Dec 02, 2025
Aris S.
9min Read
PostgreSQL is a popular open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) known for its scalability and efficiency in handling large amounts of data.
Due to its high performance, PostgreSQL is ideal for large enterprise websites or applications. It also supports various data types and programming languages, including PHP and Python.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 22.04 and later. We will also cover the pgAdmin installation process and solutions to common PostgreSQL issues.
PostgreSQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) popular for its performance. Unlike a standard DBMS, it arranges data in a logical structure for more efficient access.
Highly efficient and capable of handling many queries, the database solution is excellent for large enterprises. Moreover, it is free, open-source, and compatible with various data types.
Before proceeding, ensure your virtual private server (VPS) runs Ubuntu 22.04 or later. Otherwise, follow our guide to change the operating system in Hostinger’s VPS.
PostgreSQL installation involves executing Linux commands on your machine. For a local system, run them directly via Terminal, the Linux command prompt.
For a remote machine like VPS, connect using an SSH application or Terminal. Hostinger users can find their remote machine login credentials by navigating to the VPS overview menu in hPanel.
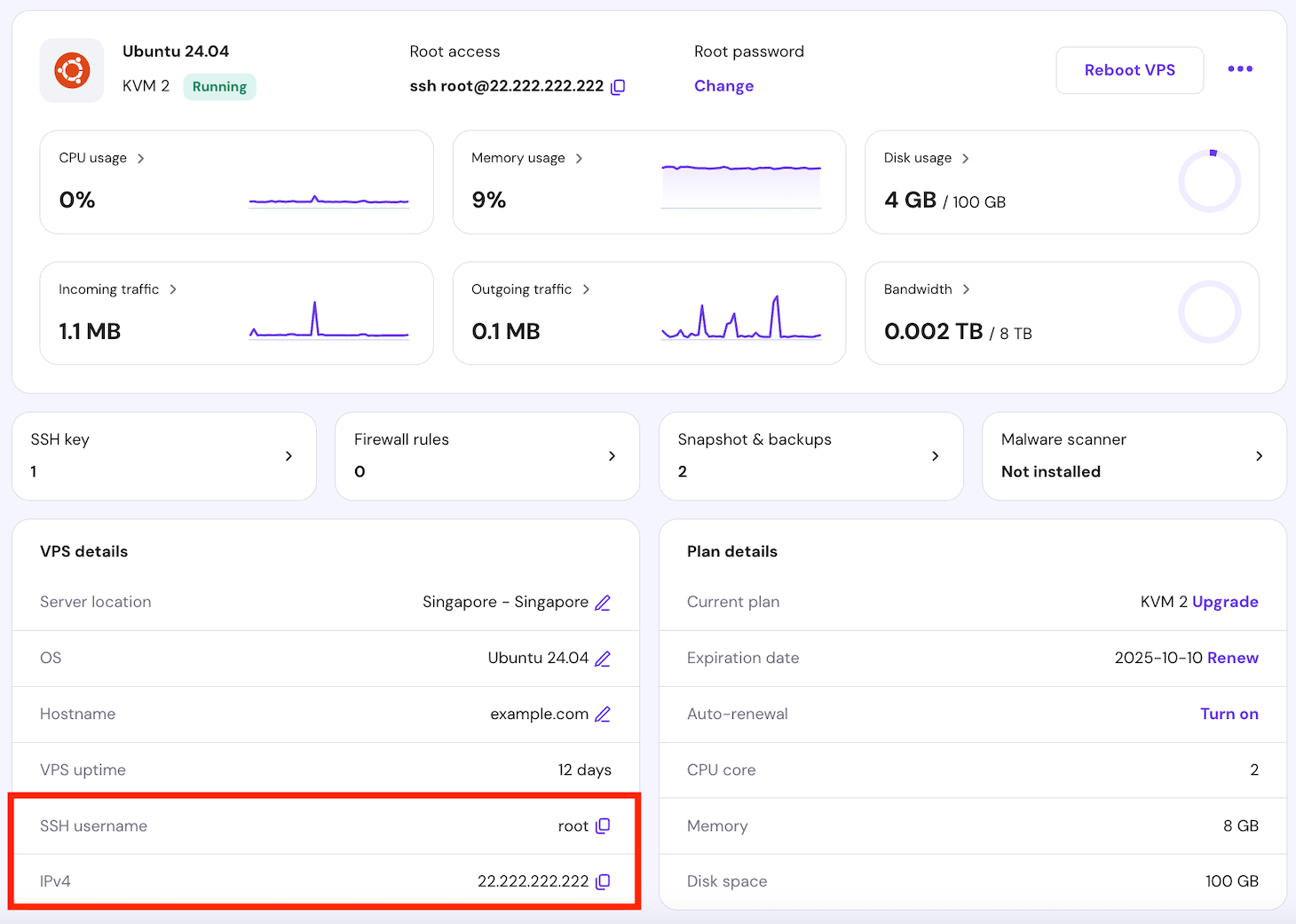
You can install PostgreSQL Ubuntu packages from the local repository or using the APT package manager. We recommend the latter to ensure you get the latest version.
Our VPS also supports other databases. For example, you can install MongoDB if you prefer a NoSQL DBMS.

