Mar 04, 2025
Dominykas J.
8min Read
Mar 04, 2025
Dominykas J.
8min Read
n8n is a workflow automation tool that enables seamless integration between various applications and APIs. The ability to self-host it on an Ubuntu VPS provides better data privacy, customization options, and cost savings compared to managed solutions.
This guide covers two installation methods: Hostinger’s easy one-click setup and a manual installation for users who prefer hands-on control. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a fully functional n8n instance running on your VPS, ready to automate workflows.
Before installing n8n, make sure your hosting environment meets the following requirements:
Minimum: 1 vCPU, 1GB RAM (KVM1)
Recommended: 2 vCPU, 2GB RAM (KVM2)
If you don’t yet have one, Hostinger offers a range of VPS options, including n8n VPS hosting.

Let’s start with the easiest method: using Hostinger’s one-click n8n template. This method automates the Ubuntu server setup and installs n8n and its dependencies.
First, you need to access your VPS dashboard.
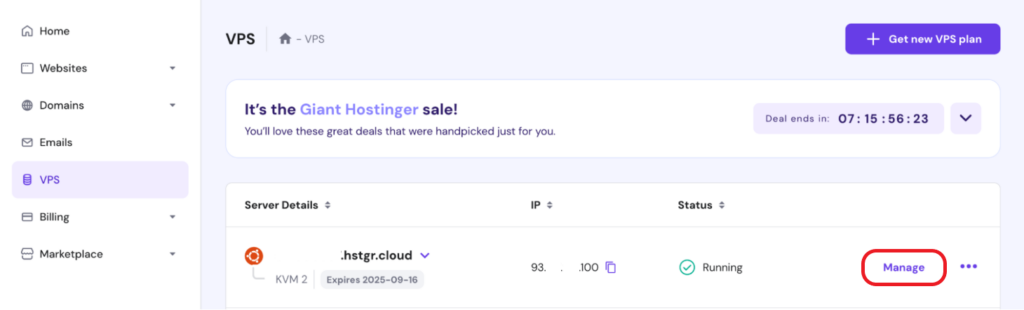
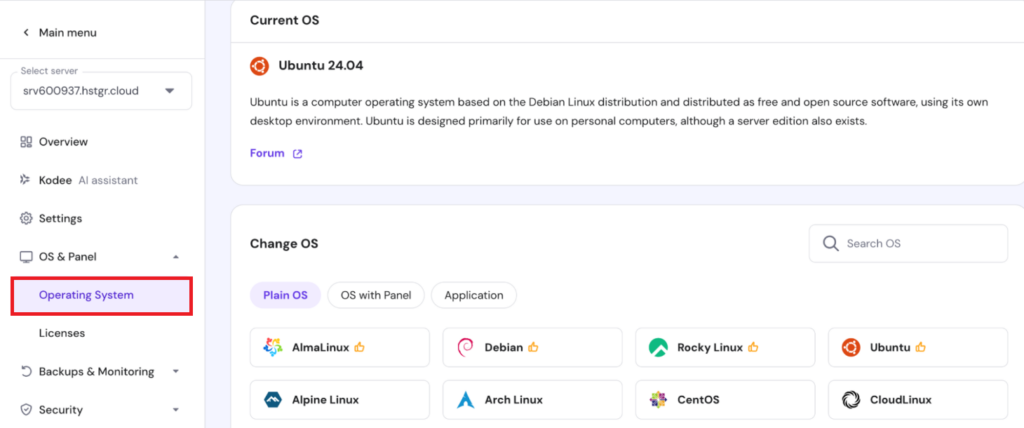
This is where you can find operating systems and their templates available for your VPS server.
