Dec 02, 2025
Andzelika D. & Valentinas C.
5min Read
Django is a high-level Python web framework that promotes rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. It simplifies many web development tasks, so you can focus on building your application without reinventing the wheel.
In this tutorial, we’ll guide you through two methods to install Django on your virtual private server (VPS): using the Hostinger template for a quick setup and manually for more control over your environment.
By the end, you’ll have Django running in a virtual environment, ready for development.
Before installing Django, it’s important to be familiar with a few key concepts:
Check out Python real-life use cases and learning tips in our article.
Hostinger makes it easy to set up Django on your VPS using a dedicated template. This method simplifies the installation process, letting you avoid command-line setup while providing a stable and optimized environment for your Django application.
To start, consider your project’s needs:
For a basic Django project, our Django VPS lower-tier plans, like KVM 1 or KVM 2, will suffice. As your project grows, you can easily scale up to a higher-tier plan.
After selecting your desired plan, set up the framework by choosing the OpenLiteSpeed and Django (built on Ubuntu 24.04) template during the onboarding process.
If you use our regular VPS plan or have previously installed a different template, follow these steps instead:
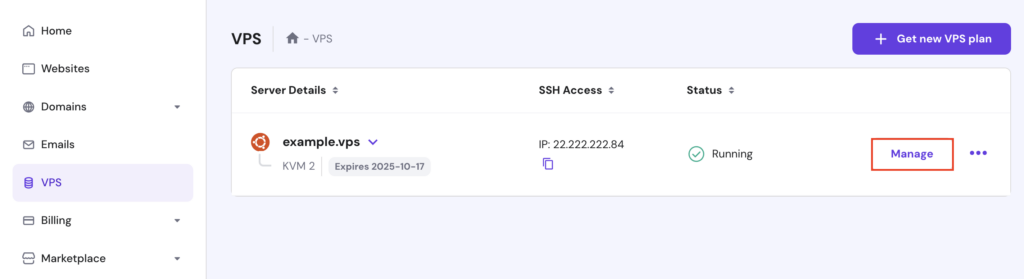
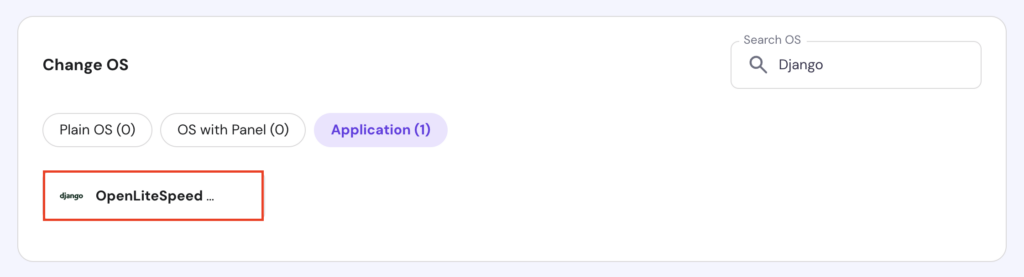
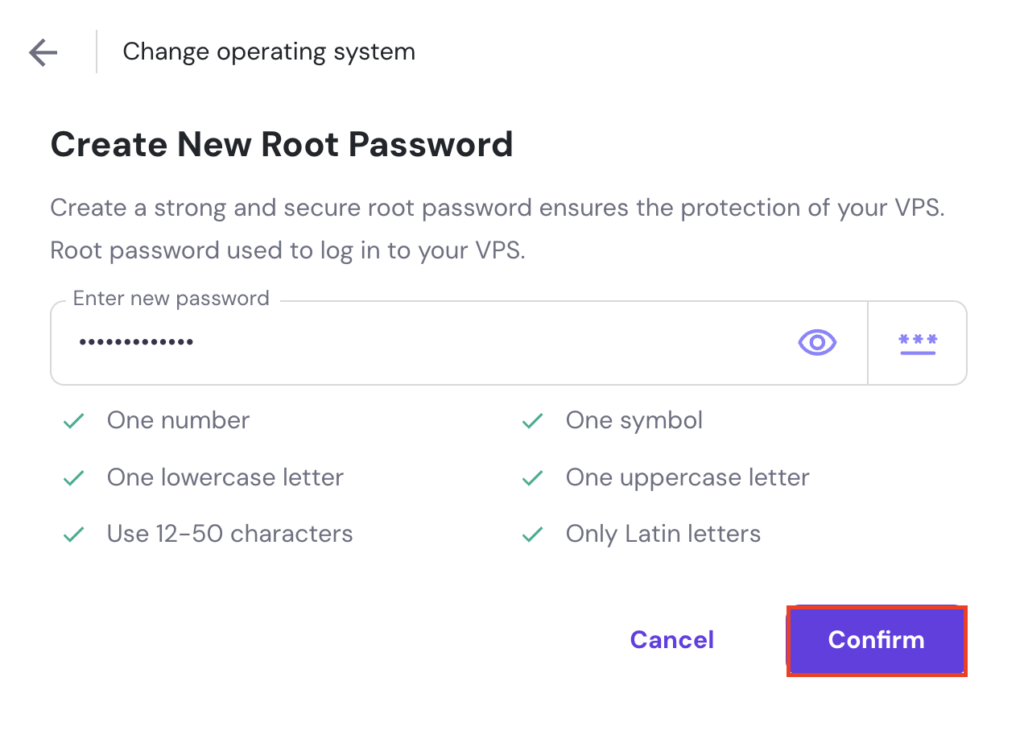
Once done, you’ll have a fully-configured server running Ubuntu 24.04 with Django and the OpenLiteSpeed web server.
You can change your server’s password later if needed, either via the Settings menu or by using Kodee, our AI assistant. Using Kodee is simpler – just type a prompt asking it to change your password and include the new one. For example: “Please change my server password to MyNewSecurePassword123.”

