Nov 28, 2025
Jordana A.
9min Read
Artificial intelligence (AI) has gained significant traction across industries in recent years, transcending theoretical discussions to become a transformative force in global business operations. Yet, quantifying its usage across industries remains a challenge. The question we set out to answer in this article is: how widely do businesses actually use it?
Drawing from proprietary research and authoritative resources, we’ve compiled 25 key statistics on AI usage by industry, region, and function, along with projections for the near future. These insights will help you understand how businesses are using AI today, and how they perceive its role in their operations.
The following statistics offer insights into AI’s role in the business landscape and how many companies operate in the AI space themselves. They’ll give you a better understanding of how popular the technology is in general.
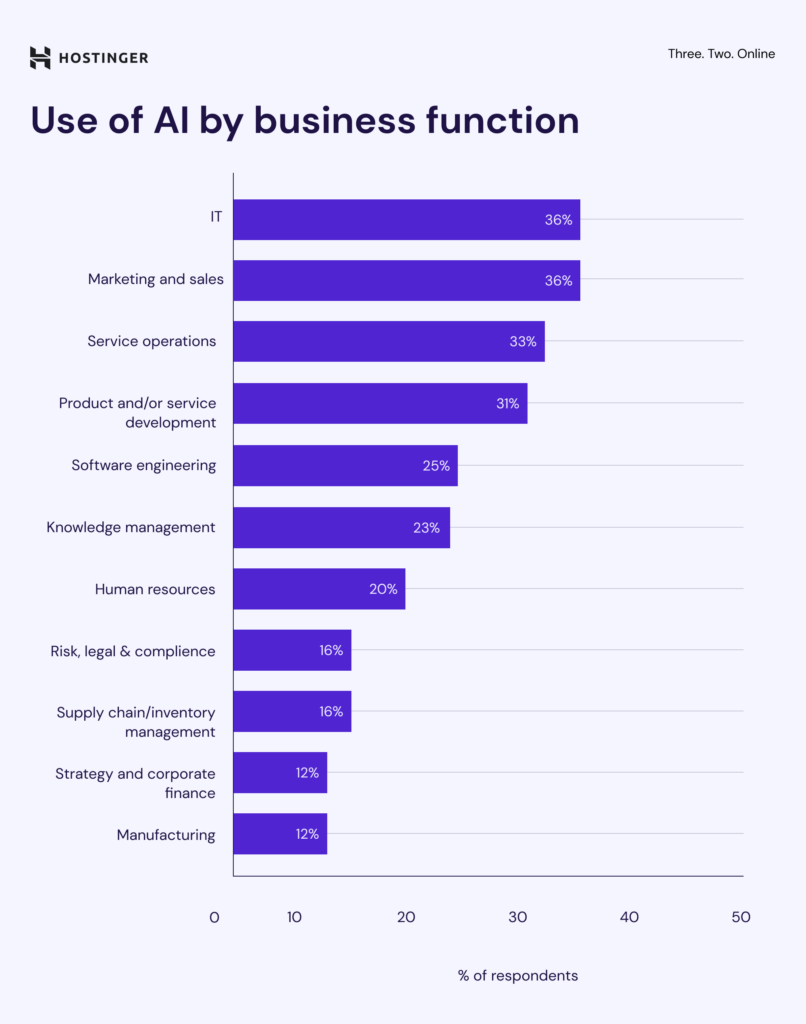
In 2024, 78% of surveyed companies reported using AI in at least one business function ‒ a 55% increase compared to the previous year. The most common areas where companies use AI are information technology (IT), marketing and sales, and service operations.
In 2023, there were about 359 million companies around the world ‒ a 9% jump from 328 million in 2020. This means there are more businesses than people living in the United States alone (347 million people).
By 2024, there were 90,904 companies working in AI, including big names like OpenAI and Google. 37% of them have received Series A funding, and 9% have reached Series A ‒ the first major investment round to grow a business after proving product-market fit.
The United States leads with 29,618 AI companies, followed by India with 8,178 and the United Kingdom with 6,270.
Overall, the AI sector has produced around 400 startups valued at over $1 billion (unicorn companies).
Continuing from the previous statistic, 2025 has seen the launch of 305 new AI companies so far. Many of them were founded by alumni from leading institutions like Stanford University, MIT, and Harvard University.
