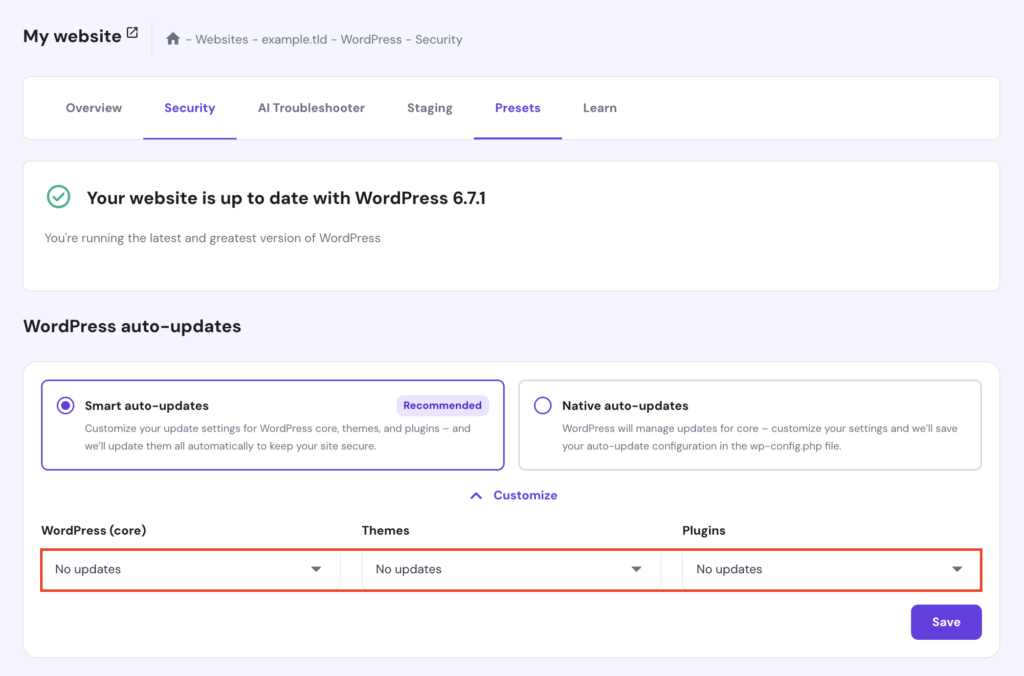
Server maintenance is important for optimizing performance and reducing security risks. However, web servers and applications often shut down automatically during updates or maintenance, which can lead to 503 Service Unavailable.
For instance, many web hosts enable automatic updates for new WordPress releases. During the process, they may issue the 503 HTTP status code on user websites until the update is completed. Hostinger customers can check real-time server updates on our status page.
You can modify your server settings to disable automatic updates and prevent unexpected downtime. For Hostinger’s web hosting users, here’s how to do so on hPanel:
Important! If you decide to disable automatic updates, make sure to manually check for updates and apply them promptly to keep your site secure.
Enable maintenance mode on your site during planned maintenance. This informs visitors about the downtime and reassures them that your website will return soon.
Examining server logs can help pinpoint the cause of the 503 error. Logs provide detailed information about your website’s activities, such as requested pages and system errors, making it easier to identify the root issue.
For WordPress websites, enable debugging mode to generate an error log. If you host your WordPress site on Hostinger, follow these steps:

define( 'WP_DEBUG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false );
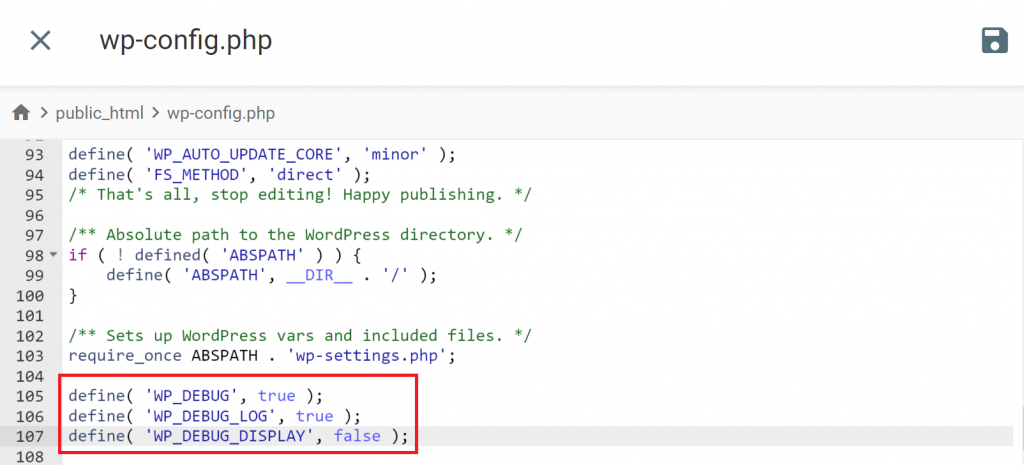
In this file, you’ll find the detailed error information, which might include:
Review the logged errors and address them accordingly, such as fixing misconfigured plugins or updating database settings.