If you prefer using a different operating system, web server, or need more flexibility in setting up Django, you can manually install it using commands. Follow these steps:
To manually install Django, you first need to connect to your VPS using a terminal or an SSH client like PuTTY. Here are the instructions:
ssh root@your_vps_ip
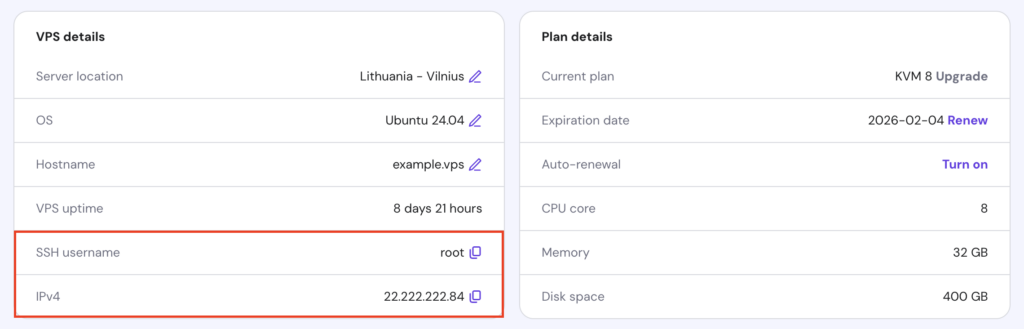
For Hostinger VPS customers, you can find your server’s IP and root login credentials by navigating to the VPS details section in your VPS dashboard.
If you don’t want to use external software, Hostinger users can also access their server via the Browser terminal feature. Simply hit the button in the top right corner of your VPS dashboard to log in automatically.
apt update && apt upgrade -y
After updating, your VPS will be ready to install Python and other required dependencies for Django development.
To run Django, you’ll need to install Python and pip on your VPS. Most modern Linux distributions, like Ubuntu, come with Python pre-installed.
Here’s how to verify if Python is installed and to install or update it if necessary:
python3 --version

sudo apt update sudo apt install python3 python3-pip -y
After that, you’re ready to set up a virtual environment for your Django project.
A virtual environment is an isolated space where you can install Python packages and dependencies for a specific project. This method doesn’t affect the system-wide Python environment or other projects.
Using a virtual environment is especially important when working with Django, as different projects may require different versions of packages. It ensures that each project’s dependencies are neatly contained and don’t conflict with others.
Follow these steps to set up a virtual environment on your VPS:
sudo apt install python3-venv -y
mkdir myproject cd myproject
python3 -m venv env_name
source env_name/bin/activate
Once activated, your shell prompt will change to reflect the virtual environment name, indicating you’re working within it.
The last step is to install Django itself. You can do it by following these steps:
pip install django
This will download and install Django and all its dependencies within the virtual environment.
django-admin --version
You should see an output showing the current Django version, indicating that installation was successful.

That’s it! Now you can start building your Django application.
In this guide, we’ve covered installing Django on your VPS using Hostinger’s pre-configured template and through manual installation.
The former simplifies the process with just a few clicks, perfect for users who prefer easy setup. In contrast, the latter offers greater flexibility, especially if you use a different OS or need more control over your configuration.
With either approach, you now have a clean, isolated environment to efficiently build your Django application.
Yes, Python is required to install Django. To install the latest version of Python and pip, run the following command: sudo apt install python3 python3-pip -y
Django supports older Python versions, but we suggest installing a newer version for better features, support, and performance. Python 3.8 or higher is ideal for compatibility with the latest Django features.
Run the django-admin –version command in your terminal. If Django is successfully installed, you will see the version number. If you see an error message, Django is not installed.