This is a lower number compared to previous years, when the industry launched an average of 7,051 new AI startups yearly. But with half the year left, the total could still grow.
In September 2023, 3.7% of U.S. firms reported using AI to produce goods or services. By February 2024, that number rose to 5.4% ‒ a 46% increase in just five months.
By late 2024, AI use reached 6.6%, confirming earlier projections. This steady growth in adoption shows that more companies are actively integrating AI into their daily operations.
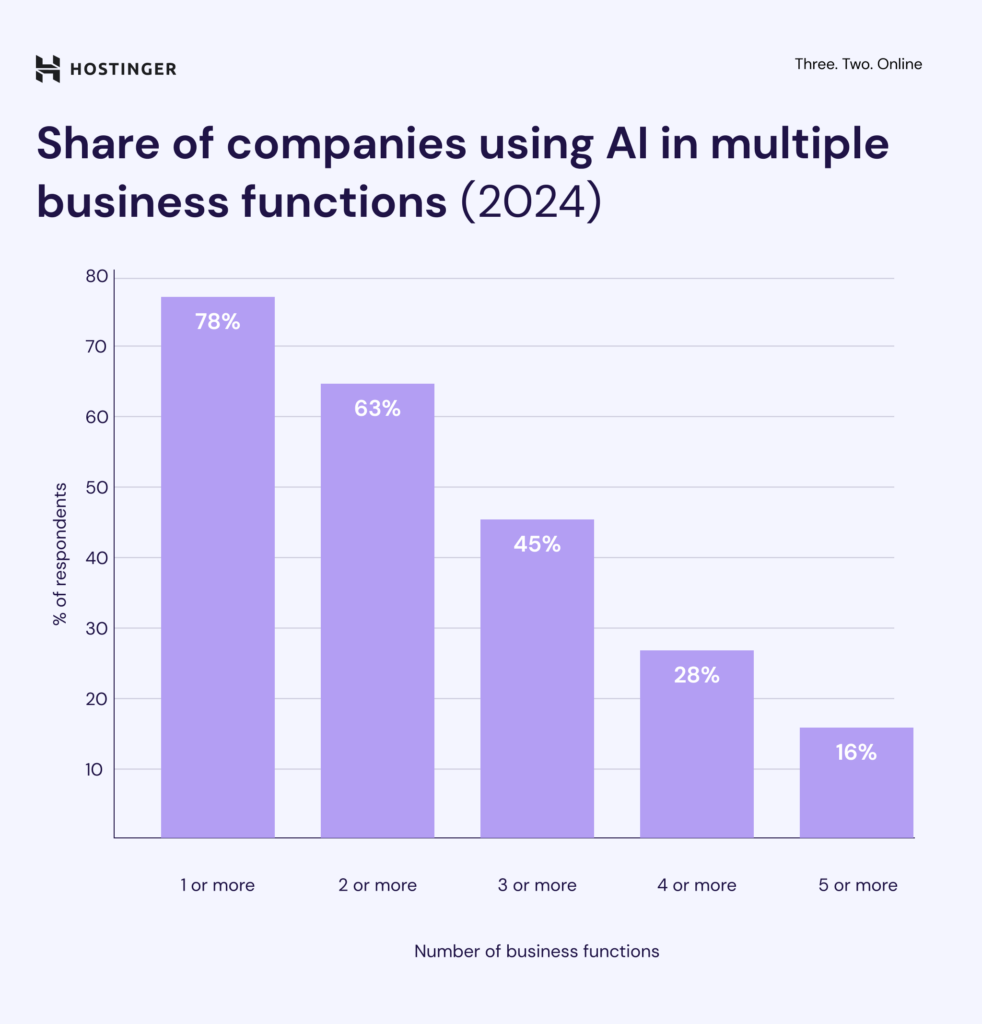
On average, companies now use AI in three different functions, which is a noticeable increase compared to early 2024. As the chart shows, 45% of organizations use AI in three or more business functions, while 63% use it in at least two.