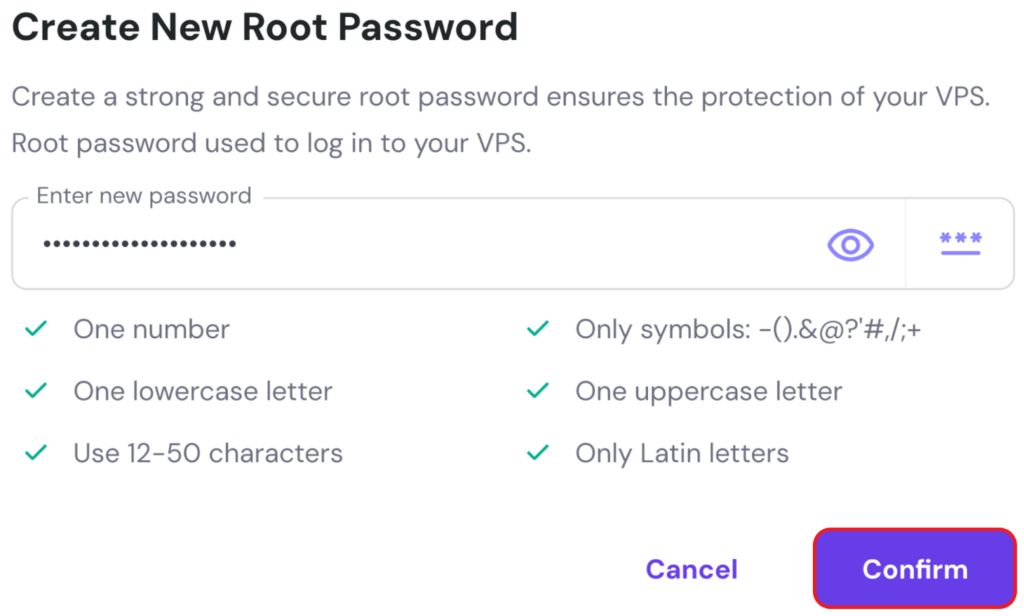
Template setup will begin. You’ll see a progress bar at the top of your dashboard, like in the example below:
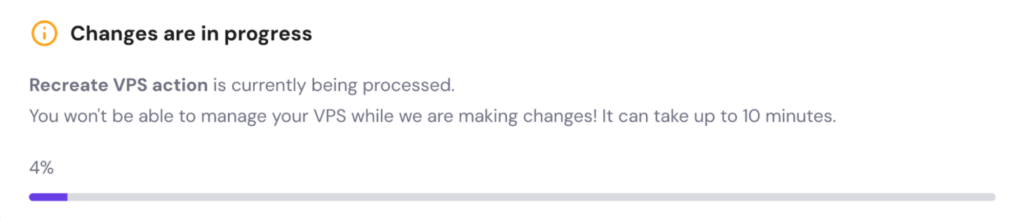
After a short wait, your n8n instance will be ready to use.
With n8n set up on your VPS, you should be able to log in and confirm that it’s working.
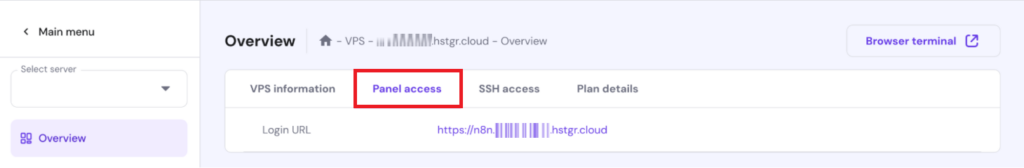
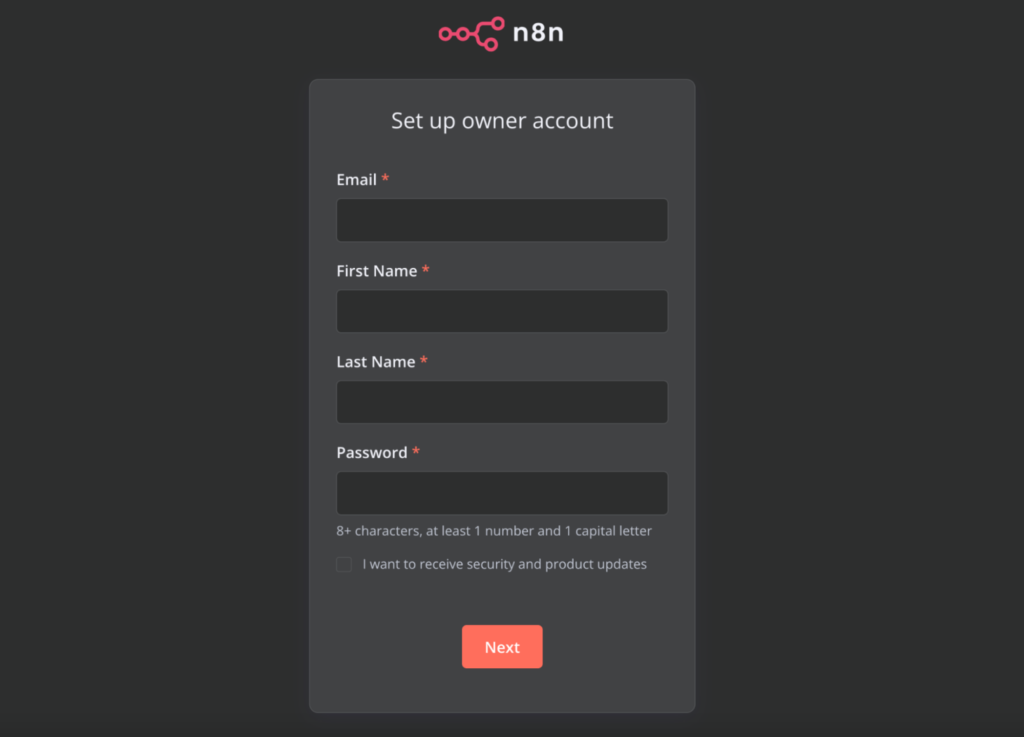
Now that your n8n instance is up and running, let’s fine-tune its settings for security and customization.
