Jan 28, 2026
Larassatti D.
7min Read
Moltbot is an open-source, self-hosted AI assistant that runs on an infrastructure you control rather than as a managed cloud service. It can be deployed on your local computer, a virtual private server (VPS), or dedicated hardware, such as a Raspberry Pi.
This self-hosted approach is central to Moltbot’s value, particularly if you prefer an AI assistant that can interact directly with your own files, processes, and operating environment while maintaining control over where your data resides.
Moltbot functions as a proactive AI agent with messaging-based control, conversational memory, and real task execution capabilities. You interact through chat-style interfaces while Moltbot interprets intent, recalls context, and carries out actions on your system, acting as a personal productivity and automation layer.
The project began in late 2025 as Clawdbot, created by Peter Steinberger. After launching publicly on January 26, 2026, it became one of the fastest-growing repositories on GitHub, surpassing 60,000 stars within three days.
The project was soon renamed Moltbot due to trademark concerns from Anthropic over the similarity between the Clawd mascot and Claude AI. It gained widespread attention by combining open-source transparency with practical execution capabilities as interest in agent-based and self-hosted AI systems accelerated.
Moltbot is best understood as a proactive AI assistant – it doesn’t simply wait for commands and respond to prompts. Instead, it runs continuously in the background, tracking tasks, monitoring conditions, and following up on work without requiring constant user input.
It has several distinct characteristics:
Together, these characteristics position Moltbot as a proactive AI automation assistant that handles routine work autonomously. It manages tasks, coordinates workflows, and automates everyday operations without constant supervision.
Moltbot interprets natural language and acts autonomously through conversation, while n8n executes predefined, trigger-based workflows built through visual logic.
Moltbot is an AI workflow automation tool that runs continuously and responds to natural-language instructions via chat apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, or Slack. It can act on your behalf, remember context, and execute tasks autonomously.
Meanwhile, n8n is a visual workflow automation tool. It lets you connect apps and services with a node-based editor and build automated processes that trigger based on events like receiving an email, a webhook firing, or a schedule.
See the table below for a quick comparison of Moltbot and n8n.
| Feature | Moltbot | n8n |
| Primary interface | Conversational (natural language chat) | Visual workflow builder |
| Execution logic | Autonomous agent decides how to act | Predefined steps executed in order |
| Memory | Remembers context over time | Stateless per workflow run |
| Use case | Ad-hoc, personal task interpretation | Structured, repeated process automation |
| Trigger | Natural language or ongoing context | Scheduled time, API, webhook triggers |
While both Moltbot and n8n enable automations, they solve different problems, so you can even use both together. For instance, you can use Moltbot to decide what needs to happen based on a chat interaction, then trigger an n8n workflow to execute the automation behind the scenes.
But, if you want to choose only one tool, Moltbot is great for:
Alternatively, choose n8n when you need:
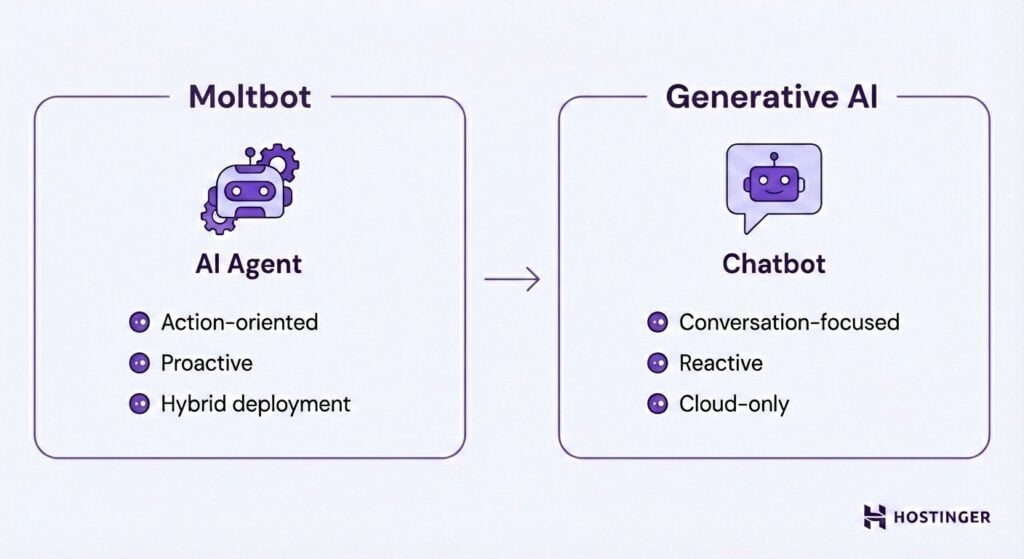
Execution capability is a fundamental architectural difference between Moltbot and ChatGPT and other large language models (LLMs).