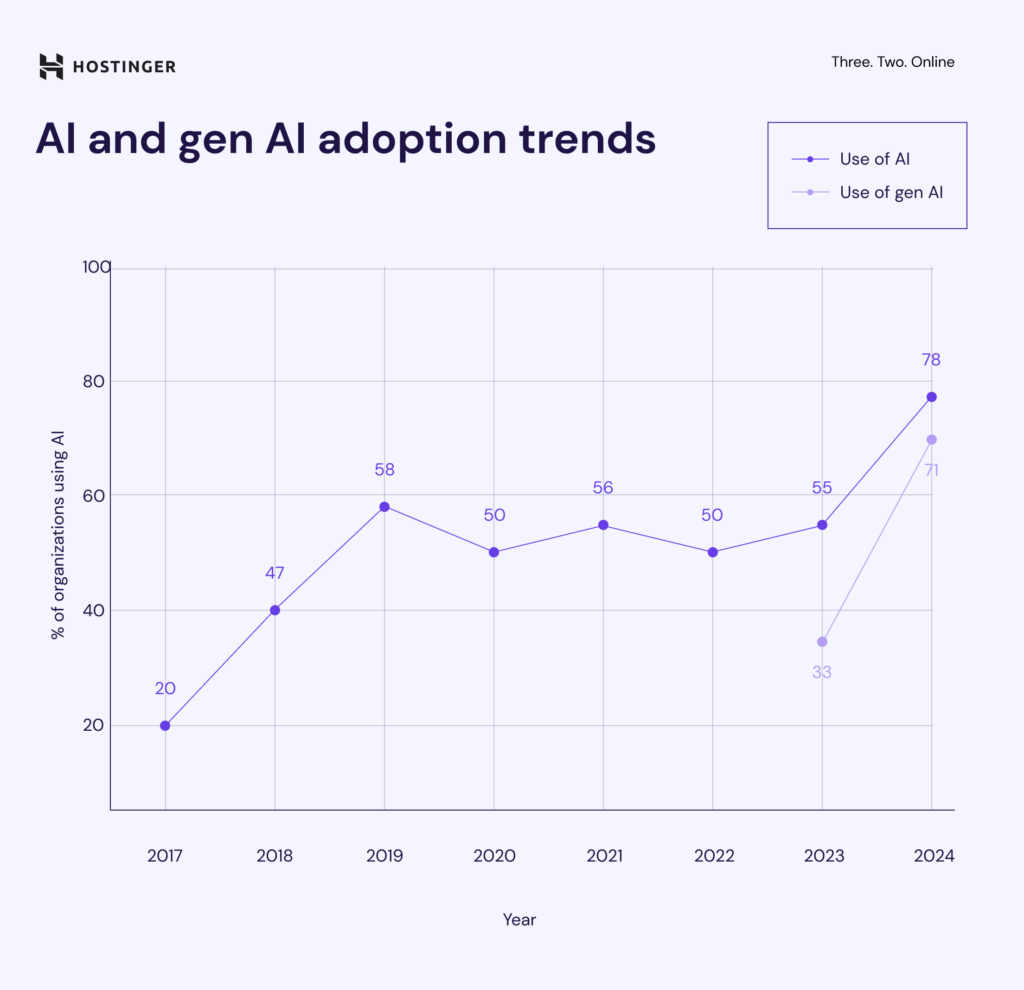
As of late 2024, 71% of organizations report regularly using generative AI (GenAI) in at least one business function. This marks an increase from 33% in 2023.
GenAI follows a similar pattern to overall AI use, with high adoption in IT, marketing and sales, and service operations. Organizations also use it in product development and software engineering, often building on existing AI tools where the impact is strongest.
Company size shapes how businesses use AI. Smaller businesses usually experiment on a smaller scale, while larger enterprises adopt it more broadly, at least in theory. This section compares AI adoption across different business sizes to see how well that holds up.
Unsurprisingly, larger companies lead in adopting and scaling AI, especially generative AI. They are more than twice as likely as smaller businesses to have clear plans in place, including phased rollouts and dedicated teams to manage adoption.
Larger organizations also take more steps to support adoption internally. They invest in role-specific training, run internal campaigns to build momentum, and focus on building customer trust in their use of GenAI.
In contrast, most smaller companies are still early adopters, with fewer practices in place to guide or expand their efforts.