Option 1 – Installation From APT Repository
The popular method to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu is from the official repository via the APT package manager. Here are the steps to do so:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list' wget --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo gpg -
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get -y install postgresql
sudo -u postgres psql
SELECT version();
To install a specific version, add the number in your command, for example sudo apt-get -y install postgresql-12. In this example, the command will install PostgreSQL version 12.
Option 2 – Installation Using Local Ubuntu Repository
The alternative PostgreSQL installation method uses the local Ubuntu repository. Here are the steps:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt show postgresql
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
sudo -u postgres psql
SELECT version();
The command line should show that the PostgreSQL server version 14.11 is successfully installed, similar to this:
After installing PostgreSQL, check whether it is enabled and active. Use the systemctl or service command utility to verify the service status:
sudo service postgresql status sudo systemctl status postgresql
If PostgreSQL is enabled, your command line will output active and loaded.
For Hostinger users, you can also check whether PostgreSQL is running by asking the Kodee AI assistant. Simply enter, “Check the postgresql service status in my VPS,” and Kodee will output the service status.
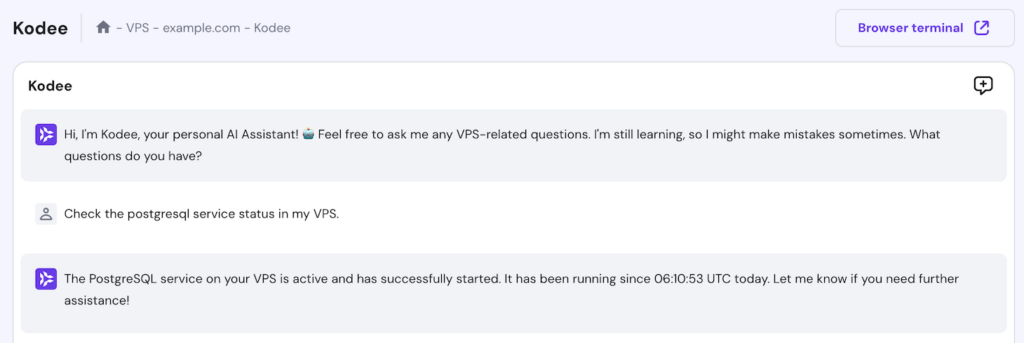
Aside from checking service statuses on your VPS, you can ask Kodee to reset services to their default settings and states.