If you’re unsure whether the issue is WordPress-specific or caused by broader PHP scripts, activate PHP error logging. Here’s how to do it on hPanel:
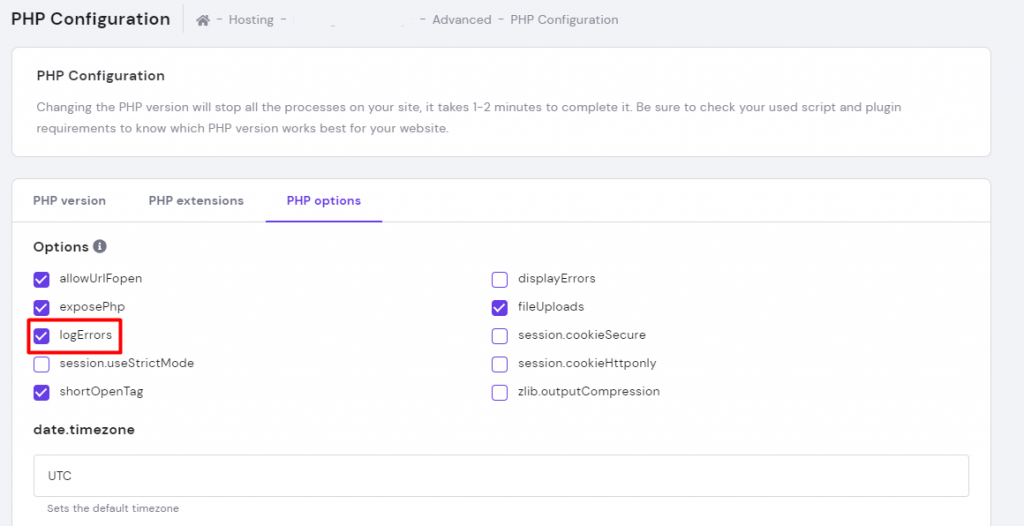
cd .logs
Locate the error log file, typically named error_log_yourdomain_tld. It records broader PHP-related issues, such as syntax errors in server-side scripts and failed server processes or script executions.
For VPS hosting users, check web server logs to investigate errors like missing files, misconfigured virtual hosts, and module failures. Depending on your server software, the log files are located in the following:
Restarting your server or specific components can often resolve 503 Service Unavailable. This clears problems such as locked files, memory leaks, or unresponsive processes so your server can start fresh.
On Hostinger’s web hosting plans, you don’t have root access to restart the server directly. However, you can stop and restart key processes using hPanel:

If you use VPS hosting, you have complete control over restarting your entire server or individual services. To reboot your VPS via hPanel:
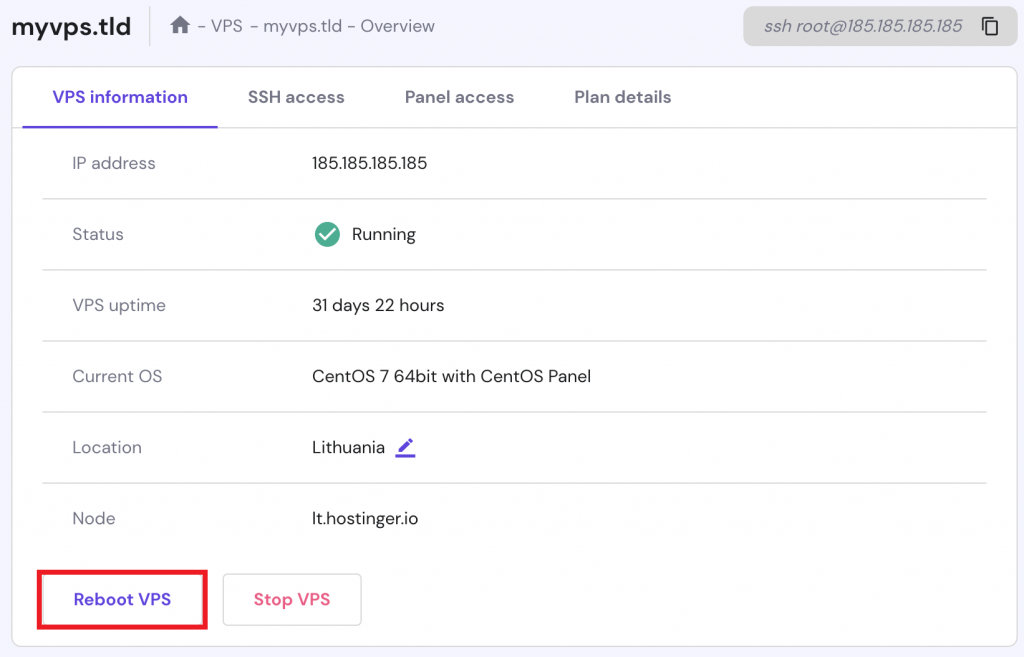
If you prefer restarting your server via the command-line interface (CLI), open your terminal and run the command below:
sudo reboot
Besides rebooting the entire server, you can also reboot individual services like Apache, NGINX, or MySQL. Use the appropriate command based on the service you want to restart:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl restart mysql
Web application firewalls (WAFs) protect your server from malicious activities. However, misconfigurations or overly strict rules can result in false positives, blocking safe traffic and triggering 503 Service Unavailable errors.
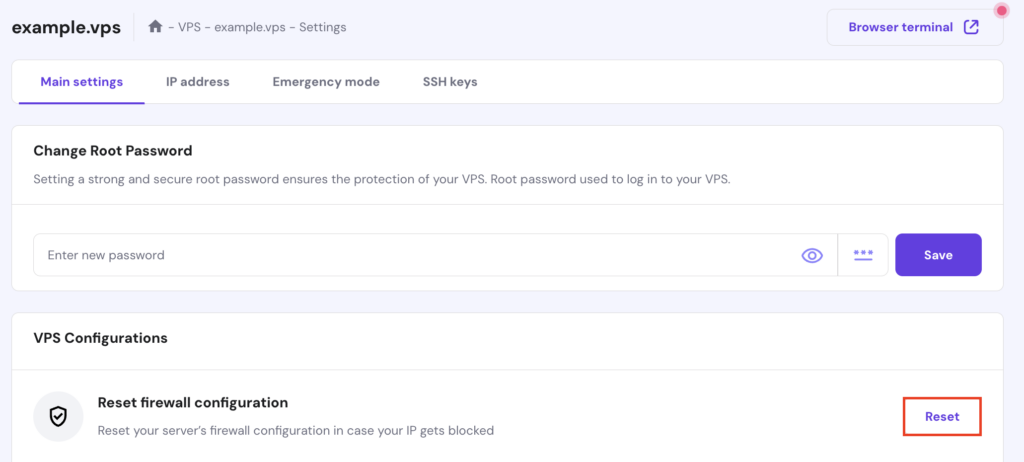
If you suspect your firewall is blocking legitimate requests, reset its configuration to default settings. For Hostinger’s web hosting users, follow these steps:
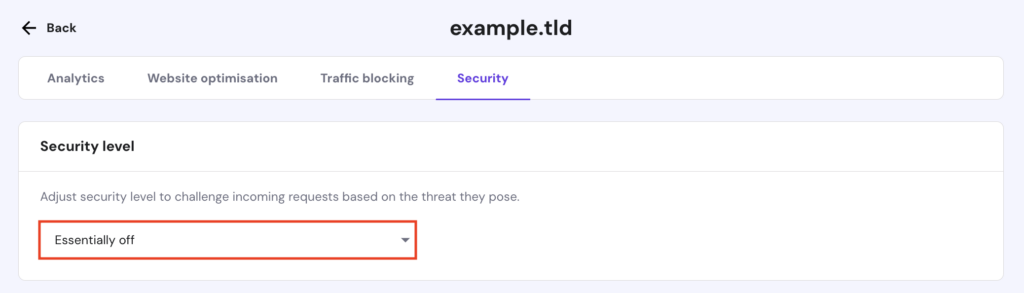
If the error continues, return to the CDN page and deactivate it entirely.