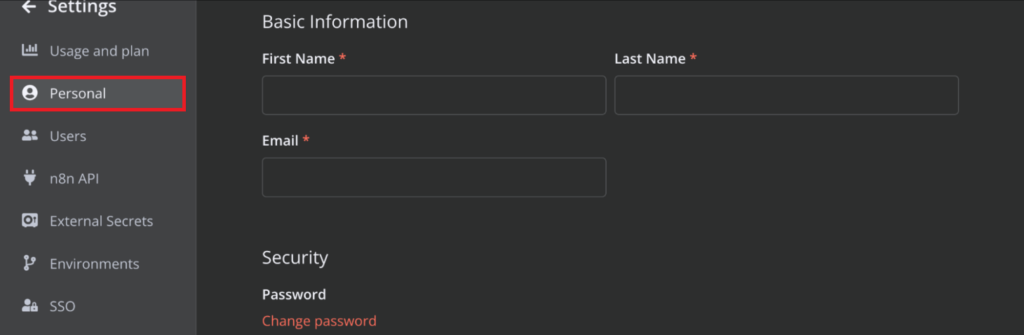
This is where you can see and adjust all of your credentials like First Name, Last Name, Email, and Password.
You can also modify n8n with environment variables:
nano ../root/docker-compose.yml
- N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true - N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=username - N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD="password"
Replace username and password above with the actual username and password of your user.
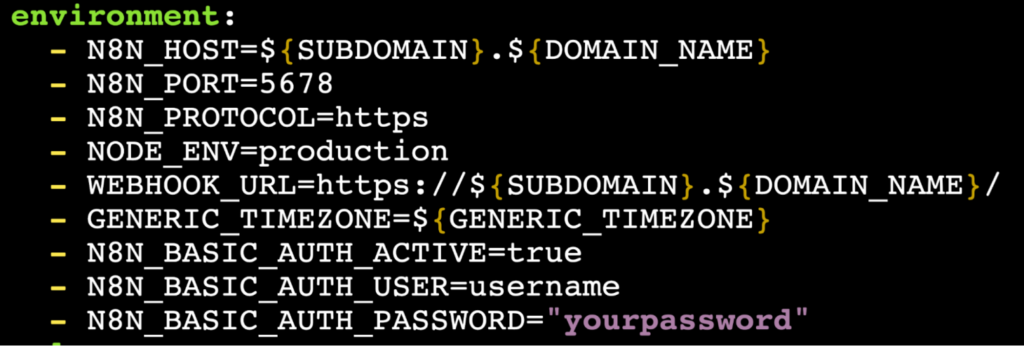
Some other commonly used environment variables you may want to include or adjust:
cat docker-compose.yml
This will return the whole Docker Compose file. You should see your changes there.
docker-compose down docker-compose up -d
After restarting Docker Compose, your changes will be implemented. n8n will then use the environment variables you’ve set.
If you’re using a custom domain, you should also set up SSL. For a secure HTTPS connection, you can use Let’s Encrypt with NGINX as a reverse proxy:
sudo apt install certbot nginx python3-certbot-nginx -y
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n
server {
server_name yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5678;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}Save and close the file with CTRL+X, then Y and ENTER.
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo certbot --nginx -d yourdomain.com
sudo certbot renew
Select nano if prompted to select the editor.
0 2 * * * certbot renew --quiet --post-hook "systemctl restart nginx"
Let’s Encrypt certificates expire every 90 days by default. With this job in place, certbot will renew your certificate automatically when needed.
nano ../root/docker-compose.yml
- WEBHOOK_URL=https://yourdomain.com/ - N8N_HOST=yourdomain.com - N8N_PORT=5678 - N8N_PROTOCOL=https
Save and close the file with CTRL+X, then Y and ENTER.
docker-compose down docker-compose up -d
With this done, your n8n instance can then be accessed securely using your custom domain name (e.g. https://yourdomain.com).
If you’re using a VPS hosting provider without a one-click n8n template, you’ll have to install n8n manually. Let’s walk through the step-by-step process to get it up and running on Ubuntu.
Before setting up n8n manually, we need to install some essential dependencies. Start by connecting to your VPS via SSH or a web-based console. Next, update your package lists and upgrade existing packages to their latest versions by running:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
This ensures that your system has the latest security patches and software versions before proceeding.
There are two main methods of running self-hosted n8n:
Containerized installation is preferred in most scenarios, however we’ll briefly describe both.