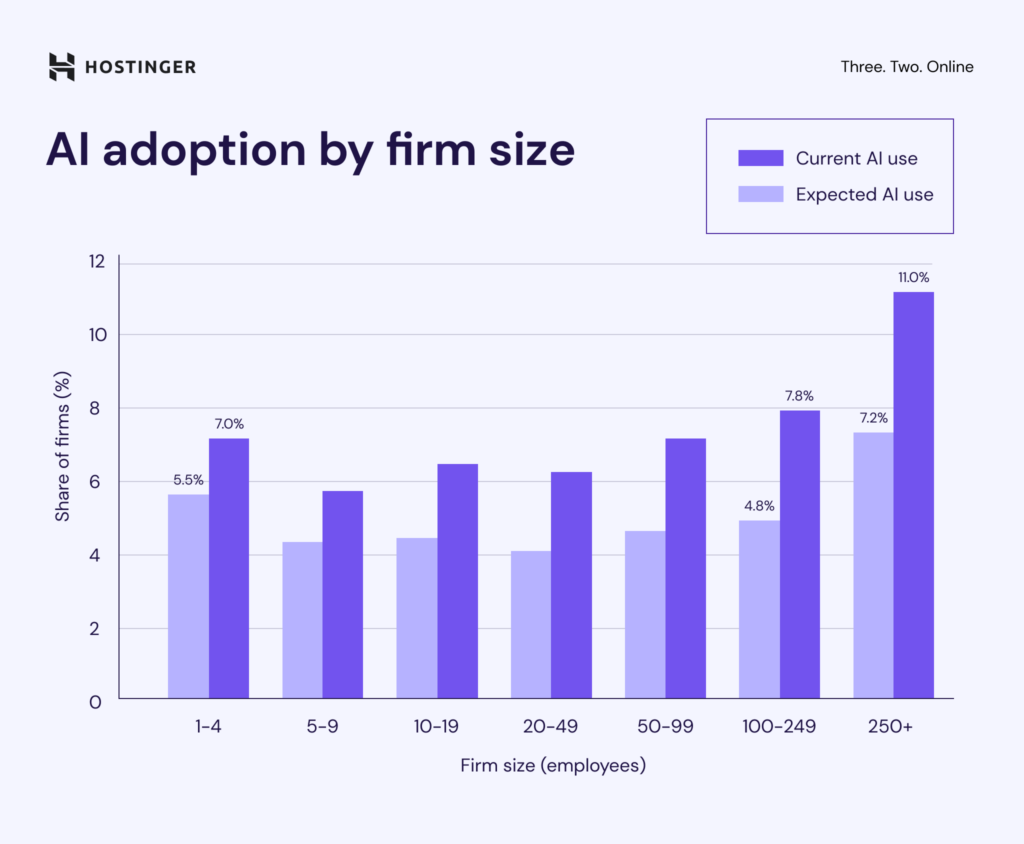
AI adoption varies by company size, but growth is expected across the board. Small businesses with 1-4 employees report a current usage rate of 5.5% and expect it to rise to 7%, which would be a 27% increase.
In comparison, companies with 100-249 employees report a lower starting point at 4.8%, with expectations reaching 7.8%. While this group also anticipates growth, it falls behind the largest firms of 250+ employees, which lead with a current rate of 7.2% and a projected rate of 11%.
Despite growing interest in GenAI, most companies are still early in their adoption journey. In a recent survey across developed markets, only 1% of executives said their GenAI rollout had moved beyond experimentation and included practices with measurable business impact, like clear road maps and dedicated teams.
Around 89% of small businesses use AI tools for everyday tasks like writing emails, creating marketing content, and analyzing data. So far, the impact looks positive ‒ over 60% of small business owners using AI report improvements in employee job satisfaction and productivity.
In businesses with employees, AI adoption is typically driven by owners or managers. While involving workers and not just management can make adoption more effective, this collaborative approach is still rare.
Regional trends, policies, and resources shape how AI adoption varies across the world. This section looks at which regions lead in AI adoption and show the biggest potential for growth.
The U.S. led with $109.1 billion in private AI investment, nearly 12 times more than China’s $9.3 billion and 24 times the United Kingdom’s $4.5 billion. GenAI in particular drew strong interest in 2024, accounting for $33.9 billion in global private investment ‒ up 18.7% from the previous year.
This year, Americans are expected to account for one-third of all new AI users ‒ more than 21 million ‒ bringing the total number of U.S. users to 133 million. That’s 50 million more than the combined total in China, Germany, and Japan, making the U.S. the global leader in AI adoption across business and consumer use.
Looking ahead, projections show the U.S. AI user base will grow by another 107 million by 2030, reaching 241.5 million users. In comparison, China is expected to reach 75 million users, while Germany will have around 52.5 million.