Traditional cloud chatbots generate conversational responses and provide guidance, but they don’t execute tasks directly. Moltbot, by contrast, is built as an AI agent that interprets natural-language instructions and carries out tasks rather than simply describing how to accomplish them.
Moltbot is also proactive rather than reactive. While most generative AI tools only respond when prompted, Moltbot can initiate messages, send reminders, and continue tasks over time without repeated instructions.
Additionally, from a deployment standpoint, Moltbot offers greater flexibility than cloud-only assistants.
You can run it on your own hardware (Mac, PC, or Raspberry Pi) for maximum privacy and control, or deploy it on a VPS for 24/7 availability.
You can also choose which AI models to use, including Anthropic’s Claude and OpenAI’s ChatGPT. This self-hosted approach contrasts with third-party services, which rely entirely on the provider’s remote infrastructure.
Moltbot operates as a self-hosted AI agent controlled through chat interfaces, combining natural language understanding with real-world task execution.
Instead of interacting through a traditional dashboard, users communicate with Moltbot through familiar messaging platforms, turning everyday chat into a command layer for automation.
You can use popular messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, or Discord as your Moltbot messaging interface, which acts as the entry point for all actions.
Instead of rigid commands or syntax, users describe tasks in natural language, such as asking Moltbot to organize files or check something online.
Moltbot also performs intent detection, translating conversational input into executable actions. This enables true chat-based automation, where instructions feel natural but trigger real operations.
Once a task is received, Moltbot retrieves relevant context from past conversations and stored data. This conversational memory allows the system to remember preferences, ongoing tasks, and prior instructions, maintaining continuity across interactions and enabling more natural long-term collaboration.
Before taking action, Moltbot determines how the task should be completed. It breaks requests into logical steps and selects the most appropriate tools – whether terminal access, file management utilities, or browser automation. This planning phase ensures actions are coherent, efficient, and aligned with the user’s intent.
After planning, Moltbot executes tasks directly on the infrastructure where it’s deployed. This allows it to run terminal commands, manage files, or browse the web within your environment.
Whether deployed on your personal computer or a VPS, actions happen on systems you control rather than within a managed cloud service. This design gives users control over their data and execution environment.
Unlike traditional chatbots that only respond when prompted, Moltbot can initiate communication on its own. It sends notifications, confirmations, and reminders as tasks progress or conditions change. These follow-ups keep users informed without requiring check-ins, reinforcing Moltbot’s role as an autonomous agent rather than a passive conversational tool.
Moltbot can handle a wide range of AI task automation use cases, especially those that benefit from autonomy and continuity.
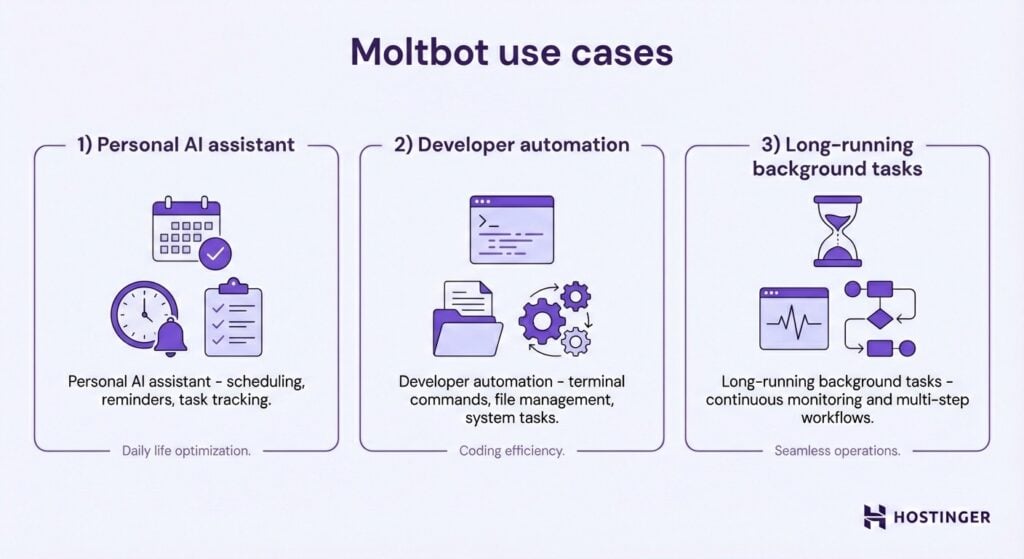
To enhance productivity, it can act as an AI personal assistant, helping with scheduling, reminders, research, note-taking, and ongoing task tracking.