In addition to the service status, check whether PostgreSQL is ready to accept a connection using this command:
sudo pg_isready
During the installation, PostgreSQL automatically creates the default postgres role for logging in to the database. To switch to this user, run the following command:
sudo su - postgres
Your command line should now begin with postgres. To connect to the PostgreSQL database, use the PostgreSQL shell using the following:
sudo psql
The psql command will create a session in the default database. If the command isn’t found, manually install the PostgreSQL client using this command:
sudo apt-get install postgresql-client
To check the connection status, run this command using the PostgreSQL prompt:
conninfo
To quit the PostgreSQL prompt and return to the regular system user, use the exit command. Meanwhile, use q to detach from the database’s interactive session.
Changing the default postgres role password is essential to improve database security. Here’s how to do it:
sudo -u postgres psql
ALTER USER postgres PASSWORD 'NewPassword';
p
sudo service postgresql restart
To manage database access and ensure proper data organization, you will need multiple PostgreSQL users. The easiest way to create one is to use the interactive mode. Here are the steps:
sudo su - postgres
createuser --interactive
sudo -u postgres psql
du
Important! As a part of security best practices for PostgreSQL, avoid granting the new role a superuser privilege unless necessary.
As shown in the output, the database successfully creates TheNewUser.
PostgreSQL assumes the role and the database will have the same name. Therefore, if you create a TheNewUser role, PostgreSQL will access a database with the same name.
Important! PostgreSQL uses Linux information for authentication. In the previous example, you need a user called TheNewUser.
Here are the PostgreSQL database setup steps:
sudo -u postgres createdb TheNewUser
sudo adduser TheNewUser --force-badname
sudo -u TheNewUser psql
conninfo
The user should now connect to the new database and be able to create a new table. For example, enter the following to create a buyer data table:
CREATE TABLE buyers(usr_id INT PRIMARY KEY, usr_name VARCHAR(240) NOT NULL, usr_location VARCHAR(240) NOT NULL);
When creating a database table, consider the six PostgreSQL constraints:
To add values to your table, use the following statement. Don’t forget to replace the placeholders with the appropriate value and adjust the number of rows accordingly:
INSERT INTO tablename (column1, column2, column3) VALUES (row1, row2, row3);
To show the table, enter the following statement:
SELECT * FROM tablename
Configure your PostgreSQL server to allow other systems to access the database remotely. To do so, let the server listen to all IP addresses by editing the configuration file.
Before proceeding, use the exit command to quit the PostgreSQL shell and return as the regular system user. Then, follow these steps:
vim /etc/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.conf
listen_addresses = '*'
vim /etc/postgresql/14/main/pg_hba.conf
connection database user ip_address encryption
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
After configuring the database, set up remote access to PostgreSQL using the psql command. To do so, use this command syntax in the client machine:
psql -h ip_address -p port -d database -U username
For example, run this command to connect to the TheNewUser database hosted in a VPS with the 185.185.185.185 IP address using the TheNewUser account:
psql -h 185.185.185.185 -p 5432 -d TheNewUser -U TheNewUser
Remember that the default PostgreSQL port is 5423. To verify if the connection is successful, run this command:
conninfo
Once connected, you can send database queries to retrieve data. To enable PostgreSQL remote access in your application, install a database driver and import the module into your code.
For this tutorial, we will show you how to do so in a Python application hosted in an Ubuntu 22.04 VPS. After connecting via SSH, follow these steps:
sudo apt-get install python-pip
pip install psycopg2-binary
import psycopg2
# Connect your app to the remote database.
conn = psycopg2.connect(host="182.182.182.182", port="5432", dbname="TestNewUser", user="TestNewUser", password="UserPassword")
# Open a cursor for database operations
cur = conn.cursor()
# Execute a query. Replace table with your own.
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM table")
# Retrieve data
records = cur.fetchall()Install the pgAdmin web-based GUI to simplify your PostgreSQL database management tasks. We will use the APT package manager to install it:
curl -fsSL https://www.pgadmin.org/static/packages_pgadmin_org.pub | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/pgadmin.gpg sudo sh -c 'echo "deb https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/$(lsb_release -cs) pgadmin4 main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgadmin4.list'
sudo apt update
sudo apt install pgadmin4
sudo /usr/pgadmin4/bin/setup-web.sh
To access the pgAdmin web-based interface, enter the following in your web browser’s address bar:
185.185.185.185/pgadmin4
Replace the IP address with your VPS’. Then, enter your email address and password. Click Login to enter the main pgAdmin dashboard.