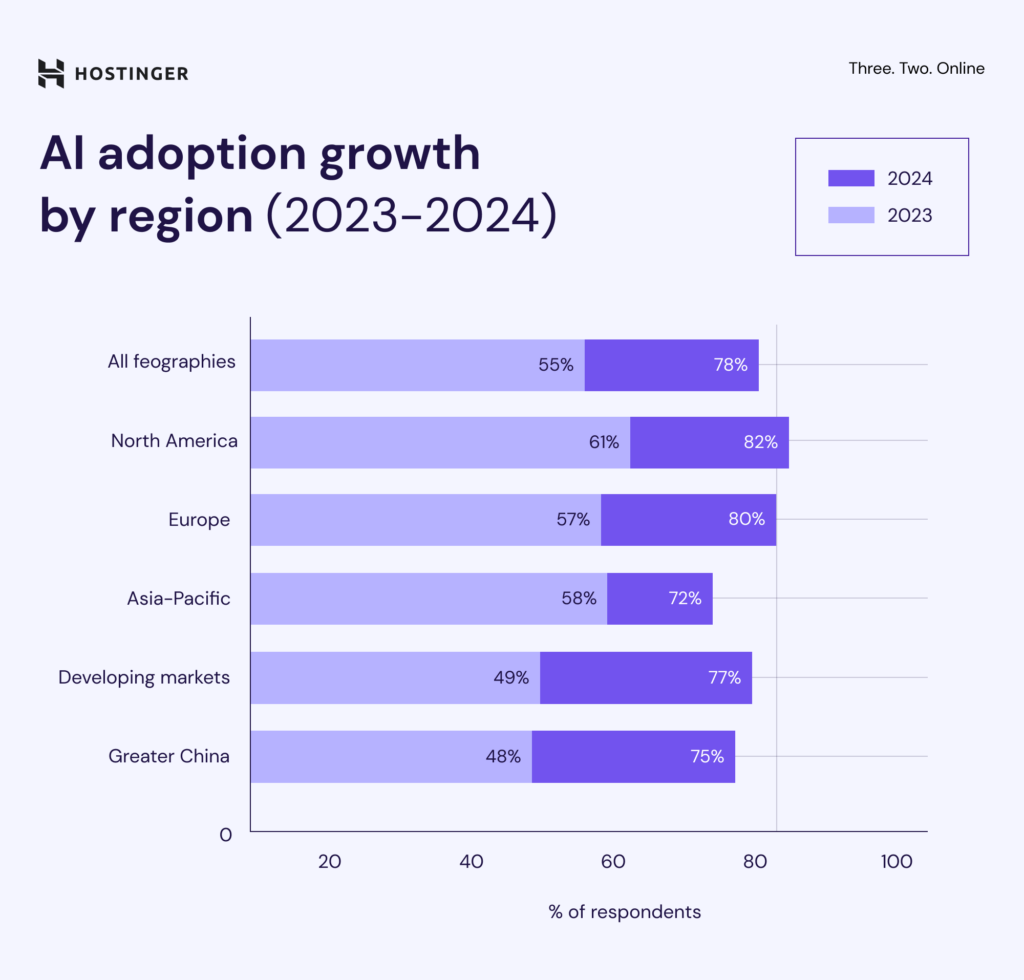
In 2024, AI adoption rose across all regions, but Greater China saw the most significant jump. Organizations there increased their AI use by 27 percentage points compared to 2023 ‒ the largest year-over-year gain globally.
North America continues to lead in overall usage, with 82% of organizations reporting AI adoption. Europe follows closely at 80%, after a strong 23 percentage point increase since last year. While adoption levels vary by region, the upward trend shows that AI use is rising fast worldwide.
2024 saw 13.5% of European Union (EU) enterprises with 10 or more employees using at least one type of AI technology ‒ a 5.45% increase from 2023. This includes tools for text mining, speech recognition, natural language generation, image recognition, machine learning, robotic process automation, and autonomous decision-making systems.
AI adoption varies not just by region but also across industries. Some sectors have moved faster than others, depending on their needs, resources, and use cases. This section explores how AI adoption compares across major industries worldwide.