Instead of one-off responses, Moltbot can remember objectives, follow up on incomplete work, and manage tasks in the background while you focus on other things.
In addition, Moltbot supports developer automation and system-level workflows.
It can run terminal commands, manage files, monitor processes, and automate repetitive system tasks directly where it’s deployed. This way, developers can offload manual, routine work such as environment setup, log checks, and scripted maintenance.
Moltbot is also well-suited for long-running background tasks. It can monitor conditions, wait for events, or continue multi-step workflows over time without needing constant input. Tasks can span hours or days, with the agent providing updates, confirmations, or reminders as needed.
Moltbot’s security model is tied to its self-hosted design. You can run Moltbot entirely on your personal hardware, deploy it on a private VPS, or selectively enable cloud-based model APIs when stronger reasoning is needed.
By running on infrastructure you control, you keep data, execution, and system access under your management rather than relying on third-party services. This approach offers privacy benefits, but it also means security depends heavily on how you configure and maintain your deployment.
Granting an AI agent permission to run commands, manage files, or control system processes introduces significant security considerations.
In January 2026, security researchers identified serious vulnerabilities in misconfigured Moltbot instances. Their findings revealed both configuration issues and risks inherent to agentic AI systems.
While these vulnerabilities stemmed partly from improper deployment practices, they highlight the real security challenges of running autonomous AI agents with system access.
To mitigate these risks, follow these security best practices before running a Moltbot instance:
➡️ You can read the detailed security guidance in the Moltbot documentation. Make sure to review it thoroughly before deployment.
Self-hosting an AI assistant shifts both control and responsibility to you. Unlike managed cloud services that handle security through provider defaults, Moltbot gives you the freedom to shape your own environment – along with the obligation to secure it properly.
Moltbot is beneficial for developers and technical users who are comfortable working with system tools, automation, and self-hosted software. Its flexibility, autonomy, and deep system integration make it a powerful option among other AI automation tools.
If you enjoy customizing workflows, running scripts, or building systems that operate continuously in the background, Moltbot offers advanced features that you won’t find in basic generative AI tools.
However, Moltbot isn’t a fully managed, plug-and-play tool. It requires initial technical setup, including self-hosting and basic configuration.
Important! Before using Moltbot, make sure you’re comfortable with:
– Command-line interfaces and terminal operations
– Server security and network configuration
– Understanding and mitigating prompt injection attacks
– Troubleshooting system-level issues
– Regular security auditing and updates
Due to documented security vulnerabilities in misconfigured instances, Moltbot requires genuine technical expertise to deploy safely.
There are two main ways to deploy Moltbot, depending on how much control you want and how hands-on you’d like to be with the setup.
Option 1: Self-managed installation
Running Moltbot on your own hardware provides direct access to local files and system resources without network latency. It supports macOS, Linux, and Windows, so it’s accessible across most modern development environments.
You can install Moltbot on hardware you manage yourself, such as:
This option is recommended if you’re comfortable working with the terminal, installing dependencies, and managing system processes.
Consult Moltbolt’s documentation to find out how you can proceed with any installation that you prefer.
Option 2: VPS-based deployment
If you want Moltbot to run continuously without relying on your own hardware, deploying it on a VPS is a practical option. A VPS keeps Moltbot online 24/7, allows it to handle long-running tasks, and makes it accessible even when your personal computer is offline.
To simplify this setup, Hostinger’s Moltbot hosting lets you install Moltbot via a Docker container (with a one-click installation template) or manually. We also provide a built-in AI assistant in hPanel to guide you through deployment, configuration, and ongoing maintenance, making VPS management simpler.
Follow our step-by-step guide to set up Moltbot on a Hostinger VPS.