Direct installation
n8n can run directly in a Node.js environment, so if you’re not using Docker, install the latest long-term support (LTS) version of Node.js:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
node -v npm -v
These commands will return versions of npm and Node.js if they are installed.
Containerized installation
If you’d prefer to run n8n in a Docker container, install Docker first.
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
docker --version
This command will return the Docker version if it is installed.
Once you have all the dependencies installed, you can set up n8n.
Direct installation
If you installed Node.js earlier, you can install n8n globally using npm:
npm install -g n8n
Start a screen session called n8n:
screen -S n8n
Run n8n inside the screen session:
n8n
To detach from the screen session, type CTRL+A then D. If you want to re-attach to interact with n8n, run:
screen -R n8n
By default, n8n runs on port 5678. You can now access it at:
http://your-server-ip:5678
You might receive a secure cookie error at this point. We will cover SSL certificate creation in later steps.
Containerized installation
Pull the latest n8n Docker image:
docker pull n8nio/n8n
Run the container with port mapping:
docker run -d --name n8n -p 5678:5678 n8nio/n8n
To access n8n in your browser, open:
http://your-server-ip:5678
As with the installation steps above, you might encounter a secure cookie error. Refer to the SSL certificate creation section below.
By default, data inside a Docker container is not persistent. To ensure your workflows and settings are saved, run n8n with a mounted volume:
docker stop n8n && docker rm n8n #stop and remove previous n8n container docker run -d --name n8n -p 5678:5678 -v ~/.n8n:/home/node/.n8n n8nio/n8n
This maps your local ~/.n8n folder to n8n’s data directory inside the container.
If the container does not start, you might lack permissions to write to the volume. Claim permissions by running:
sudo chown -R 1000:1000 ~/.n8n sudo chmod -R 755 ~/.n8n
Then start the container:
docker start n8n
By default, n8n doesn’t enforce authentication, so anyone who accesses your server’s IP can use it. To secure your instance, set environment variables before running the container.
With direct installation, you can use the export command to add variables. In the example below, be sure to replace username, password, and yourdomain.com with your chosen credentials:
export N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true export N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=username export N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=password export N8N_HOST=yourdomain.com export N8N_PORT=5678 export WEBHOOK_URL=https://yourdomain.com/ export GENERIC_TIMEZONE=UTC
When running n8n as a Docker container (containerized installation), you can pass these variables using the -e flag (again, add your own credentials below):
docker stop n8n && docker rm n8n #stop and remove previous n8n container docker run -d --name n8n \ -p 5678:5678 \ -e N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true \ -e N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=username \ -e N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=password \ -e N8N_HOST=yourdomain.com \ -e N8N_PORT=5678 \ -e WEBHOOK_URL=https://yourdomain.com/ \ -e GENERIC_TIMEZONE=UTC \ -v ~/.n8n:/home/node/.n8n \ n8nio/n8n
To protect your n8n instance and ensure encrypted connections, we’ll set up SSL (HTTPS) using Let’s Encrypt and NGINX as a reverse proxy. This is especially important if you’re using a custom domain.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nginx certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
sudo systemctl enable nginx sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n
server {
server_name yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5678; # Forward requests to n8n
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
listen 80;
}Then, save and exit by typing CTRL+X, then Y, then ENTER.
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo certbot --nginx -d yourdomain.com
sudo certbot renew
Select nano if prompted to select the editor.
0 2 * * * certbot renew --quiet --post-hook "systemctl restart nginx"
Let’s Encrypt certificates expire every 90 days by default. With this job in place, Certbot will renew your certificate automatically.
To confirm that n8n is running with HTTPS, open your browser and enter your domain name in the format https://yourdomain.com. If you see the n8n interface without any SSL warnings, your setup was successful and n8n is now ready to use!
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed and are now self-hosting n8n on your own server. Whether you used Hostinger’s one-click setup or installed n8n manually, you now have a powerful workflow automation tool at your fingertips.
Now it’s time to start building workflows and automating tasks! From simple n8n integrations to complex business processes, n8n gives you the flexibility to connect apps, APIs, and databases without writing tons of code. You can explore various n8n automation ideas that streamline workflows and simplify everyday tasks
Remember these key points:
If you run into any issues or want to explore advanced configurations, check out the n8n documentation or join the n8n community for support.
Yes, you can run n8n locally by installing it globally using npm with the command npm install n8n -g. After installation, start n8n by running n8n or n8n start.
A VPS with 2 vCores and 4GB RAM should be sufficient to get you started, in which case Hostinger’s KVM2 will be more than enough.
After installing n8n locally, you can access its interface by navigating to http://localhost:5678 in your web browser if running locally. If you’re self-hosting on a VPS with a custom domain, use http://yourdomain.com:5678, or https://yourdomain.com if SSL is configured.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.