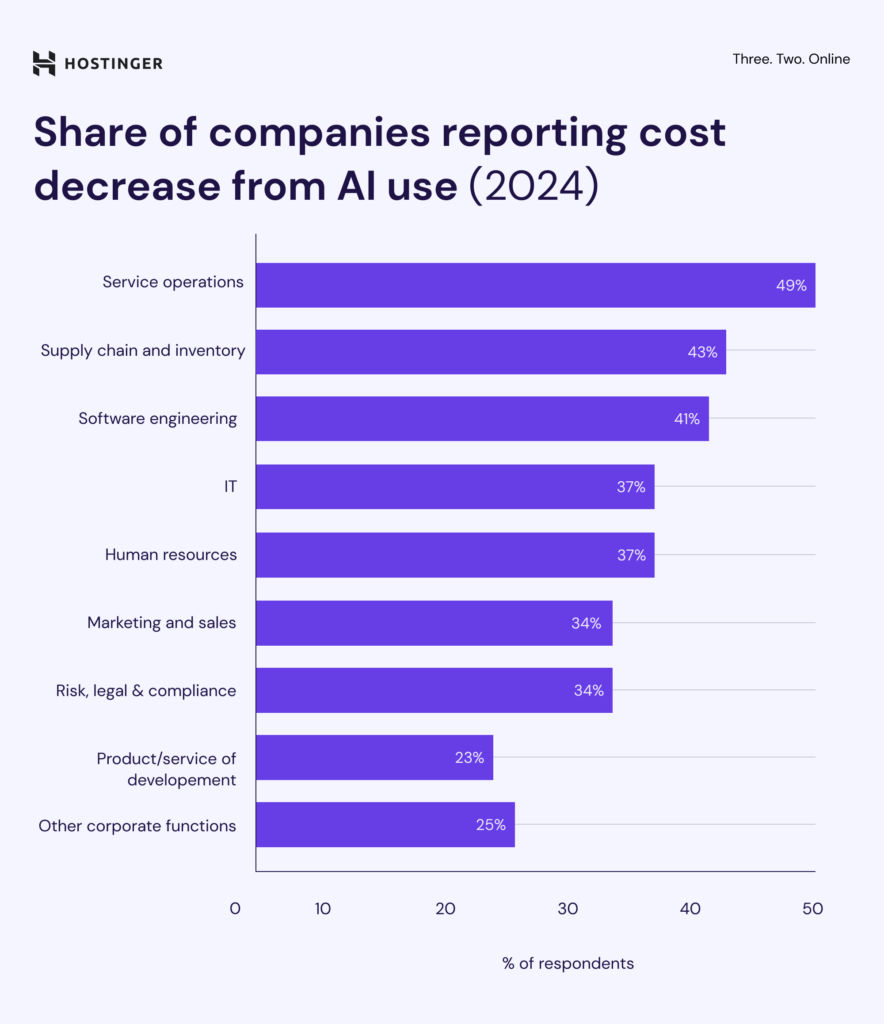
Many companies using AI report cost savings, especially in service operations. About 49% say AI helped reduce costs in this area. Other functions seeing strong savings include supply chain and inventory (43%) and software engineering (41%).
AI also helps drive revenue. The biggest gains appear in marketing and sales, where 71% of companies using AI report revenue increases. Supply chain and inventory follow at 63%, and service operations at 57%.
Most of these gains stay under 5%, but they still show that AI is starting to deliver measurable financial impact, even as many companies are early in adoption.