To connect PostgreSQL, select Add New Server and proceed with the configuration process.
In this section, we will explore common issues regarding PostgreSQL installation and their solutions.
First, you should check whether the client system is properly connected to the internet. If the internet connection isn’t the issue, other common causes for this error include an inactive database or misconfigured file permission.
Check PostgreSQL status and ensure it is loaded and active. Otherwise, restart it using the following command:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql
If that doesn’t work, check whether the PostgreSQL directory and files permissions are set to 0700 and 0600. To do so, use the following command:
ls /var/lib/postgresql/main
Then, use the chmod command to change their permissions.
A misconfigured connection policy may cause remote host issues that prevent you from accessing the PostgreSQL server. To solve it, open your pg_hba.conf file and add the access policy from every client’s IP address:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
Then, check the listen_address value in your postgres.conf configuration file. Ensure it has an asterisk to ensure PostgreSQL can listen to all IP addresses.
If that doesn’t work, check if your firewall closes the PostgreSQL listening port. For Ubuntu server, run the ufw command:
sudo ufw status verbose
If the connection from and to port 5432 is disabled, open it using the following command:
sudo ufw allow 5432/tcp
Check out our other article to learn how to configure Ubuntu firewall using Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW).
pgAdmin login issues may occur due to a database connection error. If it is network-related, try the previous solutions and reinstall pgAdmin.
If the problem is related to the user account login credentials, enter the psql session and reset the password using this statement:
ALTER USER username WITH PASSWORD 'new_password';
You may also encounter login issues if the user doesn’t have the LOGIN privilege. To grant one, use the following statement:
ALTER USER username WITH LOGIN;
Version conflicts occur when PostgreSQL is incompatible with the database or other applications. Its common cause includes not updating PostgreSQL, resulting in a version mismatch.
To solve it, reinstall or update PostgreSQL from the APT official repository. Also, update all third-party applications since they may be outdated.
We recommend testing the newest version in a development environment to avoid further issues in the live server.
An incorrect command syntax often triggers PostgreSQL user and database creation errors. To fix it, ensure your command ends with a semicolon (;).
Also, you must run the command using the postgres user and the psql command line. To do so, run this command:
sudo -u postgres psql
If your Terminal shows the following, you should be able to create a user and database.
postgres=#
How to Set Up a VPS
What is a VPS
how to install PostgreSQL on CentOS7
PostgreSQL is an open-source, community-driven database management system. It uses a logical structure to efficiently store large amounts of data and simplify access.
In this relational database management system tutorial, we have explained the steps to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 22.04 via the Linux command prompt. Here is the recap:
To avoid issues, ensure the connection policies and pgAdmin login credentials are set correctly. Moreover, install the latest version of the RDBMS via APT to avoid incompatibility issues.
In this section, we will answer several commonly asked questions about installing PostgreSQL on an Ubuntu server.
On Ubuntu, the main PostgreSQL server files are in the /usr/lib/postgresql/<version/bin/postgres directory. All database clusters are stored in /var/lib/postgresql/main directory. Meanwhile, the PostgreSQL settings are in the /etc/postgresql/main/postgresql.conf file.
The easiest way to check if PostgreSQL is installed on an Ubuntu server is to run sudo -u postgres psql or which psql. Terminal should output the installation path if it is installed.
PostgreSQL 14 has an improved connection scaling. It makes PostgreSQL 14 more suitable for large enterprises with many database connections. We recommend sticking to the newest version for the latest features, improvements, and patches.