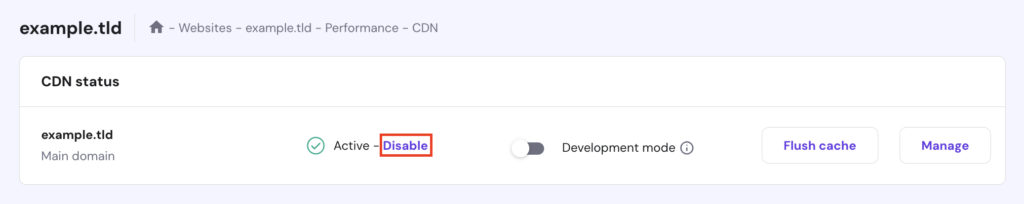
Important! Only disable the firewall temporarily. Don’t forget to re-enable it after identifying the issue to maintain server security.
If you use a firewall from a third-party content delivery network (CDN) service like Cloudflare, visit its dashboard to adjust the settings. If you need help adjusting the firewall to prevent false positives, contact its support team.
On Hostinger’s VPS, you can reset or modify firewall rules using hPanel:
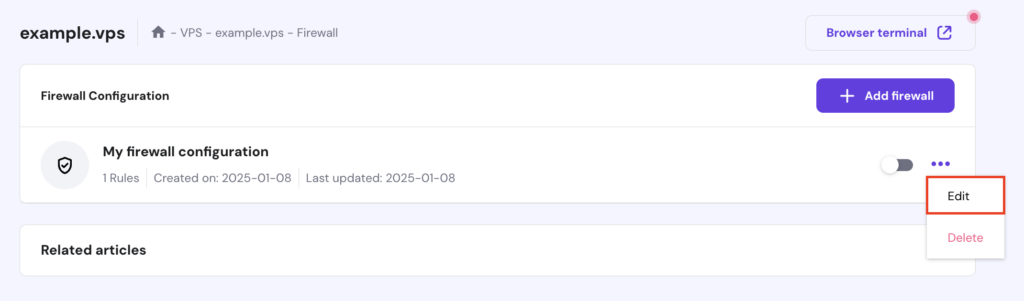
If you use Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW), you can disable or reset it via the terminal:
sudo ufw disable
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw reset
The 503 Service Unavailable error can be caused by a misconfiguration or incompatibility after an update, deployment, or code change.
On WordPress, plugins commonly cause 503 errors because they can consume excessive resources or conflict with each other. If the error occurs right after installing a specific plugin, you’ve likely found the culprit. In this case, deactivate or uninstall the problematic plugin completely.
If you’re not sure which plugin is causing the error, consider disabling all of them at once and then check your website. If the error resolves, reactivate the plugins individually to identify the root cause.
Poorly coded WordPress themes can also trigger 503 Service Unavailable. To troubleshoot, switch to a default theme like Twenty Twenty-Five. If this solves the issue, you’ll know for sure that the issue is with your theme.
If the error began after deploying new code, rolling back to a previous stable version can often fix it. Use a version control system like Git to revert recent commits:
Important! Test the rolled-back version in a staging environment to ensure compatibility and stability before deploying it to production.
git reset --hard [commit_hash] git push --force
Learn the most used Git commands to manage your deployments more efficiently.
High traffic can trigger and sustain the 503 error. When too many requests overwhelm a server’s resources, it can lead to downtime, stopping visitors from accessing the desired page.
Addressing traffic-related issues can help resolve the error and prevent it from recurring. Here are some strategies to mitigate the traffic-related problems:
503 Service Unavailable is a common server-side issue that can disrupt your website’s availability and negatively impact user experience. By understanding its causes and applying a structured approach to troubleshooting, you can resolve and prevent the issue from recurring.
Here are six ways to fix the 503 error:
To prevent this error in the future, address traffic-related causes by implementing a CDN, load balancing, and auto-scaling. Additionally, optimize resource-intensive processes like database queries and schedule cron tasks during low-traffic periods to maintain server stability.
We hope this guide has helped you resolve the 503 error code and restore access to your website. If you have further questions or need assistance, feel free to leave them in the comment section below.
No, the 503 Service Unavailable error is usually temporary. It often occurs due to server overload or maintenance. Once the underlying issue is resolved, the error disappears, and the site becomes accessible again.
You can prevent 503 errors by regularly monitoring server resources, implementing load balancing, and using a CDN. Optimizing resource-intensive tasks like database queries, enabling auto-scaling, and scheduling background processes during low-traffic periods can also help.
Other related errors under the 5xx category include 502 Bad Gateway, which indicates communication issues between servers. Another example is 504 Gateway Timeout, which occurs when a server takes too long to respond.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.