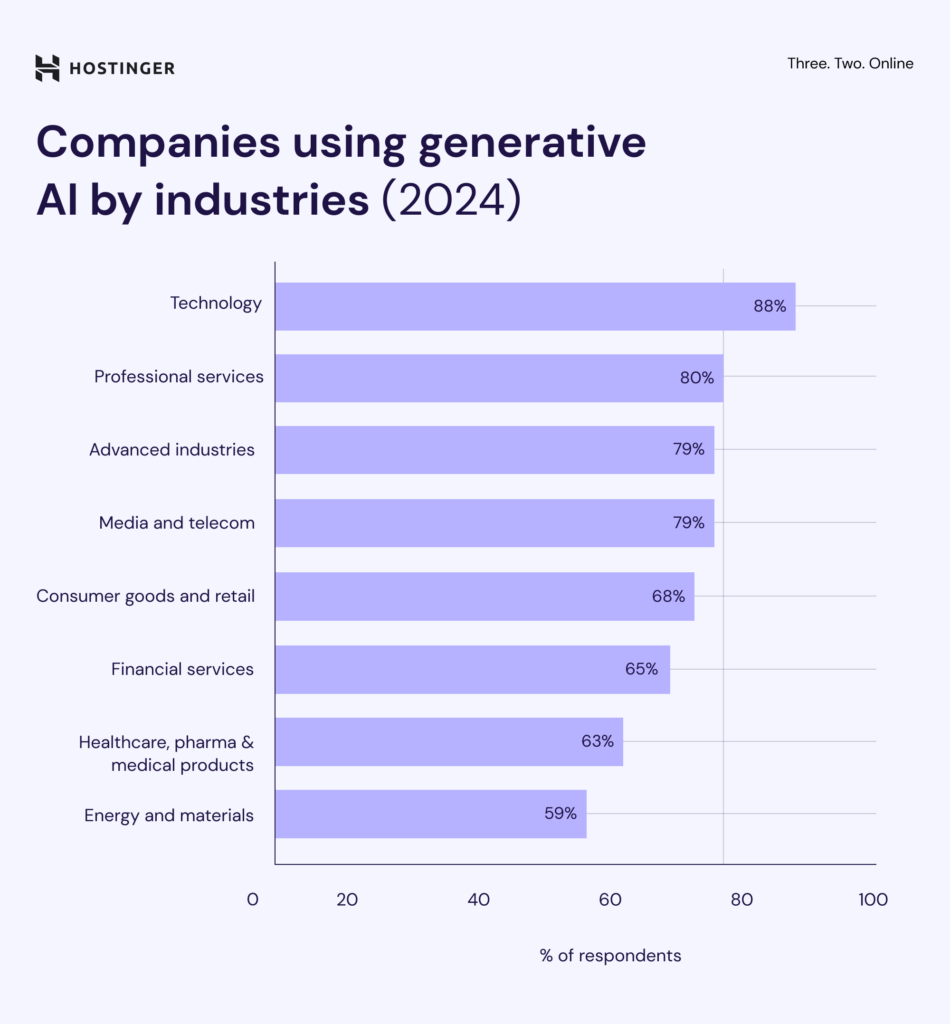
The tech industry leads all sectors in GenAI adoption, with 88% of companies reporting active use in 2024. Professional services (80%), advanced industries (79%), and media and telecom (79%) follow closely behind.
Adoption is lower but still substantial in consumer goods and retail (68%), financial services (65%), and healthcare (63%). Energy and materials show the slowest uptake, with 59% of companies using GenAI tools.
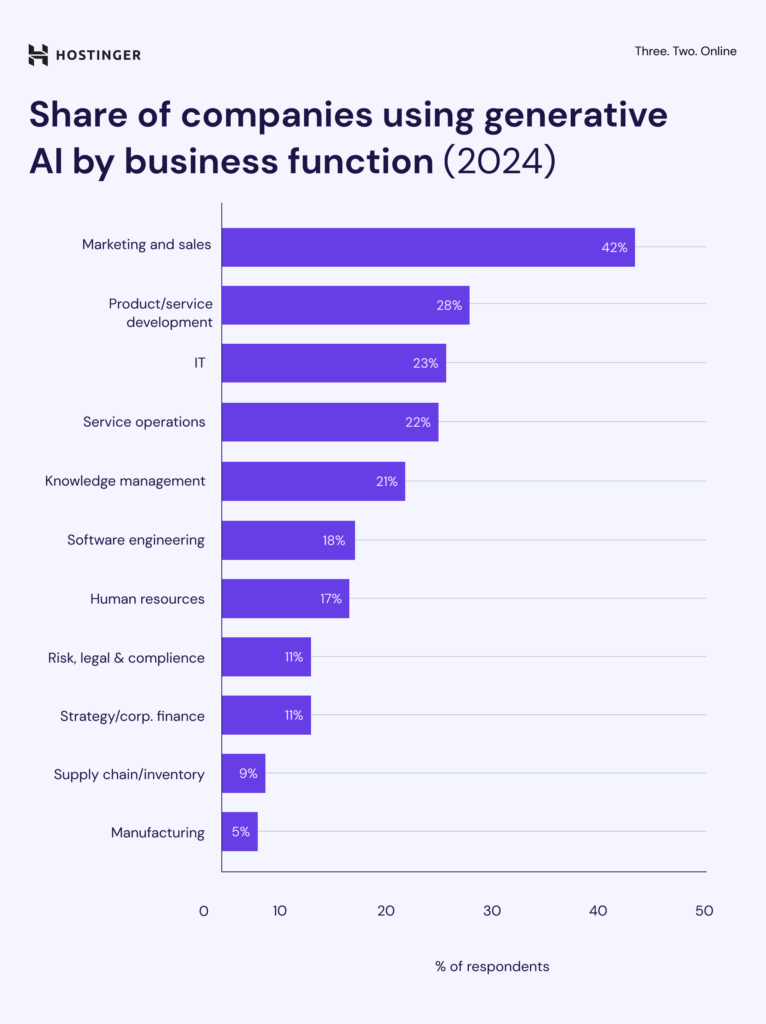
Marketing and sales lead all business functions in GenAI use, with 42% of companies adopting it in this area. This is more than twice the overall average of 19%.
Other functions where companies commonly use GenAI include product and service development (28%), IT (23%), and service operations (22%). Adoption is lower in areas like supply chain (9%) and manufacturing (5%), showing that GenAI is still more prevalent in customer-facing and digital-first functions.
The data so far makes one thing clear ‒ AI adoption isn’t slowing down anytime soon. This section looks at how fast that growth is expected in the coming years and what it could mean for the job market.
According to our AI statistics article, the global AI market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 28.46% over the next five years, reaching a value of $826.7 billion by 2030.
Our AI in business study shows that 58% of businesses are planning to increase their AI investments in the coming year. Among those already using AI, 67% are still in the early stages, while 85% of advanced adopters intend to invest even more. On the other hand, 80% of companies that haven’t yet adopted AI have no plans to do so.
Many companies are ready to embrace generative AI, with 7 out of 10 executives planning to use it to transform their business models. Additionally, 40% are planning major reorganizations of their operating models ‒ the highest in four years.
In 2024, 92% of companies already reaped the rewards of their investments in AI and cloud technologies, and expect to increase their cloud budgets in the next planning cycle. Among them, 63% intend to raise their budgets by 6% or more to improve scalability, flexibility, and accelerate R&D, driven by demand for custom cloud applications.
Additionally, one-third of the companies surveyed cited sustainability as a key reason for increasing their cloud investment.
As per our AI vs global job market study, AI-related job postings increased across most U.S. industries from 2023 to 2024, except public administration. The information sector leads with 79.56% growth, followed by professional services (31.2%) and finance (16.15%).
In response to AI’s growing role, half of employers plan to reorient their business operations, while two-thirds aim to hire talent with specific AI skills to meet new demands. As a result, 40% of employers expect to reduce their workforce due to automation.
In comparison, 52% of employers anticipate allocating a greater share of their revenue to wages by 2030, aiming to align compensation with productivity and retain top talent. Only 8% expect this share to decline.
AI is changing the way businesses operate, making them more efficient and innovative. While many companies are still getting started, it’s clear that AI adoption across industries will keep growing.
The data presented throughout this analysis shows that AI is already making an impact in various areas, from marketing and sales to service operations. Companies using AI are seeing improvements in productivity, cost savings, and revenue growth, proving how valuable AI can be for business success.
As businesses continue to adapt, AI will play a critical role in reshaping business models and driving long-term success. Your organization’s approach to AI adoption today may well determine your competitive position in tomorrow’s business landscape, so why not embrace the tech now?
Around 78% of businesses globally use AI in at least one function, up from 55% in 2023. Meanwhile, 71% report using Generative AI (GenAI) in at least one function by late 2024, marking an increase from 65% earlier that year. This shows that while traditional AI is widely adopted, GenAI is growing quickly as well.
There are 90,904 AI companies worldwide, including major players like OpenAI and Google. The United States leads with 29,618 AI companies, followed by India (8,178) and the United Kingdom (6,270).
99% of Fortune 500 companies use AI. Most of these companies apply AI in their recruitment and management processes to reduce hiring costs and improve efficiency.
According to our small business statistics, around 89% of small businesses globally use AI for tasks like writing emails, creating marketing content, and analyzing data. Over 60% of small business owners using AI report improvements in employee job satisfaction and productivity.
The industries with the highest AI adoption are information technology (IT), marketing and sales, and service operations. IT saw the biggest growth, with AI use rising from 27% to 36%.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to Hostinger's rigorous editorial standards and values.